Honors Midterm Ardoin US History (Jamestown through Reconstruction)
1/346
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
347 Terms
Elizabeth I
First attempt at English colonization began under Elizabeth I.
Roanoke Colony
this was England's first attempt for colonization in the colonies. It was located off the coast of North Carolina. The governor John White left to go back to England and get supplies. He returned after two years to find no colonists. Historians believe that the colonists were either attacked by cannibals or moved into the interior regions of the colonies where they intermarried with Native Americans.
James I
first successful attempt at colonization under his reign- Jamestown

Joint-Stock Companies
several investors pooled their monies together in hopes of finding gold in the new land and making a profit.
Jamestown
first successful attempt in establishing a colony in America. Located in Virginia on the Chesapeake Bay.
Captain John Smith
saved Jamestown by reorganizing it and appointing people to do certain jobs. His motto was "Those who do not work do not eat."
"Starving Time"
1609-1610. 60 out of 500 people survived; takes place when Captain John Smith left Jamestown.
John Rolfe
introduces tobacco to Jamestown which saved the colony
Indentured Servant
refer to those who could not pay their way to the colonies. Someone in the colonies paid their way and they worked for that person for seven years
Representative Gov.
Government where one person represents the people of an entire area. This was more conducive to the South because of the large land settlements. VA House of Burgesses was the first representative government.
Pilgrims
inhabited Plymouth in 1620; they left Holland because their children were being influenced by Dutch customs and religion, and Holland was about to have a war with Spain. They were supposed to settle in Jamestown but ended up settling in Plymouth either because their navigation was not accurate, or they wanted to practice their religion in peace.

William Bradford
Governor of Plymouth Colony
Mayflower Compact
-signed on the Mayflower by the Pilgrims. Government was based on the Mayflower Compact which they have a governor and assistants, they agreed to follow the rules of their leader and God.

Massachusetts Colonies
Established by the Puritans in 1629. The Puritans left England to establish the "city upon a hill"; Led by John Winthrop. This colony was known to be very intolerant
Harvard Colonies
The oldest college in America, which reflected Puritan commitment to an educated ministry
Rhode Island Colonies
established by Roger Williams because of the intensity of the Puritans. William has may odd beliefs including the fact that he denounced mandatory worship, freedom of religion, children decide baptism, and payment for Indian land; "Forced Religion stinks in the nostrils of God"
New York Colonies
originally Dutch (made money by fur trapping). Peter Stuyvesant was in charge before the English took over by the Treaty of Westminster, was a colony of diverse settlers.
Pennsylvania Colonies
a Quaker colony, founded by William Penn; was a colony that believed in inner light, civil disobedience, no church hierarchy, good Indian relations, city of "brotherly love", and representative assembly-freedom of religion
Georgia Colonies
was established by James Oglethorpe for the debtors in Europe. Also established as buffer between Florida and the Carolinas.
Headrights System
the headright system leads to the plantation system. In the headright system, people would get 50 acres of land per family member, but people were abusing this system by lying about the number of people in their family. Leads to the development of plantations.
Anne Hutchinson
Massachusetts Bay Puritan who had gatherings at her house after mass to discuss what she would have said in the sermon. She was put on trial for interpreting the preacher's sermon and is almost declared innocent when she claims she had a direct revelation from God. Puritans believe that only priest can talk to God. She was kicked out of the colony. She was another example of Puritan intolerance.
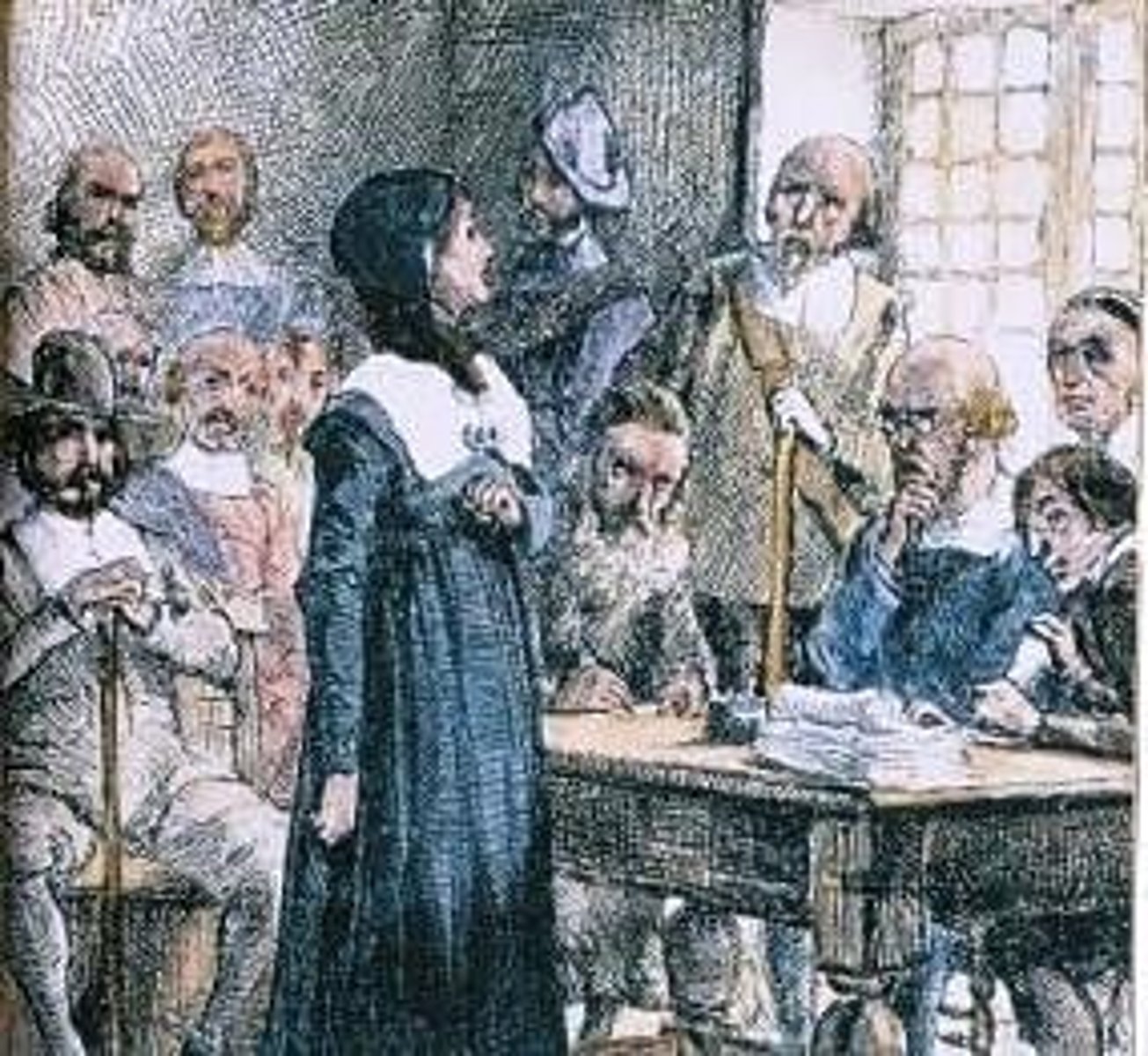

Salem Witch Trials
took place in Salem, Massachusetts because of social and economic problems in Salem. This is also an example of Puritan intolerance.

N. E. Town Meeting
The Church in center becomes the house, so there is no separation of Church and state. It is a direct democracy, so everyone has a say in the small community.
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
This was the first written constitution in the colonies; loyal males that owned property could elect a legislative assembly. First document to state "consent of the governed."
What were the reasons why England was behind Portugal and Spain in colonization? What factors eventually pushed England into exploration?
England had too many internal problems to deal with exploration. Finally, England solved its problems and because they wanted new markets and a population explosion in England exploration began.
Why did the first English attempt at colonization fail?
They didn't bring the right people for colonization and when John White left and came back no one from the colonies was anywhere to be found.
What role did joint-stock companies play in exploration?
They funded the colonies
Why did Jamestown succeed?
First, when Jamestown failed, John Smith took over and reorganized the colony. He also sought the help of the local Native American tribe, although that did not go well.
Also, John Rolfe introduced tobacco
Why was Georgia established?
Georgia was established to be a buffer between the Carolinas and Florida. Many debtors were apparently sent to Georgia. They were placed here because they thought the Seminole Indians would kill and fight with the debtors rather than the other and more important colonies. Georgia was also established as a philanthropic experiment by James Oglethorpe who wanted to send those in debtors prison to Georgia.
What are some the differences that develop between the Northern and Southern colonies? Why?
South: fertile soil, longer growing season, warm climate led to a primarily agricultural area. Economicall the South benefitted from cash crops (crops grown in large quantities) like tobacco, rice, and indigo. The headright system led to the development of plantations and slavery (1619).
The large land settlements impacted the government (formation of a representative democracy) the economy, religion (chapels of ease), and society. Because of slavery a social hierarchy developed. The social hierarchy included planters, yeomen farmers, indentured servants, and slaves. Ship building was also conducive to the south because of the abundance of trees.
North: because of the fact that the soil in the north was infertile, the northern economy depended on fishing, ship building, and trade. Socially, slavery does not develop in the area because of the fact that the plantation system does not develop in the north. Instead, there were small family farms. Religion was more important in the north because many of those that migrated to the area came because of religious persecution. Also, families were more stable because they came over in family units. Regarding the government, direct democracy developed because of the grid-pattern system of land development.
James Town Virginia
established in 1607 by the Virginia Company of London for economic purposes (gold) Although unsuccessful at first, it eventually profited from fertile soil and a warm climate. Slavery developed as a result. Religion was very relaxed- primarily Anglican. Known for the establishment of the first representative government in the colonies- the Virginia House of Representatives.
Plymouth
was founded in 1620 by the Pilgrims. The Pilgrims were Puritans who separated themselves from the church and became Separatist and left England to found Plymouth where they could freely practice their religion. The Pilgrims were supposed to land in Jamestown but ended up founding Plymouth instead. They depended primarily on ship building and fishing because of infertile soil. Religion was very important-the colony was established for this reason. Eventually the New England Town Meeting was established in the New England area with meetings being held in the Church at the center of town. Not separation of church and state.
Massachusetts Bay 1629
The Puritans established this colony to create the "city on a hill" because they did not want to admit that they could not reform the Church of England. Depended on fishing and ship building because of infertile soil. Very religious colony because they were founded for religious reasons. New England Town Meeting will develop here.
Maryland 1624
Catholic colony established by Lord Baltimore.
Rhode Island 1636
was founded by Roger Williams after he was kicked out of Mass. Bay Colony. It was known for Williams' odd beliefs and very liberal views.
The Carolinas
were established strictly as proprietary colonies and for profit. Barbados slave code known here.
New York 1664
established by Peter Stuyvesant. Was originally owned by the Dutch but was eventually taken over by England in the Treaty of Westminster.
Pennsylvania
established by William Penn. It was a Quaker colony founded for religious purposes.
Delaware 1682
was originally part of Pennsylvania, but William Penn cut it off and gave it a separate government.
Georgia 1732
founded by James Oglethorpe for debtors in Europe. It was made to be a buffer between the Carolinas and Florida where the Seminole Indians were.
Enlightenment
the search for the laws that govern the universe. Move from a God-centered to a people-centered universe. Man realizes that he is intelligent enough to make his own decisions and not depend on God.
Divine right of kings
James I said that kings get their power from God; therefore to question the King is blasphemy.
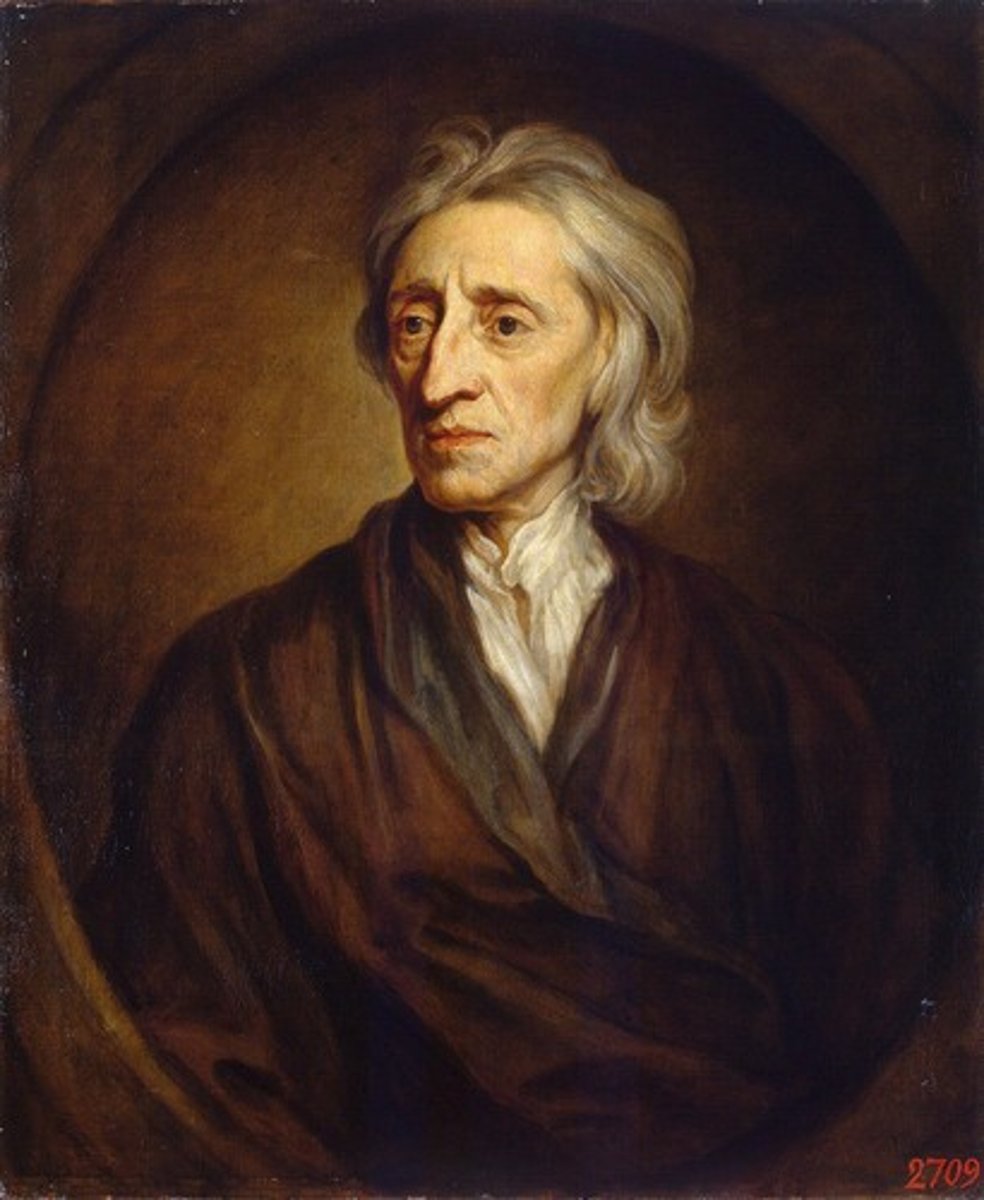
John Locke
British philosopher who believed in tabula rasa, consent of the governed, the social contract, life, liberty, and property, right to revolution; He is a major source of inspiration for the founding fathers and one of the indirect causes of the American Revolution... (big nose= big ideas)

Two Treatises on Government
essay written by John Locke
Benjamin Franklin
invented many things, was the first colonist to talk to the king, and was an example of the Enlightenment because he used his mind to invent and write
Great Awakening
a religious revival that was started by the decline of the Puritans and resulted in colleges, free will over predestination, growth of religious toleration, people have more self-worth, and formation of new religions. This is an indirect cause of the American Revolution. It is also characteristic of evangelical preachers like Jonathan Edwards and George Whitefield.
Jonathan Edwards
Preacher in the Great Awakening who wrote Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God.
George Whitefield
Anglican preacher in the Great Awakening.
Predestination
the belief that people are destined to heaven or hell at birth. Puritans believed in predestination.
French and Indian War - 1754-1758
(peace treaty ending the war was the Treaty of Paris 1763) war between the French and their Indian allies and the British and the colonists. Britain won and France lost all territory in North America. also an indirect cause f the American revolution
William Pitt
British Prime Minister who helped to win the war by sending more troops to North America.
George Grenville
prime minister of England after the French and Indian war who taxed the colonists to pay for the debt of the war.
Proclamation line of 1763
line established after the French and Indian War to keep the colonists out of the new territory gained from the war
Sugar Act
taxed legal documents, playing cards, and dice. Most hated of the acts because it affected everyone.
Currency Act
made colonial money illegal tender
Stamp Act
taxed legal documents, playing cards, and dice. Most hated of the acts because it affected everyone.
Quartering Act
Stated that colonists living on the frontier had to house British soldiers while the soldiers protected them from Indians
Salutary neglect
time from 1607-1754 when England has nothing to do with the colonies; the colonies settle on their own and establish their own governments
Virtual representation
British argument to counter "no taxation without representation." One representative in parliament represents the entire British realm
Sons of Liberty
they went after the stamp collectors; tarred and feathered them.
Samuel Adams
the cousin of John Adams; led the Sons of Liberty
Stamp Act Congress
They said parliament had the right to legislate over the colonies, but they did not have the right to tax them without representation. Met in 1765.
Boston Massacre
British soldiers fired on a mob of angry colonists who were antagonizing them. Paul Revere drew an engraving that turned into propaganda.
Boston Tea Party
Because Britain was allowing the struggling British East India Company to sell tea directly to the colonists which hurt the colonial merchants. Even though the colonists were getting cheaper tea, they were unhappy because it would cut out colonial merchants.
Coercive Act (Interable Acts)
Acts established by Britain to punish the colonists for the Boston Tea Party; The acts closed the port of Boston until the tea was paid for by the colonists, colonial meetings had to have royal permission, and a military governor was put in charge.
First Continental Congress
1774 meeting in which the colonists decide that the colonies have the right to tax and legislate for themselves, formed the Continental Association, decided to boycott British goods. The significance is that the colonies, are uniting based on common goals and agree to fight back if the British use force against them.
Lexington and Concord
- the colonists were stockpiling ammunition and weapons and British General Gage wanted to destroy the weapons. Fighting began when the minutemen (colonists) intercepted the British and began firing. Americans hid behind bushes and fired unlike the British who marched in lines (British complained that Americans weren't fighting fairly) Americans loss 94 men, while the British lost over 200 men. First shots of the American Revolution.
Continental Association
Established a boycott on British goods. Primarily women participated which allowed them some part in the American Revolution.
Paul Revere
colonial engraver who drew a picture of the Boston Massacre. Becomes colonial propaganda. Also a minuteman.
Second Continental Congress
they met in May in Philadelphia. Washington was appointed as leader of the Continental Army; committee was sent to France; Olive Branch petition and the Declaration of Independence were written.
Olive Branch Petition
One last petition to King George from the colonists; this was written for those in the Continental Congress who wanted to make sure that the King understood that the colonists were on the verge of revolution; the King responded by sending more troops to the colonies.
Declaration of Independence
Official declaration of the war; written by Jefferson, Adams, and Franklin. Taken from the philosophy of John Locke.
Thomas Jefferson
author of the Declaration of Independence.
Bunker Hill
First major battle of the Revolution. Colonists lost because they ran out of ammo.
Trenton
Washington crosses the Delaware into New Jersey on Christmas night. Captures the British. Boosted the moral of the colonists.
Saratoga
Colonial win that will encourage the French to help the Americans.
Valley Forge
Colonial encampment during the American Revolution. Symbol of the fact that Washington's men were very loyal.
Yorktown
Last battle of the American Revolution; Cornwallis surrendered in October of 1781.
Cornwallis
Cornwallis was the British commander in the Battle at Yorktown. He was aggravated and harassed and wanted the British to pick him up at Yorktown. The French navy shows up instead of the British navy, and this traps Cornwallis because Greene and Morgan are behind him. He surrenders.
What was Locke's philosophy? How did his writings influence Thomas Jefferson?
He talked about self-evident rights: life, liberty, and property. He also believed in tabula rasa, refuted the divine rights of kings, the social contract, and the right to revolution. Thomas Jefferson copied his philosophy into the Declaration of Independence and used those ideas to make it as successful as it was.
What was the overall effect of the Great Awakening?
New colleges, free will over predestination, growth of religious toleration, formation of new religions (Baptists and Methodists) and feelings of self-worth.
How did the French and Indian War begin?
Overpopulation in the colonies, decisions made in Europe between the leaders of France and Britain. The immediate cause was the battle initiated by George Washington at Fort Dusquesne.
What was the overall effect of the French and Indian War on the coming of the American Revolution?
France lost all territory east of the Mississippi River; more land will result in more protection which will lead to taxation, increase in confidence.
Why did Greenville feel the need to establish taxes on the colonists?
He established taxes so that the colonists would help contribute to paying off the debt of the French and Indian War and to protect the colonists in the new territory.
Why did Americans dislike the taxes, especially the Stamp Act? How did salutary neglect play a part in this?
Stamp Act of 1765 placed taxes on legal documents, playing cards, dice, newspapers, almanacs, and college diplomas. Most people disliked taxes because England hadn't been governing the colonies for a while (salutary neglect) and also because they felt that they shouldn't be taxed until they had proper representation in Parliament.
How do colonial attitudes toward Britain change from early colonization to 1776?
By the time of the start of the American Revolution, colonists felt that they didn't need England because the colonies had been running independently for a while.
For what audience did Thomas Jefferson write the Declaration of Independence?
The colonists, the French, and the British.
What were the advantages and disadvantages for the Americans and British in the American Revolution?
The advantages that the Americans had over the British were that they were fighting on their territory, had better Generals like George Washington, had better lines of communications, and had an inspiring cause to fight for. The disadvantages that the Americans had to deal with were the problems of having no formal government, no money, no navy, no trained army, and no supplies. The advantages that the British had over the Americans were that they had a strong, well-trained army and navy, strong central government with funds, and support of the colonial loyalists ( in the South) and the Native Americans. The disadvantages that the British had to deal with were the problems of the large distances that separate Britain from the battlefields, the British troops were unfamiliar with the terrain, and they had weak military leaders.
French and Indian War
1754-1763
Salutary Neglect
1607-1754
American Revolution
1776-1783
Articles of Confederation
was the 1st form of government established at the Second Continental Congress. They don't last because they are problematic but it gets through the Revolution. Federal government was not able to pass anything because 9 of 13 colonies must agree. They don't give the federal government much power because they are afraid of tyranny. All power was in the hands of the state governments.
Land Ordinance of 1785
one of the only successful areas of the Articles of Confederation. It involved the sale and survey of land from New York and Ohio
Northwest Ordinance
Another successful aspect of the Articles. It dealt with how a territory became a state. When the state had 60,000 it could apply for statehood.
James Madison
James Madison was the Father of the Constitution. He was the first one to say that the Articles weren't working. Called the Annapolis meeting.
Annapolis meeting
meeting originally called to discuss trade and navigation in hopes that the delegates would realize the need to change the Articles of Confederation.
Daniel Shays
Led a rebellion of farmers in Springfield, Massachusetts that go to the courthouse before they foreclose on farmers. They are in debt and they want inflation but they don't realize it will make the worth of the dollar go down. Massachusetts tried to call out a federal army to fight the rebellion, but they don't have one. Small group of farmers were able to have a rebellion in a small state government because state government took care of inflation. Overall significance is that it makes many realize the need to have a federal government that could call out an army and deal with the currency
Constitutional Convention
Meeting called in May of 1787 to discuss changing the Articles of Confederation. Ultimately delegates at this meeting decide to get rid of the Articles and establish a new government.
Virginia Plan
The powers of the government would be divided among three separate branches: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The legislature would consist of two houses (bicameral). The first would be chosen by the people; the second by the members of the first house from among persons nominated by the state legislators. Each state's representation in the legislature would be in proportion to the taxes paid to the national government, or in proportion to its free population. An executive of unspecified size would be selected by the legislature and serve for a single term. Proposed by James Madison.
New Jersey Plan
Proposed by William Patterson, this introduced a single-chamber legislature (unicameral congress) would have the power to raise revenue and regulate commerce. Representation would be based on population.