Core Concepts: Lipids
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
1
New cards
What **three** biological molecules do lipids contain?
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
2
New cards
What unique component do phospholipids have?
Phosphorus
3
New cards
**True/ False:** Lipids dissolve in water
**False:** They are **non-polar** + **do not** dissolve in water
4
New cards
Lipids dissolve in nonpolar substances. **True/False?**
**True -** i.e other lipids
5
New cards
Why are lipids suited as energy storage/sources?
**1 gram of fat** provides twice as much energy as the **same mass of carbohydrates**
6
New cards
Give **5 functions of lipids**
* **Protects** the delicate internal organs like the kidneys
* **Oxidation of triglycerides** produces **metabolic** **water**- cools camels down
* **Phospholipids** are a key component in **cell membranes**
* Leaves have a **waxy cuticle layer** to reduce water loss
* Fats are **poor conductors of heat** meaning they **retain body heat**
* **Oxidation of triglycerides** produces **metabolic** **water**- cools camels down
* **Phospholipids** are a key component in **cell membranes**
* Leaves have a **waxy cuticle layer** to reduce water loss
* Fats are **poor conductors of heat** meaning they **retain body heat**
7
New cards
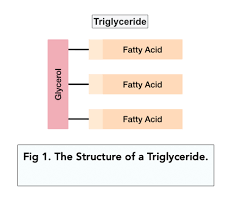
What makes up a **triglyceride?**
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
8
New cards
Describe the features of a **fatty acids** have
* **Long** molecules
* **Polar hydrophilic** __**end**__ + **non-polar hydrophobic** __**tail**__
* **Polar hydrophilic** __**end**__ + **non-polar hydrophobic** __**tail**__
9
New cards
What are **saturated fatty acids?**
Fatty Acids in which all carbon atoms are joined by **single bonds** in the hydrocarbon chain **(SATURATED WITH HYDROGEN)**
10
New cards
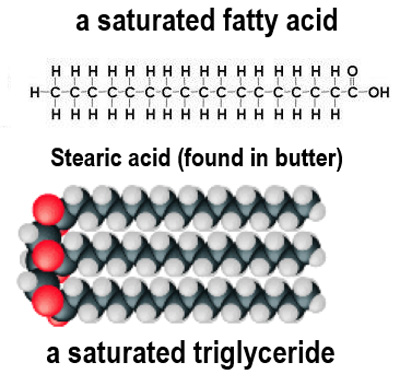
Describe **2 features** of **saturated fatty acids**
* Straight chains
* High melting points
* High melting points
11
New cards
Why do **saturated fatty acids** have a high melting point?
This is because the **fatty acid** tails are **straight** and **can pack closely together**. Stronger forces of attraction can form which means more **energy is needed to break the bonds** and melt the fat
12
New cards
At room temperature, **saturated fatty acids** are **_____**
Fats
13
New cards
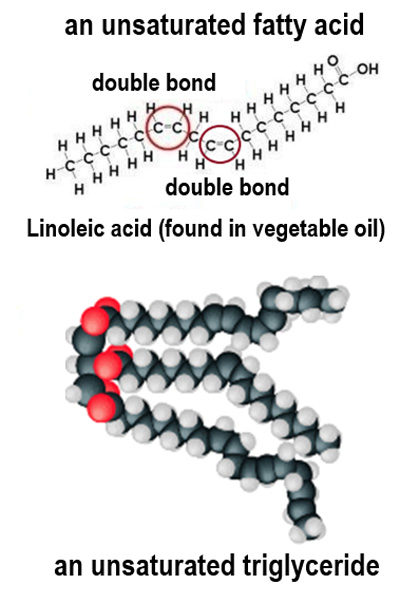
What are **unsaturated fatty acids?**
Fatty acids where **not every carbon is saturated with hydrogens** - there must be one or more **double bonds**
14
New cards
What are **unsaturated fatty acids** with **more than one double bond** called?
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
15
New cards
At room temperature, **unsaturated** **fats** are_____
Oil
16
New cards
Why do **unsaturated fatty acids** have low melting points?
The **double bonds** make the fatty acid tails **less straight** so they cannot pack as closely together. The **forces of attraction** between the fatty acids are **weaker**, so less energy is needed to break the bonds and melt the fat
17
New cards
Describe the **formation of triglycerides**
* **1 molecule of glycerol** joins with **3 fatty acid molecules** to form **a triglyceride**
* This happens in a **condensation reaction**
* A **water** molecule is **removed** and an **ester bond is formed**
* This happens in a **condensation reaction**
* A **water** molecule is **removed** and an **ester bond is formed**
18
New cards
Are triglycerides polymers?
**No** (duh) - they are made of only one glycerol and 3 fatty acids which have different structures
19
New cards
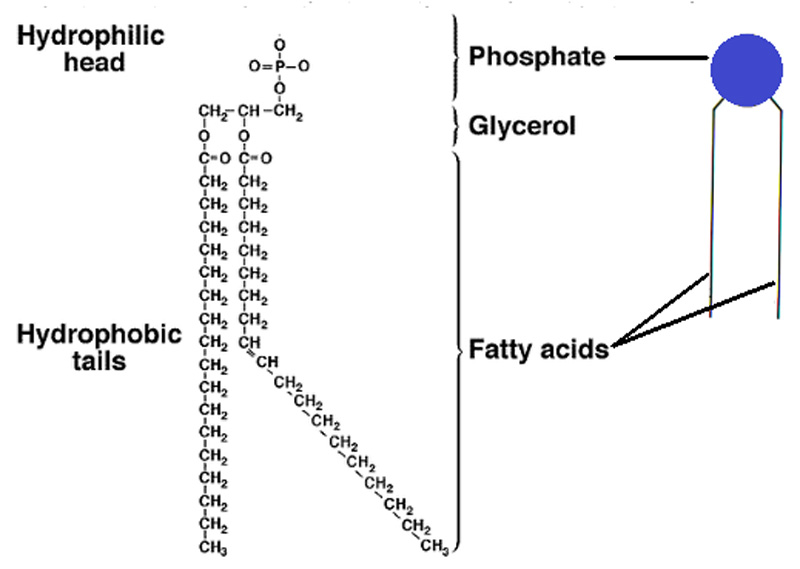
What is the **structure of phospholipids?**
* 1 molecule of glycerol
* A **hydrophilic** phosphate head
* **2 hydrophobic** fatty acid chains
* A **hydrophilic** phosphate head
* **2 hydrophobic** fatty acid chains
20
New cards
Describe a **phospholipid** bilayer
* The **hydrophilic** phosphate groups are *attracted to water molecules* in the cytoplasm and outside the cell.
* The **hydrophobic** tails are ***repelled*** *by water molecules* **turn away** from water in the cytoplasm and outside the cell
* The **hydrophobic** tails are ***repelled*** *by water molecules* **turn away** from water in the cytoplasm and outside the cell
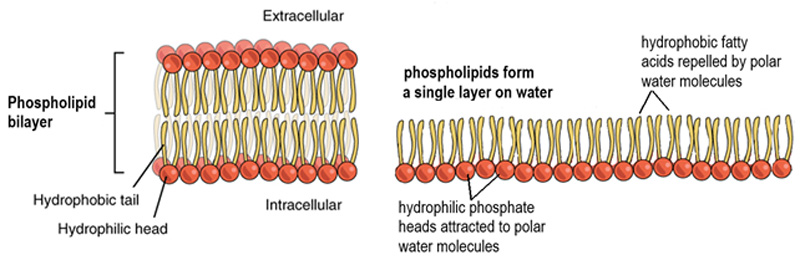
21
New cards
What is meant by membrane **fluidity?**
How easy it is for the cell membrane to move
22
New cards
How do phospholipids affect the **fluidity** of membranes?
* Phospholipids where only **saturated fatty acids** are present are the **least fluid**
* Phospholipids where only **unsaturated fatty acids** are present are the **most fluid**
* Phospholipids where only **unsaturated fatty acids** are present are the **most fluid**
23
New cards
What are the **two main causes** of heart disease?
fatty deposits on the inner wall of the coronary artery (*atherosclerosis)* and hypertension
24
New cards
Name 3 **contributing factors** to heart disease
* Diet - **high in saturated fats**
* **Smoking**
* **Lack of exercise**
* **Smoking**
* **Lack of exercise**
25
New cards
What happens to **lipids and proteins** after they’ve been absorbed into the small intestine?
They become **lipoproteins** which travel around the body in the bloodstream
26
New cards
If a diet is **high in saturated fats…**
* LDL builds up + **causes harm**
* **Atheroma** (fatty material) is deposited in the coronary arteries
* This **restricts blood flow** + **oxygen delivery** to the heart
* This causes **angina** + may cause a heart attack
* **Atheroma** (fatty material) is deposited in the coronary arteries
* This **restricts blood flow** + **oxygen delivery** to the heart
* This causes **angina** + may cause a heart attack
27
New cards
If a diet is **high in unsaturated fats…**
* Makes more **HDL**
* This **carries away harmful fats** to the **liver** for disposal
==**The higher the HDL : LDL ratio, the lower their risk of heart disease**==
* This **carries away harmful fats** to the **liver** for disposal
==**The higher the HDL : LDL ratio, the lower their risk of heart disease**==
28
New cards
What is **polyunsaturated fat**?
An **essential fat** that we must get from food because our bodies cannot produce it. **It lowers LDL (bad cholesterol)**
29
New cards
Where is polyunsaturated fat found?
**Omega-3** in fish
30
New cards
What is **monounsaturated fat?**
‘Healthy Fat’ - **lowers LDL and maintains HDL**
31
New cards
Where is **monounsaturated** fat found?
Olive oil, nuts and avocado
32
New cards
What is **Trans fat**?
By-product of **processing healthier fats to give them a longer shelf life**. Raises LDL (bad cholesterol) and lowers HDL (good cholesterol).