COMPLEXOMETRIC TITRATIONS
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
acidic and basic radicals
The simple salt consists of two radicals:
Basic radical
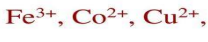
Acidic radical
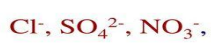
metal complexes or coordination compounds
The chemical species are called
complexation
The formation of a coordination compound form a metal ion is called
complex species of complex ion

bracket [ ]
The formula of the complex species is written within __
ligands
The six NH3 groups are called the ___
ligand
The ___ can be defined as any molecule or ion that has at least one electron pair (lewis base) which can be donated to a metal ion (Lewis acid)
primary valence and secondary valence
Transition elements exhibit two types of valencies, namely ____ and ____
ionisable valence
The primary valence is also know as _____
nonionisable valence
secondary valence is known as ____
anions
____ can satisfy primary valence
anions or neutral
____ molecules can satisfy secondary valence
oxidation number
primary valence corresponds to the _____
coordination number
secondary valence corresponds to the ____
Monodentate ligands
When the ligand has only one donor atom
Monodentate ligands
It may be a neutral molecule such as carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia
Monodentate ligands
a negatively charged ion such chloride ion, cyanide ion, hydroxide ion
Chelation
When the ligand has two or more donor atoms, the terms bidentate, tridentate, tetradentate … etc., generally multidentate frequently used
cyclic compound
The _____ form when the multidentate ligand attached to the central metal ion or ion by more than one coordination atom, is called chelate
Bidentate ligands
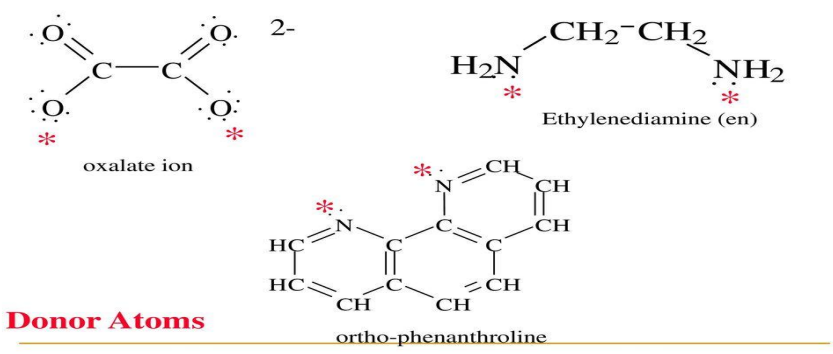
Polydentate ligands
Polydentate ligand and chelation
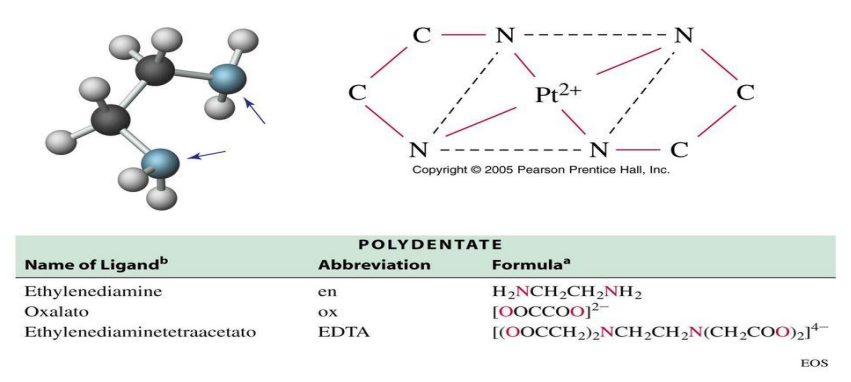
Pt2+ and ethylenediamine
The square planar complex of ____ and _____ has two ligands with a total of four points of attachment
two
ethylenediamine has __ nitrogen atoms that can donate electron to a single metal ion
cationic, neutral and anionic
different types of complex species
cationic

Neutral
Anionic

Complex ion
Species where transition metal ion is surrounded by a certain number of ligands
Coordination number
The total number of monodentate ligands attached to the central metal ion in the complex molecule
Coordination number
it can be also known as the number of sigma bonds between the ligands and the central metal ion
Complex ion
____ is formed by the union of a simple ion with the either other ions of opposite charge or with neutral molecules as shown by the following examples
complex ion

complex molecule

complex molecule

Complexation process
is a reaction with a metal ion involves the replacement of one or more of the coordinated solved molecules by other nucleophilic groups. The groups bound to the central ion are called ligands and in aqueous solution the reaction can be represented by the equation
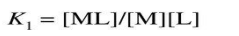

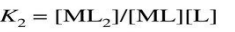

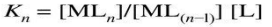

zwitterions
The formula (I) is preferred to (II), since it has been shown from measurements of the dissociation constants that two hydrogen atoms are probably held in the form of ___
2.0
2.7
6.2
10.3
20 °C
The values of pK are respectively pK1 = ___, pK2 = ____, pK3 = ___, and pK4 = ___ at _____
6.3; 11.5
dicarboxylic acid with two strongly acidic groups and that there are two ammonium protons of which the first ionize in the ph region of about ____ and the second at a pH of about _____
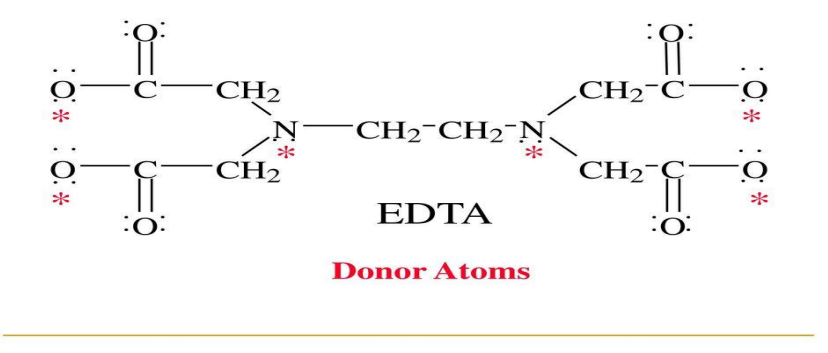
H4Y
To simplify the following discussion EDTA is assigned the formula ____
Na2H2Y
the disodium salt is therefore __
H2Y2-
affords the complex forming ion ____ in aqueous solution
1:1
it reacts with all metals in a ___ ratio
carboxyl protons
pK1 = 0.0
pK2 = 1.5
pK3 = 2.00
pK4 = 2.69
the first four pK values apply to ___
ammonium protons
pK5 = 6.13
pK6 = 10.37
The last two pK values are for the ____
tetraprotic; 140 °C: 2 hours
The neutral acid is ___ with the formula H4Y, which can be dried at ___ for __ and used as a primary standard
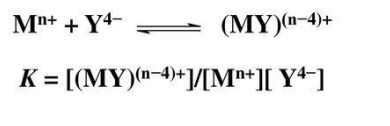
The stability of a complex is characterized by the stability constant (or formation constant) K
color reaction
the ____ should be specific or a least selective
metal-indicator complex
the ____ must possess appreciable stability, but ____ must, however, be less stable than the metal-EDTA complex
free indicator and metal indicator complex
The color contrast between the _____ and the ____ should be such as to be readily observed
metal ions
The indicator must be very sensitive to ____
pH range; titration
The above requirements must be fulfilled within the ___ at which the ___ is performed
1:1 complexes
The indicators which form complexes with specific metal cations can server as ____
1:1; 1:2; 2:1
The molar ratio metal: indicator = _____ are common, but ____ complexes and ___ complexes also occur
chelating agents
The metal ion indicators, like EDTA itself, are chelating agents
red - blue - yellow orange
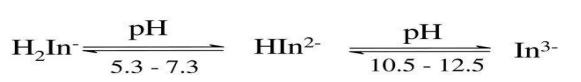
Direct titration
The solution containing the metal ion to be determined is buffered to the desire ph (e.g. to pH = 10 with NH4Cl/NH4OH, i.e. the ammoniacal buffer) and titrated directly with the standard EDTA solution

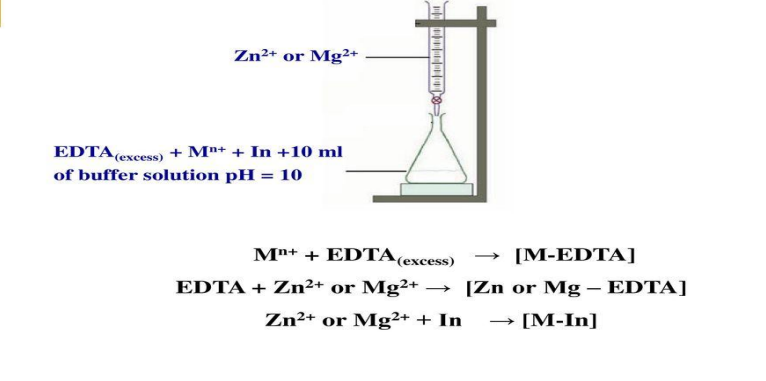
Back titration
Many metals, cannot, for various reasons, be titrated directly: thus they may precipitate from the solution in the pH range necessary for the titration, or they may form inert complexes, or a suitable metal indicator is not available
Back titration
In such cases an excess of standard EDTA solution is added, the resulting solution is buffered to the desired pH, and the excess of the EDTA is back-titrated with a standard metal ion solution
Back titration
A solution of zinc chloride or sulphate or of magnesium chloride or sulphate is often used for this purpose
Back titration
The end point is detected with the aid of the metal indicator which responds to the zinc or magnesium ions introduced
Back titration A
Replacement or substitution titration
It may be used for metal ions that do not react (or react unsatisfactorily) with a metal indicator or for metal ions which form EDTA complexes that are more stable than those of other metals such as magnesium and calcium
Replacement or substitution titration
The metal cation Mn+ to be determined may be treated with the magnesium complex of EDTA, when the following reaction occurs:

Replacement or substitution titration
The amount of magnesium ion set free is equivalent to the cation present and can be titrated with a standard solution of EDTA and a suitable metal indicator
Replacement or substitution titration
In the direct titration of calcium ions, Solochrome black gives a poor end point; if magnesium is present, it is displaced from its EDTA complex by calcium and an improved end point results
Alkalimetric titration
When a solution of disodium EDTA, Na2H2Y, is added to a solution containing metallic ions, complexes are formed with the liberation of two equivalents of hydrogen ion
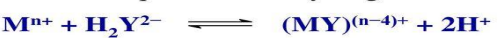
Alkalimetric titration
The hydrogen ions thus set free can be titrated with a standard solution of sodium hydroxide using an acid-base indicator or a potentiometric end point; alternatively
Miscellaneous methods
Exchange reactions between the tetracyano-nickelate (II) ion [Ni(CN)4]2- and the element to be determined, whereby nickel ion are set free, have a limited application
Miscellaneous methods
Thus silver and gold, which themselves cannot be titrated complexmetrically, can be determined in this way

Miscellaneous methods
The equivalent amount of nickel thereby set free is determined by rapid titration with EDTA using an appropriate indicator (murexide, bromo pyrogallol red)
Murexide

Solochrome black

Calmagite

Pyrocatechol violet

Region 1: before the equivalence point
The concentration of free metal is equal to the concentration of excess, unreacted M^n+
Region 2: at the equivalance point
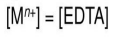
Region 3: after the equivalence point
The concentration of free EDTA can be equated to the concentration of excess EDTA added after the equivalence point