Bootcamp.com - Endocrine System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
the _____ system is a communicator system that monitors slower acting responses
endocrine
endocrine secretions involve cells secreting hormones into the _____
bloodstream
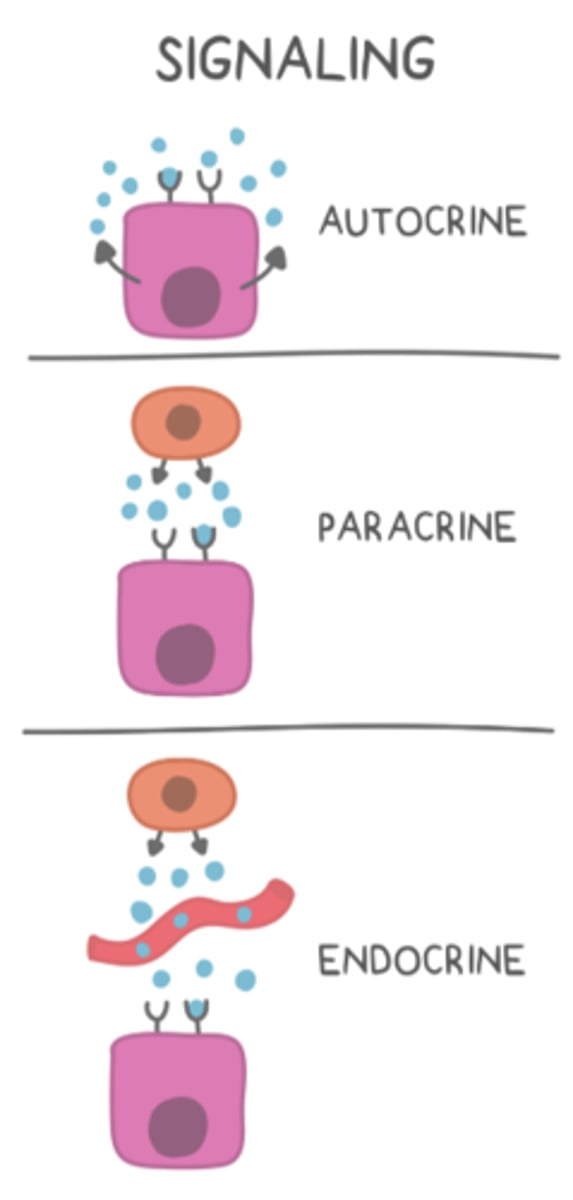
exocrine secretions involve cells secreting hormones into _____
ducts
_____ secretions involve cells secreting hormones to neighboring cells
paracrine
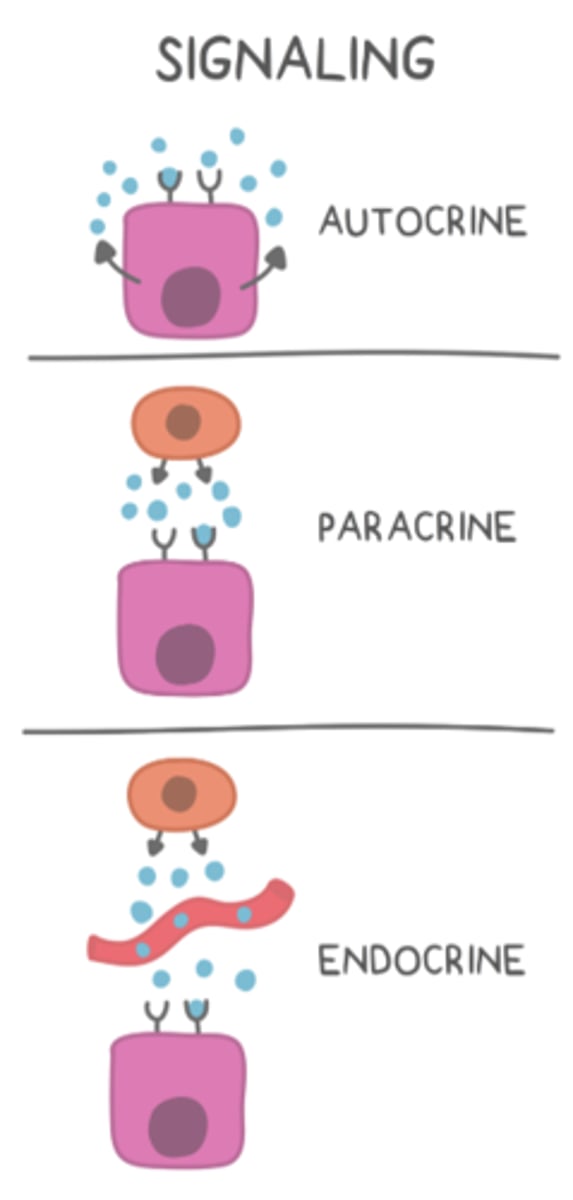
_____ secretions involve cells secreting hormones to themselves
autocrine
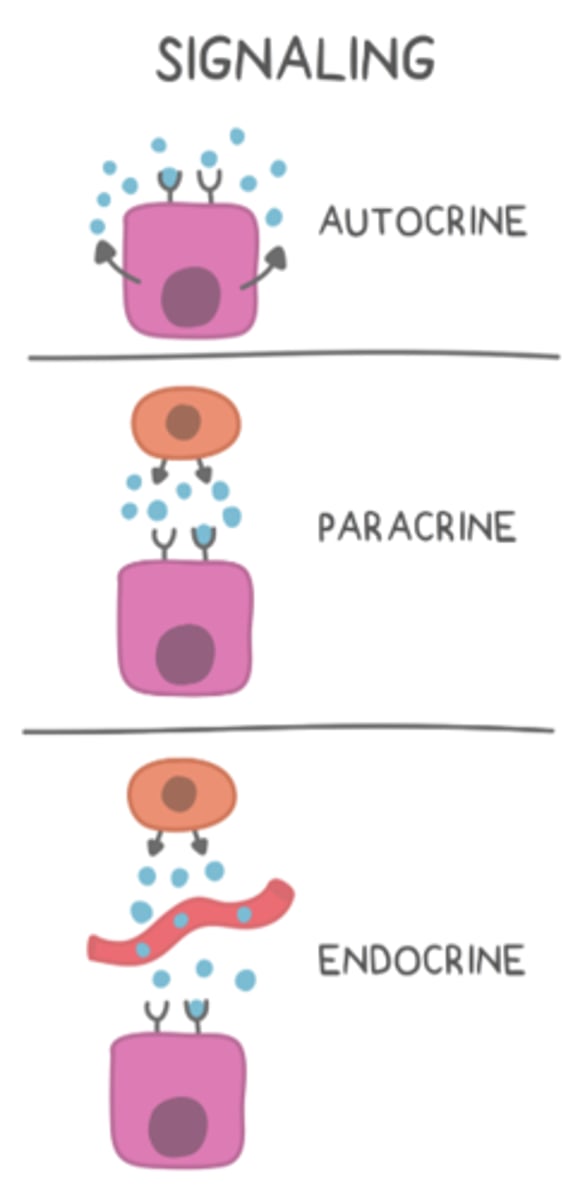
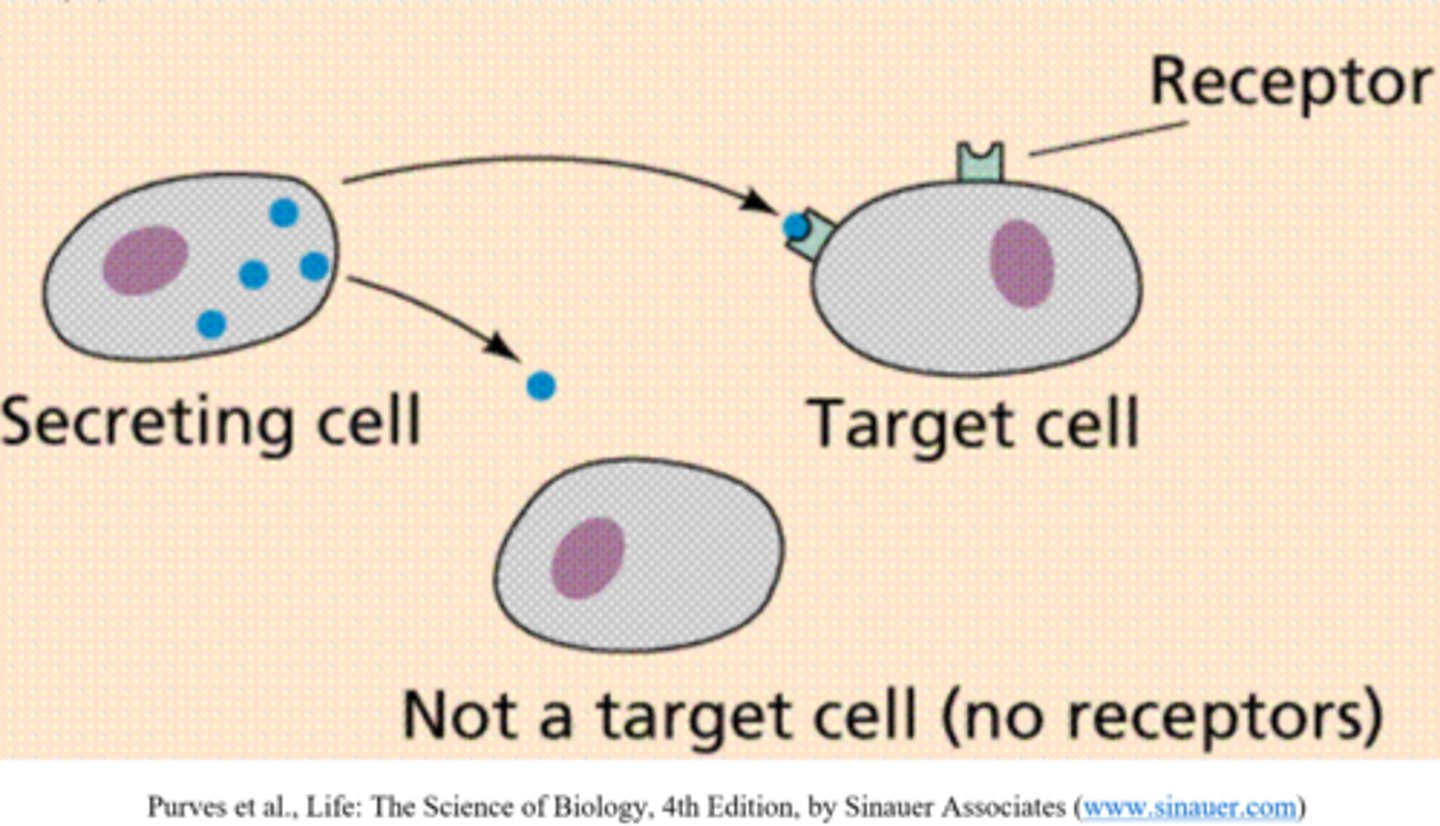
hormones bind to very specific _____
receptors
a single type of hormone can elicit _____ in the body
multiple/different effects
hormones are _____ (faster/slower) acting than electrical signals
slower
what are the three different types of hormones?
peptide; steroid; amino-acid derived
_____ hormones are made of short amino-acid chains
peptide
where are peptide hormones synthesized?
the rough ER
peptide hormones include:
all hormones from the hypothalamus & anterior pituitary; glucagon & insulin; calcitonin & PTH
peptide hormones (are/are not) H2O soluble, so they (do/do not) need carriers to travel through the blood
are; do not
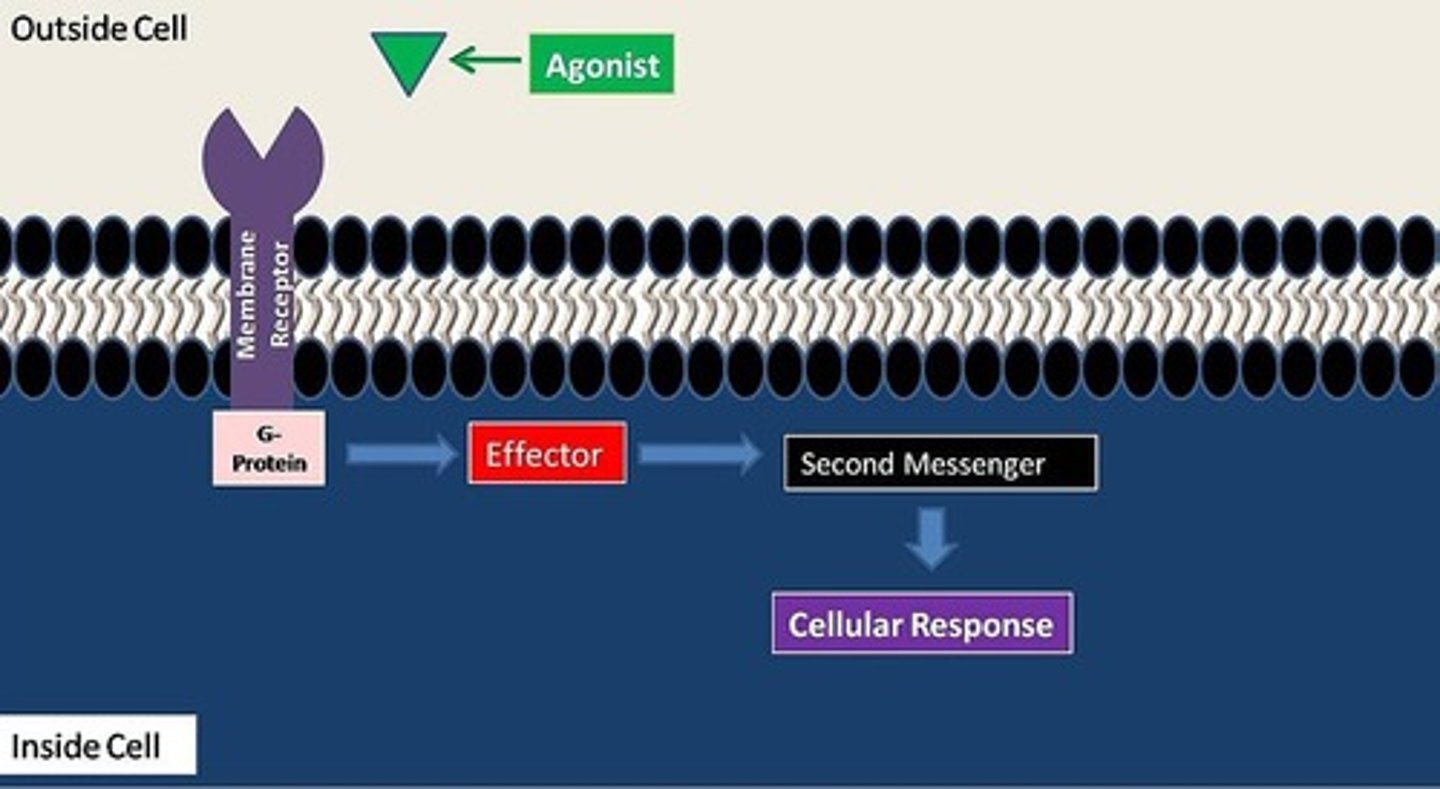
peptide hormones _____ (directly/indirectly) stimulate receptor cells - why?
indirectly; peptide hormones are not lipid soluble, so they can't pass through the phospholipid bilayer. They bind to a receptor on the cell surface to trigger changes/secondary messengers in a cell
secondary messengers are produced by _____ (direct/indirect) stimulation of receptor cells
indirect
(such as with peptides)
what are some common secondary messengers?
cAMP; IP3; DAG; Ca2+
what are the three main receptors peptide hormones will bind to indirectly stimulate target cells?
G protein-coupled receptors; receptor tyrosine kinases; ligand-gated ion channels
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are a type of _____ (location) receptor that can trigger _____
cell surface; 2nd messengers
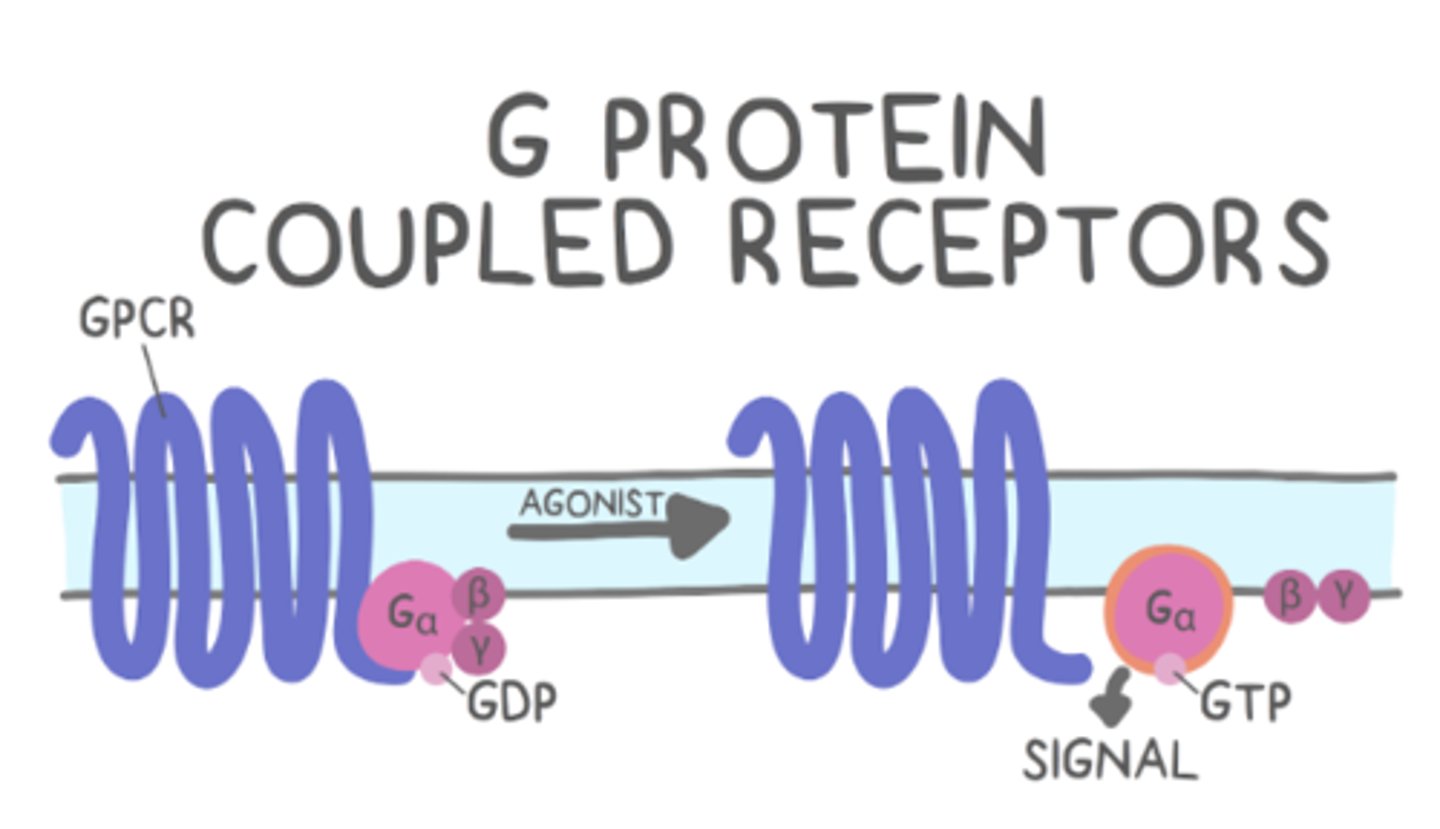
GPCRs consists of _____ transmembrane domains that pass back and forth through the cell membrane
7
G proteins _____ (activate/deactivate) other substrates
activate
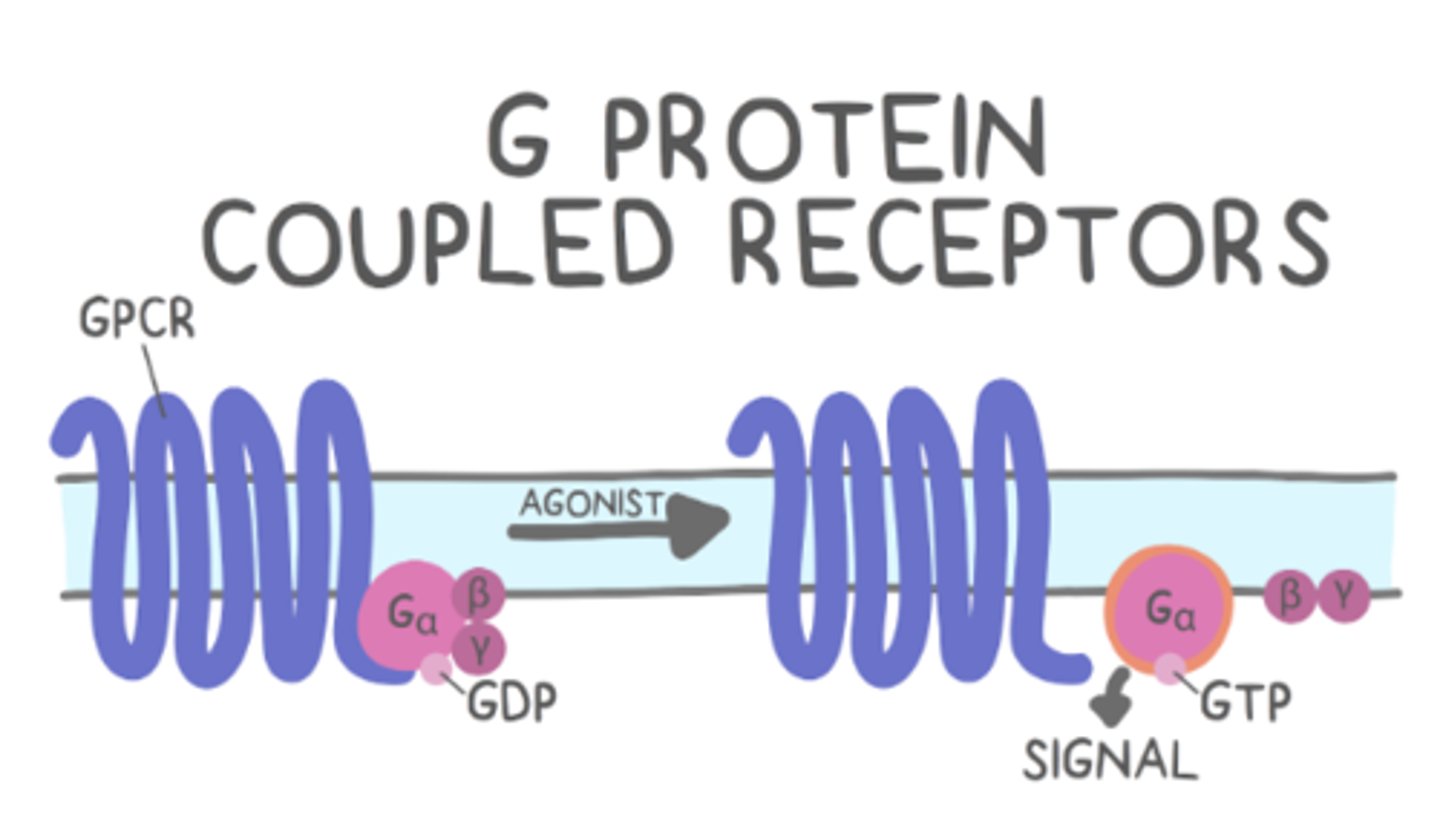
what are the G protein subunits?
alpha, beta and gamma subunits
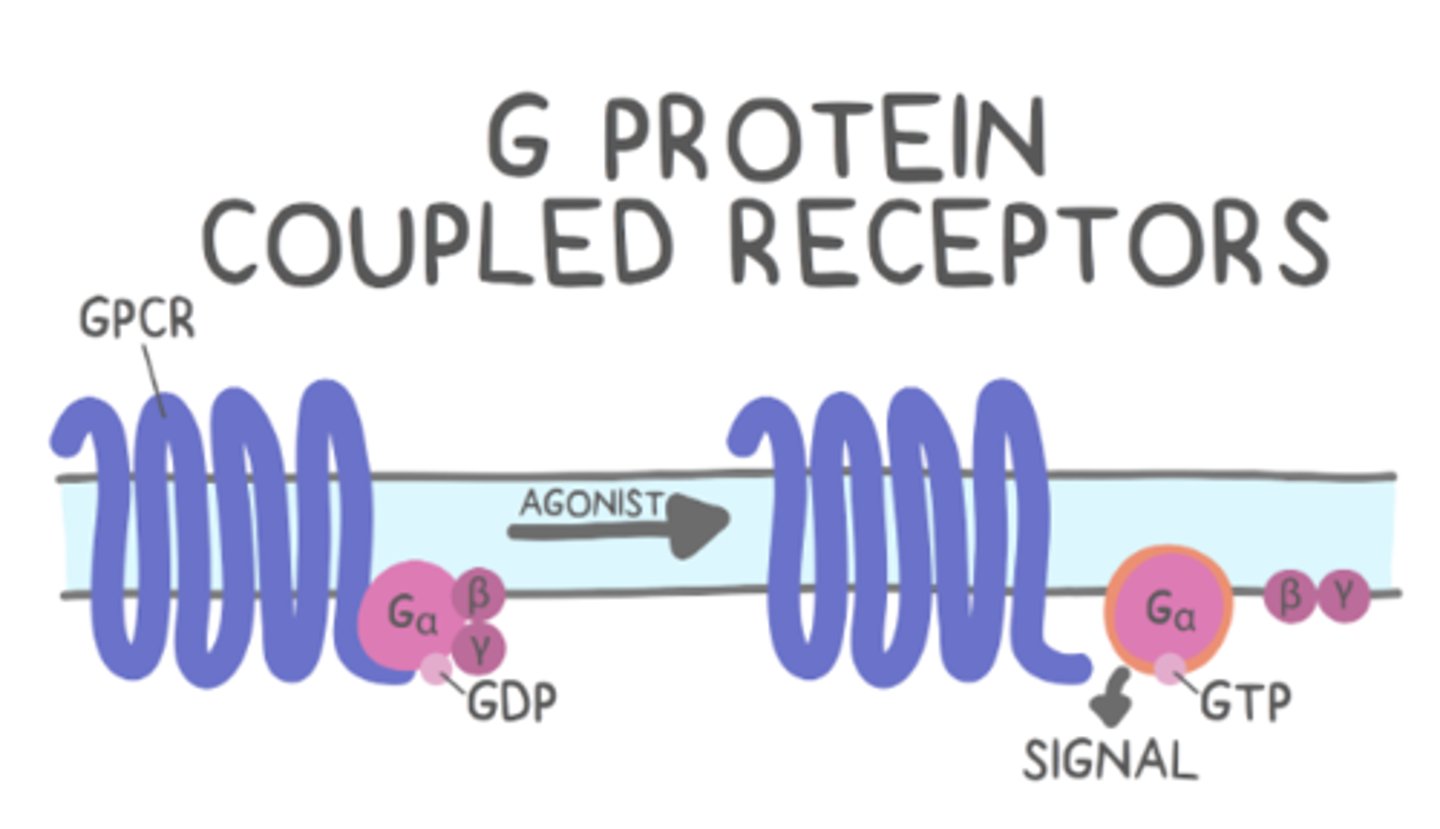
insulin acts through _____ and 2nd messengers
receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs)
RTKs will _____ & _____ when their hormone binds to them
dimerize, cross-phosphorylate
peptide hormones can also bind to _____-gated ion channels
ligand
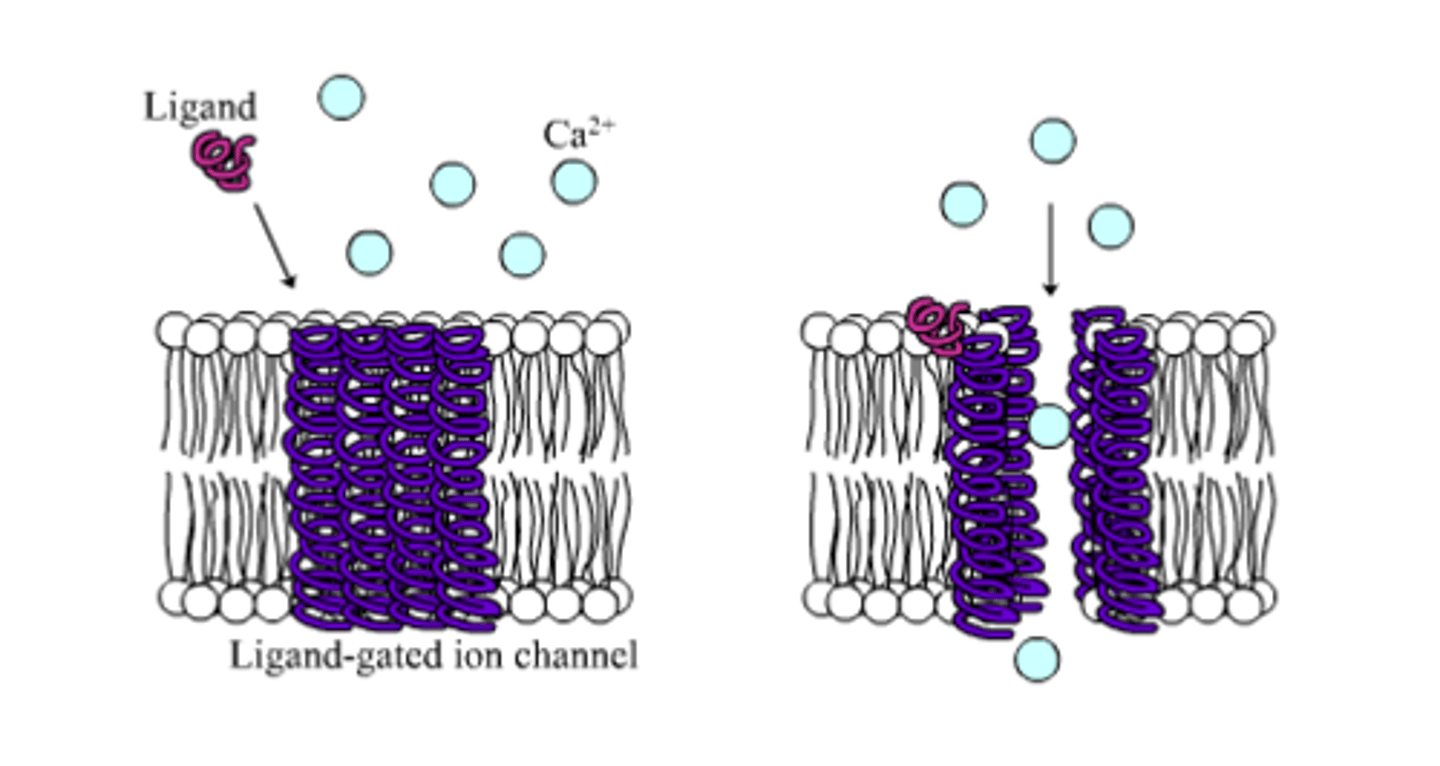
what happens once a ligand binds a ligand-gated ion channel?
the channel changes its shape to allow certain ions to pass through
_____ hormones are 4-ring structures that belong in the same family as lipids
steroid
where are steroid hormones synthesized?
smooth ER
steroid hormones include:
all adrenal cortex and reproductive organ hormones
steroid hormones are _____ (lipid-soluble/lipid-insoluble)
lipid-soluble (hydrophobic)
steroid hormones require a _____ to travel in the blood
carrier
steroid hormones _____ (can/cannot) pass directly through the cell membrane
can
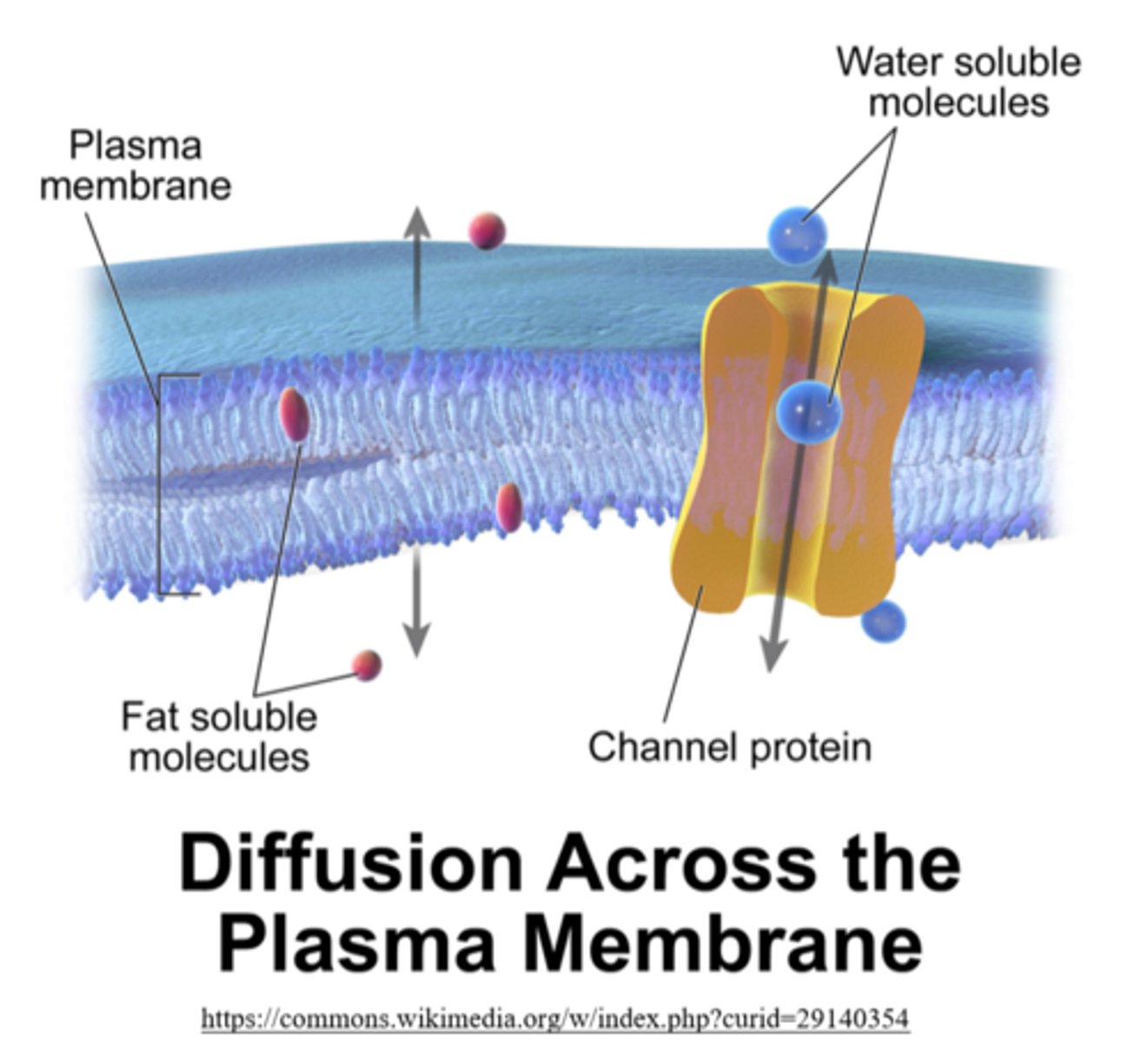
steroid hormones _____ (directly/indirectly) stimulate receptor cells
directly
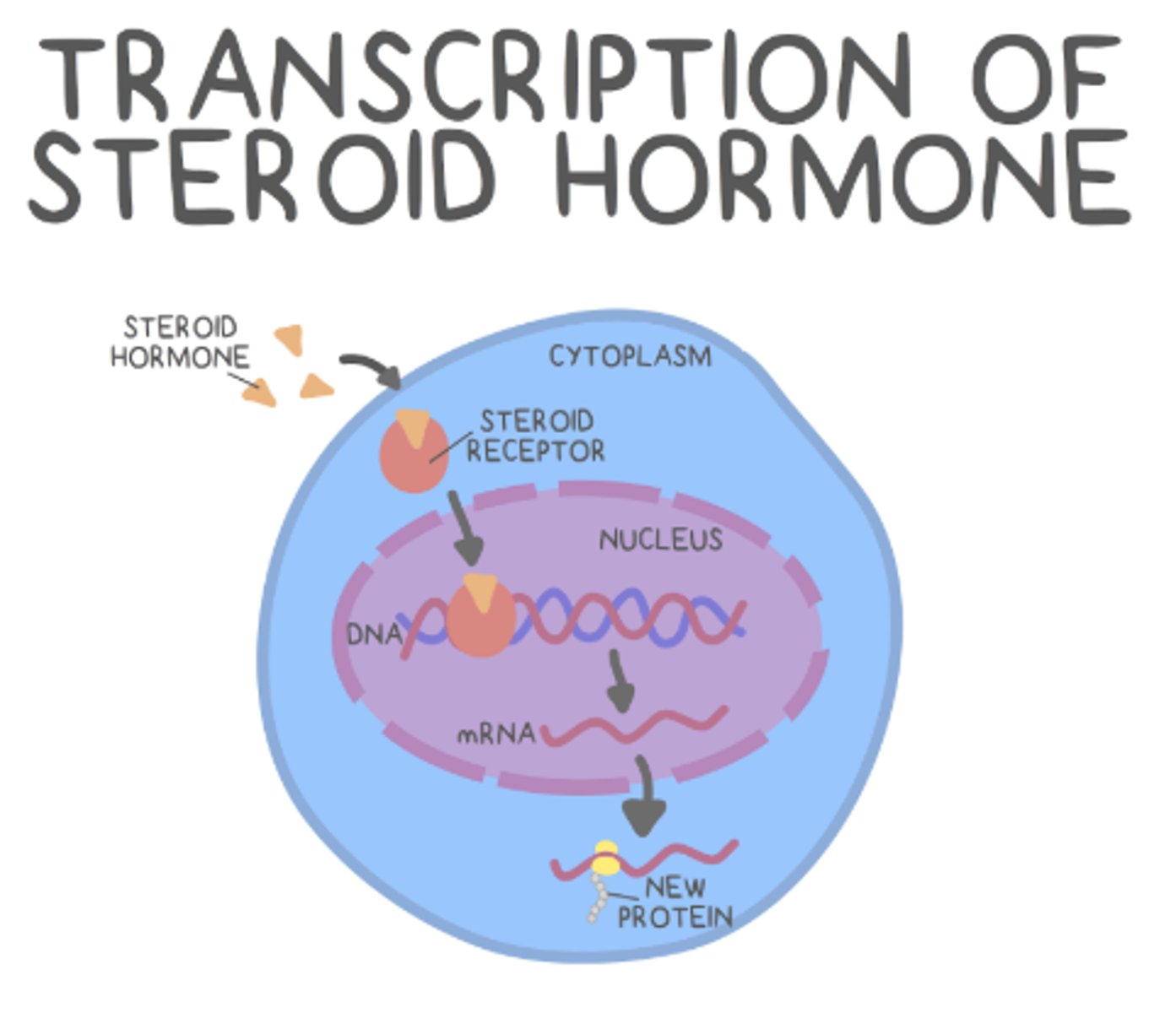
do peptide hormones or steroid hormones have a slower action time?
steroid hormones
steroids trigger changes from a _____ level
transcriptional
what is the main amino acid of amino acid derived hormones?
tyrosine
where are amino acid derived hormones synthesized
rough ER and cytosol
what are the main amino acid derived hormones?
all hormones made by the adrenal medulla; T3 and T4; melatonin
epinephrine and norepinephrine are amino acid derived hormones that act similarly to _____ hormones
peptide
(indirect stimulation)
T3 and T4 are amino acid derived hormones that act similarly to _____ hormones
steroid
(direct stimulation)
the hypothalamus is involved with maintaining _____
homeostasis
what are the two lobes of the pituitary gland?
anterior and posterior
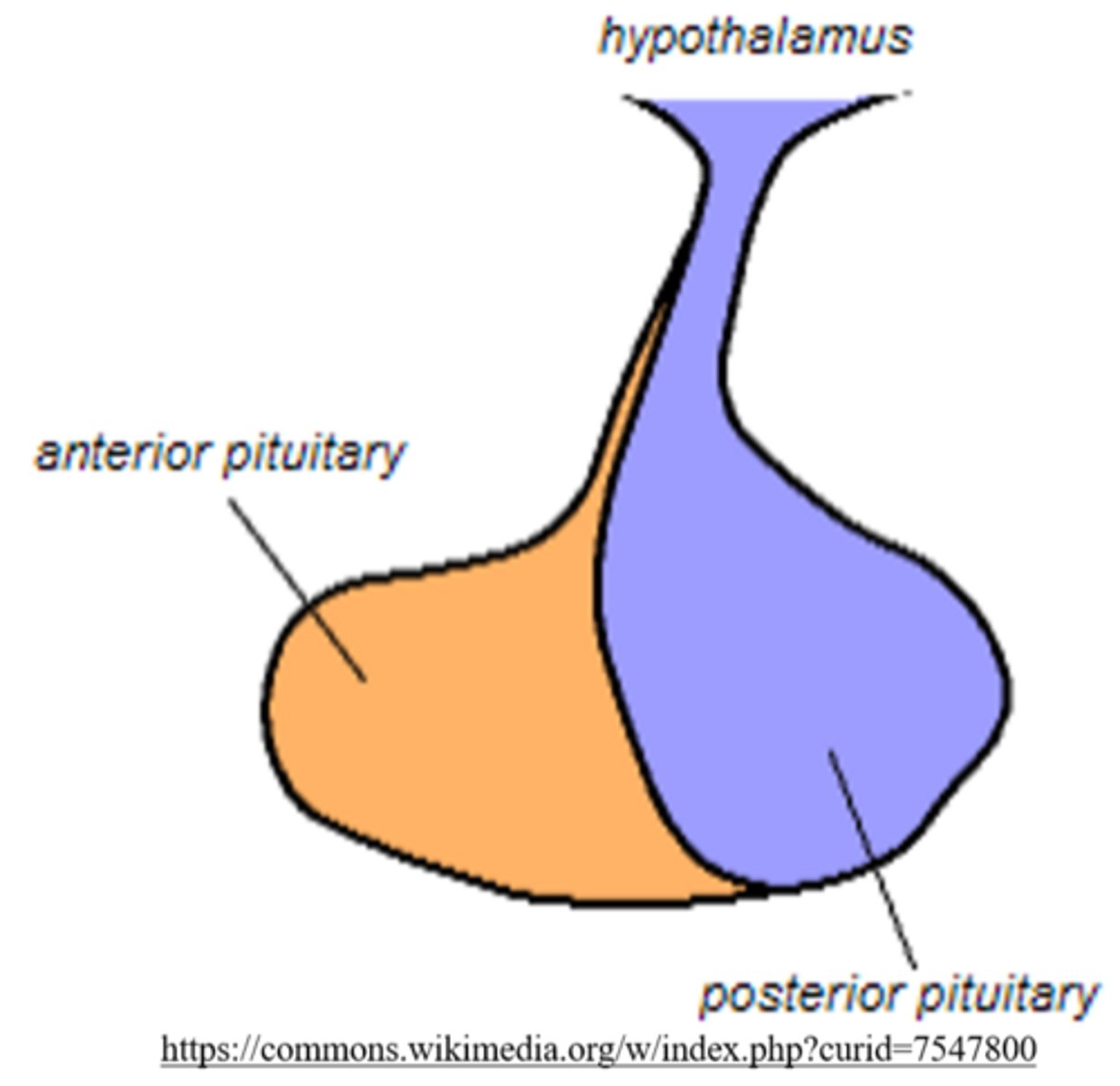
the _____ is an extension of neurons from the hypothalamus also known as the _____
posterior pituitary; neurohypophysis
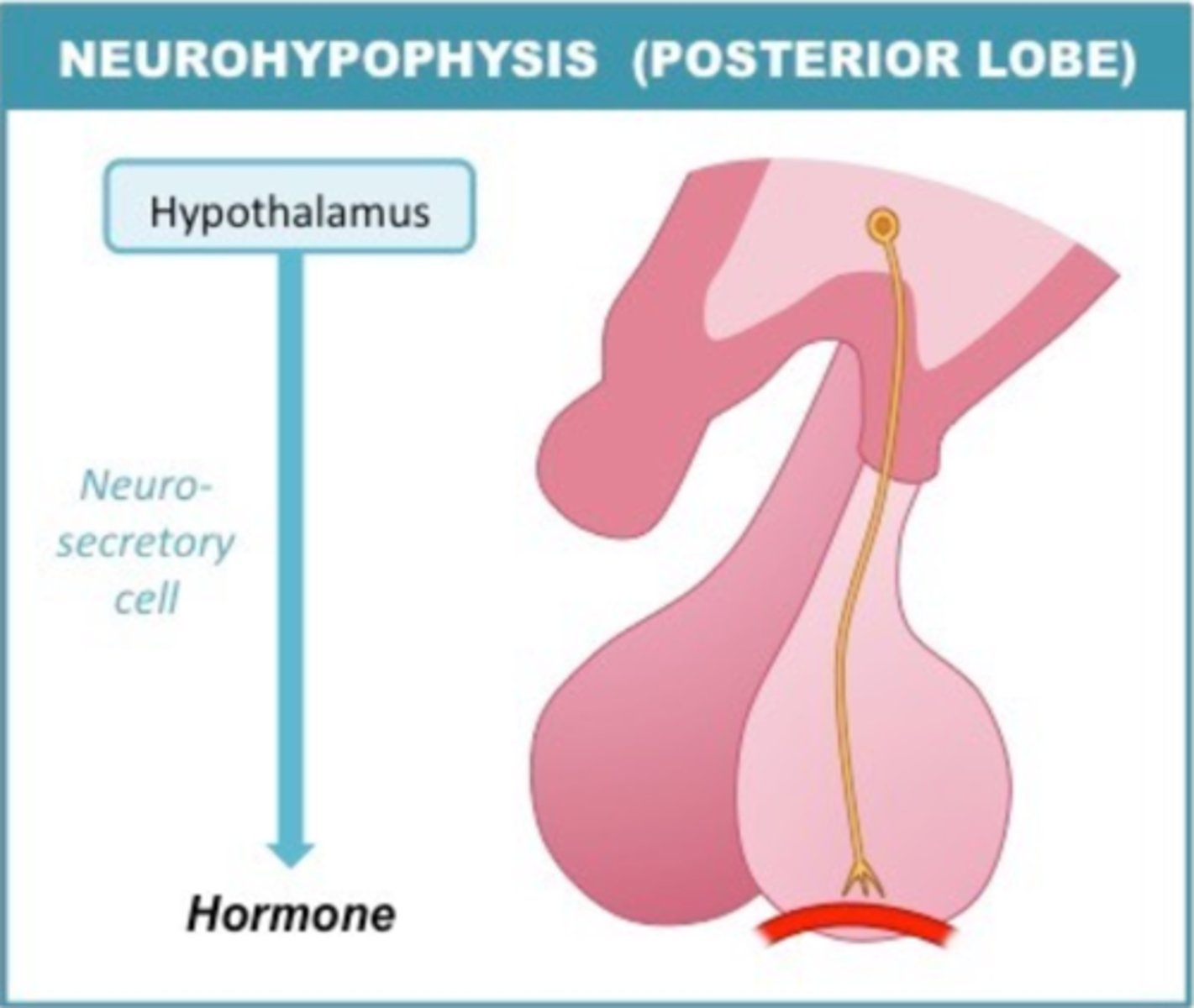
which two hypothalamic hormones does the posterior pituitary store and release
ADH; oxytocin
The posterior pituitary does not produce these hormones
antidiuretic hormone (_____) targets _____ of the kidney to reabsorb water and increase blood volume/pressure
ADH/vasopressin; nephrons
ADH/vasopressin is made by the _____ and stored in the _____
hypothalamus; posterior pituitary
oxytocin targets the _____ and _____
uterus; mammary glands
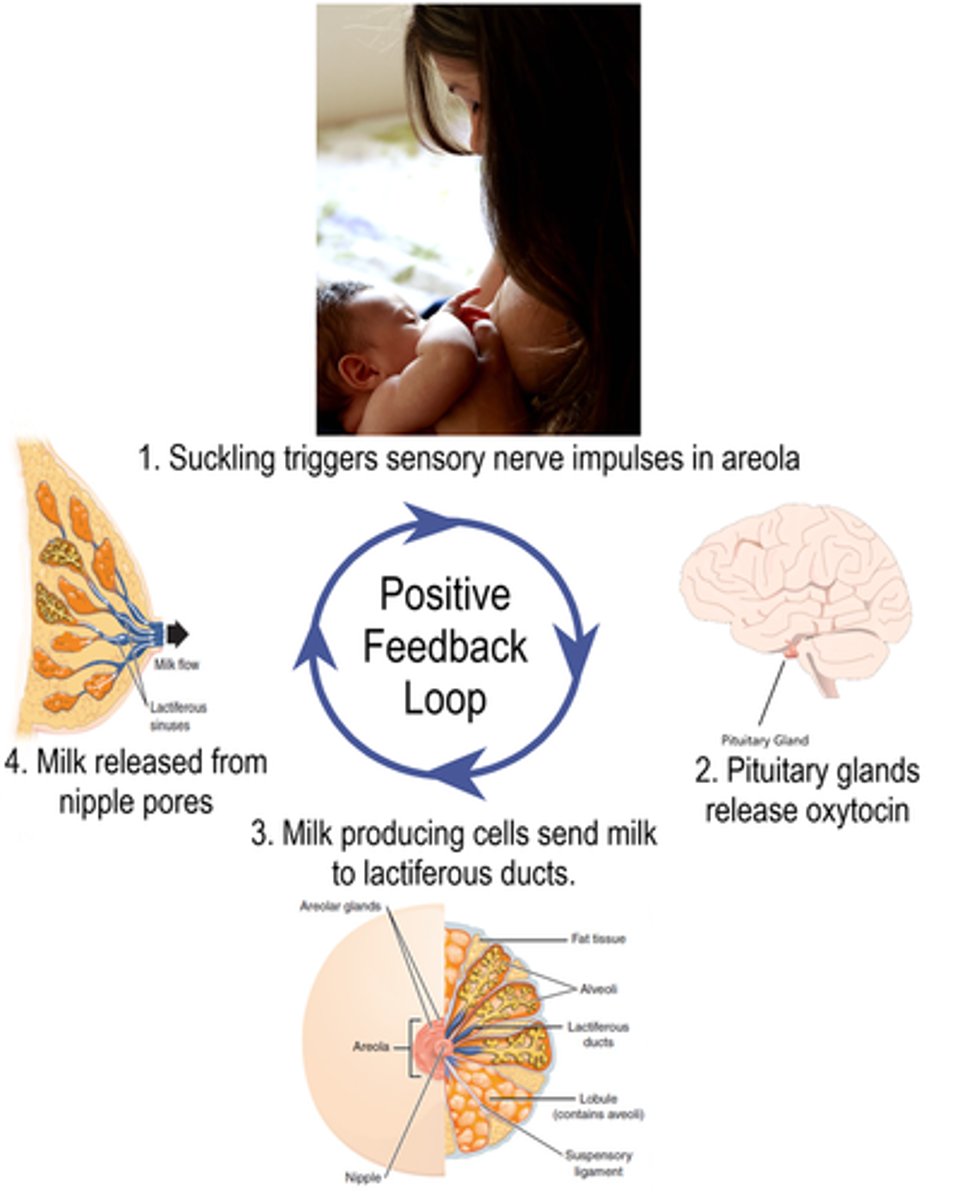
oxytocin provides positive feedback for _____ and _____
labor contractions; milk letdown
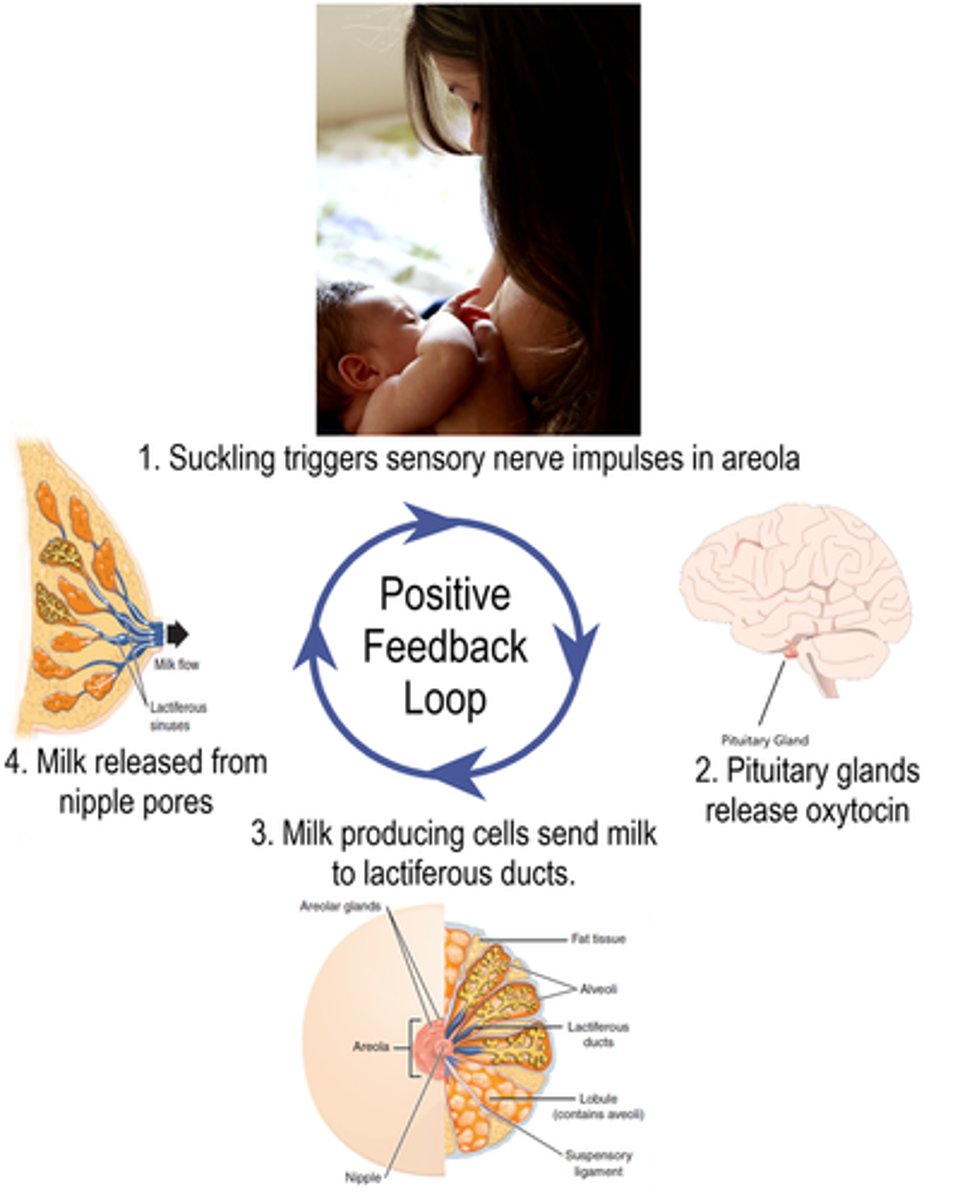
oxytocin is made by the _____ and is stored in the _____
hypothalamus; posterior pituitary gland
the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) is made of _____ tissue, so it _____ hormones
glandular; produces its own
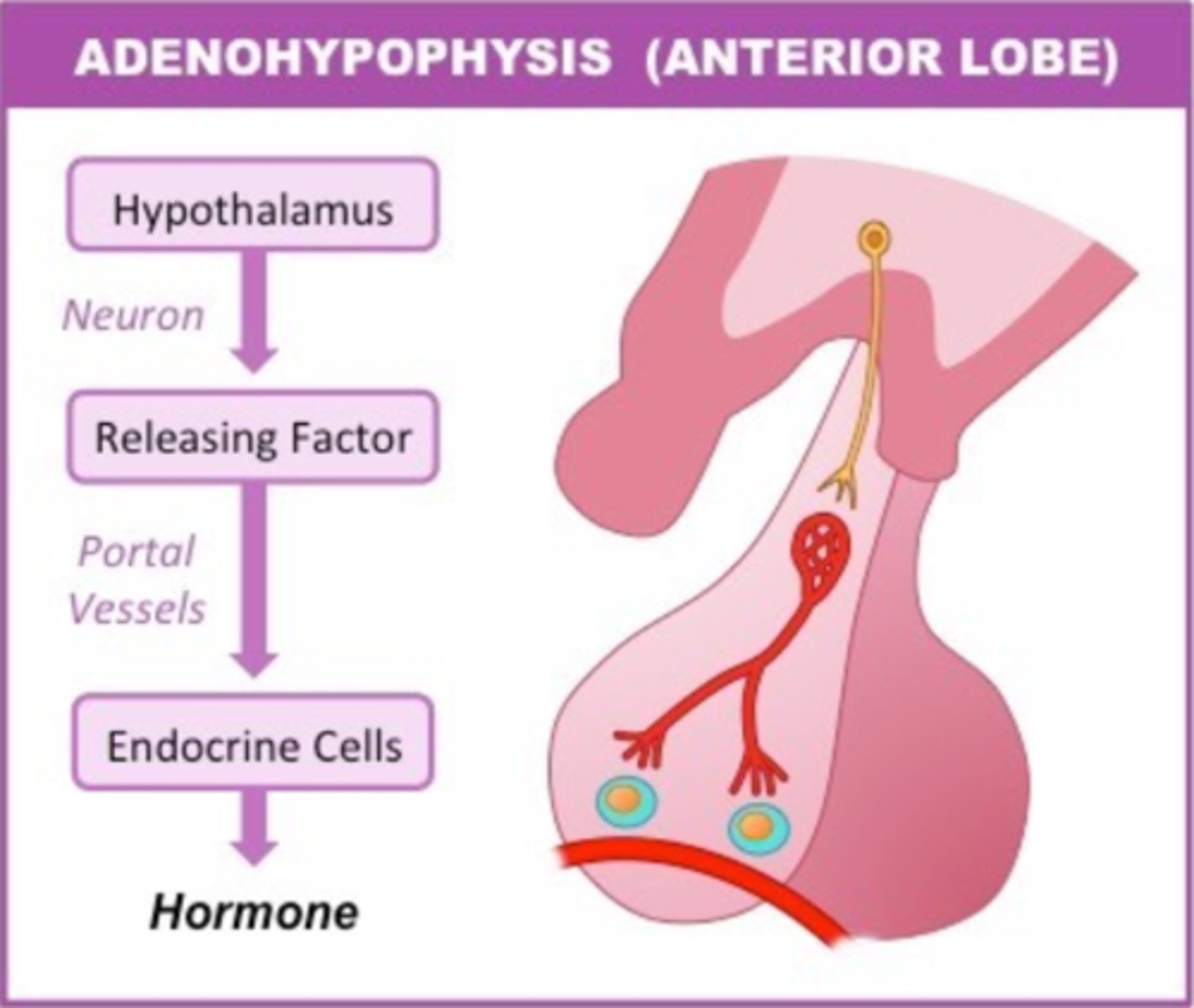
the _____ connects the anterior pituitary and the hypothalamus
hypophyseal portal system
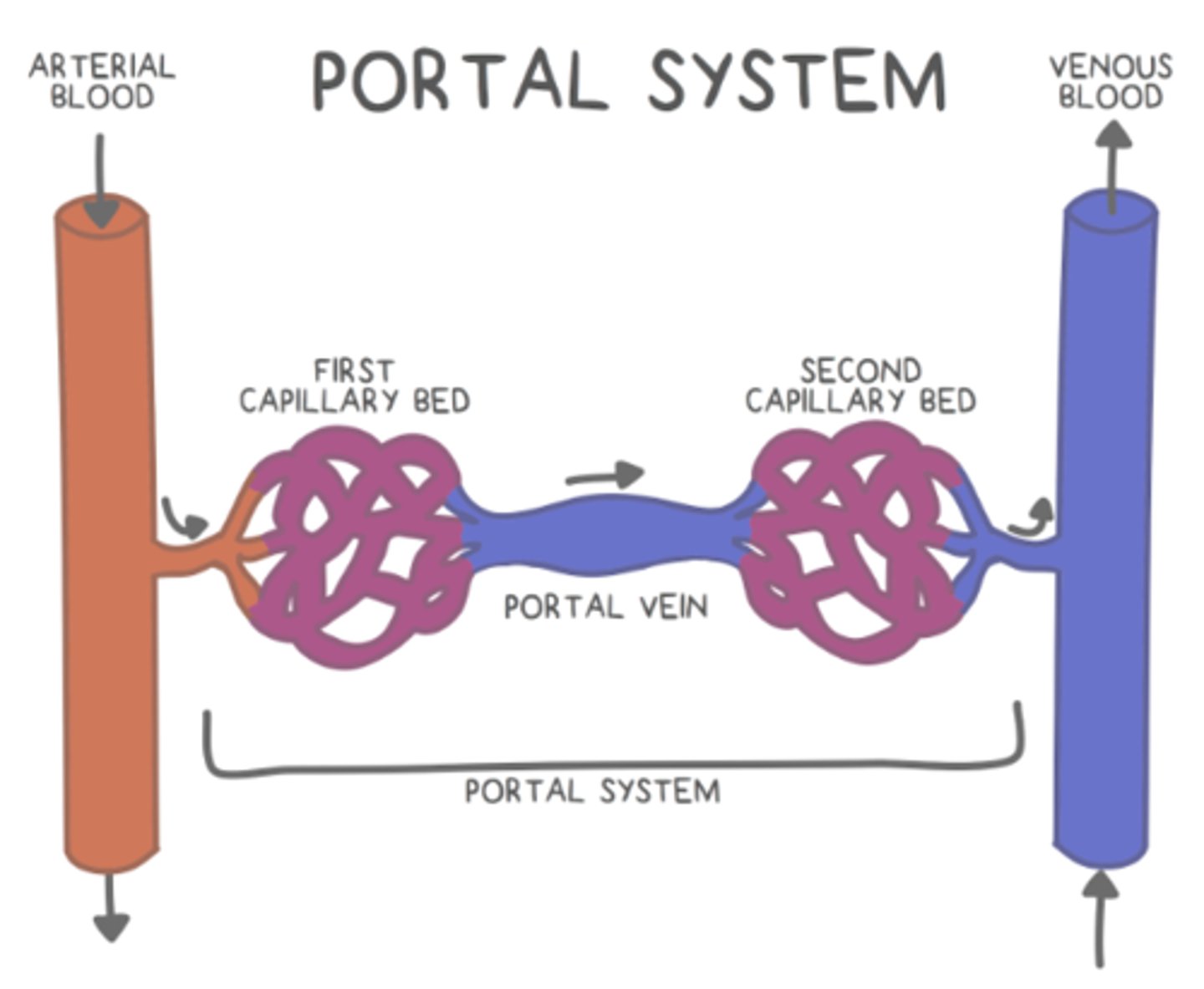
a _____ is when a capillary bed is connected to another capillary bed through a portal vein
portal system
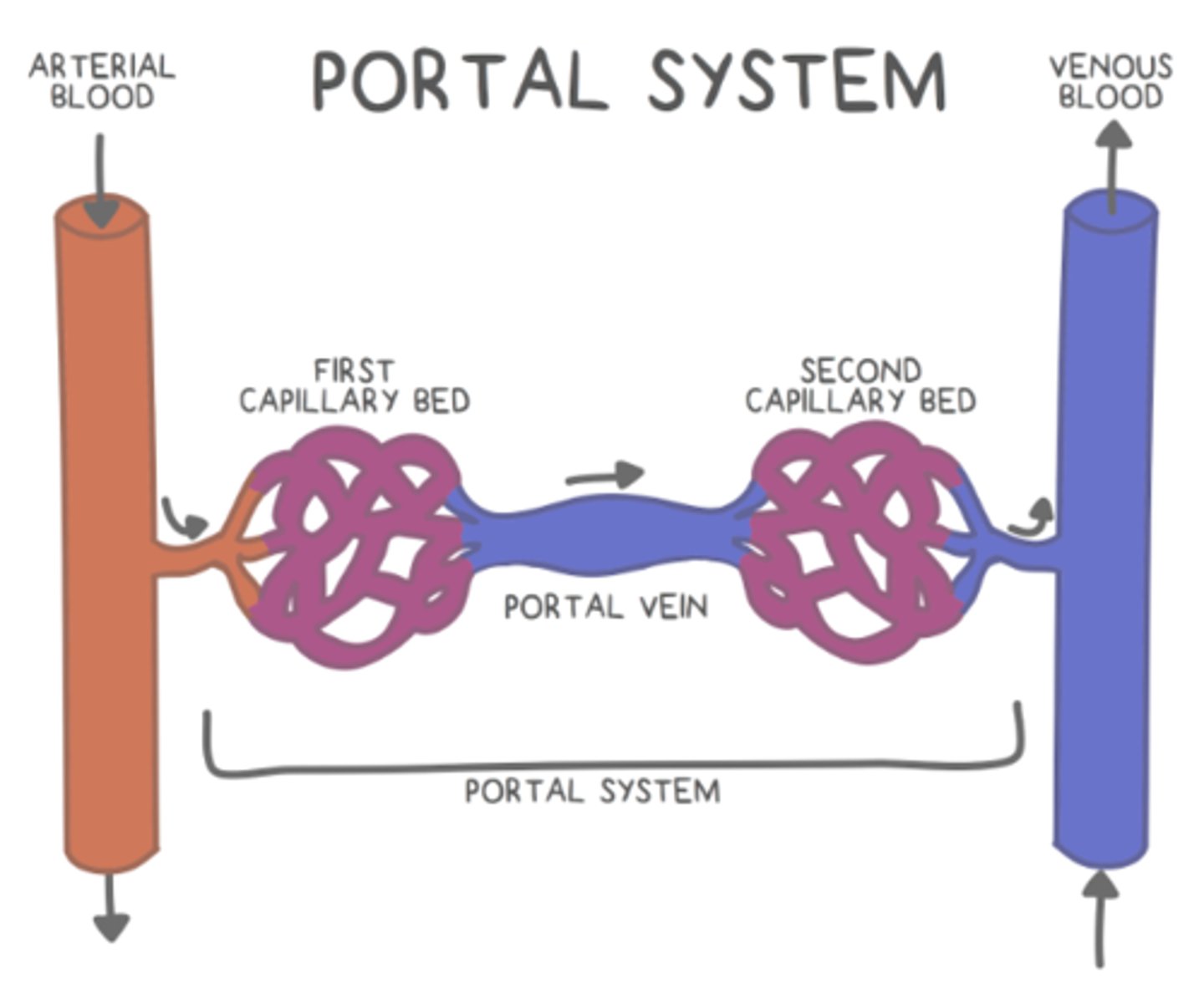
what are some of the key hypothalamic-releasing hormones, which act on the anterior pituitary (telling it to release the hormones it makes)
GnRH; TRH; CRH; GRH
Mnemonic: all hormones with the letter "R" in their abbreviations are secreted from the hypothalamus (R = releasing)
what are the effects of GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) from the hypothalamus?
tells the anterior pituitary to release LH and FSH to the gonads
what are the effects of TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) from the hypothalamus?
tells the anterior pituitary to release TSH to our thyroid glands
(also stimulates the anterior pituitary to release prolactin)
what are the effects of CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone) from the hypothalamus?
tells the anterior pituitary to release ACTH
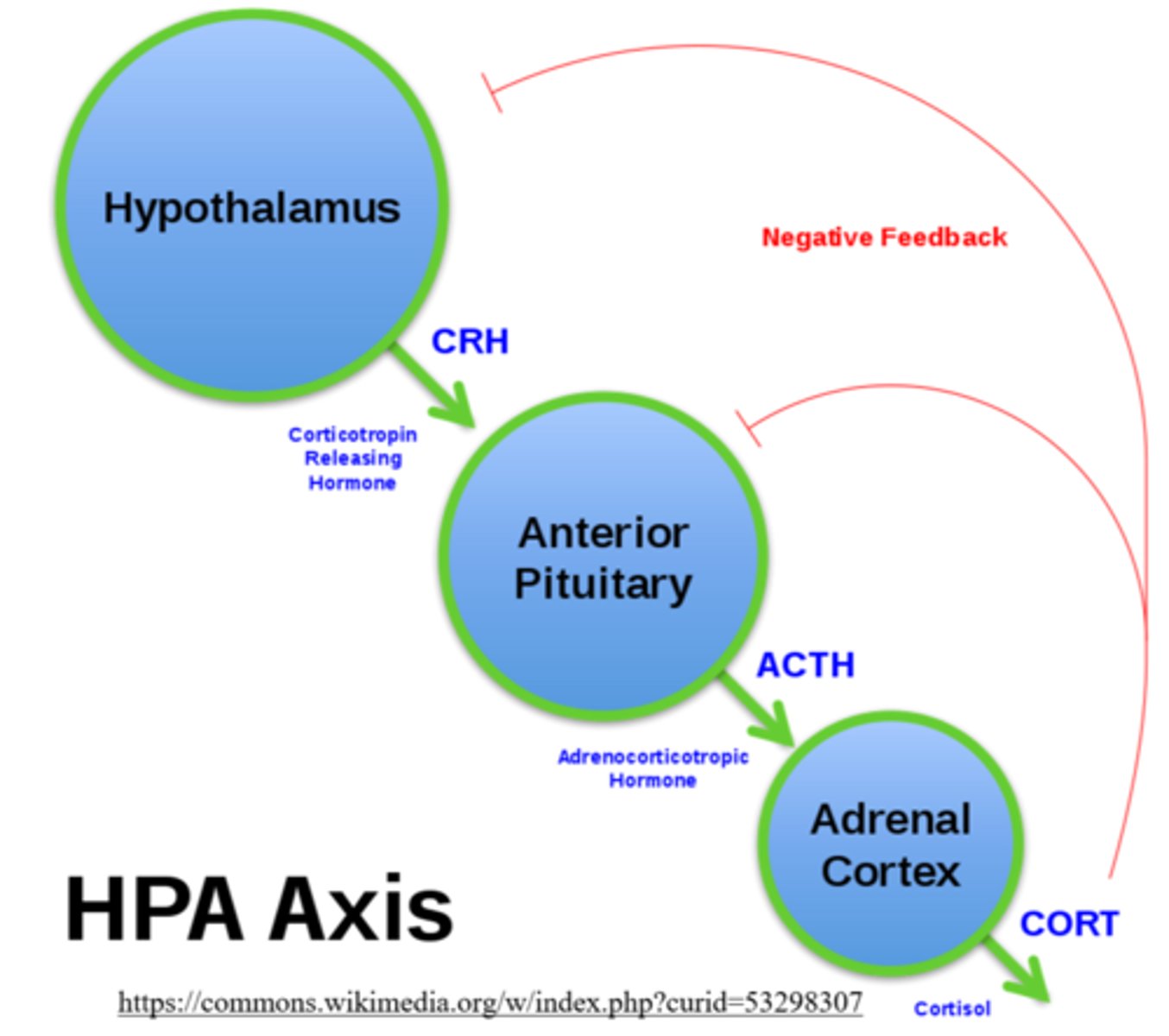
what are the effects of GHRH (growth hormone-releasing hormone) from the hypothalamus?
tells the anterior pituitary to release GH
what are the two classes of hormones released by the anterior pituitary?
tropic and direct
_____ hormones target and act on other endocrine glands
tropic
_____ hormones stimulate/act on organs
direct
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is a _____ hormone from the _____
tropic; anterior pituitary
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates _____ and _____
follicle growth (ovary); sperm maturation (testis)
luteinizing hormone (LH) is a _____ hormone from the _____
tropic; anterior pituitary
luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers _____ and the production of _____
ovulation; sex hormones
stress leads to the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which is a _____ hormone from the _____
tropic; anterior pituitary
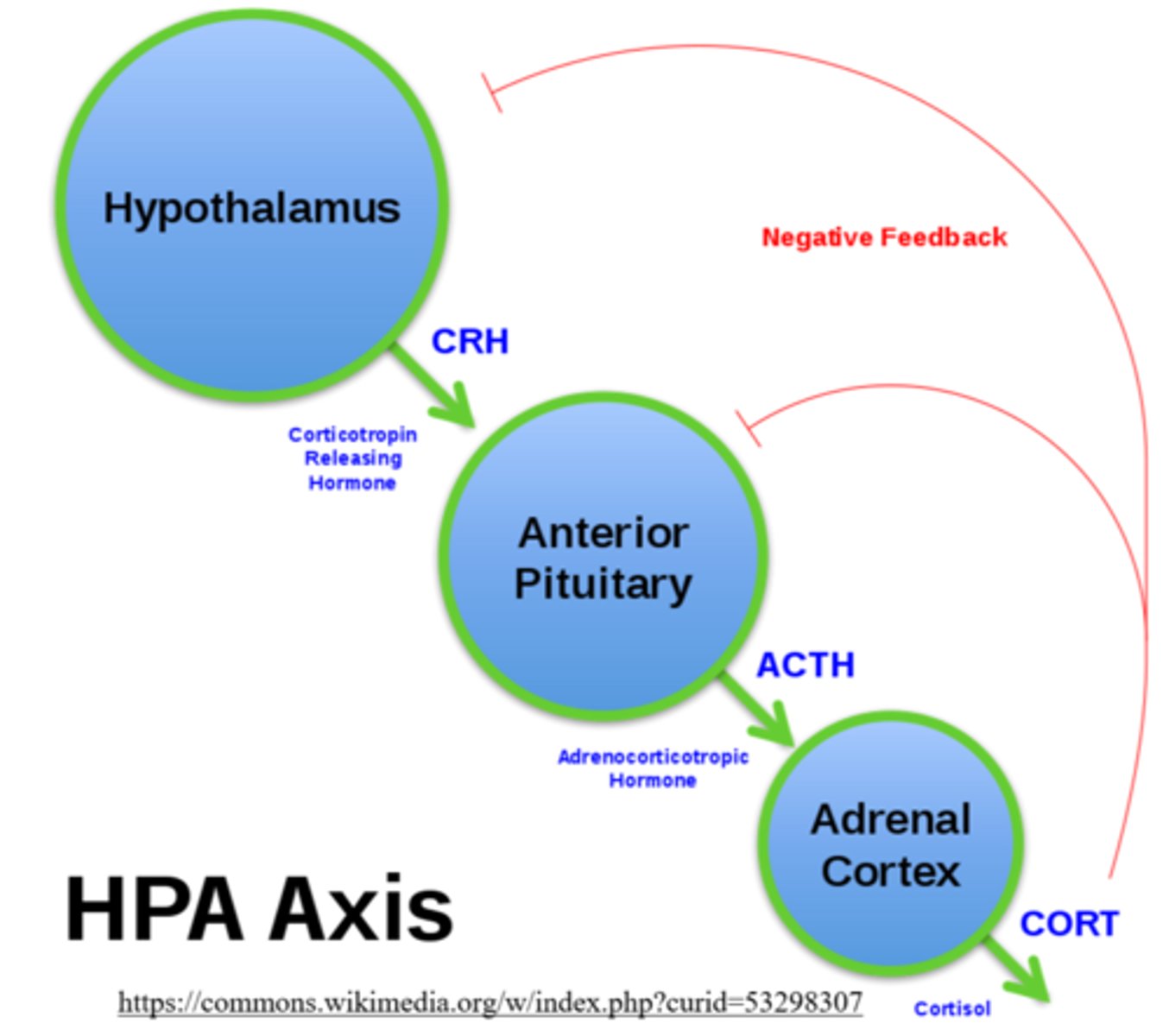
ACTH stimulates the adrenal _____ to release _____ to combat stress
cortex; glucocorticoids
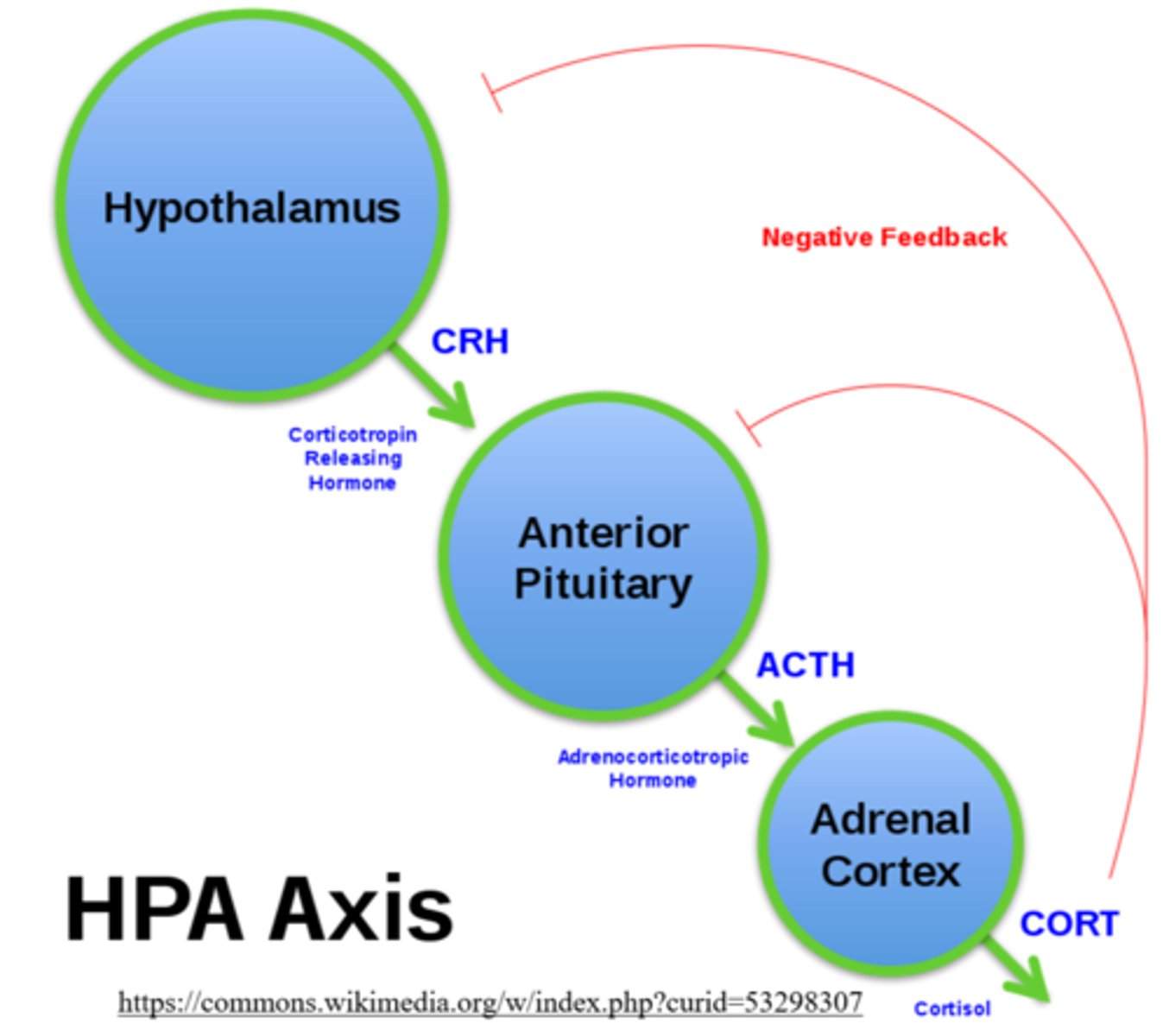
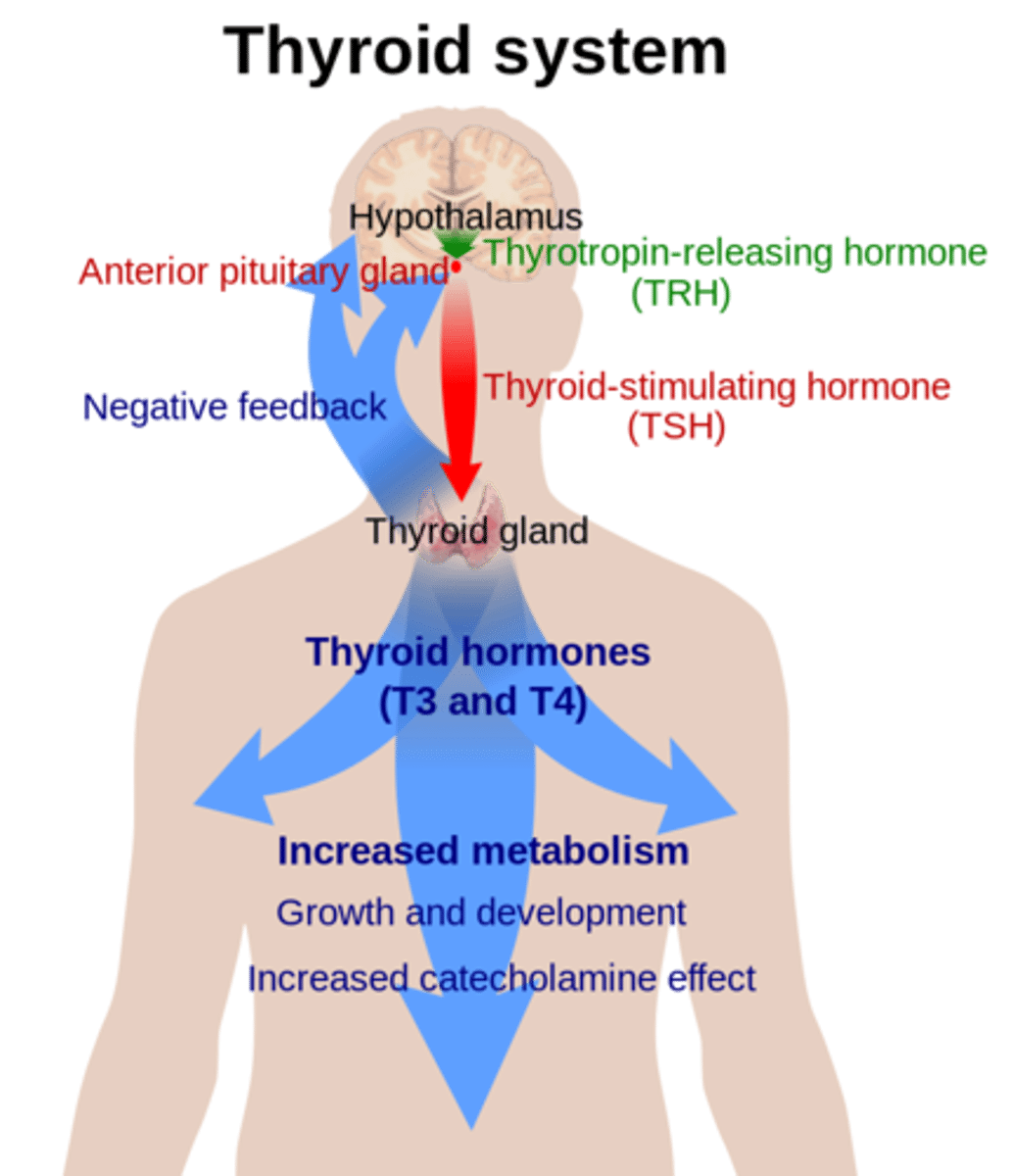
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) is a _____ hormone from _____, which stimulates the thyroid to produce T3 & T4
tropic; anterior pituitary
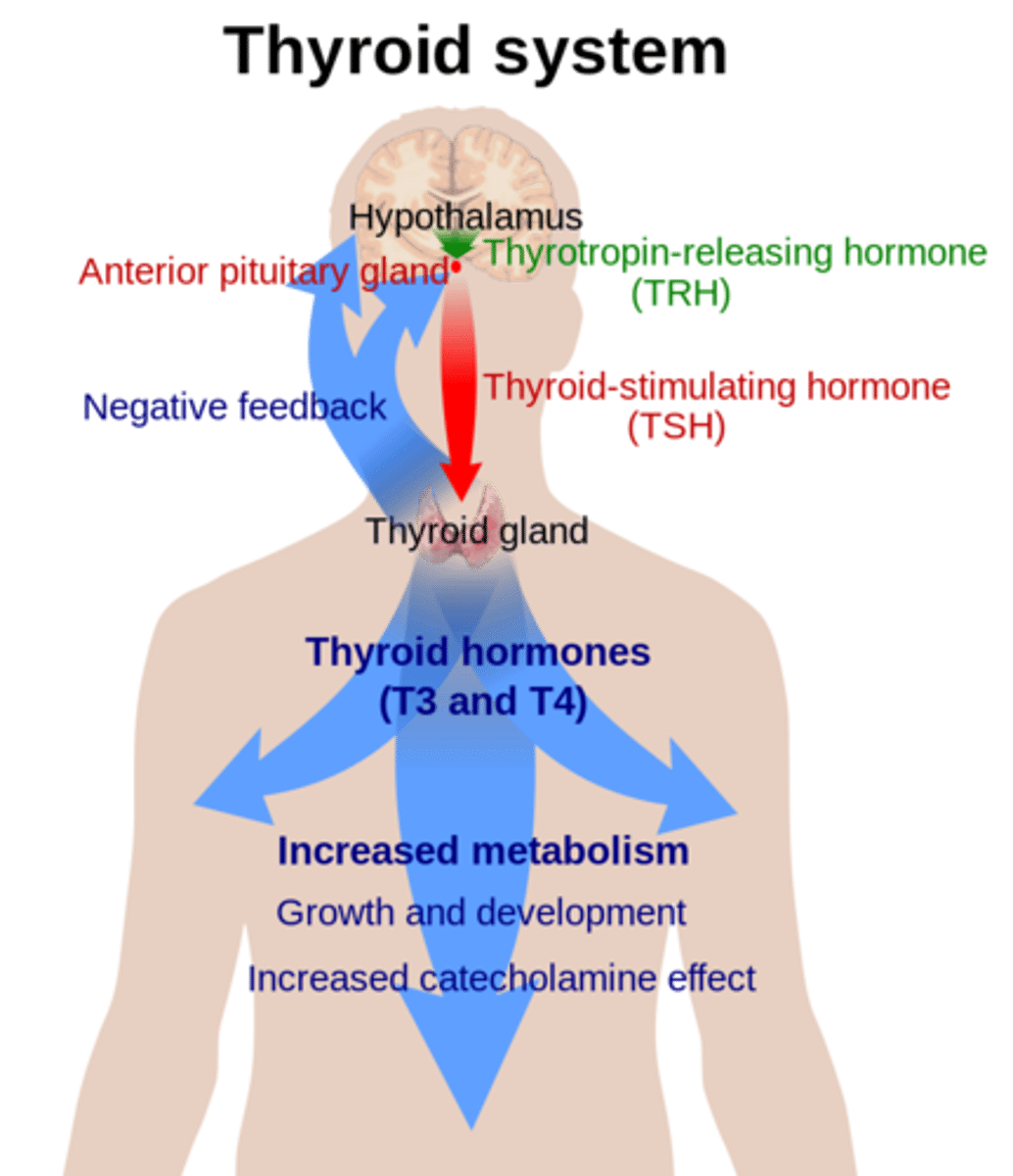
T3 & T4 are regulated by _____ feedback
negative
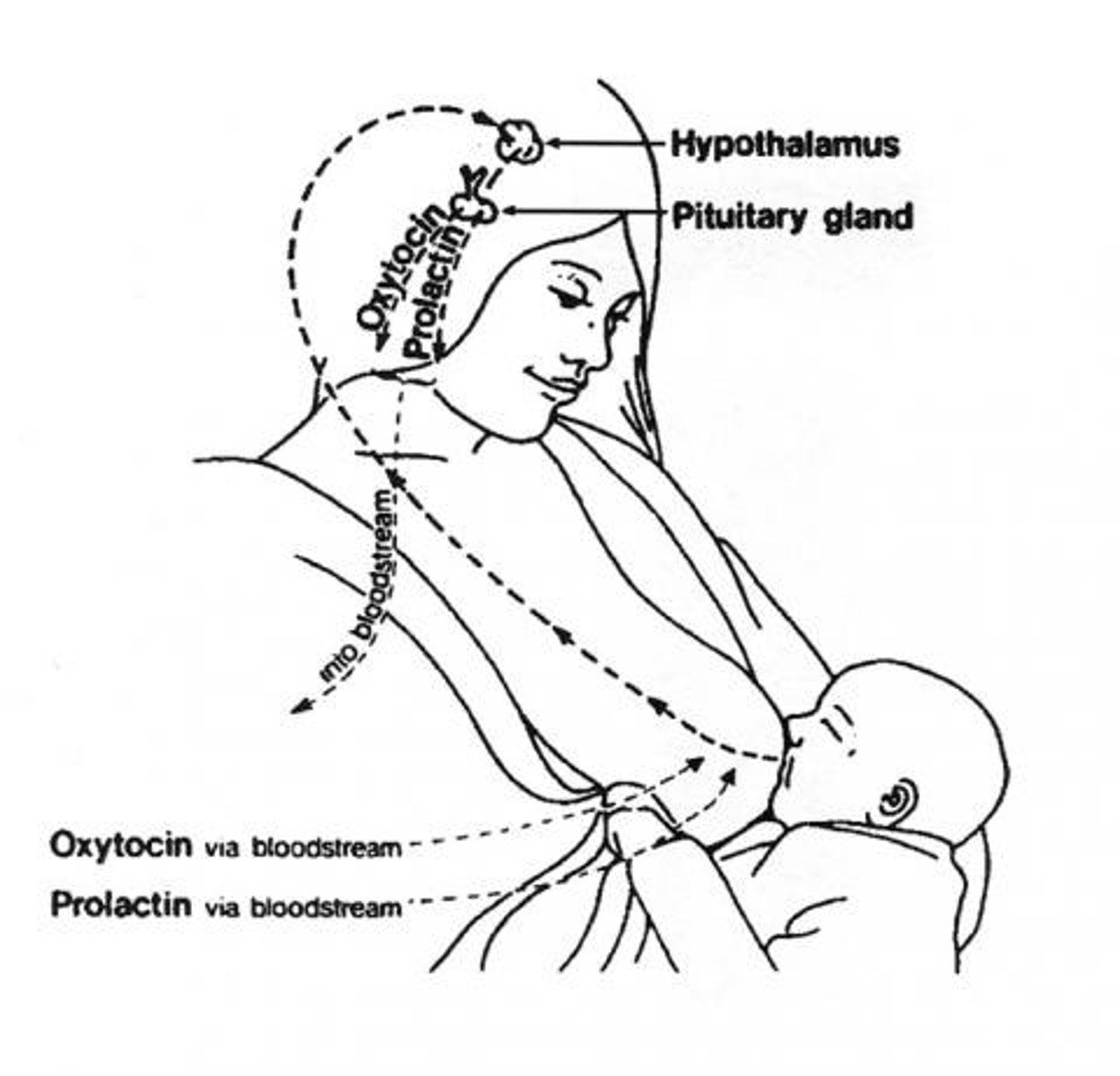
prolactin is a _____ hormone from the _____
direct; anterior pituitary
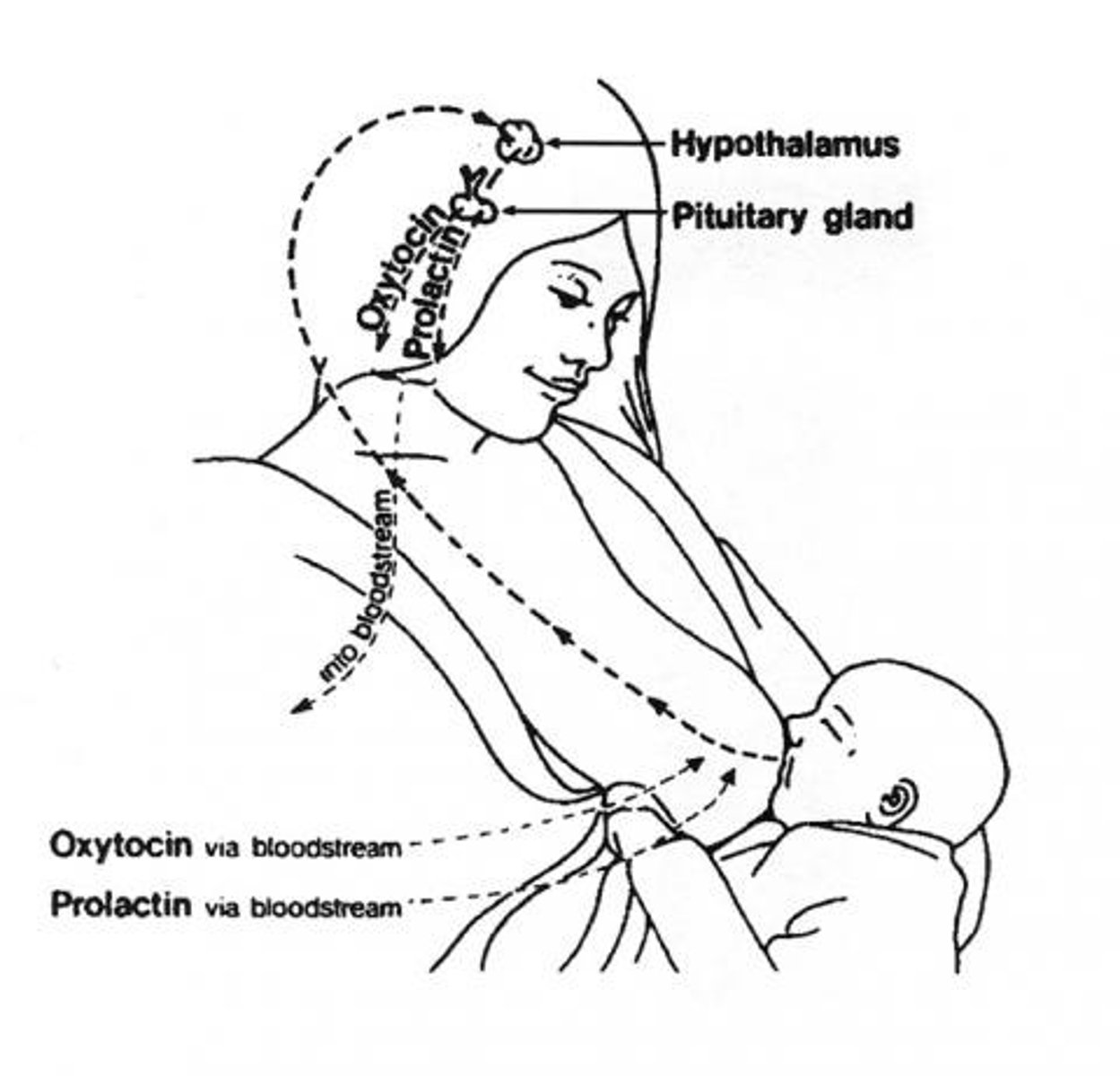
what are the two phases of prolactin effects?
stimulates mammary gland development during pregnancy; increases milk production after birth
growth hormone (GH) is a _____ hormone from the _____, which stimulates cell growth, reproduction, division
direct; anterior pituitary
another name for GH is _____
somatotropin
what is an acronym to remember the hormones the anterior pituitary gland produces?
FLAT PiG
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Prolactin
- ignore
- Growth Hormone (GH)

the _____ is a small gland in the brain that secretes melatonin
pineal gland
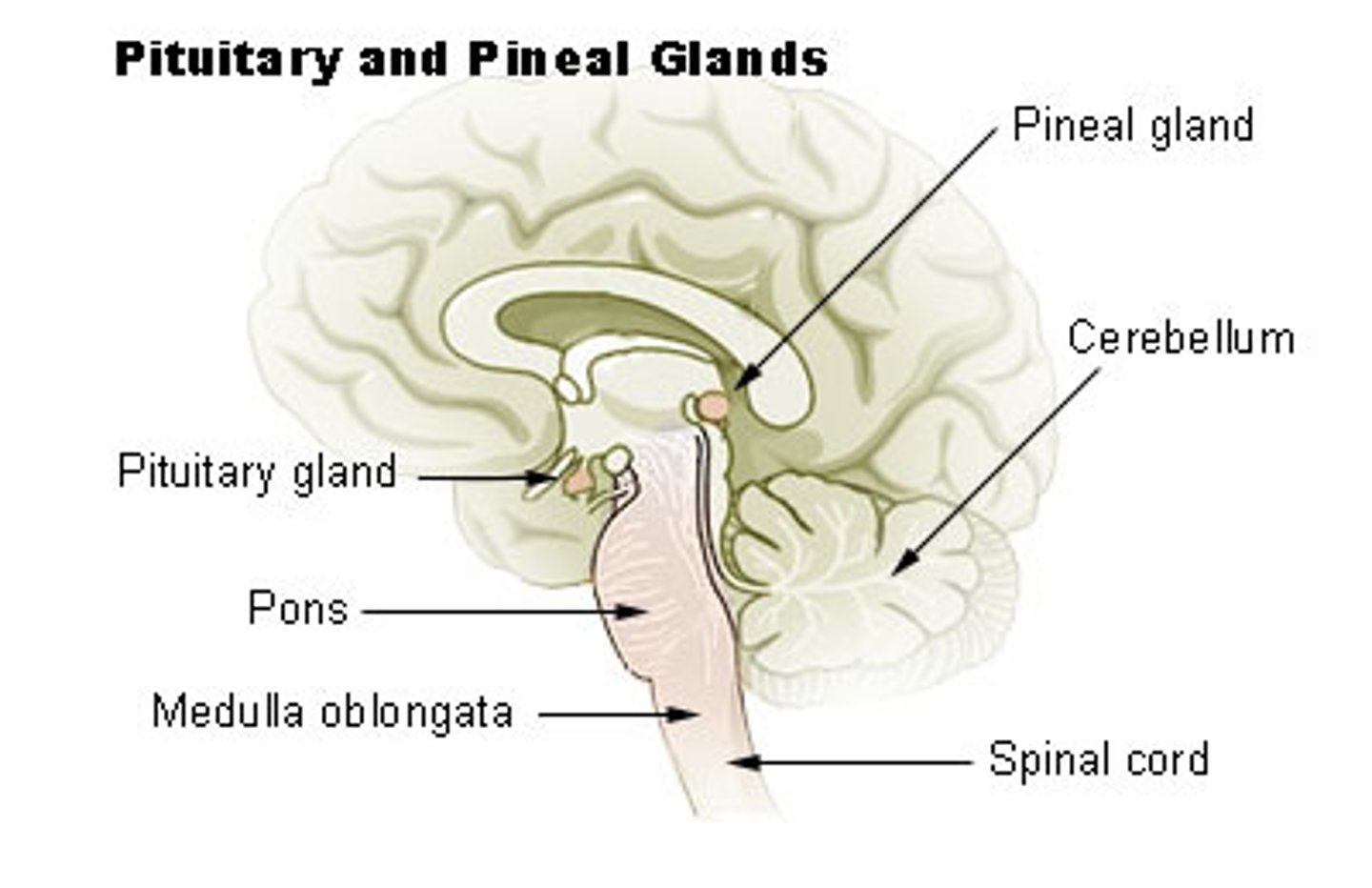
_____ regulates the circadian rhythm
melatonin
the largest endocrine organ in the body is the _____, which is located in front of the trachea
thyroid gland
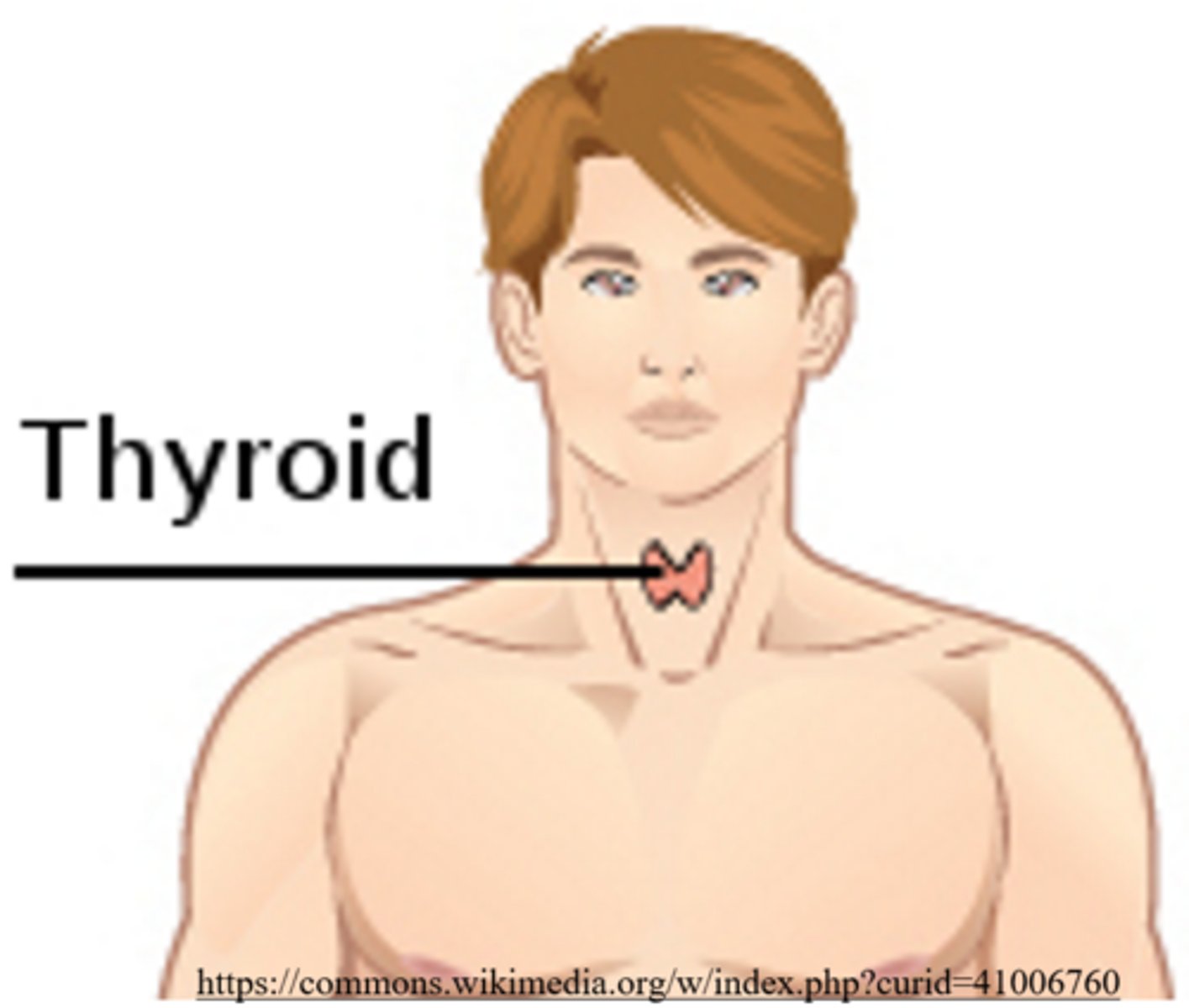
what three hormones are manufactured/secreted by the thyroid gland?
T3, T4, and calcitonin
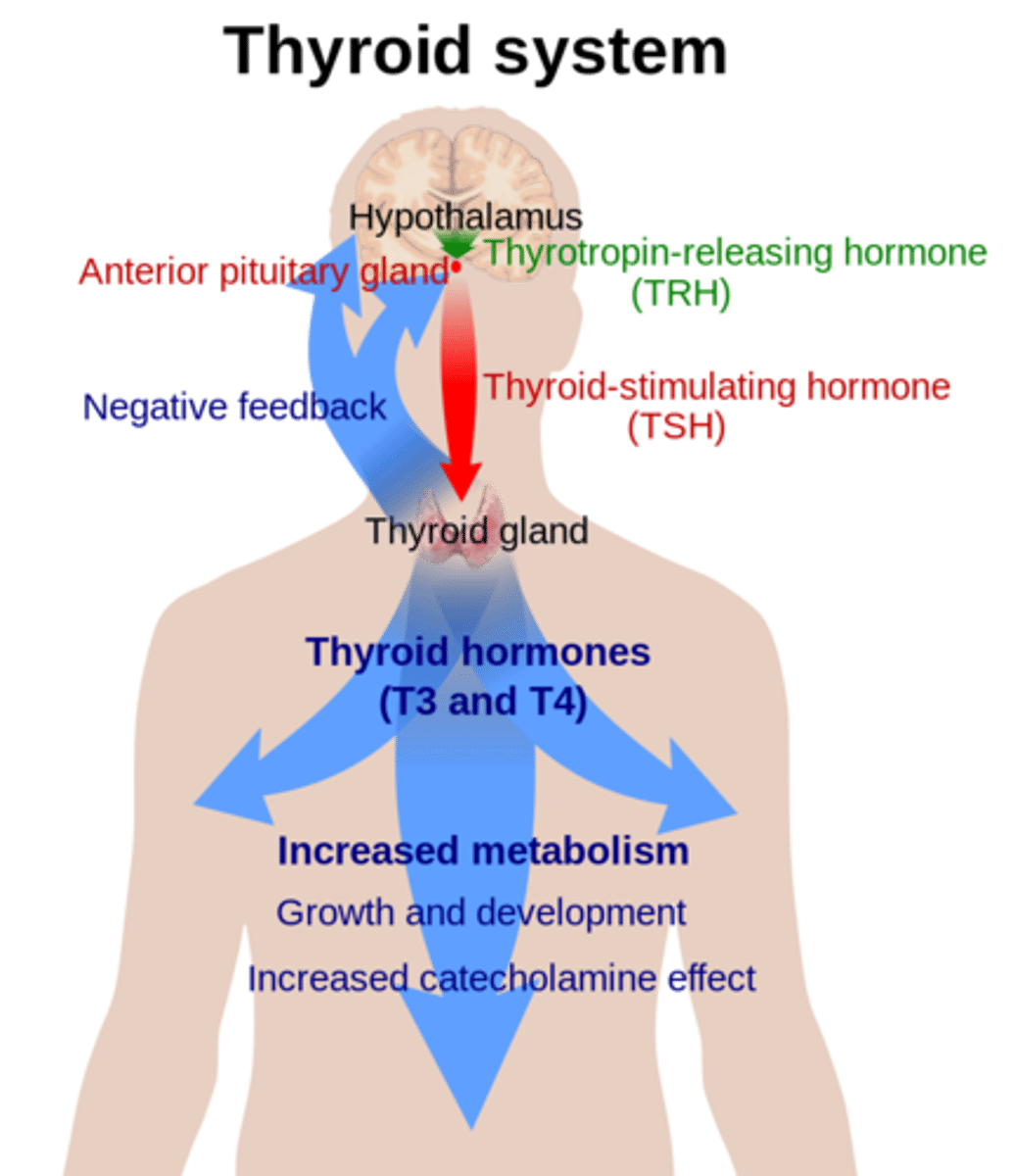
T4 has one more _____ atom than T3
iodine
T3 is the _____ form of the hormone
active (4x more potent than T4)
(T4 loses an iodine atom to become active T3)
which hormone (T4 or T3) is the main circulating form and why?
T4; it is more stable
under-secretion of T3 and T4 leads to _____ & a(n) _____ (increased/decreased) metabolic rate
hypothyroidism; decreased
over-secretion of T3 and T4 leads to _____ & a(n) _____ (increased/decreased) metabolic rate
hyperthyroidism; increased
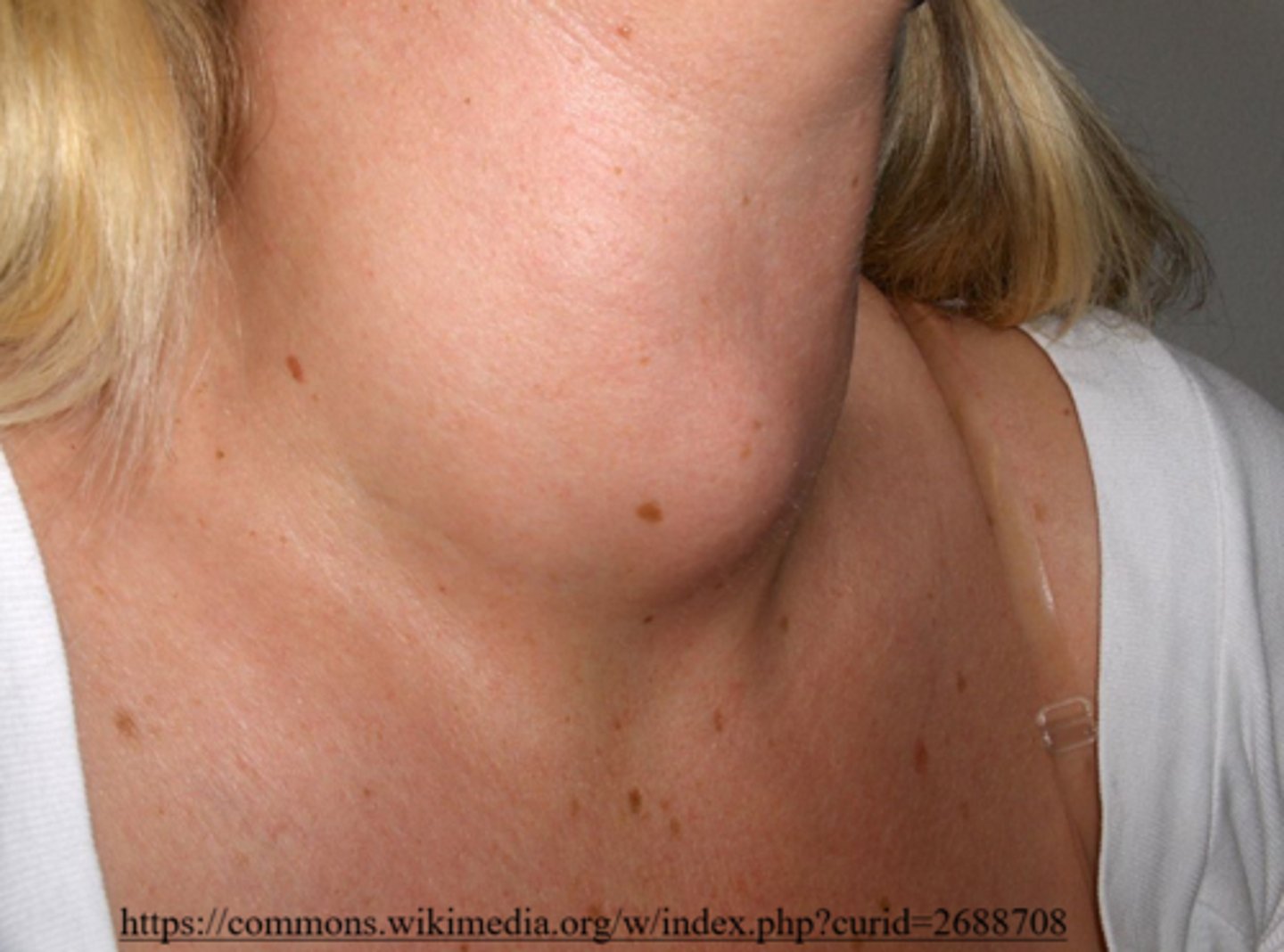
hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can cause _____, which is the physical enlargement of the thyroid gland
goiter
where is calcitonin secreted?
parafollicular cells of the thyroid
what are the main functions of calcitonin?
decrease blood calcium
calcitonin inhibits _____ (cell types)
osteoclasts
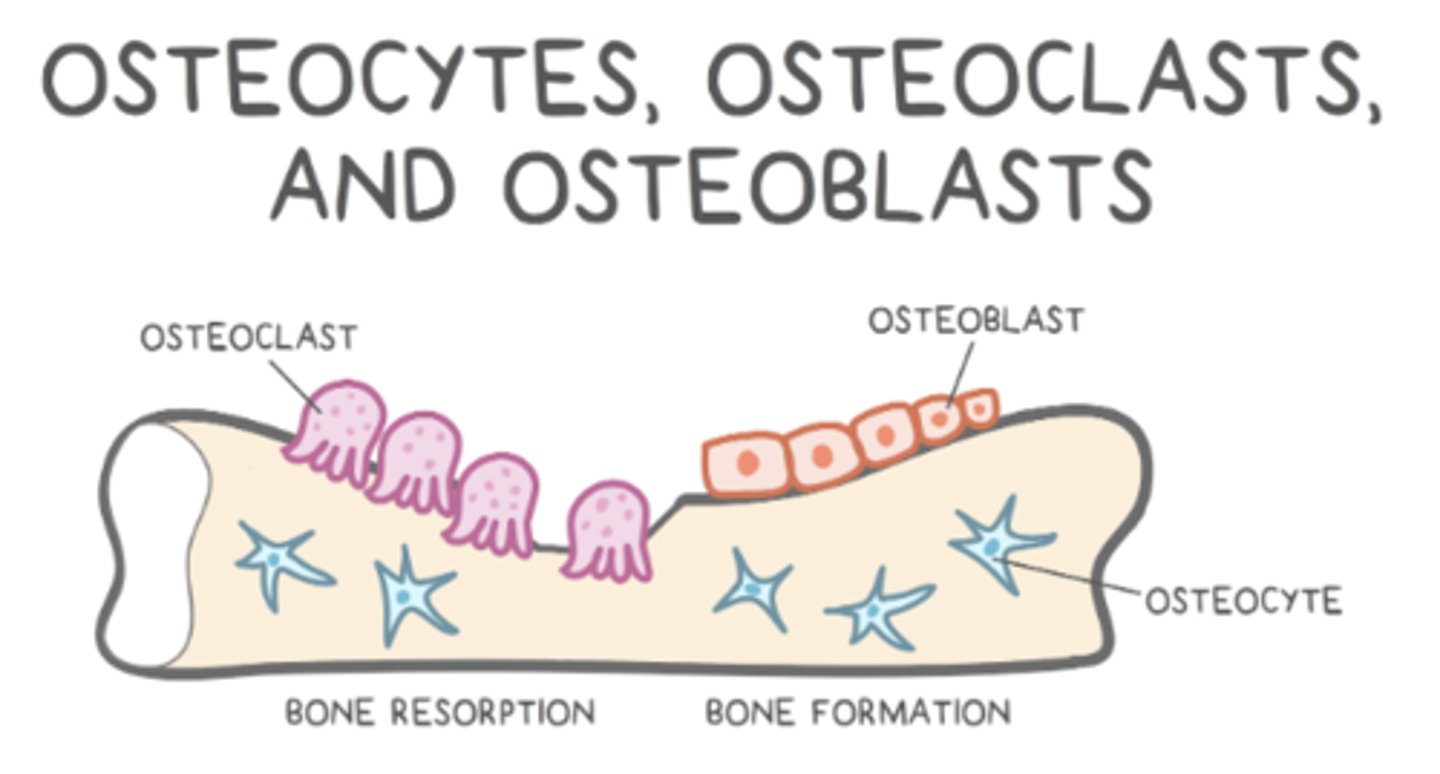
what is calcitonin's effect on the kidneys?
it decreases Ca2+ reabsorption in these areas
what hormone does the opposite function of calcitonin?
parathyroid hormone (PTH)
from where is PTH secreted?
parathyroid gland
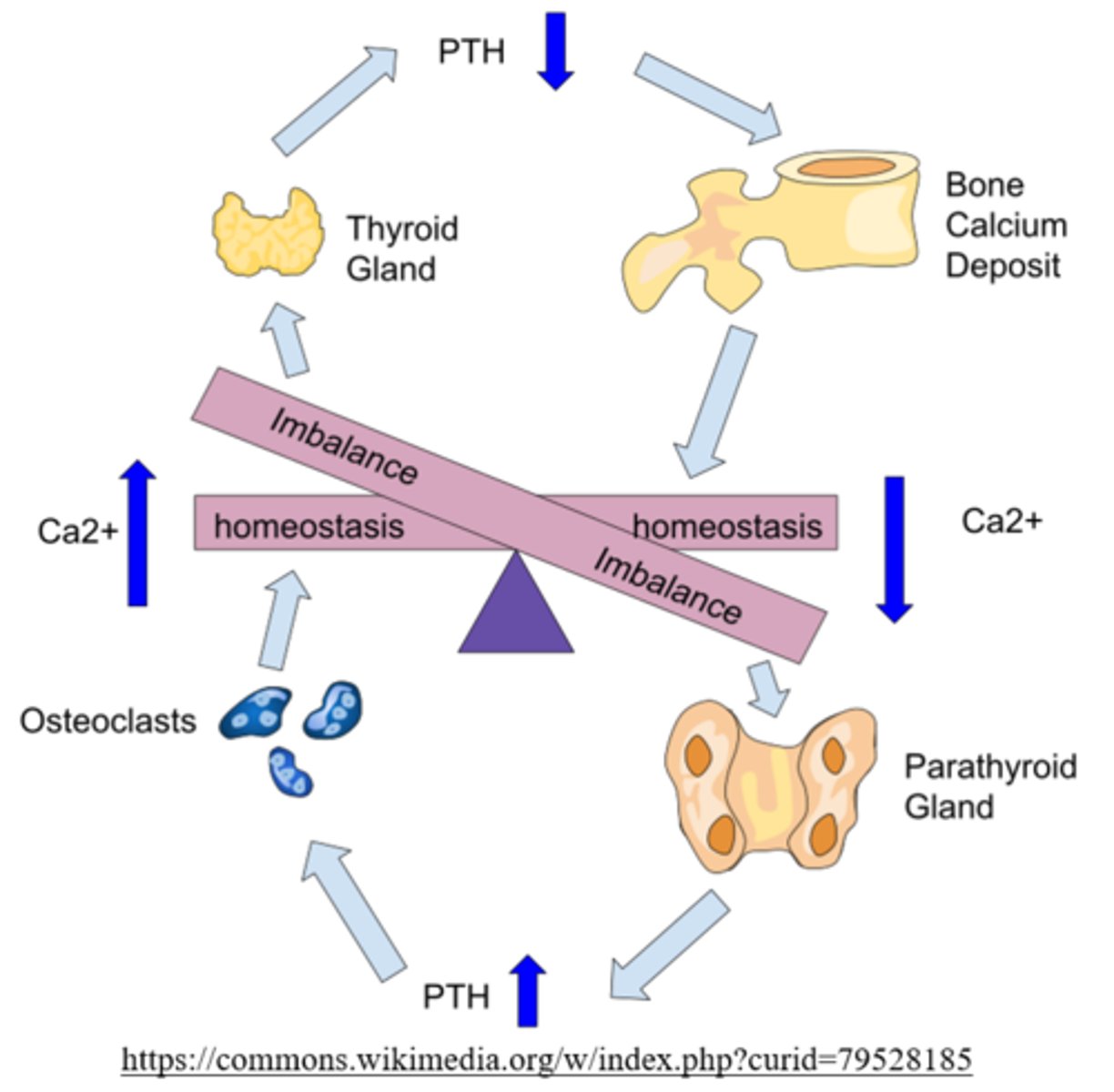
what is the primary function of PTH/the parathyroid gland?
increase blood calcium level
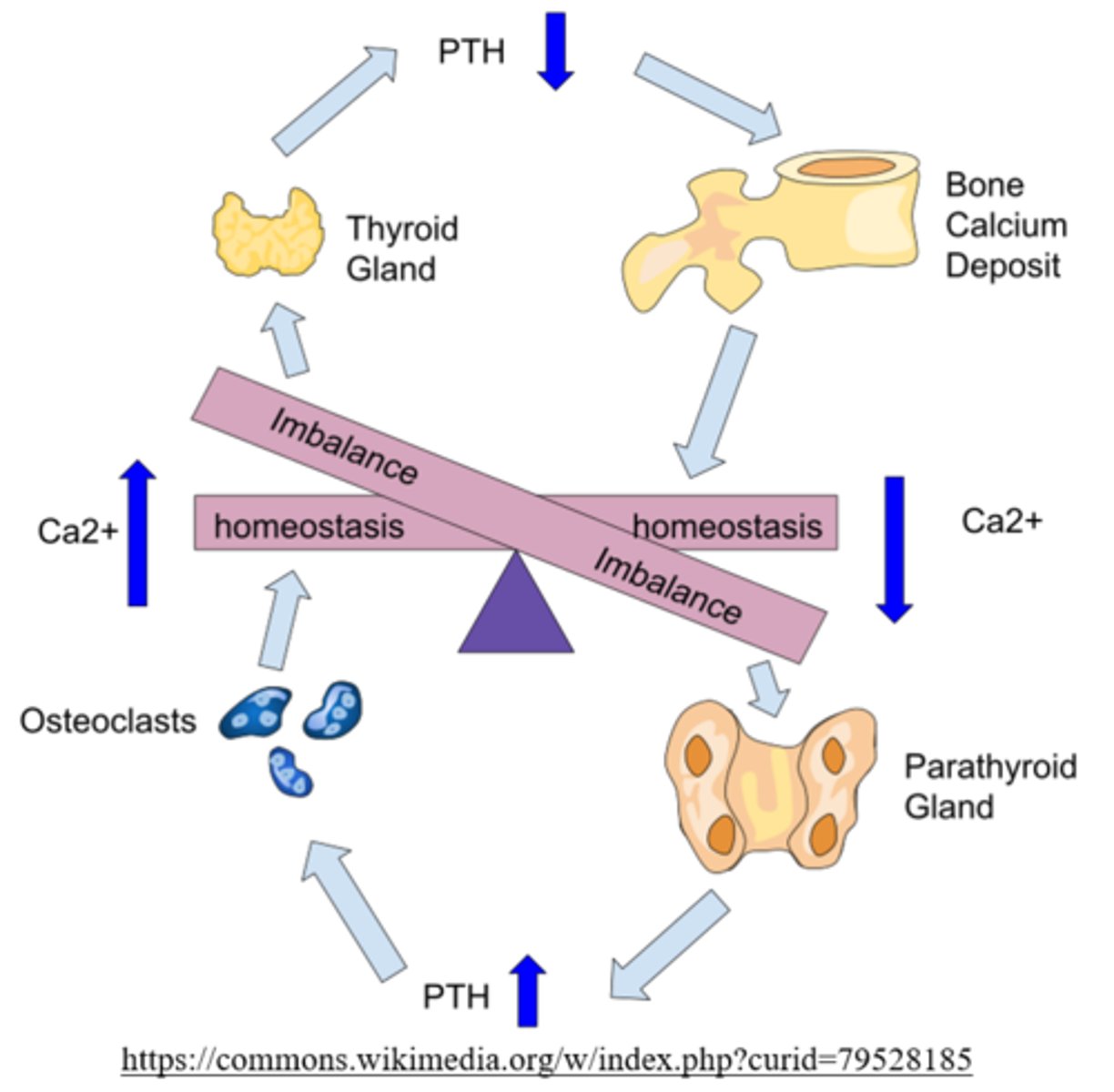
PTH stimulates _____ and _____ (increases/decreases) Ca2+ reabsorption in the kidneys and intestines
osteoclasts; increases
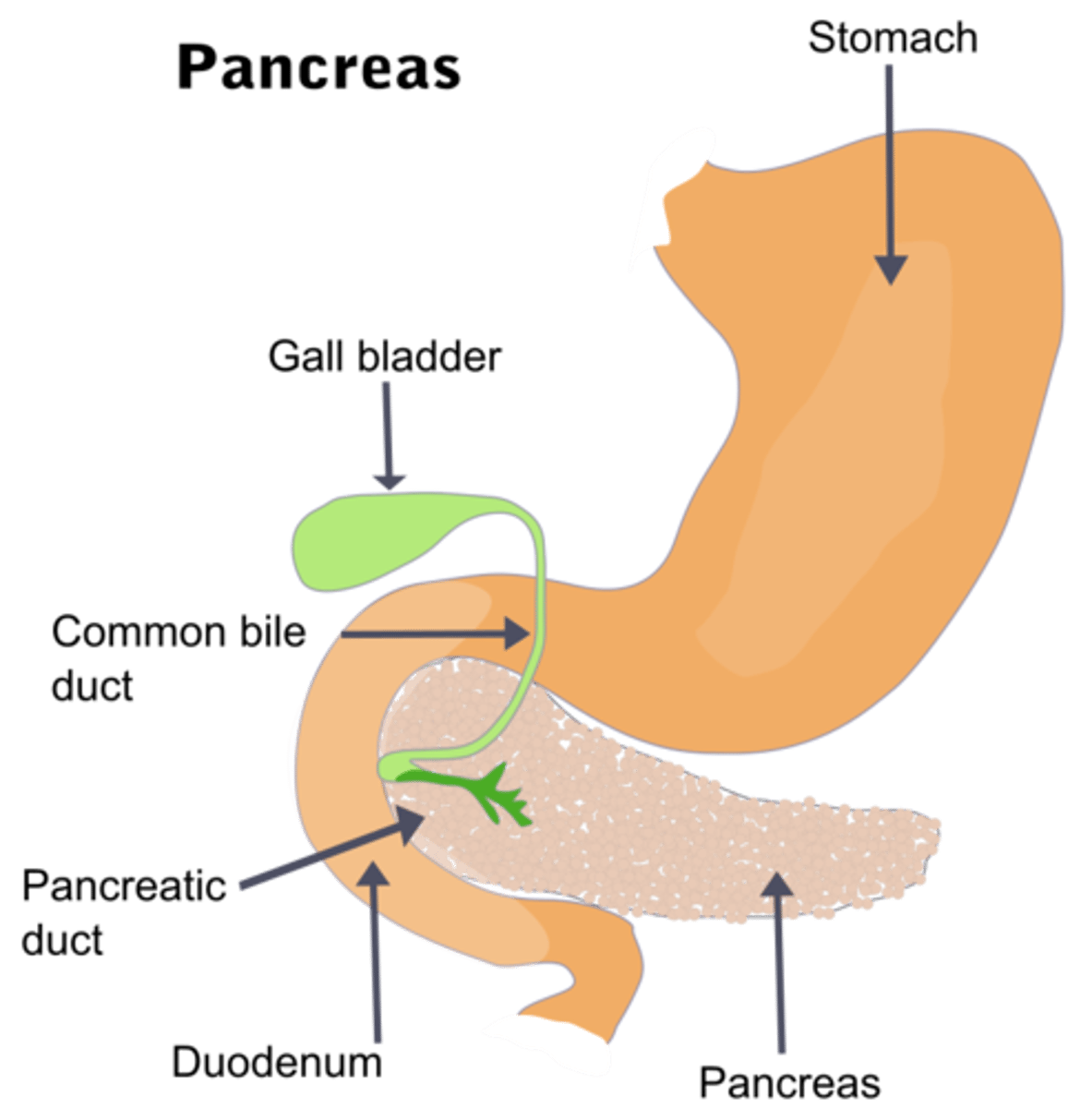
the pancreas has _____ and _____ functions
exocrine; endocrine
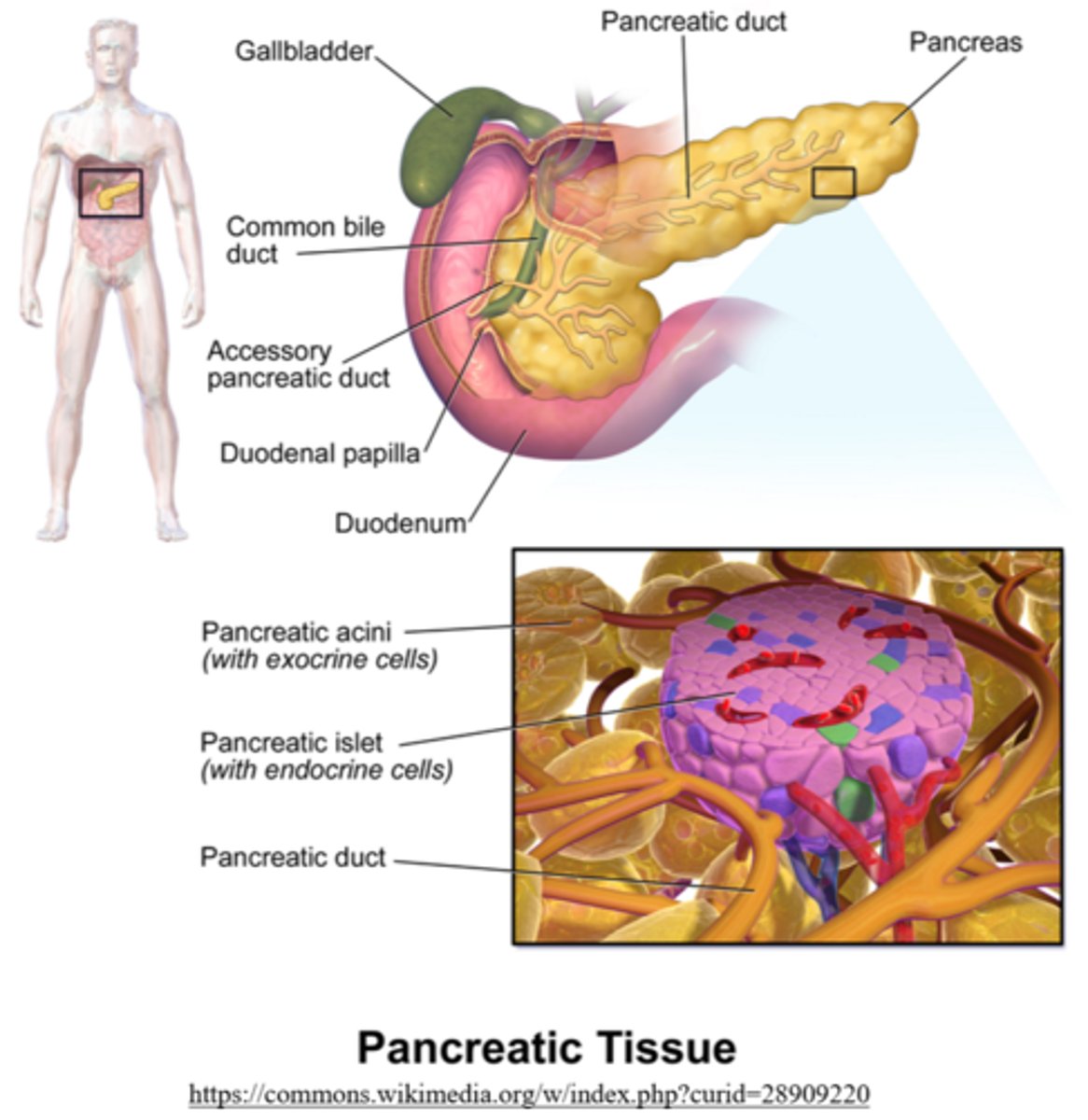
the _____ tissue of the pancreas secretes digestive enzymes through the pancreatic duct
exocrine
where does the pancreatic duct connect to?
duodenum of the small intestine
the _____ are endocrine pancreatic tissue
islets of Langerhans
what are the three key islet of Langerhans hormones?
insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin
(somatostatin =/= somatotropin (GH))
The ____ releases insulin and glucagon to help maintain glucose concentration in the blood.
pancreas
what are the three key islet of Langerhans cell types?
alpha (α); beta (β); delta cells (δ)
alpha (α) cells of islets secrete _____
glucagon
when is glucagon secreted from the alpha (α) cells of the islets?
during a low blood glucose level (typically during fasting or between meals)
what is the function of glucagon secreted from the alpha (α) cells of the islets?
increase blood glucose levels