Economics Homework for Exam
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Which of the following is included in M2?
Money market mutual funds
The federal funds rate is the
interest rate at which banks lend reserves to each other over night
The Federal Reserve
is the central bank of the United States.
The discount rate is
the interest rate the Fed charges banks.
Which of the following both increase the money supply?
A decrease in the discount rate and a decrease in the interest rate on reserves
Which of the following is NOT an example of monetary policy?
The Federal Reserve decides to increase the amount of tax.
When the Fed decreases the discount rate, banks will
borrow more from the Fed and lend more to the public. The money supply increases.
Which of the following is included in both M1 and M2?
Currency, demand deposits, and other checkable deposits
If the public decides to hold more currency and fewer deposits in banks, bank reserves
decrease
When conducting an open-market sale, the Fed
sells government bonds, and in so doing decreases the money supply.
Which of the following groups meets to discuss changes in the economy and determine monetary policy?
The Federal Open Market Committee
A problem that the Fed faces when it attempts to control the money supply is that
the Fed does not control the amount of money that households choose to hold as deposits in banks
Which of the following is correct?
The Federal Reserve has 12 regional banks. The Board of Governors has up to 7 members who serve 14-year terms.
Which of the following does the Federal Reserve not do?
Conduct fiscal policy
The measure of the money stock called M1 includes
wealth held by people in their checking accounts.
The money supply increases when the Fed
buys bonds.
The idea that nominal variables are heavily influenced by the quantity of money and that money is largely irrelevant for understanding the determinants of real variables is explained by the
classical dichotomy.
The principle of monetary neutrality implies that an increase in the money supply will increase
the price level, but not real GDP.
When the price level falls, the number of dollars needed to buy a representative basket of goods
decreases, so the value of money rises.
The price level is determined by the supply of, and demand for, money.
true
The inflation tax refers to
the revenue a government creates by printing money.
In order to maintain stable prices, a central bank must
tightly control the money supply.
According to the assumptions of the quantity theory of money, if the money supply increases by 5 percent, then
nominal GDP would rise by 5 percent; real GDP would be unchanged.
The supply of money increases when
the Fed makes open-market purchases.
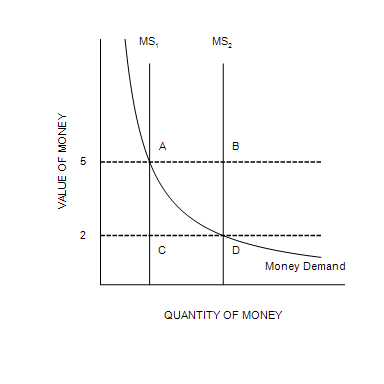
When the money supply curve shifts from MS1 to MS2,
the equilibrium value of money decreases.
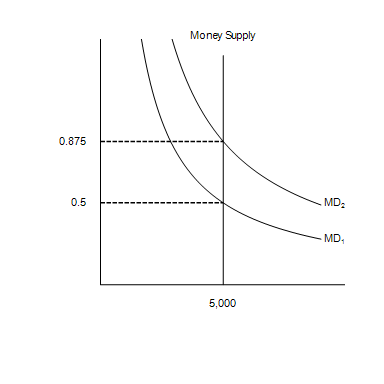
In the graph, MS represents the money supply and MD represents money demand. The vertical axis is the value of money measured as 1/P and the horizontal axis is the quantity of money.
Suppose the relevant money-demand curve is the one labeled MD1; also suppose the velocity of money is 4. If the money market is in equilibrium, then the economy's real GDP amounts to
10000
The price level is a
nominal variable.
To explain the long-run determinants of the price level and the inflation rate, most economists today rely on the
quantity theory of money.
The money demand curve is downward sloping because as the value of money falls people desire to hold a larger quantity of money.
true
According to the classical dichotomy, which of the following increases when the money supply increases?
The nominal wage
Changes in nominal variables are determined mostly by the quantity of money and the monetary system according to
both the classical dichotomy and the quantity theory of money.
The Fisher effect is crucial for understanding changes over time in the
nominal interest rate.
Katarina puts money into an account. One year later she sees that she has 6 percent more dollars and that her money will buy 4 percent more goods. The nominal interest rate was
6 percent and the inflation rate was 2 percent.
The claim that increases in the growth rate of the money supply increase nominal interest rates but not real interest rates is known as the
Fisher Effect.
The nominal interest rate is 5 percent and the inflation rate is 2 percent. What is the real interest rate?
3 percent
If M = 2,000, P = 2.25, and Y = 6,000, what is velocity?
6.75