The muscular system
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
The muscular system
The human body has >600 distinct skeletal muscles
The face includes 60 muscles in which >40 are used to frown and 20 to smile
Functions of muscle tissue
Movement-Walking, running,talking
Stabilising body positions-Standing, sitting, keeping head up
Regulating organ volumes-Sustained contraction of sphinceters to prevent an outflow from hollow organs
Movement of substances-Contraction/relaxation of muscles in blood vessels,gastrointestinal tract, reproductive system,cardiac muscles for blood flow
Heat production-Contraction of muscle tissues,involtunatry contractions of skeletal muscle (shivering)
Properties of mucle tissue
Excitability – responds to chemicals released from nerve cells
Conductivity – ability to propagate electrical signals over membrane
Contractibility – ability to contract and generate force
Extensibility – ability to be stretched without damaging the tissue
Elasticity – ability to return to original shape after being stretched
Types of muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle tissue – attached to bones of skeleton
Smooth muscle tissue – forms the walls of hollow internal structures
Cardiac muscle tissue – forms the wall of the heart
3 types of muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle tissue
Cardiac muscle tissue
Smooth muscle tissue
Skeletal muscle
Attaches to bonds, skin or fascia
Conscious control of muscles (voluntary tissue)
Cells are long and threadlike with alternate light and dark cross-markings called striations
Cells are multinucleated
Skeletal muscles move the head, trunk and limbs
Smooth muscle
They are shorter than skeletal muscle cells and are spindle shaped
Cells do not have striations (unlike skeletal muscle cells) = smooth
Cells are mononucleated
Located in the walls of hollow internal organs (stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, uterus, blood vessels)
Involuntary muscle movements
Cardiac muscle
Found in the heart & makes up the bulk of the heart
Cells are striated and branched, joining end to end and form complex networks
Cells are mononucleated
Involuntary
What is the skeletal muscle composed of
Composed of a variety of tissues including layers of connective tissue
Fascia (dense connective tissue) covers the surface of the muscle
The epimysium lies beneath the fascia
Perimysium extends into the structure of the muscles to group muscle cells into fascicles (bundles of skeletal muscle fibres)
Endomysium separates individual muscle fibres within fascicles
Skeletal muscles at a microscopic level
Beneath its cell membrane (sarcolemma) is the
cytoplasm (sarcoplasm), which has many small, oval
nuclei and mitochondria
The sarcoplasm also contains many threadlike
myofibrils (essential in muscle contraction)
Myofibrils consist of 2 types of protein filaments:
Thick filaments composed of myosin
Thin filaments composed of mainly actin
(others: troponin & tropomyosin)
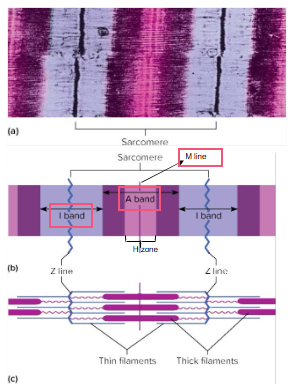
Myofibrils consist of repeating units called sarcomeres
Sarcomere at a microscopic level
A sarcomere is the functional unit of muscle contraction
The striations of skeletal muscle result from a repeating pattern of units (sarcomeres)
The myofibrils are essentially sarcomeres joined end to end
I bands:
Composed of thin filaments attached to structures called Z lines
A bands:
Have a central region (H zone) – only thick filaments
Two regions on either side of H zone are where the thick and thin filaments overlap
The M line consists of proteins which help hold thick filaments in place
Role of actin and myosin
The actin and myosin slide into each other for muscle contraction
Neuromuscular junction
Neurons (nerve cells) are important for communication within the body through a conduction of electrical impulses.
A skeletal muscle fibre usually contracts only when simulated by a motor neuron (Neurons that control effectors).
Each skeletal muscle fibre is connected (through a synapse) to the axon of a motor neuron that passes outward from the brain or the spinal cord.
A neuromuscular junction is the synapse between a motor neuron and the muscle fibre that it controls.
Structures of NMJ region
Synaptic and bulbs are swellings of axon terminals
The end bulbs contain synaptic vesicles filled with acetyl chloride (ACh)
Motor and plate membrane contains 30 million ACh receptors
Interaction of skeletal muscles
They function in groups and arrange in opposing pairs at joints with apposing movements (Flexion and extension)
Isometric contraction
A muscle contraction without motion. Isometric contractions are used to stabilize a joint like when a weight is held at waist level neither raising and lowering it
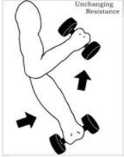
Isotonic contraction
When a muscle shortens to overcome resistance. When a muscle shortens, at least one joint moves, and body movement occurs. The resistance comes from lifting a weight, pulling up your body.
Dynamic contractions
Muscle contractions with a fixed amount of weight.
What is skeletal muscle fibre?
A single cell that contracts in response to stimulation and then relaxes when the stimulation ends
Muscle movement
When the upper limb straightens at the elbow
Rigid bar= Forearm bones
Fulcrum= Elbow joint
Object moved against resistance= Hand moved against resistance provided by the weight
Force=Supplied by the posterior muscles of thr arm (triceps brachii)
When the weight is lowered (rope pull down) the biceps relax and the triceps contract
Agonist (prime mover) – generates the majority of the force to cause the desired action
Antagonist
muscle that brings about the opposite reaction
Synergist
aids the prime mover during the desired reaction or inhibits the opposing action