Exploring Biomedicine - Module 3
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
cue
Incident information, not under selection
signal
purpose information, evolve under selection
Cost to signaling
Physiology: energy cost, and exploitation: eavesdropper
camouflage
Changes to resemble its surroundings => reduce the probability of being detected
mimicry
The resemblance of one species to another species
aggressive mimicry
predator secrete something mimic its prey's food to trick its prey or predator has the same smell as its prey
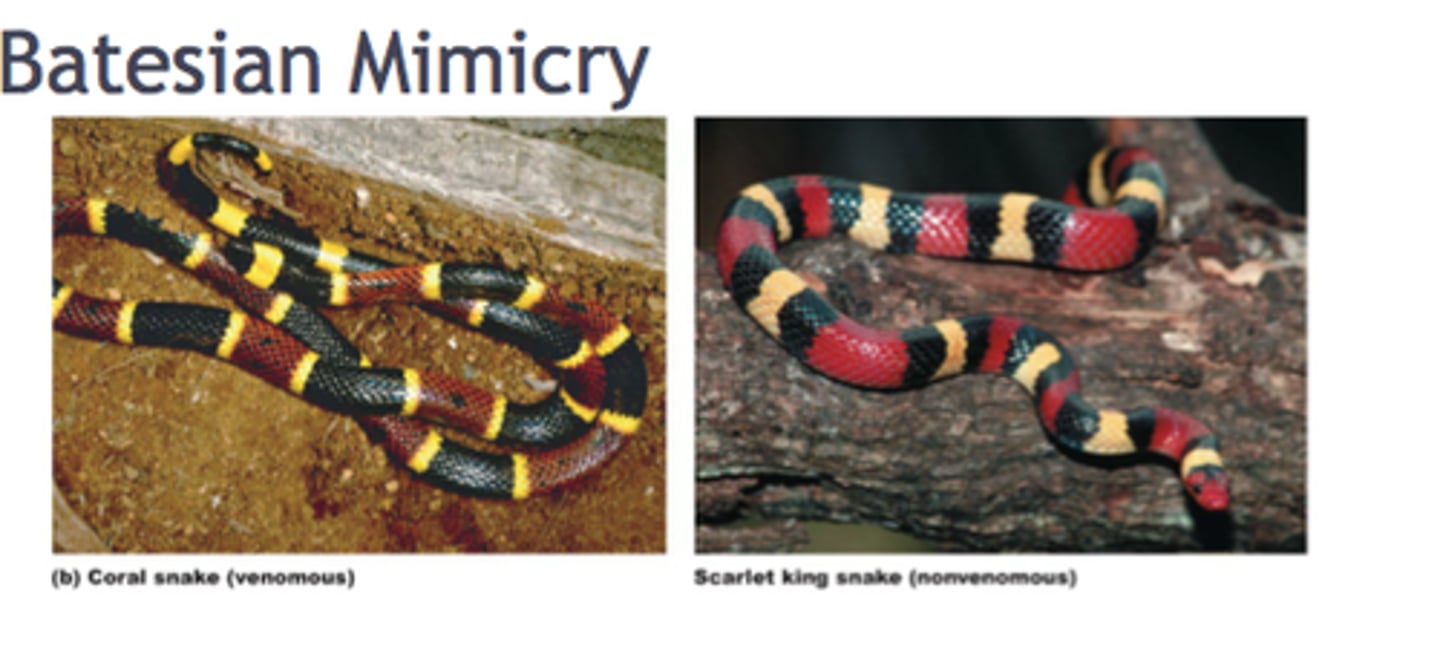
Batesian mimicry
Harmless organism evolved to look like harm one

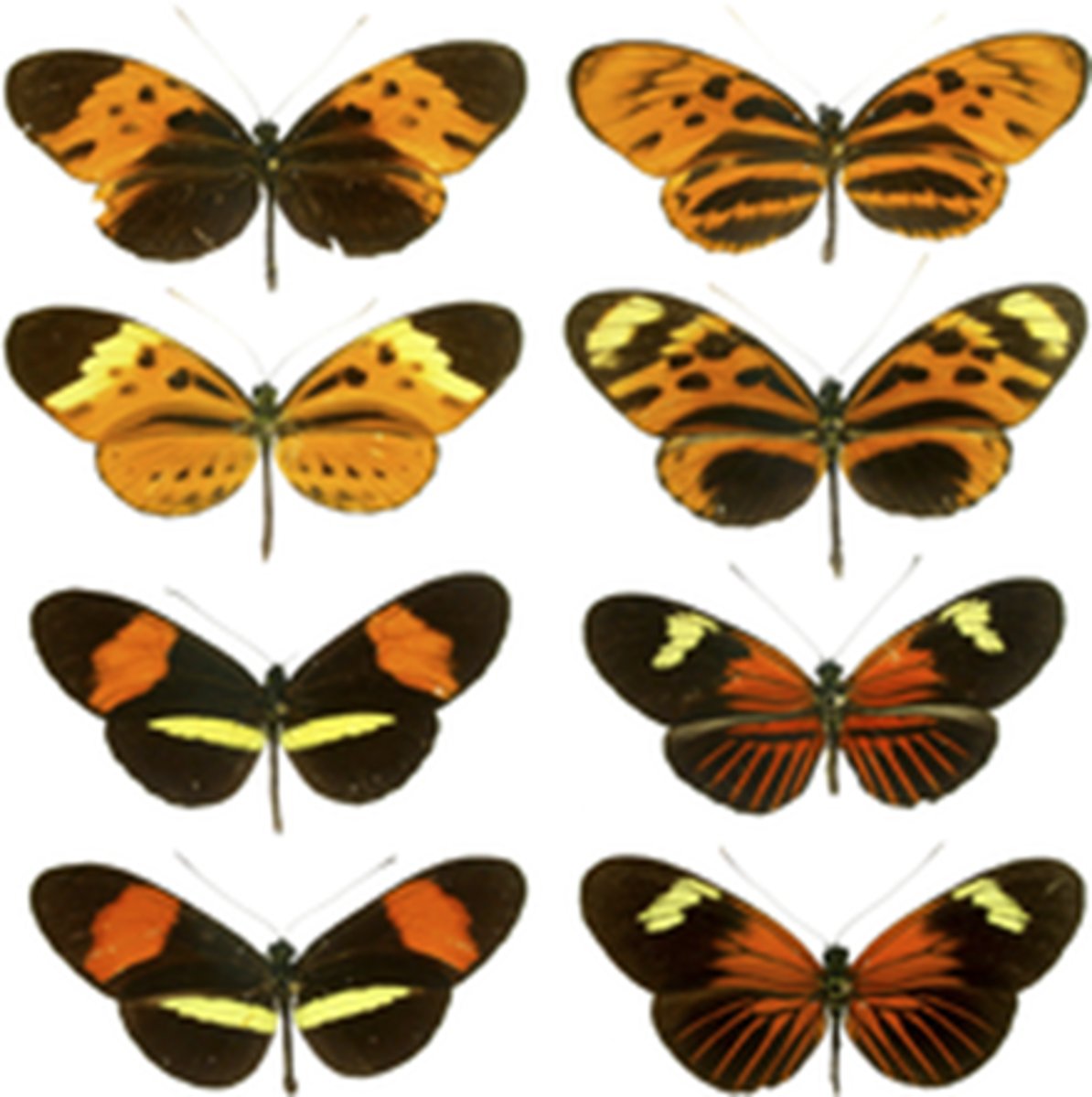
Mullerian mimicry
two or more harmful species resemble each other

Automimicry
When a vulnerable part of a plant (i.e. a bud) mimics a defensive part (i.e. a prickle)
(ex: rose buds)

Mimicry and Camouflage, which provides more effective strategy for avoiding or protection to predators ?
Depends on ecosystem if mimic is overcrowded so they will eat both model and mimic, depend on predators if predator has known that prey
How might artificial light be affecting the information the birds collect about their surroundings ?
Mistake artificial light to natural light => affect sleep-wake cycle
However, some birds not use light information for sleep-wake so less affected to sleep cycle
facultative parthenogenesis
female can produce offspring asexually or sexually
Hermaphroditism
A condition in which an individual has both female and male gonads and functions as both a male and female in sexual reproduction by producing both sperm and eggs.
sexual dimorphism
Differences in physical characteristics (secondary charateristics) between males and females of the same species.
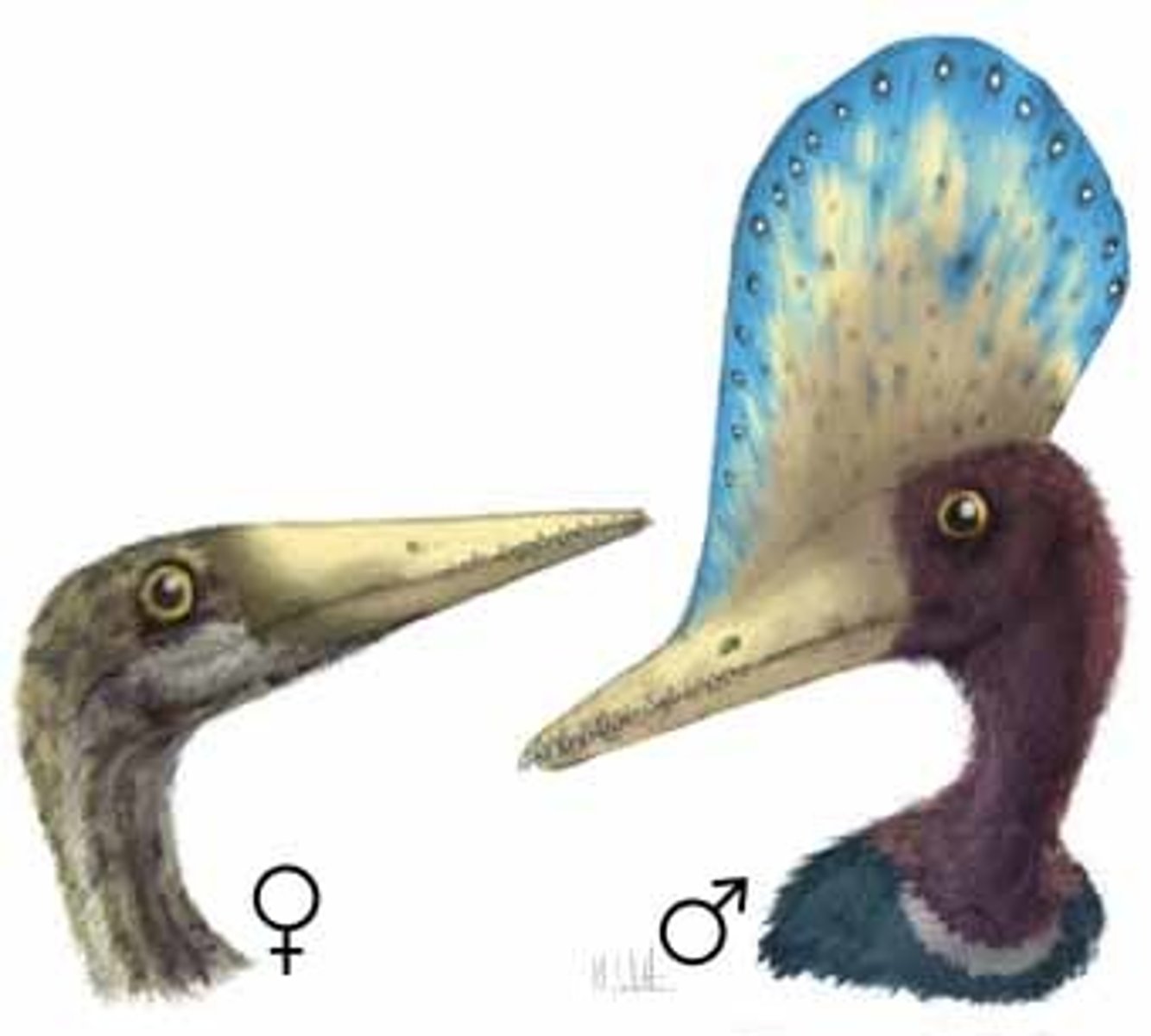
secondary characteristics
nonreproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts and hips, male voice quality, and body hair
Polyandry
One female mates with several males.
Polygyny
one male mates with several females
Why living things don't violate the second law of dynamics?
Second law : entropy of a closed system always increase overtime
However, human is not a closed system, gain energy by eating to maintain body entropy to maintain metabolic processes. ( because less entropy, less changing activities in body )
Microhabitat
A very small specialized habitat, such as the space under a rock.
metabolic rate
Amount of energy an animal uses in a unit of time; the sum of all the energy-requiring biochemical reactions.
The idea of the Maxwellian demon is relevant to biology because
Explain how organisms can be more energetically efficient by using information
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level ( maintenance of order in living things)
basal metabolic rate (BMR)
The metabolic rate of a nongrowing, resting, fasting, nonstressed endotherm (metabolic rate measured under strict conditions to aid)

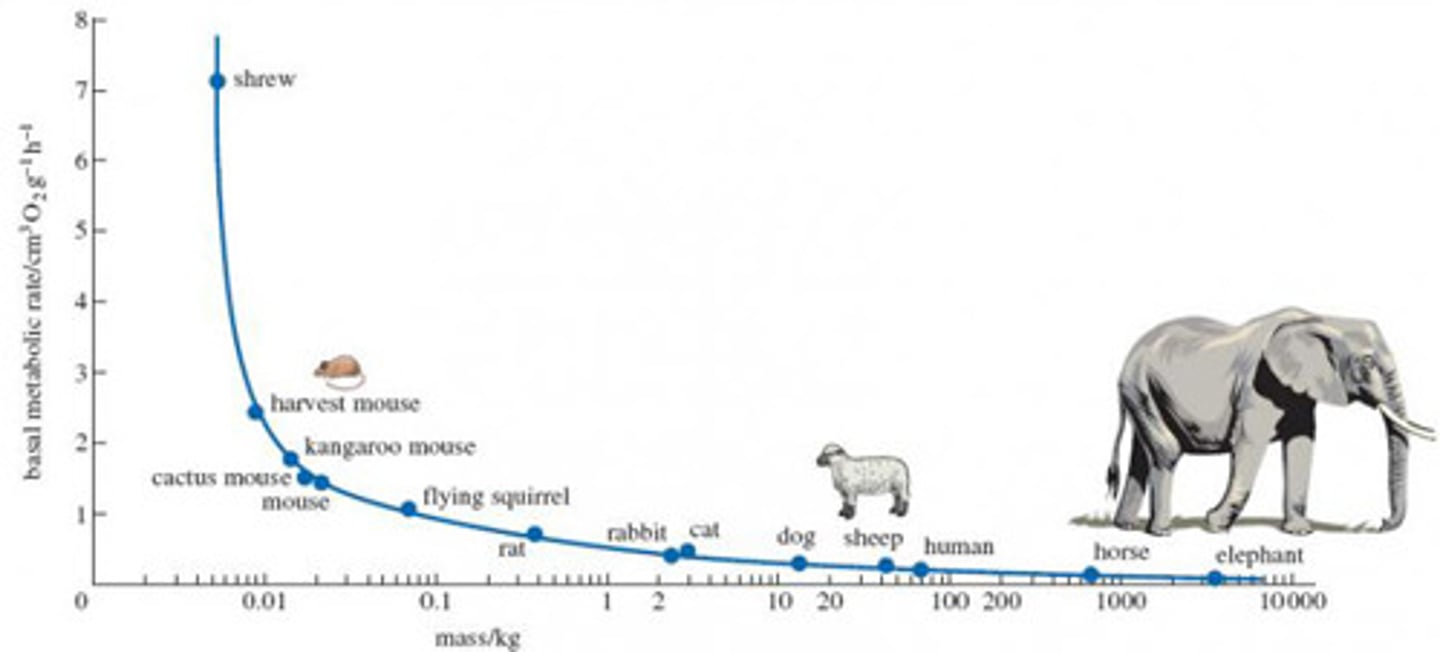
Metabolic rates of different species of animals been observed to change with their body size :
The metabolic rate per gram of tissue decreases with size
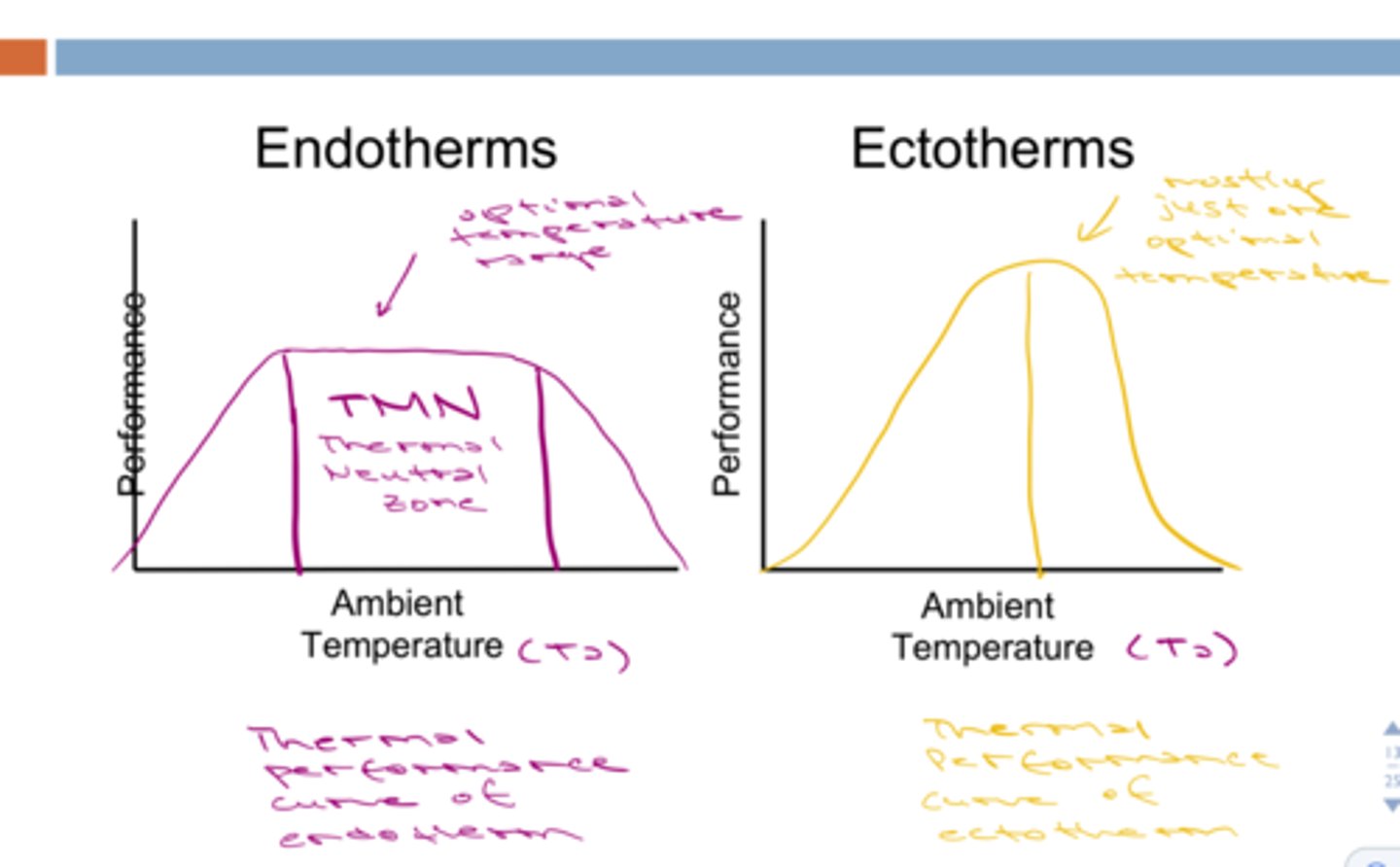
The thermoneutral zone
The range of temperatures over which an endotherm does not have to expend extra energy to thermoregulate. (The air temperature range where endotherms have no heating cost)
For ectotherms if temperature rises, tropical species will be more negatively affected than temperature species because:
Tropical species tolerate a narrower range of temperatures than temperate species
The nestlings within the nest compete among each other to obtain food from their parents by making begging calls. These calls may attract predators, such as currawongs (large crow-like birds), who search the dense bushes for nests. How chick deduce the probability of being caught:
Chicks increase their rate of begging calls in the presence of their parents.
rsfield's Bronze cuckoo is a brood parasite of the Fairy-wren. Unlike European cuckoos, the hatchling Horsfield's Bronze cuckoo chick does not eject the Fairy-wren eggs, and so it shares the nest with the Fairy Wren chicks. The female Horsfield's Bronze cuckoo, male and female Fairy-Wren, and their respective eggs and nestlings are shown above.Which of the following evolutionary scenarios is the most likely?
The colour and shape of the egg no longer provided a species-specific signal for Fairy-Wrens, shifting the antagonistic co-evolutionary process to the chick stage
standard metabolic rate (SMR)
the metabolic rate of a fasting, non stressed ectotherm at rest at a particular temperature
Metabolic rate vs size
smaller animals (high S/V) tend to have higher per-gram basal metabolic rates than larger animals (low S/V)
S/V high => lost more heat => need more energy to maintain body temp
Examples of an organism controlling its metabolism
Excreting nitrogenous wastes, sweating, eating, taking in water, panting, etc
The evolution of polyandry arguably created the opportunity for an evolutionary conflict of interest between females and males. Which best characterises that conflict of interest?
Polyandry can improve female fitness through either material or genetic benefits, while compromising male reproductive success
antagonistic coevolution
Sexual antagonistic co-evolution is the relationship between males and females where sexual morphology changes over time to counteract the opposite's sex traits to achieve the maximum reproductive success.