1.3.1: Marketing objectives and strategy
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
marketing objectives
increase market share
increase revenue
build a brand
increase market share
gives a business a competitive edge
businesses can exploit economies of sale as output increases as a result of growing market share
better prices from suppliers
influences prices charged in the market
businesses may have to invest in an advertising campaign or adjust pricing strategy
increase revenue
higher revenue = higher profit
investing in marketing activities helps increase revenue
build a brand
businesses wanting to establish the name of their company or products
gives products brand names that can be easily recognised
strong brands generate huge returns
important for highly competitive markets
exploits USP and invests heavily in marketing
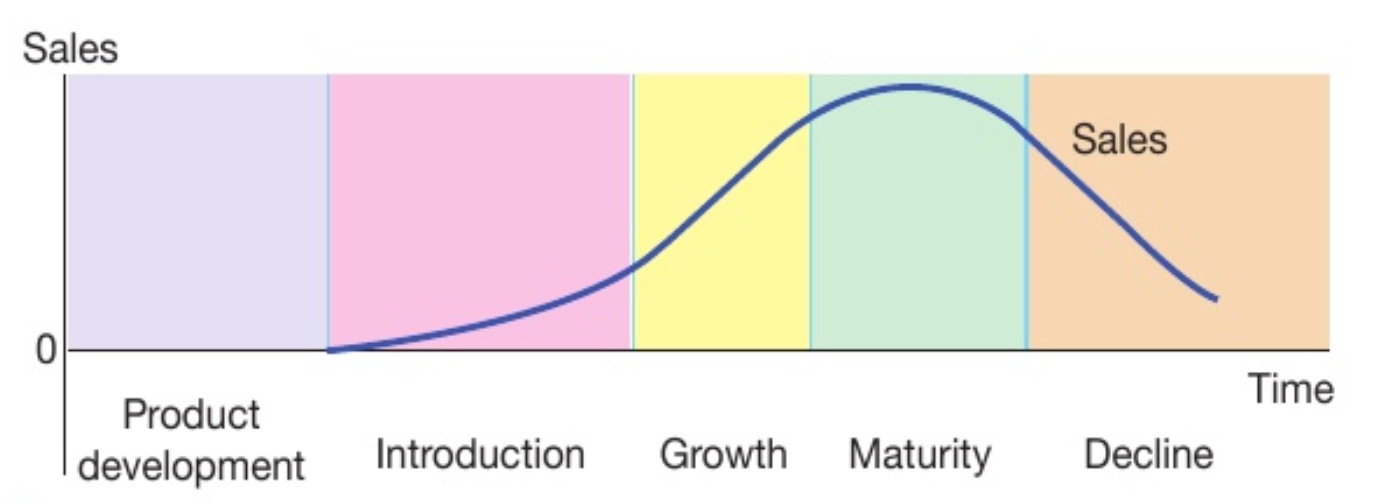
product life cycle
shows the different stages a product passes through over time and the expected sales
six stages of the product life cycle
development
introduction
growth
maturity
decline
development
product is researched and designed
ideas are investigated
prototypes are made
large number of products never progress beyond this stage
businesses are reluctant to take risks associated with new products
business spends largely to develop the product
no sales, high costs
introduction
product is launched
slow initial sales
incurred costs upon product launch
firm has to meet promotion and distribution costs of building a new production of line or plant
businesses spend on promotion to attract customers
product still isn’t profitable
high prices to cover promotion costs or low prices to break into the market
few outlets stock products
length varies based on product
growth
new customers + repeat purchases
unit costs fall as production increases
product becomes profitable
competitors may launch their own versions leading to a slowdown of the rise in sales
businesses should consider prices and promotion over time
maturity and saturation
product is established with a stable market share
sales reach highest point
competitors entered the market to take advantage
market becomes saturated as firms enter
businesses are forced out of the market because of competition
businesses use extension strategies to extend product life
decline
sales decline due to change
consumer taste, technology, new products
product loses appeal
may be withdrawn or sold to another business
profit can still be made at a high price and low cost
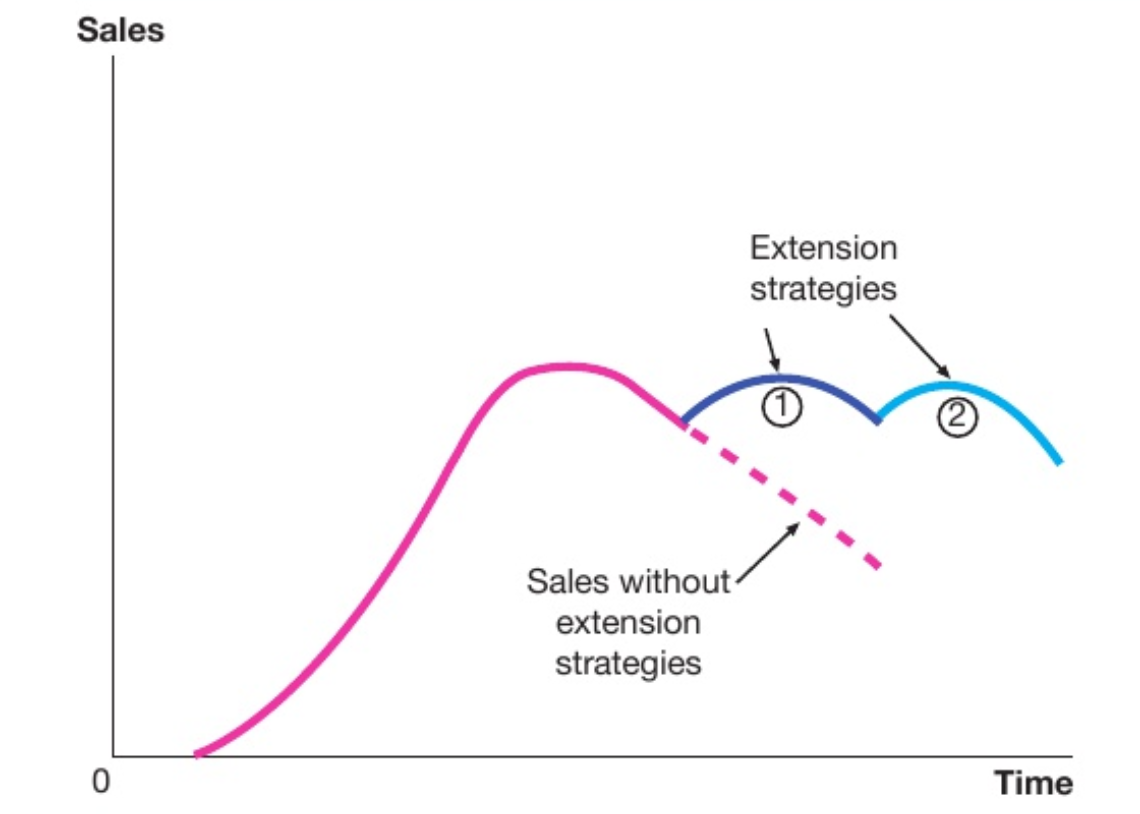
extension strategies
prolong life of a product before decline and help generate more cash
2 extension strategies
product adjustments: prolongs product life by ‘freshening’ it up
promotion: focuses on campaigns to boost sales
product adjustments
product is updated commonly for technical products and consumer durables
add value to products by making improvements
product range is extended
modified packaging gives the impression that the product has been changed
promotion
finding new uses
finding new markets
investing in advertising campaigns
encourages frequent use of product
effect of extension strategies on the product life cycle
when the market becomes saturated and sales begin to fall, decline in sales is delayed when the strategy is used
some firms use extension strategies at the maturity stage before the decline as they can forecast the falling sales in the market
product portfolio
made up of product lines
constant launch of new products = business can make sure gaps aren’t created
i.e. 3 products in a line released at regular intervals means there isn’t a gap in the line
profit from mature products subsidises launch of new products which would be costly at first
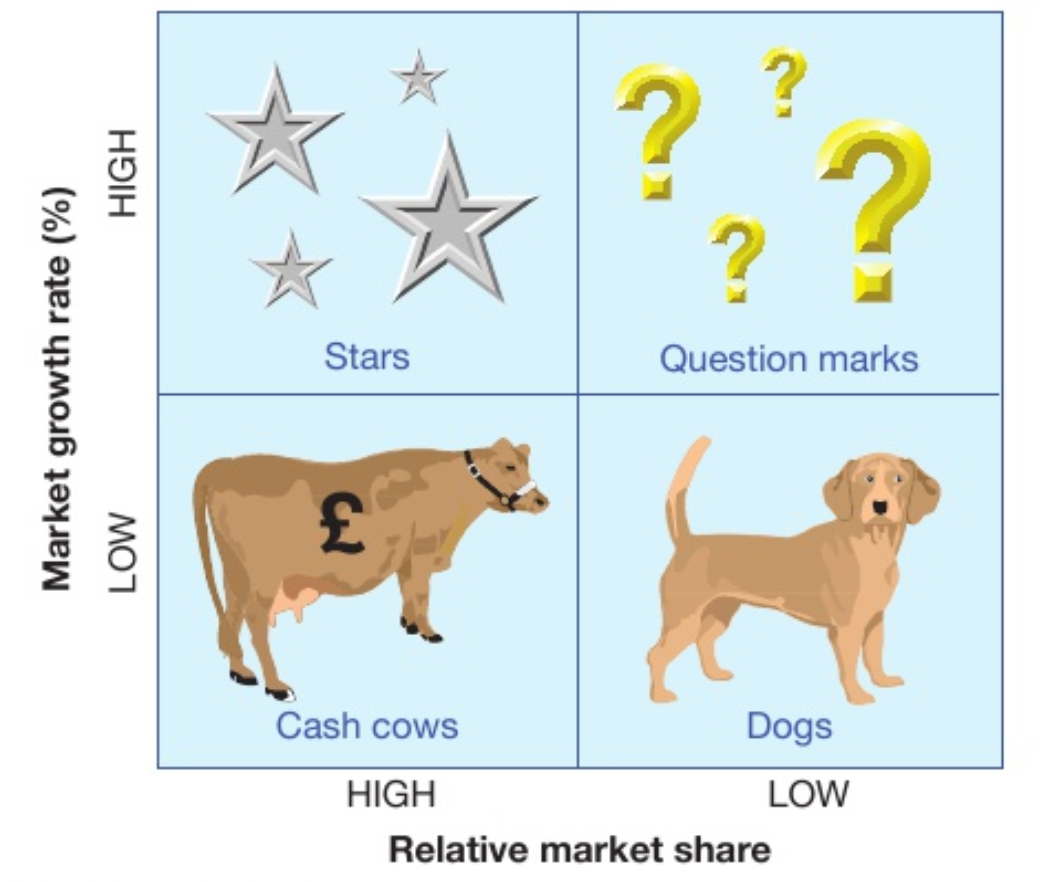
boston matrix
difficult for firms to tell what stage of the life cycle a product is at
useful for forms to analyse product portfolios
criterias the products are categorised in in the boston matrix
market growth
relative market share
4 categories on the boston matrix
stars: high market growth, high market share
valuable
strong position
fast-growing market can be exploited
business wil need to invest to come in the growing market i.e. new facilities, promotion
nearly zero net cash flow
high profit, high investment
cash cows: low market growth, high market share
well positioned
profitable
little chance of increasing sales and profit
little need for investment
slow growth in sales
little need for new premises
strong positive net cash flow
question marks: high market growth, low market share
‘wildcat’ products
fast growing market - potential to turn into a star
problematic as the business won’t know what to do with the products
weak products aren’t profitable
zero or negative net cash flow
investment may be needed to cope with growing sales
dogs: low market share, low market growth
poor prospects for future sales and profit
may generate positive cash flow
need little investment
balancing product lines
there mustn’t be too many items within each category in the boston matrix
products on top - early stages of product, growing markets, unrecovered cost of development and promotion using up resources
positive net cash flow from cash cows in a product line can support products in a growing market
taking appropriate decisions
stars have great future potential as cash cows and the business should build the brand of these products to increase sales and fight off competition
cash cows can be milked for cash to develop other products or used as holding
question marks can turn into a star by building the brand and harvesting the product to increase profit or divest the product by withdrawing it
dogs may be divested or harvested
marketing mix
elements of a firm's marketing strategy that are designed to meet the needs of its customers
4 elements of the marketing mix (4 P’s)
product
price
promotion
place
product
how consumers use a product
appearance of product
financial factors - price, value for money, after sales service
product life cycle
USP - competitive edge
price
pricing policy is a reflection of market
prices will not always be set at the level which will maximise sales or profit
promotion
businesses choose from a wide range of different promotional methods
i.e. advertising, sponsorship, coupons, free gifts, competition
place
convenient locations for customers to buy
decisions about physical distributions
e-commerce
marketing strategy
set of plans aiming to achieve a marketing objective
strategies for mass markets
relevant to huge, global markets with millions of potential customers
mass market - product
most successful businessesa re likely to be those that can differentiate their product in some way - developing a USP or relying on the marketing mix
mass market - price
prices charged in a mass market are similar
businesses fear a price war as the revenue is reduced for every competitor
businesses are happy to charge the ‘going rate’ in the market
price leadership is common for a dominant business in the market
mass market - promotion
invest heavily in ads and promotion
marketing plays a major role in the mass market
occurs in absence of price competition
mass market - place
businesses use multiple channels to distribute their goods
some manufacturers pay sellers to display their goods in prominent places
internet and e-commerce allowed small business to have access to mass markets
online banking, delivery, click and collect
strategies for niche markets
have very particular needs which are sometimes neglected by larger firms, therefore creating a gap in the market for a business to satisfy a small customer group
niche markets - product
products are significantly different than that of rivals
i.e. restaurants with michelin stars cater to very specific needs
designed carefully to meet the specific needs of the customer group
niche markets - price
flexible pricing
less competition
higher prices can be charged without losing out on market share
if needs are being met, customers may be willing to pay extra
niche markets - promotion
targeted advertising
smaller markets don’t use as much national media
businesses should be well aware of customer profile to ensure advertising and expenditure isn’t wasted
adverts placed in specialised publications/channels
niche markets - place
more selective choosing distribution channels
use exclusive distributors or handle it privately
may also use the internet
B2B
business-to-business
B2B marketing strategies
business supplying goods and services to other businesses
outbound marketing strategies
inbound marketing strategies
hybrid strategies
B2B - outbound marketing strategies
involves direct marketing material at potential customers
i.e. direct mail, email, telephone, sponsorship, targeted ads
drawbacks:
ignored adverts
annoyance at being contacted by phone
repeated approach may ruin brand image
potential customers obtained usually don’t lead to sales
B2B - inbound marketing strategies
involves attracting potential customers to websites when they’re looking for suppliers or solutions
common techniques:
blogging - providing content on company blogs
social media marketing - developing a following on any social media
search engine optimisation - increasing website traffic by getting a high-rank placement in searches
free e-books - offering useful information for visitors to download
video marketing - producing short and informative video clips for visitors
targeted email marketing - sending personalised emails targeted to people
challenges:
requires effort and resources
recruitment of experienced marketers is difficult
tricky to keep up strategy with rapid trends
B2B - hybrid strategies
combination of outbound and inbound methods
helps reduce costs and creates sustainable growth in market share
how do businesses develop customer loyalty
communication
customer service
customer incentives
personalisation
preferential treatment
loyalty - communication
mass market: national advertising campaigns
reassuring adverts
regular newsletters
loyalty - customer service
high quality customer service
employees who interact must be professional, reliable and conduct themselves honestly
improved by dealing with matters promptly
involves providing a more effective after-sales service
‘pleasant’ purchasing experience
loyalty - customer incentives
loyalty/reward cards upon returning
value of rewards linked to amount spent by customers
loyalty programme makes customers want to spend more
loyalty - personalisation
personal level
customisation
addressing customers by name
dealing with customers at this level is easier for smaller businesses
loyalty - preferential treatment
vip lounges/etc.
if a business can provide customers with preferential treatment they return for more