Glass Ionomer
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Main types of GIC based on composition
Conventional glass ionomer (GI), resin modified glass ionomers (RMGI), Glass-hybrids, metal reinforced GI
Glass Ionomer cements classification
Type I:
Type II a:
Type II b:
Type III:
Type I: luting crowns, bridges, ortho brackets
Type II a: esthetic restorative cements
Type II b: reinforced restorative cements
Type III: lining cements, bases
Fuiji is what type
type IIa
What kind of reaction is it between the powder (fluoroaluminosilicate glass) and the liquid (aqueous solution of polyacrylic acid?
Acid base
Gi composition: essential components (4)
fluoroaluminosilicate glass (powder)
Polyacrylic acid (liquid)
Water
Tartaric acid
What is the water for in the GI acid base reaction
Helps ion transport in the acid-base reaction and fluoride release
What is tartaric acid for the GI composition reaction?
Helps to control the working time and setting characteristics of the material
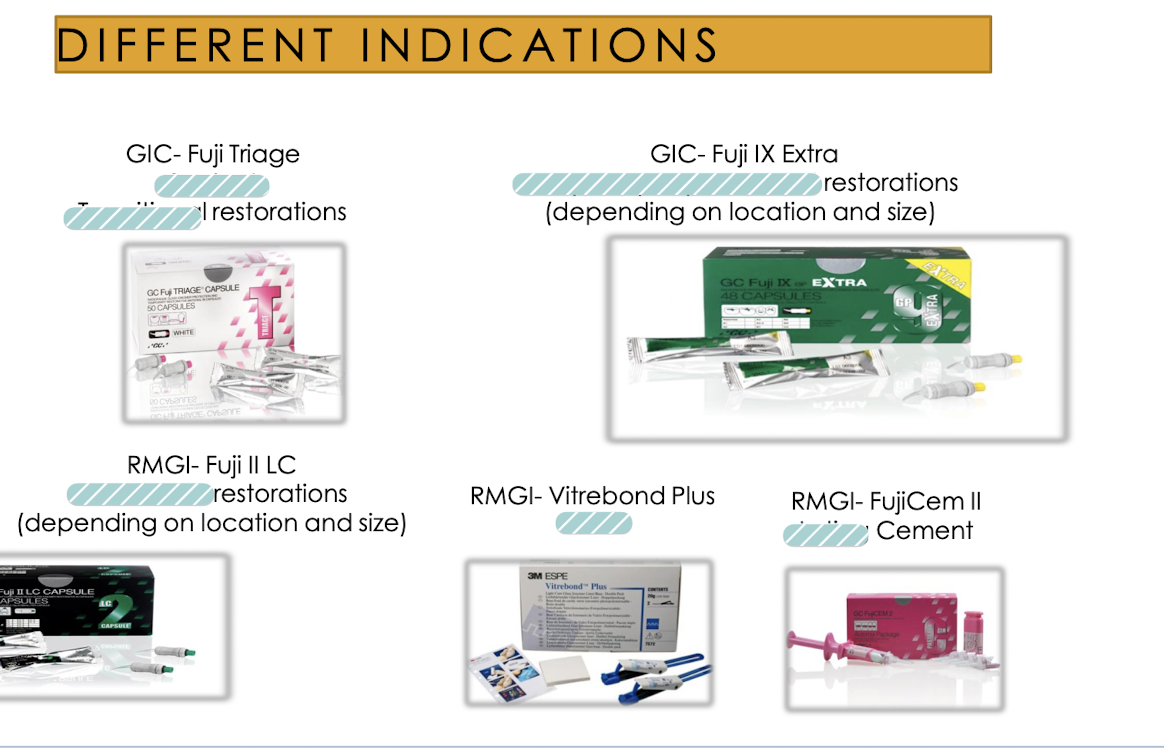
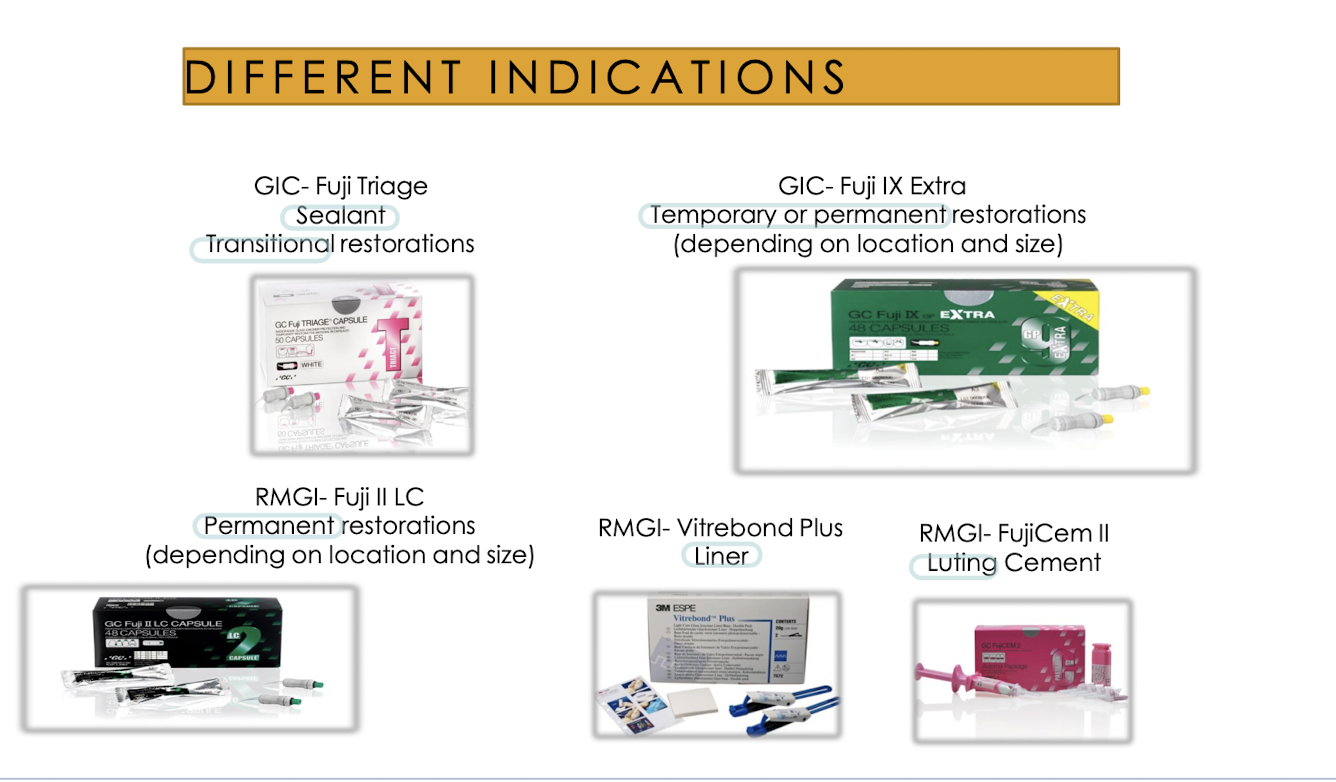
GIC-Fuji Triage is used for (2)?
Sealant, transitional restorations
RMGI-Fuji II LC uses
permanent restorations (depending on location and size)
GIC - FUJI IX extra uses
temporary or permanent restorations (depends on location and size)
RMGI - Vitrebond plus uses
Liner
RMGI - FujiCem II uses
luting cement
3 main parts of the setting reaction
dissolution, gelation and initial setting, hydration of salts and maturation
What happens during gelation and initial setting
The carboxylate ions react w metallic ions to form salt bridge, resulting in gelation and setting, release of F-
Hydration of salts and maturation:
Strength of the cement builds with?
Silicic acid rapidly polymerizes to form?
with time, silica hydrogel
RMGI compositon components (4)
Polycarboxlic acid, fluroaluminosilicate glass, water (ion transport for acid-base rxn and fluoride release), hydrophilic methacrylate monomer (photo-initated redox rxn), free radical initators (trigger curing of methyl groups_
IN RMGI the..
Hydrophilic methacrylate monomer does what?
Free radical initaors do what?
Photo-initated redox reaction, trigger curing of methacrylate groups
RMGI two type of rxn?
Traditional acid base, free-radical methacrylate polymerization
Setting reaction RMGI:
water-soluble resin monomers into an aqeuos soltution of polyacrylic acid… next step
ion released from glass particle reacts with polyacrilic acid while hema occurs
compressive strength (mPA) place in order of least to most
RMGI, RBC, enamel, dentin, GI
GI
RMGI
dentin
RBC
enamel
Flexural Strength (MPa)
place in order: RMGI, RBC, enamel, dentin, GI
GI
RMGI
RBC
Tensile strength
RMGI, RBC, enamel, dentin, GI
GI/enamel
RMGI
RBC
Dentin
Fracture toughness (MPA m1/2)
RMGI, RBC, enamel, dentin, GI
GI
RMGI
RBC
enamel
dentin
Wear rate
RMGI, RBC, enamel, dentin, GI
RBC
enamel
GI
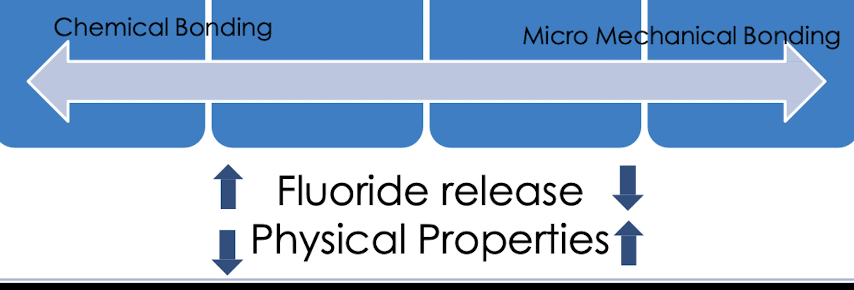
from left to right? Compomer, GI, RMGI, Resin composite
GI, RMGI, Compomer, Resin composite
Fluoride release and recharge. Highest level is from ?
Recharged with?
Best balance of F- release, recharge, physical properties is?
GI and RMGI
f toothpaste, rinses, varnishes
Resin modified glass ionomer (RMGI)
Conditioning: what the rule?
rule of 200: % * time = 200
Two mechanisms of adhesion
micromechanical interlocking interdiffusion layer
chemical bonding: ionic bonds between carboxyl groups and calcium from hydroapatite
Do not desiccate dentin before?
application (needs to be moist in clinic)
craze lines are due to?
loss of water
What is recommended to protect GI from loss and uptake of water during setting
transient surface protectant (vaseline)
what are two cititical roles water plays in setting of GIC
Rxn medium in intial dissolution
Hydration over time as it matures