Cells & Microorganisms
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Channel Protein
Allows certain substances in and out of cells without using energy
Phospholipid Bilayer
The main ‘framework’ of the cell membrane
Integral Protein
Proteins that are inserted into the phospholipid bilayer
Cholesterol
Spaces out phospholipids in low temperatures, stabilises phospholipids in high temperature
Glycoprotein
Cell recognition and helps binding to other cells
Carrier Protein
Bind to specific substances and transfer them across the cell membrane using energy
Glycolipid
Maintaining structure of the cell membrane and assist with cell recognition
Peripheral Protein
Can detach and reattach to membrane. Responsible for cell signalling.
MRS GREN
Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Excretion, Nutrition
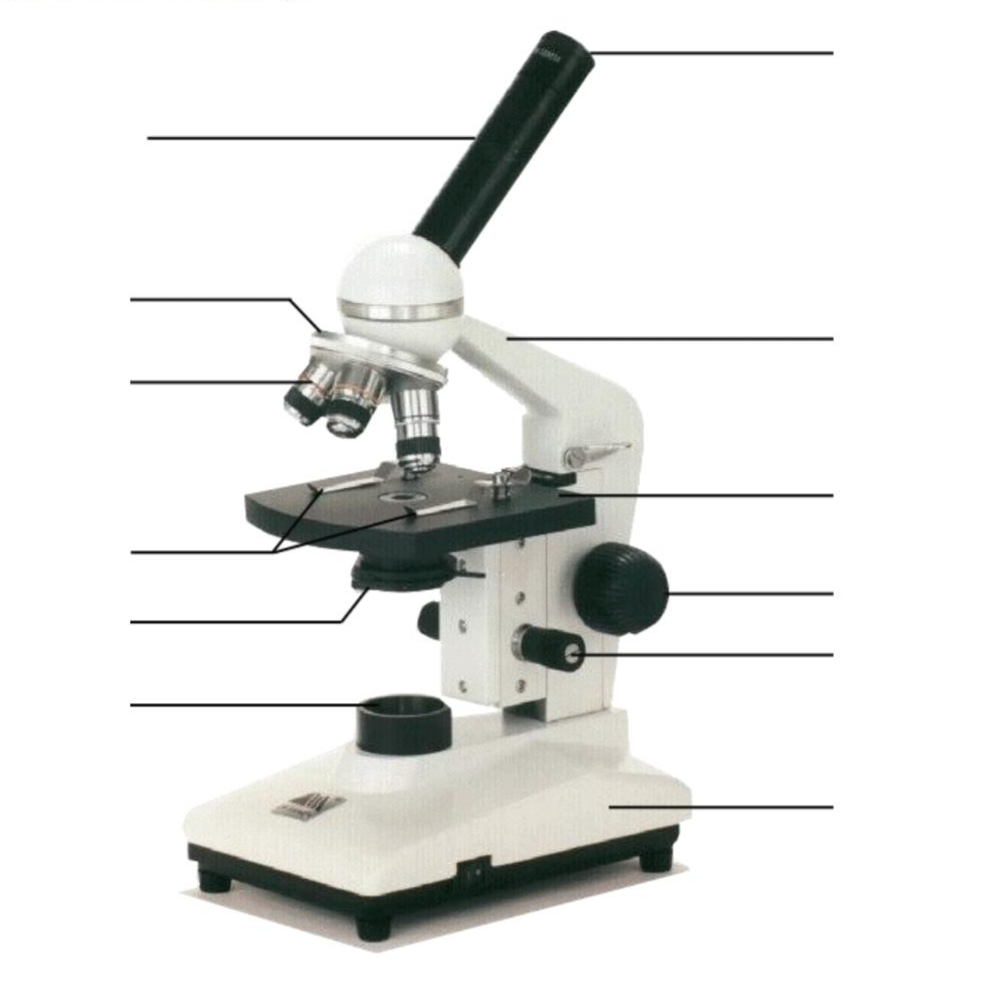

Parts of the microscope
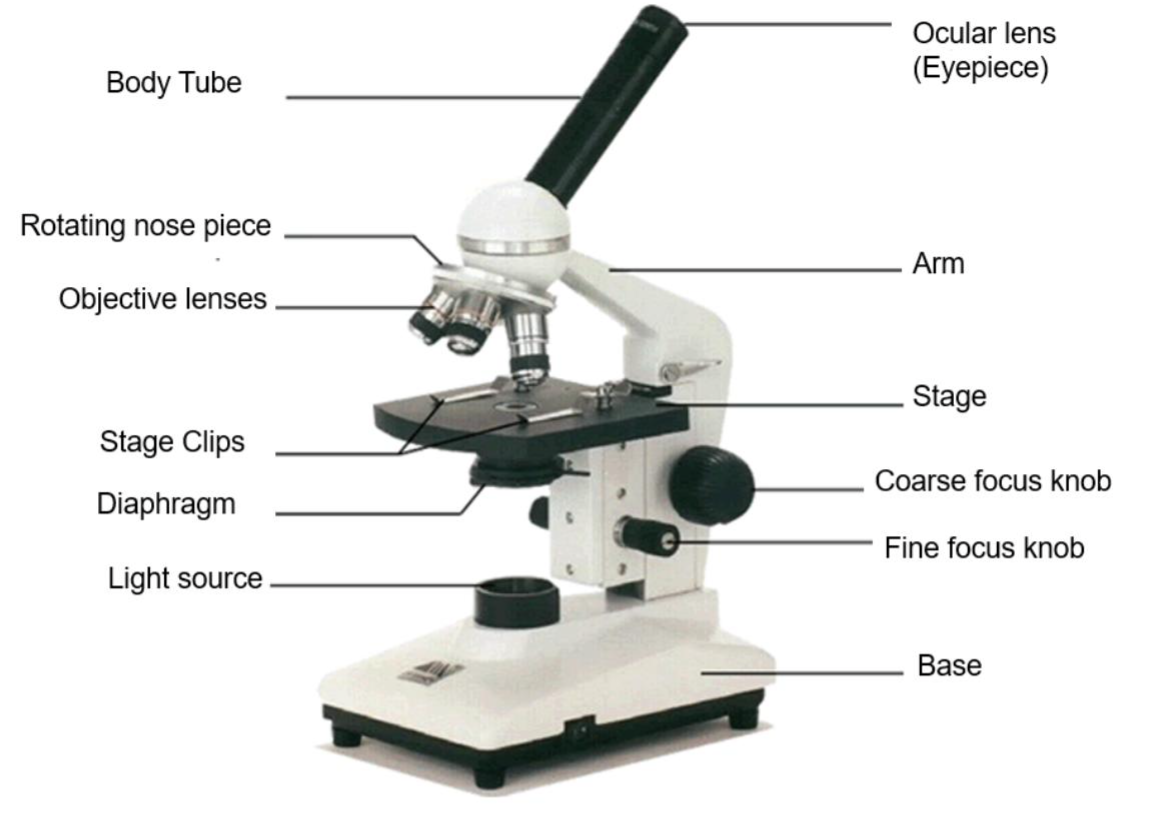
Five Kingdoms
Animal (animale), plant (plantae), protist (Protista), fungi, monera
Unicellular
Organisms that are only made up of one cell
Multicellular
Organisms that are made up of two or more cells
Difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Prokaryotes are unicellular, lacks nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotes are multicellular, has a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Difference between a plant and animal cell
A plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplast and a central vacuole.
Cell membrane
Controls the entry of dissolved substances into and out of the cells.
Cell Wall
Functions to support and protect the cell and limits its volume.
Cytoplasm
To contain the cytosol, which is the fluid in the cytoplasm and provide a medium suitable for biochemical reactions to occur.
Nucleus
The ‘control centre’ of the cell
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
To package proteins made by the ribosomes into small vacuoles for transport to a Golgi body.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
To synthesis lipids and metabolise carbohydrates
Ribosomes
Site of protein production
Golgi body
Packages materials into membrane bound bags
Vacuoles
Storage of waste, minerals sugars and wastes.
Lysosomes
Membrane bound vesicles containing powerful enzymes that break down debris and foreign materials
Mitochondrion
Converts chemical energy into compounded call ATP
Chlorplasts
Site for photosynthesis
Cellular respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy
Respiration equation
glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + energy
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy
Photosynthesis equation
carbon dioxide + water + light energy = glucose + oxygen
The cell membrane is selectively permeable
Only some materials will pass through while other will not
Surface area to volume ratio
Cells need a large SA:Vol ration - allows for efficient exchange of materials
Passive Transport - Diffusion
The movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
Passive transport - osmosis
A type of diffusion involving water molecules. Molecules will move from areas of low solute concentration to areas with high solute concentration
Passive Transport - facilitated diffusion
The movement of molecules across a cell membrane via special transport proteins, from high to low concentration.
Active transport
The movement of molecules against their concentration gradient, requiring energy input, typically through ATP.
Exocytosis
Occurs by fusion of a vesicle membrane. The vesicles contents are then released to the outside of the cell (exiting the cell)
Endocytosis
The plasma membrane fold in around the molecules to be transported into the cell
Types of endocytosis
Pinocytosis - Phagocytosis
Types of Microorgansims
Bacteria - Archaea - Fungi - Protista - Algae
Bacterial Growth
Bacteria are prokaryotes that divide by binary fission
Optimal conditions of bacterial growth
Nutrients - temperature - acidity/alkalinity - oxygen - water