Kidney & Osmoregulation
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the structure and function of the mammalian kidney in osmoregulation, including ultrafiltration, selective reabsorption, and the roles of key structures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is Osmoregulation?
Maintenance of the osmotic potential (Salt & Water Concentration) in the tissues of a living organism within narrow limits.
What is the main organ involved in the homeostatic control of water balance in mammals?
Kidney
During deamination, what do hepatocytes do with excess amino acids?
They remove the amino group and convert it first into ammonia (very toxic) and then to urea (less toxic) that gets excreted by KIDNEY.
What is a hepatocyte?
A type of cell found in the liver that helps to keep the body healthy and balanced through various functions.
What is the simplified equation for the ornithine cycle?
Ammonia + carbon dioxide to urea + water.
What is the function of the renal artery?
Carries oxygenated blood (containing urea and salts) to kidneys.
What is the function of the kidney?
Regulates water content of blood and filters blood.
What is the function of the ureter?
Carries urine from kidneys to bladder
What is the function of the urethra?
Releases urine outside of the body
What are the three main structures of the kidney?
Cortex, Medulla, and Renal Pelvis
What are the functional units of the kidney?
Nephrons
What structures of the nephron are located in the cortex?
Glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, and distal convoluted tubule
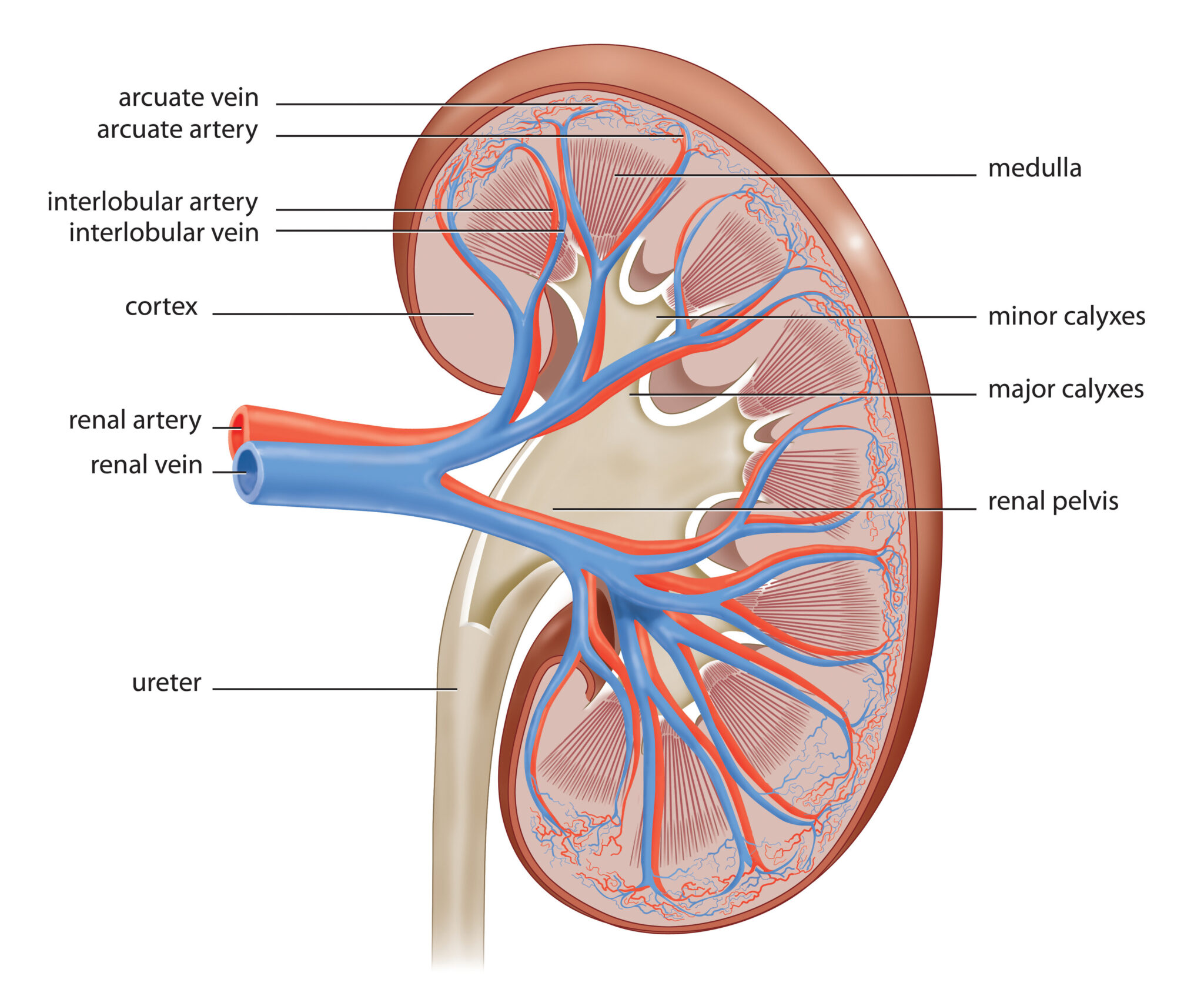
What are the two main functions of the mammalian kidney?
Excretion and Osmoregulation
What small molecules are filtered out during ultrafiltration?
Water, glucose, mineral ions, and urea.
What is the main function of the kidney tubule (nephron) after ultrafiltration?
To return most of what has been removed during ultrafiltration back into the blood.
Where in the nephron does most of the reabsorption occur?
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
What specialized feature increases the surface area for diffusion in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Microvilli.
What is the role of the loop of Henle?
To create a solute concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.
What is the permeability of the descending loop of Henle?
Permeable to water but impermeable to salt ions.
Why is the descending limb permeable to H2O but not to NaCl?
High solute concentration in medulla draws water out of filtrate which moves out by osmosis.
What is a countercurrent multiplier?
A biological system that uses active transport to establish and maintain concentration gradients.
In the distal tubule and the collecting duct, what function does the body regulate?
It balances its water needs.
The permeability of the collecting duct is strongly affected by what hormone?
ADH