LAB EQUIPMENTS, MICRO-PIPETTING AND THE USE OF pH METER
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Reagent preparation room
also known as pre-PCR activities
Sample preparation room
PCR room
includes PCR execution
Buffer
where the medtech will decontaminate to ensure that there are no contaminants that might go inside the areas
Work Table
where we will mix the reagents; calculate solutions, etc.
Pass Box
where we will put the prepared solution
1 Billion
A typical PCR generates as many as ____ copy of target sequence
1 Million
Aerosols from pipettes will contain as many as _____ amplification
products
CONTAMINATION IN A PCR LAB
• Amplification product contamination
Cross contamination between specimens - To avoid this, use different pipette tips
• Laboratory surfaces (e.g. fomites)
• Ventilation ducts (e.g. exhaust products or system, etc.)
• Reagents/supplies
• Hair, skin, saliva, and clothes of lab personnel (have DNA and RNA)
HOW TO CONTROL CONTAMINATION:
- Correct Laboratory Design – must be one-way
- Laboratory Practices – follow the laboratory rules such as no eating, drinking, etc. in the laboratory
Chemical/Enzymatic Control
Chemical Control
Lysol, sodium hypochlorite, alcohol
Enzymatic Control
prevent unnecessary nucleic acids (e.g.: DNAse = remove DNA; RNAse = remove RNA)
Incorrect results
Require extensive clean-up
Loss of credibility
Impact on economy and performance
WHAT HAPPENS IF THERE IS LACK CONTAMINATION CONTROL?
BIOSAFETY CABINET
Protection to the user, product, and environment
Decontamination
10% Bleach→70% Ethanol
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS I
Sash/window is opened up to protect the use from the sample or specimen we’re working on
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS I
Unfiltered air enters and filtered air comes out
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS I
Protect the environment
• Does not protect the sample because of the unfiltered air passing through the specimen or sample
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS I
Air goes inside cabinet without filtration, comes out of cabinet with filtration
• No product protection needed
Biosafety Cabinet Class I
- Opening suspicious mail
- Running Centrifuges
- Housing fermenters
- Aerating cultures
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS II
• Better than BSC Class I
• Provides personnel, product, and environmental protection
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS II
• Does not provide absolute containment, can only provide if these 3 aspects are maintained: - Open front with inward airflow - Downward HEPA Filtered Laminar Airflow - HEPA Filtered Exhaust Air
Positive Pressure
Pushes Air
Negative Air
Pulls Air
TYPE A1
- Plenum is under positive pressure
- Some air will be exhausted and some will be recirculated
- Without Canopy/exhaust connecting to the outside of the facility
TYPE A2
- Plenum (air-filled space where air is distributed) is under negative pressure
- Two types:
1. Without Canopy
2. With Canopy (can minimize release of chemical fumes in the room)
- 60-70% is recirculated; 30-40% is exhausted
Type B1
- 40% Air circulated
- 60% exhausted outside thru hard ducting (HEPA filters)
Type B2
- 100% air exhausted via hard ducting (HEPA filters)
Type C1
- Similar mechanism with Type B, but more available and flexible mechanism
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS III
• Safest; used for higher level of BSL organisms such as Bacillus anthracis
• Gas tight, under negative pressure
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS III
• No recirculation of air
• HEPA Filtered air supply
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS III
• Exhaust air: Double HEPA-filtered or HEPA-Filtered and Incinerated
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS III
• Operation inside thru Rubber Gloves [built-in gloves that is also called as glove boxes]
BIOSAFETY CABINET CLASS III
• Cabinet connected to a double-door autoclave and/or chemical dunk tanks to sterilize/disinfect all exiting materials
DRY BATH
• Not commonly used in molecular biology laboratory. Instead, we use ice basket
• For heating/warming/boiling of samples
• Physical Inactivation
Digital
Analog
Two types of Dry bath
ELECTROPHORESIS APPARATUS
PCR → needs electrophoresis
DNA, RNA, Protein separation
• Used for: - Detection - Purification
Anion
negatively-charged particles
Cation
positively-charged particles
Anode
Positive Electrode
Cathode
Negative Electrode
MICROCENTRIFUGE/MICROFUGE
Principle: Sedimentation by Centrifugal force
For samples less than 2 mL
MICROCENTRIFUGE/MICROFUGE
Used to mix or separate particles in suspension, used for PCR techniques
Speed: Up to 17000 x g
Max samples: 24 per run
MICROPIPETTES
For volume measurements <1000 uL
MICROPIPETTE
Principle: Plunger depressed and when released, liquid is drawn into disposable plastic tip.
P2
(0.2–2uL)
P10
(1-10 uL)
P20
(2-20 uL)
P100
(20-100 uL)
P200
(20-200 uL)
P1000
(100-1000 uL)
Filter
serve as a stopper
Gel loading tips
needle-like- thus we need to be very careful when loading
Gel loading tips
used when putting sample in agarose gel or polyacrylamide
Gel loading tips
must not puncture the gel because it can inaccurate the gel, all the specimen will move to the puncture site and will not migrate
PCR CABINET
Also known as “Clean Bench”
PCR CABINET
Similar to biosafety cabinet, but instead of having vertical laminar flow, the air will be coming under and come out horizontally, blown towards the samples
PCR CABINET
• For preparation of PCR Master Mixes
• Product protected from contamination
PCR CABINET
• Air flow: filtered first before going inside the cabinet
• Delivers HEPA-Filtered Air across work surface
- Facilitates worker exposure to materials in use
PCR Machine
considered as the heart of molecular laboratory
PCR Machine
Also known as Thermocycler
PCR Machine
Principle: DNA Replication
PCR Machine
Technically an IN VITRO method of DNA Replication
Reverse Transcriptase
If sample is RNA:
PCR Machine
• One run = ~40 cycles
- Run time: 1 hour 30 mins – 2 hours
Denaturation
Annealing
Extension
Three major cycles of PCR Machine
Denaturation
94 degrees celsius
Annealing
55 degrees celsius
Extension
72 degrees celsius
RT-PCR
used for the detection of RNA (qualitative)
Conventional PCR
used for the detection of DNA (qualitative)
Real-time PCR- aka. Quantitative (Q) PCR
usually used to measure the amount of what is being produced
REFRIGERATOR
Temperature: 2 to 6 degrees Celsius
REFRIGERATOR
For reagents and samples that will be processed immediately
• Storage only until 24 hours or less
ULTRA LOW FREEZER
Also called Minus 80 or Negative 80 Freezer
ULTRA LOW FREEZER
Temperature: -60 to -80 degrees Celsius
- Common is -80 Degrees Celsius
ULTRA LOW FREEZER
For fast freezing of samples
• Best for:
- Eluates
- Storage of specimens
ULTRA LOW FREEZER
What to avoid: Freeze-thaw cycles
SPECTROPHOTOMETER
Principle: Measures light absorbance across the visible and ultraviolet ranges of the spectrum.
SPECTROPHOTOMETER
Used for: Quantification of analytes
SPECTROPHOTOMETER
Asses if the sample is enough or the extracted/isolated DNA
Beer’s Law / Beer Lambert Law
concentration of the solute in the solution is directly proportional in the absorb light and inversely proportional to the transmitted light
High Concentration of Solute
↑ Absorption light, ↓ Transmitted light =
Low Concentration of Solute
↓ Absorption light, ↑ Transmitted light =
VORTEX MIXER
• For mixing of small bottles of liquid
• For suspension or re- suspension of cells
Vortex Mixer
• Principle: transmission of vortex motion
MICROPIPETTES
• Tools used to measure extremely small volumes of liquid
• is accurate to measure a defined range of volume
Push Button
Tip Ejector Button
Tip Ejector Collar
Volumeter
PARTS OF THE MICROPIPETTE
Push Button
It is used for aspiration or dispensing the fluid
• It has 2 stops (when pushed or pressed): First stop and Second stop
It is adjustable by rotating it
First stop
used for aspiration
Second Stop
is used for dispensing the fluid that was aspirated
TIP EJECTOR BUTTON
• It removes the micropipette tip after use. After using the tip, dispose it in a yellow bag.
• If it is infectious, you must dispose it in a solution of sodium hypochlorite.
TIP EJECTOR COLLAR
It will push down the micropipette tip so that it will be removed automatically.
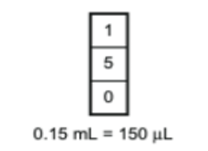
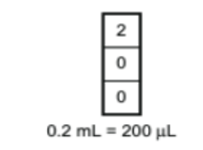
VOLUMETER
• Where the dial windows or numbers are.
Micrometer
used to adjust the numbers shown in the volumeter
P1000
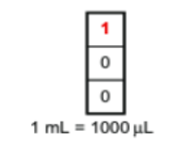
P1000
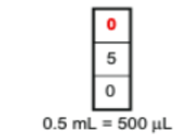
P1000
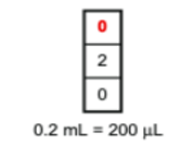
P200
P200