Module 2: Circuits and Currents & Module 3: Electrical Standards and Practices
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
283 Terms
Current
the rate of flow of electrons/charge
Current is abbreviated as:
I
Current is measured in:
amperes (A)
One ampere is defined as:
one coulomb of electrons flowing past a point each second
(Q/s)
Voltage
a force that pushes/drives the electrons/charge
also referred to as electrmotive force or difference in potential
Voltage is abbreviated as
E, or
EMF
Voltage is measured in:
Volts (v)
Voltage source will have:
a polarity (negative and positive side)
Current flows from:
negative to positive (changing conventions)
AC/DC
AC: Alternating current (polarity of source reverses)
DC: Direct current (polarity is constant)
Alternating Current (AC)
polarity of source reverses
Direct Current (DC)
polarity is constant
Resistance
barriers to the flow of charge
Resistance is abbreviated as
R
Resistance is measured in
ohms (Ω)
Cell
stores chemical energy
transfers it to electricial energy
when a circuit is connected
Battery
when two or more cells are connected together
The cell’s chemical energy is used up by:
pushing a current round a circuit
Electric current
flow of microscopic particles callled electrons flowing through wires and components
In which direction does the current flow?
from the Negative terminal to the Positive terminal of the cell
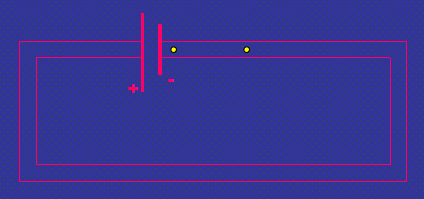
Parts of a simple circuit
cell
switch
wires
lamp
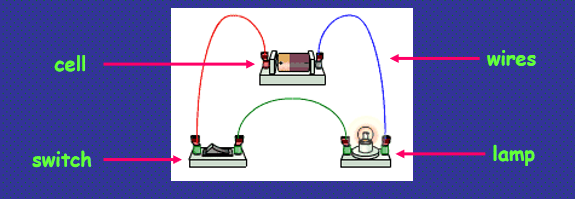
To make the circuit:
these components (cell, switch, wires, lamp)
are connected together
with metal connecting wires
When the switch is closed, why does the lamp light up?
Because there is a continuous path of metal for the electric current to flow around
Cell symbol (circuit diagram)

Lamp symbol (circuit diagram)

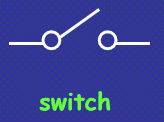
Switch symbol (circuit diagram)
Wires symbol (circuit diagram)

Circuit diagram components are represented by the following symbols:
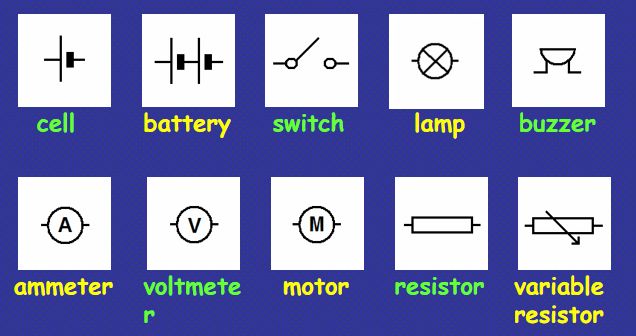
Battery symbol (circuit diagram)
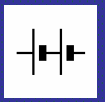
Buzzer symbol (circuit diagram)
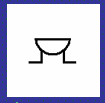
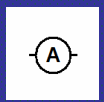
Ammeter symbol (circuit diagram)
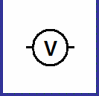
Voltmeter symbol (circuit diagram)
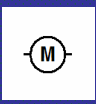
Motor symbol (circuit diagram)
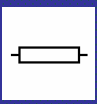
Resistor symbol (circuit diagram)
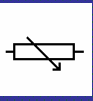
Variable resistor symbol (circuit diagram)
2 types of electrical circuits
Series circuits
Parallel circuits
Series Circuit sample
Series Circuit diagram
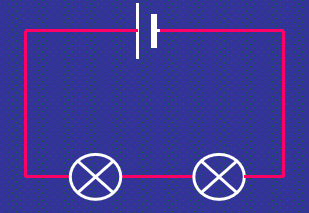
Series Circuit
components are connected end-to-end, one after the other
makes a simple loop for the current to flow round
if one bulb blows, it breaks the whole circuit and all the bulbs go out
Parallel Circuit sample

Parallel Circuit diagram
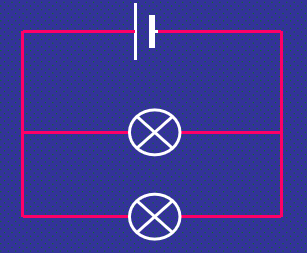
Parallel Circuit
components are connected side by side
current has a choice of routes
if one bulb blows, it will still be a complete circuit therefore the other bulb stays alight
Electric current is measured in ————- using an —————-- connected in series in the circuit
measured in amps (A)
using an ammeter
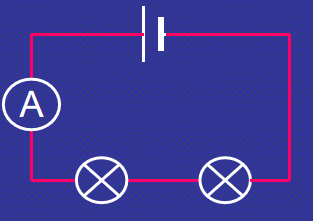
Ammeter in a circuit diagram (Series Circuit)
Ammeter in a circuit diagram (Parallel Circuit)
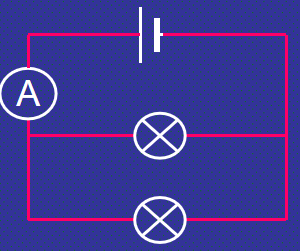
Measuring current (Series Current)
current is the same at all points in the circuit
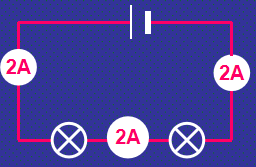
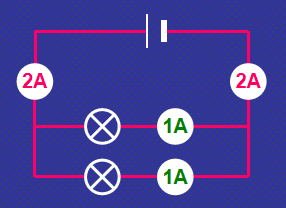
Measuring current (Parallel Circuit)
current is shared between the components
The electrical push (voltage) is measured in ————— on a —————-
measured in volts (V)
on a voltmeter
Different cells produce——
—-—-different voltages
The bigger the voltage supplied by the cell———-
—-—-the bigger the current
A voltmeter is——-
—-—-connected across the components
Potential Difference
term usually used by scientists when talking about voltage
Measuring voltage (Series Circuit)
voltage is shared between the components
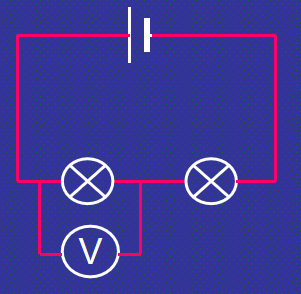
Measuring voltage (Parallel Circuit)
voltage is the same in all parts of the circuit
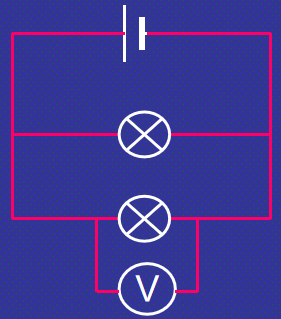
PEC
Philippine Electrical Code
Philippine Electrical Code content:
Chapter 1: General
Chapter 2: Wiring and Protection
Chapter 3: Wiring Methods and Materials
Chapter 4: Equipment for General Use
Chapter 5: Special Occupancies
Chapter 6: Special Equipment
Chapter 7: Special Condition
Chapter 8: Communication System
Chapter 9: Watercrafts
Two (2) categories of PEC rules
Mandatory rules
Advisory rules
Mandatory Rules (PEC rules)
characterized by the use of the word, “SHALL”
Advisory Rules (PEC rules)
characterized by the use of the word, “SHOULD”
or are stated as recommendations that which is advised but not required
Objectives of PEC
Safe Use of Electricity
Adequacy
Safe Use of Electricity (PEC objectives)
To establish basic materials quality and electrical work standards
for the safe use of electricity for light, heat, power, communications, signaling
and for other purposes
(PEC 2017 1.0.1.1)
Adequacy (PEC objectives)
Strict compliance with the provisions of this Code
will ensure safety in electrical installation and construction,
but not necessarily efficient, convenient, or adequate for good service or future expansion of electrical use.
(PEC 1.0.1.1 B)
INTENTION: (PEC Part I 2017 Edition)
This Code is intended as a design specification or an instruction manual to qualified persons.
(PEC 2017 1.0.1.1 C)
Covered scope of PEC 2017 1.0.1.2
covers the installation of electrical conductors, equipment, and raceways, monitoring, signaling, communication conductors and optical fiber cables and raceways installed within or on, to or from:
Public and private buildings
including but not limited to residential, commercial, industrial, institutional, cultural, agricultural, agro-industrial, planned unit development and all other buildings/premises
Electric generating plants
Industrial plants
Transformer stations
Permanent and temporary substation, etc.
Airfields
Railway switchyards
Yards, carnival, parks, parking and other lots
Quarries and mines
Watercraft
Dockyards
Trailers
Mobile homes and recreational vehicles
Offshore facilities
Not covered scope of PEC 2017 1.0.1.2
installation in railway, rolling stack, aircraft, or automotive vehicles
installation of railways for generation, transformation, transmission, or distribution of power used exclusively for operation of rolling stock
The use of PEC is mandated by
R.A. 7920
formely R.A. 184
also known as the new electrical engineering law
R.A. 7920
new electrical engineering law
formerly R.A. 184
Referral codes that are mandated by their corresponding laws:
P.D. 1096 – National Building Code (PEC 2017 1.0.1.4)
P.D. 1185 – Fire Code of the Philippines
Structural Code R.A. 7920 – is an act providing for a more responsive and comprehensive regulation for the practice, licensing and registration of electrical engineers and electricians.
P.D. 1096
National Building Code (PEC 2017 1.0.1.4)
P.D. 1185
Fire Code of the Philippines
Structural Code R.A. 7920
an act providing for a more responsive and comprehensive regulation
for the practice, licensing and registration
of electrical engineers and electricians.
Government Authorities who implement PEC:
Office of the Building Official
Office of the City Electrician (City Electrical Supervising Engineer)
Office of the Municipal Electrician (Municipal Electrical Supervising Engineer)
Regional Office of the DOLE
Scope of the PEC
PEC covers the electric conductors including optical fiber cable and installed within or on, to or from:
Public and private buildings
Electrical generating plants
Temporary and permanent substations
Industrial plants
Transformer stations
Railway switchyards
Yards, carnival, parking, etc.
Watercraft
Dockyards
Airfields
Quarries and mines
Mobile homes, travel trailers and recreational vehicles
Offshore facilities
Other premises which requires electrical installation except to those which are done in;
a) Aircraft
b) motor vehicles
c) railway rolling stocks
Permits and Insperction Certificates (PEC 2017 Article 1.2)
A permit is required before undertaking any electrical installation
An inspection is also required after which certificate final electrical inspection (CFEI) is issued by the authority.
A permit is required before undertaking any electrical installation
True
An inspection is also required after which certificate final electrical inspection (CFEI) is issued by the authority.
True
A permit is not required ofr:
the installation of electrical portable equipment rated not more than 1,200 VA.
reconnection of disconnected service due to non-payment of electric bill or change of occupants for a period of one year.
DPWH form No. 77-001-E
specific application form needed for an electrical permit
Requirement for Electrical Permit
an application form (DPWH form No. 77-001-E) must be accomplished, signed, and submitted by a duly registered Professional Electrical Engineer.
if installation does not exceed 20 lighting and/or receptacle outlets or 4000 volt-amperes, 230 volts, the application may be prepared, signed, and submitted by a duly registered electrical engineer or master electrician.
application shall include the name and signature and seal of the electrical practitioner who will take charge of the installations as well as the signature of the owner or their authorized representative
4 600 mm
over residential property and driveways,
and those commercial areas not subject to truck traffic.
5 500 mm
over public streets, alleys, roads, parking areas subject to truck traffic,
driveways on other than residential property,
and other land transversed by vehicles such as cultivated, grazing, forest, and orchard.
Underground Service-Lateral Conductor
underground service conductor
between the street main, including any risers at a pole or other structure or from transformers,
and the first point of any connection to the service-entrance conductors in a terminal box or meter or other enclosure with adequate space, inside or outside the building wall.
Insulation (PEC)
service-lateral conductor shall withstand exposure to atmospheric and other conditions of use without detrimental leakage of current
A grounded conductor shall be permitted to be uninsulated as follows:
a) Bare copper used in a raceway.
b) Bare copper for direct burial where bare copper is judged to be suitable for the soil conditions.
c) Bare copper for direct burial without regard to soil conditions where part of cable assembly identified for underground use.
d) Aluminum or copper-clad aluminum without insulation or covering where part of a cable assembly identified for underground use in a raceway or for direct burial.
Size and Rating (PEC)
General
Minimum Size
General (Size and Rating)
Service lateral conductors shall have sufficient ampacity to carry the current for the load and shall have adequate mechanical strength.
Minimum Size
The conductors shall not be smaller than 5.5 mm2copper or 8.0 mm2 aluminum or copper-clad aluminum.
Exception for Size and Rating
For installations to supply only limited loads of a single branch circuit such as small polyphase power, controlled water heaters and the like, they shall not be smaller than 3.5 mm2 copper or 5.0 mm2 aluminum or copper-clad aluminum.
Service
the portion of the supply which extends from the street main duct or transformer to the service switch or switchboard of the building supply.
Service Entrance
the conductor and equipment for delivering energy from the electricity supply system to the wiring system of the premises served.
Types of Service Entrances
Overhead Service Entrance
Underground Service Entrance
Overhead service entrance
most common type of service entrance employed by the power companies
supplies electricity which is either a 2, 3 or 4-wire connection.
the overhead service cable between the building property line and the supply point is supplied by electric company to a limit of 30 meters.
Underground service entrance
consists of a raceway conduit extending from the building to the property line where it is tapped to the main.
type of cable recommended is the underground service entrance cable commonly referred to as USE.
Service Entrance Conductors
No. of Service-Entrance Conductor Sets Each service drop or lateral shall supply only one set of service-entrance conductors.
Service Entrance Conductors Exceptions
Buildings with more than one occupancy.
Where two to six service disconnecting means in a separate enclosures are grouped at one location and supply separate loads from one service drop or lateral.
Service entrance conductors shall be of sufficient size to carry the computed loads.
True
Ungrounded conductors shall not be smaller than:
100 A —- For one family dwelling with six or more 2-wire branch circuits.
60 A —- For one family dwelling with an initial computed load of 10 kVA above.
40 A —- For other loads.
100 A (min. A for ungrounded conductors)
For one family dwelling with six or more 2-wire branch circuits.
60 A (min. A for ungrounded conductors)
For one family dwelling with an initial computed load of 10 KVA above
40 A (min. A for ungrounded conductors)
for other loads