Unit 10 - Cell Motility
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Types of Cell Motility
Actin-dependent migration
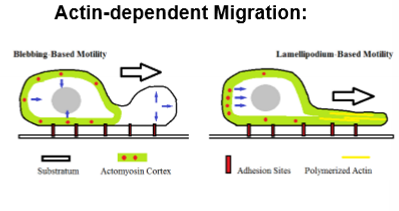
Actin Dependent Migration
Cell Signaling
signals from outside - chemical, neighbor cells, mechanics, electrical, photo; responses inside the cell (change in cell phenotype) - trigger new gene expression, cel movement or shape change, cell cycle, or apoptosis
Movements of the cell
driven by the cytoplasm and associated motor proteins - ex. migratory frog cell expressing EGFP-CLIP1, a live-cell reporter of MT dynamics; can also be corrdinated and is responsible for buidling structures and organs - ex. migration of epithelial cell cluster produces the sensory lateral line in fish (sends out a migratory cluster of stuff down the line)
Why we don’t always use human cells?
ethics
experimental design
time
money
Why do we use yeast cells?
function of a protein in yeast is the same in us; cheap, abundant, and reproduce rapidly; form distinctive polarized structures under defined conditions (“on-demand”) and can be synchronized
Why are yeast cells not useful?
because they can’y make multicellular organisms
Cell Motility - Cell Shape and Locomotion
cell polarization (in yeast cells → cells want to polarize), RNA localization (putting proteins where it wants), plasma membrane protrusion, external signals guide cell migration, cell ex. keratocytes (good migration cells) and neurons;
Cell Motility - Cell Needs
to sense cues from environment, ability to directionally organize and polarize their cytoskeleton (all about location), generate physical force to move, persistence to keep “on-track”
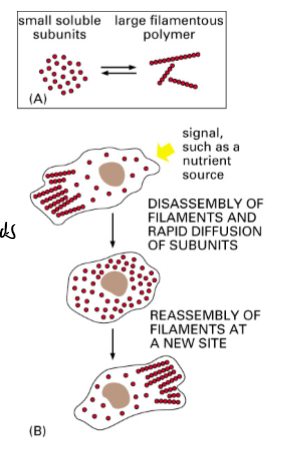
Involves a coordinated deployment of components and processes of the cytoskeleton
cell polarization, shape change, and motility involves a coordinated deployment of components and processes of the cytoskeleton - dynamic assembly and dissaembly of polymers (non covalent bonds), regulation and modification of their structure by associated proteins, and actions of motor porteins among the polymers
Yeast: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
single cell eukaryote; type of fungus with a chitin cell wall; complex life cycle with asexual and sexual reproduction; can be haploid or diploid - budding; conjugation - a and alpga haploid cells fuse; most have human homologs (can use them to understand human protein-protein interactions); can polarize by conjugation/shmooing or cell division/budding
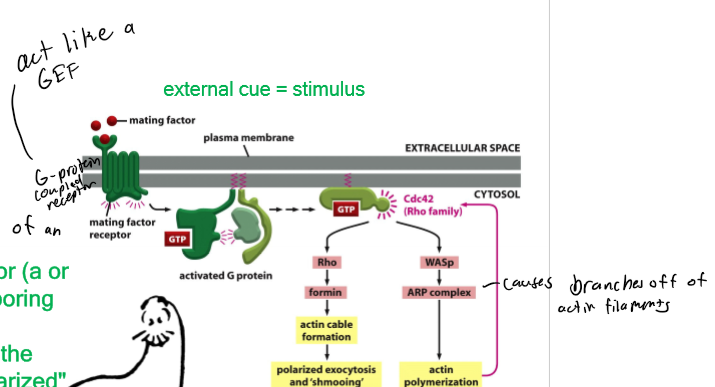
Conjugation/schmooing
polarized behavior during conjugation; each haploid cell can secrete a diffusible mating factor (signal) which activates a pathway that triggers the cell to produce a “polarized” response; 2 types - a and alpha; ex. a extends a protrusion in response to an alpha mating factor
Cell Division/Budding
polarized assembly of a new daughter cell during cell division; creates 2 cells - mother and daughter; mother selects site for new daughter cell next to old bud scar and directs protein complexes to that site; steps - cel cycle, mitosis, and cytokinesis; daughter cell is different than mother cell - yeast wants to put things (proteins and different genes that are on/off) in the daughter cell (differential transport of ash1 mRNA → daughter recieves ash1 and mother is depleted of ash1) ; generates a “polarized” response to an internal stimulus
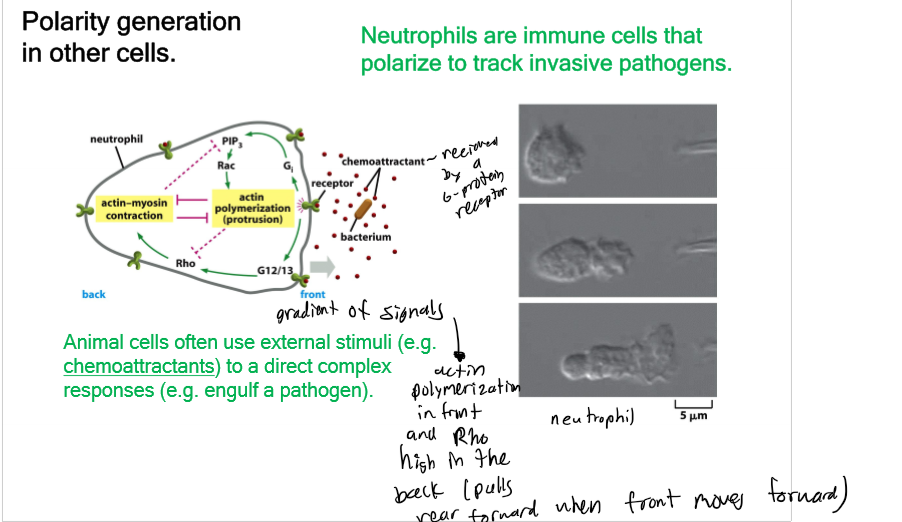
Polarity Generation in other cells
animal cell suse extrernal stimuli (chemoattractants) to direct a complex response - neutrophils are immune cells that polarize to track invasive pathogens; keratocytes are epidermal cells from fish/amphibian skin and are useful for studying cell motility because they are big and fast; extrernal cues can guide cell migration - chemotaxis, haptotaxis, durotaxis, and galvanotaxis
Chemotaxis
cells follow gradients of diffusible factors
Haptotaxis
cells track immobilized molecules (Hansel and Gretel)
Durotaxis
cells follow gradients in substrate stiffness (soft vs stiff in places)
Galvanotaxis
cells guided by applied voltage (follow voltage gradient low → high)
Disadvantages of a pyrene actin assay
it is an average (bulk assay)
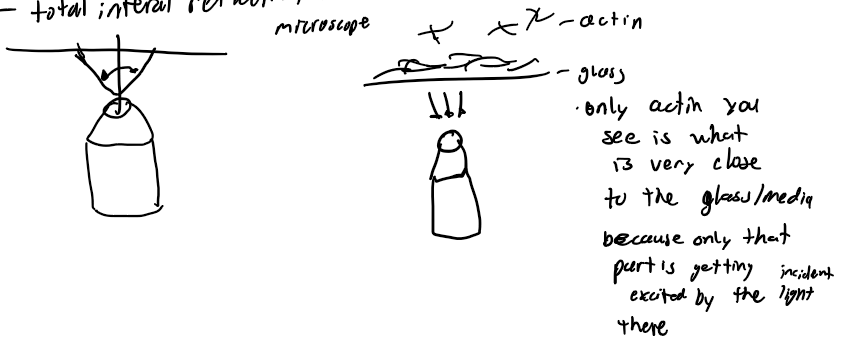
TIRF
total internal reflection fluorescence
Polarity
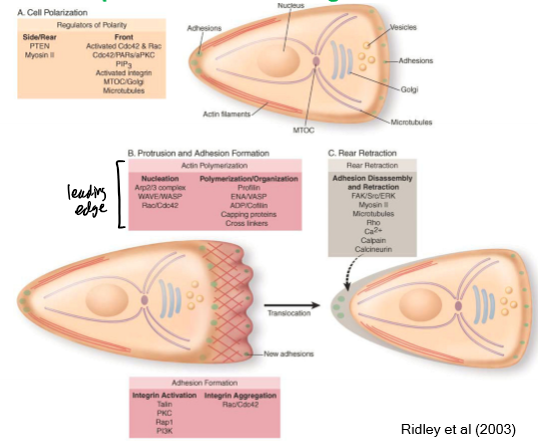
input layer - intracellular (inside) and signaling (outside); core processes can be polarized - universal processes (Rho/Rac/Cdc42); must occur at the output layer (most important part about cell motility - intracellar - ex. Ameboid motility - branched actin at front and actomyosin contraction at rear
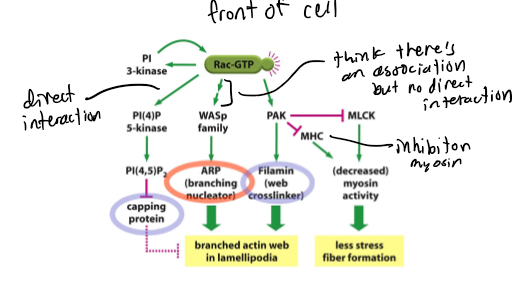
Rac
front of cell; has a direct interaction with PI 3-kinase, PI(4)P and PAK and indirect with WASp family; causes decreased myosin activity so less stress fiber formation; causes branches actin web in lamellipodia (capping protein, ARP, and filamen)
Problem about cells
come in a variety of shapes and use different strategies for migration but they do share a common set of molecular machines for all steps of polarization and movement
Universal Principles of Cell Motility
F-actin assembly and myosin contractility controlled by G-proteins; there are numerous downstream effectors of Rac (front of cell) and Rho (back of cell); these are biomolecular switches;
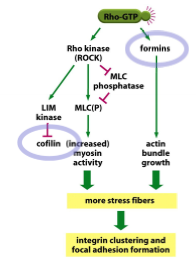
Rho
direct interaction with Rho kinase (ROCK); formins control actin bundle growth; more stress fibers and integrin clustering and focal adhesion formation
Universal Principle of Cell Motility
assembly of branched F-actin at the leading edge; actin polymerization drives the membrane forward
the process at a neutrophil changing direction as it hunts bacteria is most like what event is the yeasts’s life
conjugation/schmooing
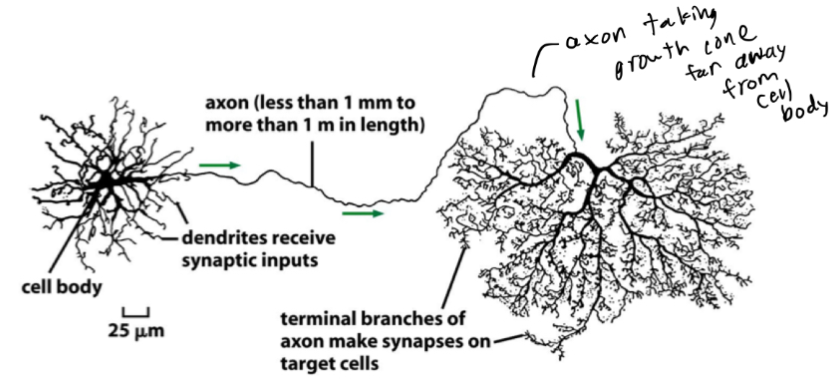
Neurons vs Fibroblasts
actin - cell cortex and allows extension and growth via “growth cone”; microtubules - oriented asssembly in axon to deliver vesicles to synapse; intermediate filaments - neurofilaments hold the axon together into compact structure; nuerons - send out processes to connect (dendrites - short - receive signals - associated with yje cell body and axons - long - transmit signals)
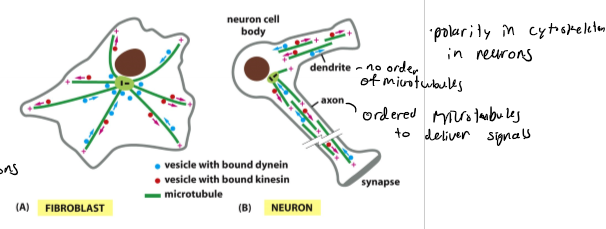
Growth Cones
how neurons connect to other cells; they leave the axons or dendrites to connect to the neuron cell body left behind; migrate according to tropic cues; neuron version of the front end of a migratory cell; steps - filopedia explore micro-environment → cells bind and modify diverse signals → at target form finer structures such as synapses, bouttons, etc. → connect source and target cells; a neuron can have many of these that move to find targets like other neurons or muscles
Complex Multicell Structures
self-assembled using basics of cell migration machinery coordinated with cues from the local microenvironment then need to be maintained
Actin and Tubulin (microtubules) filaments
both are polarized with specialized directed motor proteins; both bind porteins that control their stability; tubulin is anchored at the centriole and is a GTPase that slowly converts GTP to GDP
Permissive Factor
factors that are required for any movement; ex. f-actin; (for humans and cars - shoes, map/GPS, gas/lunch); “activate” a cell prior to its polarization and movement (ex. glucose); provide a polarity/prime the cell
Instructive Cue
cues that are required for directional movements but not movement itself (what is it from teh outside world that tells the thing where to go); street lights, signs, “path”; provides polarity within the cell that is already prepared for directed movements
Duty Cycle
steps: cell must polarize → directed polymerization of F-action at leading edge → attachament of leading edge to the substratum/substrate (extending like catching something with a rope or lasso) → contractivity as rear pulls cell forward and rear detaches → keep repeating for as long as the signal persists (if teh signal stops, the cell will get distracted and stop heading in that direction); if using a pipette to pipe a chemoattractant, that is an instructive cue
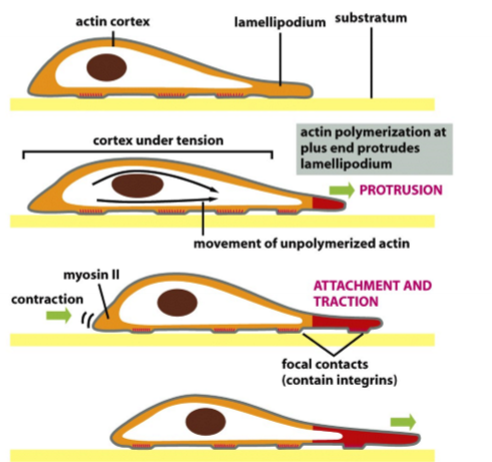
Experimental Tests
knockout, widespread over expression, and perturb or relocate gradient of signaling “cue”
Knockout
does not distingush whether the factor is permissive or instructive bu it does tell you if the protein (or whatever you are testing) is a factor or not; if motility is broken when the factor is removed, then it is a motility factor
Widespread over expression
elimnates the possible graident of an instruction; a lot of concentration of the factor (no gradient now for teh cell to follow)
Perturb or relocate gradient of signaling “cue”
changes the direction of cell movements; relocate gradient and see if cell will move with it (if it does → instructive cue); this is teh gold star test
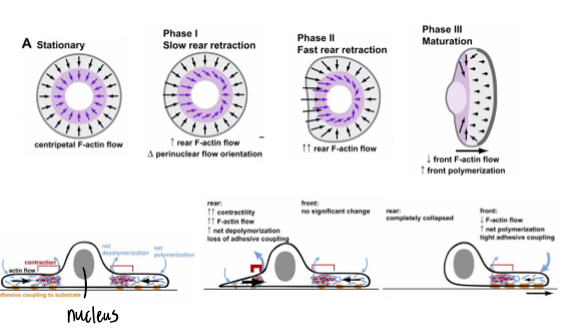
Testing the Duty Cycle
proteins do not change they are just organized and activated in different ways; stationary - polarized all the way around but when it gets to matuartion it is only polarized at the leading edge
Different Forces Involved in Cell Migration
protrusion of membrane lamellipodia or filopodia requires force production (polymerization causes force); contractivity from detachament of the cell rear after protrusion becomes apparent to the substratum; traction at front can be low as long as contraction at the back is high
Integrin Adhesion Receptor Dynamics in Cell Migration
membrane and adhesion factors need to move as much as F-actin and myosin II; duty cycle
Proteins in Cell Migration
cell polarization (side/rear - PTEN and myosin II, front - activated Cdc42 and Rac, PIP3, activated integrin MTOC/golgi, and microtubules), protrusion and adhesion formation(nucleation - Arp2/3 complex, WAVE/WASP, and Rac/Cdc42, polymerization/organization - profilinm ENA/VASP, ADP/cofilin, capping proteinsm and crosslinkers), and rear retraction (adhesion disassembly and retraction - FAK/Src/ERk, myosin II, microtubules, Rho, Ca2+, calpain, and calcineurin)
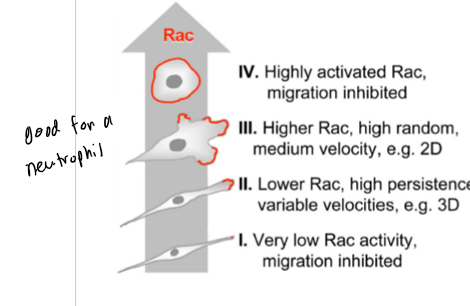
Gradient and levels of G-proteins RAC activity control what
cell velocity and persistence
Optogenetic Control of RAC
LOV and J-alpha allow plants to control photosynthesis
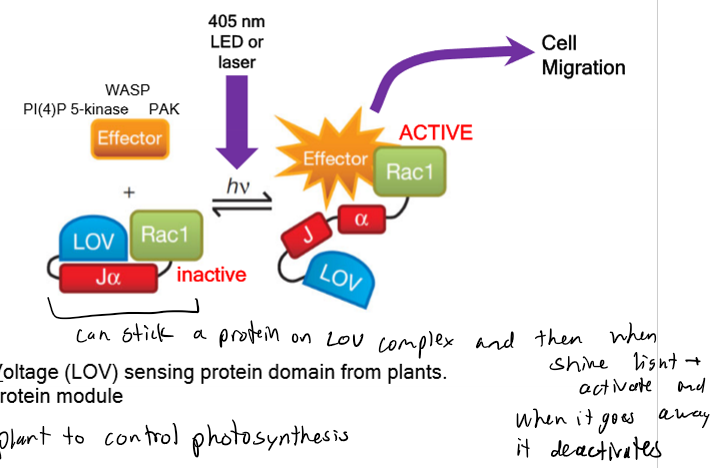
LOV
light oxygen voltage sensing protein domain from plants
J alpha
inhibitory protein module