Chapter 3: Introduction to Prokaryotic Cells
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Name two prokaryotic domains.
Bacteria and archaea.
Do prokaryotic organisms contain membrane-bound organelles? Are prokaryotes multicellular, unicellular, or can be both?
Unicellular, lack membrane-bound organelles
What does it mean if a bacterium is pleomorphic?
Pleomorphic bacteria are able to change shape and form depending on their needs or environment.
How do most prokaryotes obtain nutrients?
Obtained through diffusion
Know the prokaryote shapes and arrangements presented in Figure 3.5 Prokaryotic Shapes and Arrangements
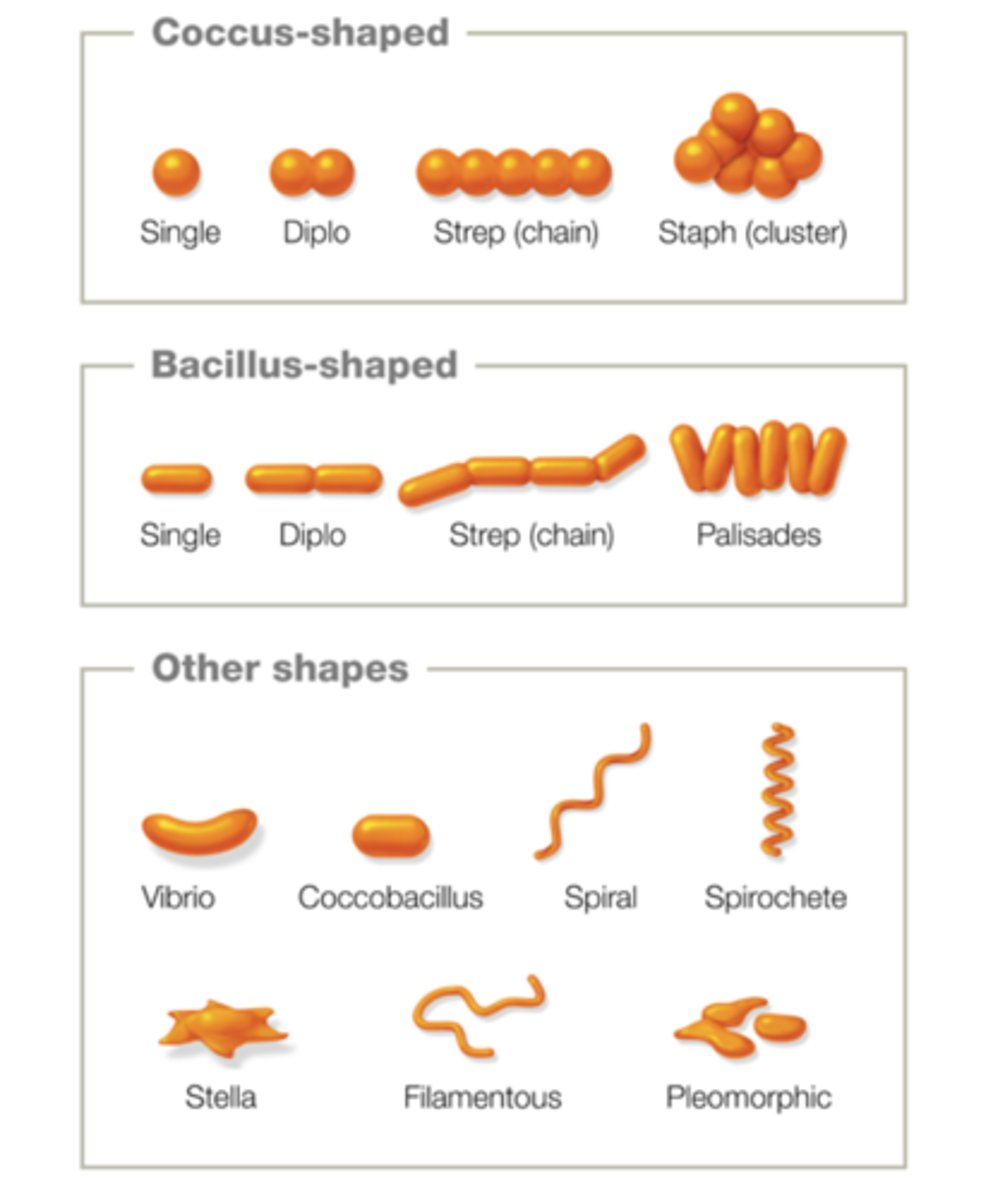
What reproduction process is used by most prokaryotes? Is the process sexual or asexual?
Binary fission (asexual)
What is the function of a cell wall?
Cell walls offer an extra layer of rigid protection.
What is the core component of bacterial cell walls?
Peptidoglycan
What is the core component of archaea cell walls?
Pseudopeptidoglycan
Gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer of peptidoglycan that is surrounded by an outer membrane.What molecule enriches the outer membrane?
Lipopolysaccharide
Which part of lipopolysaccharide is an endotoxin?
Lipid A.
Where in the body would you find enteric bacteria?
Intestines
What is lysozyme? Where is it found?
Naturally occurring enzyme found in various bodily secretions (tears, saliva, mucus), capable of breaking down cell walls of certain bacterias
What is the physical reason why Gram-negative bacteria are not as susceptible to penicillin as Gram-positive organisms are?
gram negatives contain a thin peptidoglycan cell wall as outer membrane
What two general are the best-known examples of acid-fast bacteria? ("genera" is the plural form of"genus")
Nocardia and mycobacterium.
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
Passive transport does not require energy from the cell and active transport does require energy from the cell.
What is diffusion? Is it an active or passive process?
Diffusion is the simplest form of exchange between cells and their environment. It is a passive process along the cell's concentration gradient.
What is the difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion?
Simple diffusion does not require transporters (small, noncharged molecules use simple diffusion). Facilitated diffusion requires the help of transporter proteins.
What is the difference between diffusion and osmosis? Is osmosis a passive or active process?
Both diffusion and osmosis are passive forms of transport, but osmosis relates specifically to water and in osmosis, water is traveling toward the area where solutes are more concentrated.
Define active transport.
Movement of substances along or agaisnt a concentration gradient, requires energy
What are flagella and what are their function?
Filament-like extracellular structures built from protein called flagellin
Define chemotaxis, phototaxis, and aerotaxis.
Chemotaxis is movement in response to a chemical stimulus. Phototaxis is movement in response to a light stimulus. Aerotaxis is movement in response to a change in oxygen levels.
What is the structure and function of fimbriae and pili?
Fimbriae and pili enhance a cell's motility and allow cells to adhere to each other and surfaces in order to create a biofilm. Pili are similar to fimbriae, but they tend to be longer and more rigid.
What is the difference between a slime layer and a capsule?
A slime layer is sticky, loosely attached to a cell wall, and fairly unorganized. A capsule is more rigid, organized, and tightly bound to a cell wall.
What are two ways that a bacterial capsule increase pathogenicity of the bacteria?
preventing phagocytosis by immune cells and facilitating adherence to host tissues
What is the main molecule contained in the nucleoid region of a bacteria?
Prokaryotic DNA
What is the function of ribosomes?
builds proteins by linking amino acids.
How are prokaryotic ribosomes different than eukaryotic ribosomes? What is the sedimentation rate of complete prokaryotic and complete eukaryotic ribosomes?
Easily differentiated by sedimentation rate, which is how fast various particles in solution settle out. P=70S, E=80S
What property of chloroplasts and mitochondria support the endosymbiotic theory?
They both have 70S DNA.
What are inclusion bodies and what is their function?
Inclusion bodies are distinct collections of substances consisting of insoluble granules. Inclusion bodies are storage means for bacteria to access carbon and energy in times of need.
What are endospores?
Endospores are metabolically inactive structures that allow certain cells to enter a dormant state. It is called a spore once it is released.
How does an endospore differ from a vegetative cell?
An endospore is different from a vegetative cell because they are not considered reproductive structures and only become active when environmental conditions are favorable.
What are the three most clinically important genera of bacteria that produce endospores?
Bacillus, Clostridium, and Clostridioides