AP Bio Unit 1
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
1
New cards
Ionic bonding
Transfer of electrons
2
New cards
Covalent bonding
Between non-metals, which cannot lose electrons.
3
New cards
Metals have a tendency to _____ electrons, which is why ionic bonds form
Lose
4
New cards
Amount of electrons per ring
2, 8, 8
5
New cards
H2O is a ______ bond
Covalent
6
New cards
Oxygen is _______ electronegative than Hydrogen, causing it to become partially negative.
More
7
New cards
In an H2O molecule, oxygen is ____ and hydrogen is ______ (charges)
Negative, positive
8
New cards
The difference in charges of an H2O molecule makes water _____
Polar
9
New cards
Polar = _______ sharing of electrons
Unequal
10
New cards
Hydrogen bonds are created because of the ________
Difference in charge of hydrogen and oxygen
11
New cards
Water has a ______ ______ tension because of cohesion, because of hydrogen bonds, because water is polar, because oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen.
High surface
12
New cards
Cohesion
Attraction between 2 like molecules (water)
13
New cards
Adhesion
Attraction between 2 different molecules
14
New cards
Water adheres to other _______ molecules (all caps)
POLAR
15
New cards
LIKE ______ LIKE
Dissolved/attracts to
16
New cards
Polar substances will dissolve in ___ substances, while nonpolar substances will dissolve in ______ substances.
Polar, nonpolar
17
New cards
Capillary action
Movement of water against gravity in narrow spaces
18
New cards
Through ______, stoma (pores of plants) lose water, creating a negative pressure, causing the water molecules to move up/to the stoma
Transpiration
19
New cards
Cohesion and adhesion _____ cause capillary action
Together
20
New cards
Water is _____ dense as a solid (ice) than as a liquid
Less
21
New cards
Ice ______ in water
Floats
22
New cards
Hydrogen bonds in solid water (ice) are more ______ compared to the hydrogen bonds in liquid water.
Stable
23
New cards
Pond for example: as ____ freezes, the less dense ice floats up to the surface. Ice is a bad conductor of heat, so under the layer of ice on the surface, the heat of the pond is able to maintain itself.
Water
24
New cards
Water has a ______ heat capacity, allowing it to prevent the heat of the air to increase rapidly.
High
25
New cards
\
NaCl are held together by ionic bonds, so when they break apart they are _____ (charged). This allows water to dissolve them, as the negative oxygen molecules are attracted to the positive Na, while the positive hydrogen molecules are attracted to the negative Cl.
NaCl are held together by ionic bonds, so when they break apart they are _____ (charged). This allows water to dissolve them, as the negative oxygen molecules are attracted to the positive Na, while the positive hydrogen molecules are attracted to the negative Cl.
Ions
26
New cards
The 4 macromolecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
27
New cards
Ratio of CHO in carbohydrates
CH2O
28
New cards
Structure of lipids (what elements make them up)
CHO
29
New cards
Structure of proteins (elements that make them up)
CHONS
30
New cards
Structure of nucleic acids (elements that make them up)
CHONP
31
New cards
Lipids ___ polymers. (CARBS, PROTEINS, + NUCLEIC ACIDS ARE)
Are not
32
New cards
Dehydration synthesis
Monomers are put together to form a polymer by TAKING OUT a water molecule →replacing it with a covalent bond.
33
New cards
Hydrolysis
Polymers are broken down to monomers through the addition of a water molecule
34
New cards
Carbohydrates are involved with short-term _____ storage
Energy
35
New cards
Simple carbohydrates (Monosaccharides)
Glucose, fructose, galactose
36
New cards
Simple carbohydrates (disaccharides)
Lactose, maltose, sucrose
37
New cards
Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides)
Starch, cellulose, glycogen
38
New cards
Monomer for all 3 complex carbs is _____
Glucose
39
New cards
Cellulose + starch are found in _____ cells
Plant
40
New cards
Glycogen is found in ______ cells
Animal
41
New cards
Starch is a ______ polysaccharide
Storage
42
New cards
Starch is to plant cells what _____ is to animal cells
Glycogen
43
New cards
Cellulose is a ____ polysaccharide, that forms the cell ____ of plant cells
Structural, wall
44
New cards
The way individual glucose molecules are bonded to each other, and the way they branch out gives the molecules different ______.
Functions
45
New cards
Lipids are hydro____, because they are NONPOLAR (electrons are distributed equally)
Phobic
46
New cards
Monomers of DNA and RNA (nucleic acids) are ____
Nucleotides
47
New cards
3 parts of a nucleotide
1. Phosphate group
2. 5-Carbon sugar
3. Nitrogenous base
48
New cards
2 base pairs of DNA
Adenine - Thymine
Guanine - Cytosine
Guanine - Cytosine
49
New cards
Base pairs are held together by ______ bonds
AT has 2, while GC has 3
AT has 2, while GC has 3
Hydrogen
50
New cards
\# of base pairs measures the _____ of DNA
Length
51
New cards
Adenine and Guanine are ____, so they have a _____ ring
Purines, double
52
New cards
Thymine and Cytosine are _____, so they have a ______ ring
Pyrimadine, single
53
New cards
Carbon # _ is the connection point of the bond with phosphate group
3
54
New cards
The covalent bond between phosphate group and carbon #3 is called
Phosphodiester bond
55
New cards
Phosphodiester bonds are formed by __________ _________
Dehydration synthesis
56
New cards
DNA top and bottom are determined by the # of Carbon that is exposed, either __ or __
3’, 5’
57
New cards
DNA strands run ____________, the nucleotides are upside down on one side, and rightsideup on the other
Antiparellel
58
New cards
RNA is ____-stranded
Single
59
New cards
Base pairs of RNA
Adenine - Uracil
Guanine - Cytosine
Guanine - Cytosine
60
New cards
RNA is ___ sugar while DNA is ______ ribose sugar
Ribos, deoxy
61
New cards
Cells are constanly forming proteins for survival, in processes called
Protein synthesis
62
New cards
Ribose sugar
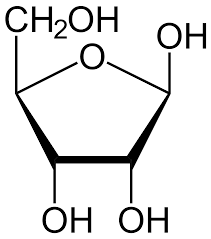
63
New cards
Deoxyribose sugar
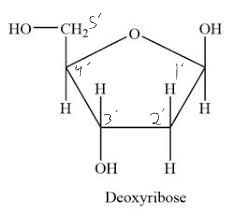
64
New cards
Monomer of proteins
Amino acid
65
New cards
Structure of amino acid
\
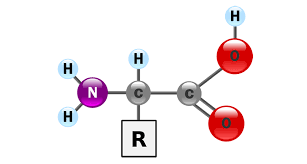
66
New cards
5 parts of amino acid
1. Amino group (NH2)
2. Central Carbon
3. Hydrogen atom
4. Side chain (R)
5. Carboxyl group (COOH)
67
New cards
____ bonds link amino acids
Peptide
68
New cards
Polypeptides
Polymers of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
69
New cards
What differentiates the 20 amino acids
Side chain/ R group
70
New cards
In a very long polypeptide, the LEFT side would be called the _- terminal (amino group)
N
71
New cards
In a very long polypeptide, the RIGHT side would be called the _-terminal (carboxyl group)
C
72
New cards
The amino group, central carbon, and carboxyl group are the _______ of a polypeptide
Backbone
73
New cards
Proteins need a specific ______ to be functional (primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary)
Structure
74
New cards
Polypeptides are not _______ unless they are put into a structure
Proteins
75
New cards
Primary strucuture
Specific sequence of amino acids for a particular protein. Held by covalent (peptide) bonds
76
New cards
Secondary structure
Alpha helices (helix) and beta sheets are formed by hydrogen bonding. The backbone fold into these structures with and hydrogen bonds between the carboxylic and amino group of the polypeptide backbone.
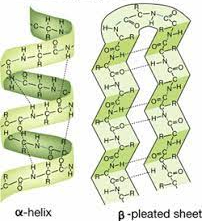
77
New cards
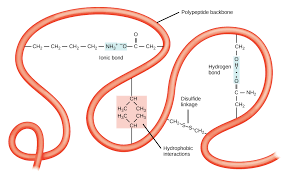
Tertiary structure
The R groups are attracted to each other, causing __ionic__ bonds, changing the structure of the protein. This level causes the protein to form a 3-D shape.
78
New cards
Ionic bond between ________
(Tertiary structure)
(Tertiary structure)
R groups
79
New cards
Hydrogen bonds between ______
(Tertiary structure)
(Tertiary structure)
Side groups of backbone
80
New cards
Disulfide linkage is ______
(Tertiary structure)
(Tertiary structure)
Between Sulfurs
81
New cards
Quaternary structure
Proteins consisting of multiple polypeptide chains
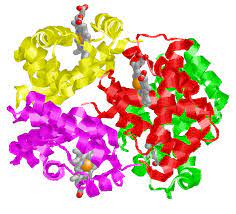
82
New cards
3 common forms of lipids in the human body
Triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesterol
83
New cards
The body stores fats as ___
Triglycerides
84
New cards
Fatty acids are composed of …
Carboxyl group and hydrocarbon chains
85
New cards
4 parts of triglyceride
Glycerol & 3 fatty acid chains
86
New cards
Unsaturated fats are ____, due to a double bond between Carbons
Bent
87
New cards
Saturated fats are ______ (structure)
Straight
88
New cards
The head of phospholipids (________ group) are polar
Phosphate
89
New cards
UNsaturated fats are ______ at room temperature, while saturated are _______ at room temperature.
Liquid, solid
90
New cards
Unsaturated fats are commonly produced by____
Plants (olive oil)
91
New cards
Saturated fats are commonly produced by ______
Animals (butter, lard)
92
New cards
Function of lipids
Energy storage, and protection of organs/insulation
93
New cards
Structure of phospholipids
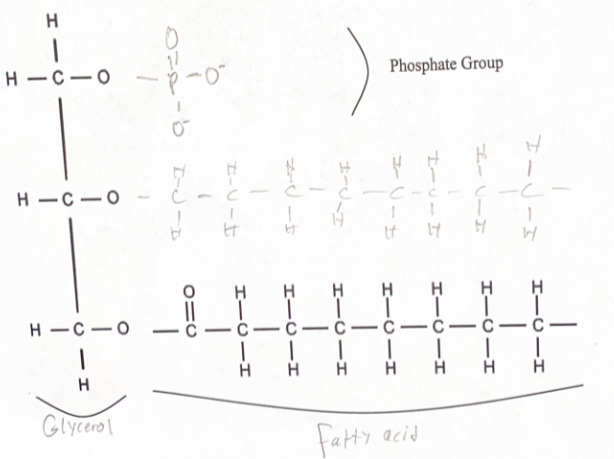
94
New cards
Phospholipids are made up of …
Polar phosphate group head
Nonpolar fatty acid tail
Nonpolar fatty acid tail
95
New cards
Phospholipids are found in the …
Cell membrane
96
New cards
Direction of phospholipids
The polar head faces the extracellular (and intracellular) environment, while the nonpolar tails face inward, inbetween the 2 heads
97
New cards
In ionic bonds, electrons are ______
Transferred
98
New cards
The polarity of the R group becomes the foundation of how to differentiate the amino acids into 3 different groups…
Nonpolar
Polar
Ionic (basic and acidic)
Polar
Ionic (basic and acidic)
99
New cards
Nonpolar groups of amino acids have _____ charge
No
100
New cards
Polar groups of amino acids have ______ charge
Slight