BTech Module 1: Masonry
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Masonry
Building with units of various natural or manufactured products as stone, brick or concrete block usually with the use of mortar (grout) as a bonding agent.
3/8, ½ inched
Standard mortar joint widths vary from ___ to ___ inch?
3/8 inched
The standard mortar joint thickness is?
The Lime Cycle
Turning of limestone into a lime mortar gradually replacing mud as bonding agent.
Middle Ages (5th-15 Century)
The age where Stone was frequently used to build castles, bridges, cathedrals and mosques. Support much heavier superstructures.
Industrial Revolution
The time where technology made it easy to quarry especially in transporting materials. More elaborate structures were made as a part of experimenting design and workability of the material.
Modern Times
The time period where there’s a decline usage of these materials due to other new materials emerging-faster production, versatility is just some of the factors.
Metals, Concrete blocks
______ & ________ ______ are widely used in construction today
Steel reinforced masonry
_____ __________ _______ considered as high strength masonry units.
Clay Brick
A masonry material where:
Very common for fences
Used in general works (easy works), walls and facades.
Structures that will not carry heavy loads
Does not need to be massively supported
Ex. Non-load bearing walls or fences
Clay Brick
A masonry material where it is the most resistant to building fires of any masonry unit.
Kiln
Bricks are dried for one to two days in a low-temperature dryer called?
Firing / Burning
Will be ready then for transformation into their final form by a process known as?
Soft-Mud Process
A method of forming bricks where relatively moist clay pressed into simple rectangular molds.
Water Struck Bricks
Where bricks produced with relatively smooth, dense surface.
Dry-Press Process
A method of forming bricks besides Soft-Mud Process and Stiff Mud Process
Stiff Mud Process
A method of forming bricks which is the least costly and most widely used today and are highly uniform in dimension and shape.
Tumbling
A process that soften edges and corners and introduces a greater individuality in appearance among units.
Clamp
stacking of bricks in a loose array
Covered with earth or clay, built wood under the clamp and maintaining the fire for a period of several days.
Clinker Bricks
It is a method of sorting of bricks where bricks are placed closest to the fire
over burned and distorted
unattractive; unsuitable for exposed brickwork
Bricks in a zone of the clamp near fire
It is a method of sorting of bricks where bricks are fully burnt but undistorted
Suitable for exterior-facing bricks with a high degree of resistance to weather.
Farther from the fire
It is a method of sorting of bricks where bricks are softer; set aside for use as a backup brick
Bricks from around the perimeter of the clamp
It is a method of sorting of bricks where the bricks are not burned sufficiently which are discarded
Periodic Kiln
It is a is a fixed structure that is loaded with bricks, fired, cooled and unloaded
Tunnel Kiln
For higher productivity, bricks are passed continuously through ______ _____ on special railcars to emerge at the far end fully burned.
Darker bricks
High temperature produces?
Fly ash
A waste product from coal-fired power generation), sand and water. It acts as the binder and the sand as the aggregate.
Stretcher
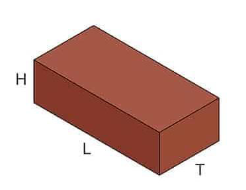
Soldier
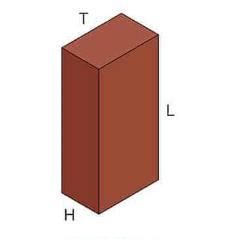
Header
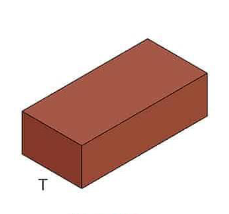
Rowlock Stretcher
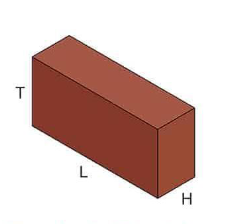
Sailor
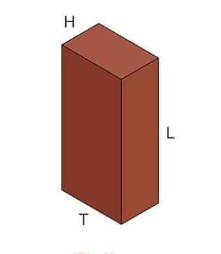
Rowlock
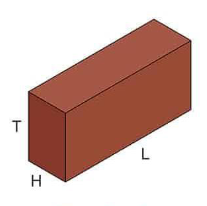
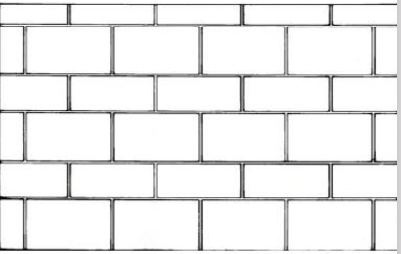
Bond patterns / bonds
Bricks can be assembled in a wall in several patterns, refer to as?
GARDEN-WALL BOND
Lightly loaded boundary walls
Sequence of a header and three stretchers in each course, with each header being centered over a header in alternate courses.
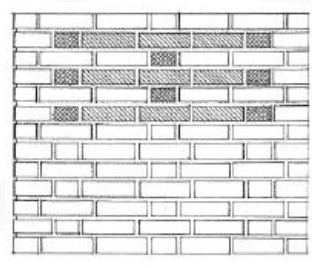
GARDEN-WALL BOND
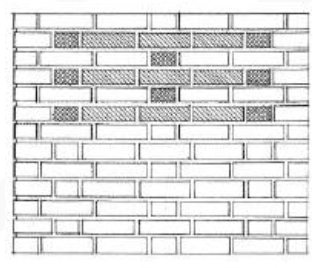
ENGLISH BOND
Alternate courses of headers and stretchers in which the headers are centered on stretchers and the joints between stretchers line up vertically in all courses.
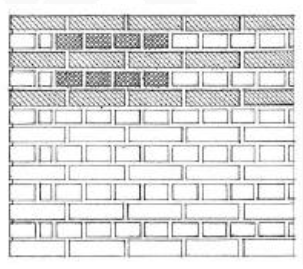
ENGLISH BOND
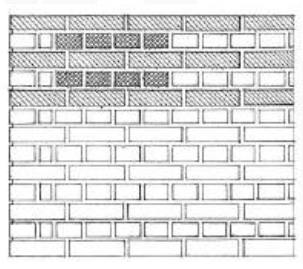
RUNNING BOND
Commonly used for cavity and veneer walls, is composed of overlapping stretchers.
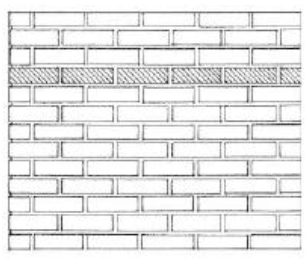
RUNNING BOND
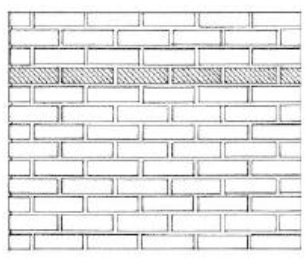
COMMON BOND / AMERICAN BOND
Has a course of headers between every five or six courses of stretchers
COMMON BOND / AMERICAN BOND
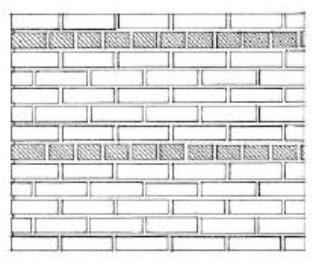
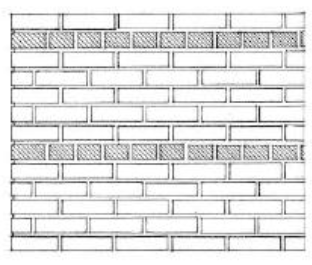
STACK BOND
Has a successive courses of stretchers with all head joints aligned vertically. Because units do not overlap, horizontal joint reinforcement is required.
STACK BOND
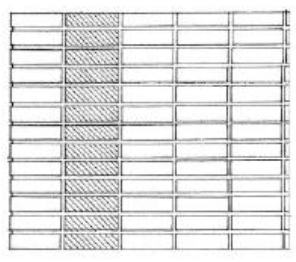
FLEMISH BOND
Has alternating headers and stretcher is in each course each header being centered above and below a stretcher. Flare headers with darker ends are often exposed in patterned brickwork.
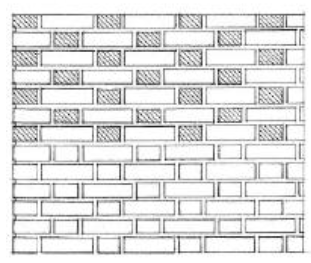
FLEMISH BOND
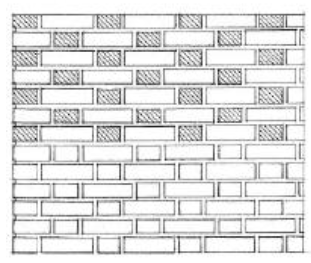
FLEMISH CROSS BAND
Modified Flemish bond in which courses of alternate headers and stretchers alternate with stretching courses.
FLEMISH CROSS BAND
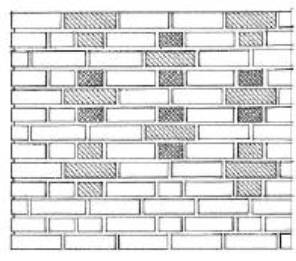
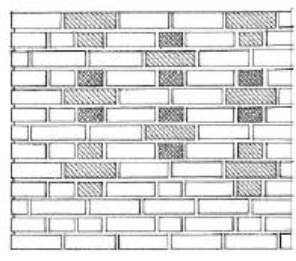
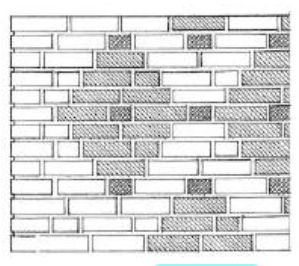
FLEMISH DIAGONAL BOND
Is a form of Flemish in which the courses are offset to form a diamond pattern.
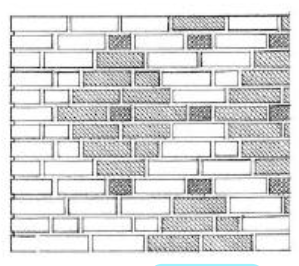
FLEMISH DIAGONAL BOND
Course
The horizontal layer of bricks or other
Wythe
A vertical layer of masonry unites one unit thick
Tooled joints
This type of joint are mortar joints compressed and shaped with any tool other than a trowel.
Troweled joints
This joint is finished by striking off excess mortar with a trowel and where the mortar is cut or struck off with trowel.
Weathered joint
it is the most effective joint as it sheds water
Raked joint
It is a joint that is made by removing mortar to a given depth with a square-edged too before hardening. It is used for interior use only.
Reinforced Brick Masonry
It is analogous to reinforced concrete construction. The same deformed steel reinforcing bars used in concrete are placed in thickened collar joints or the cores of hollow brick to strengthen a brick wall or lintel.
Building stone
It is obtained by taking rock from the earth and reducing it ti the required shapes and sizes for construction.
ASTM C119
It classifies stone used in building construction in 6 groups
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials)
It is an international standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems, and services.
Granite
Is the igneous rock most commonly used for construction (North America).
It is a mosaic of mineral crystals, principally feldspar and quartz (silica), and can be obtained in a range of colors that includes gray, black, pink, red, brown, buff, and green.
nonporous, hard, strong, and durable, and is the most nearly permanent of building stones.
ASTM C615
The ASTM code for granite dimensions’ specifications
Basalt “Black Granite”
Very dense, durable igneous rock; usually found in dark gray color
ASTM C568
The ASTM code for limestone dimensions’ specifications
Slate
one of the two metamorphic stone groups utilized in building construction.
It is formed from clay.
Dense, hard stone with closely spaced planes of cleavage, along which it is easily split into sheets.
Useful for paving stones, roof shingles, and thin wall facings.
ASTM C629
The ASTM code for Slate dimensions specifications
Marble
is the second of the major metamorphic rock groups.
Recrystallized form of limestone
Easily carved and polished
ASTM C503
The ASTM code for marble dimension specifications
Sandstone
second major sedimentary rock type used in building construction.
formed in ancient times from deposits of quartz and (silicon dioxide
Brownstone
One of the 2 familiar forms of sandstone for wall construction
Bluestone
One of the 2 familiar forms of sandstone that is durable stone; paving and wall copings
ASTM C616
he ASTM code for quartz-based dimensions specifications
Quartz countertop
It is called engineered stone countertops, are man-made products
Quartz countertop
They are made of 93% to 95% ground-up natural quartz stone and a small number of other minerals and colorants. The rest is a durable resin that holds it all together.
Granite Countertops
It is 100% natural rock that is taken out of the ground, cut to fit and installed.
Stone Masonry
It may be laid in mortar, much like bricks or concrete blocks, to make walls, arches, and vaults, a method of construction referred to as?
Stone cladding
It may be mechanically attached to the structural frame or walls of a building as a facing, called?
Random rubble
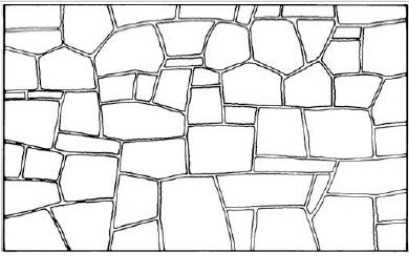
Coursed rubble
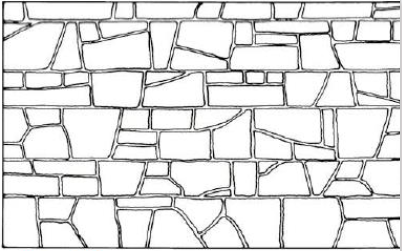
Random ashlar
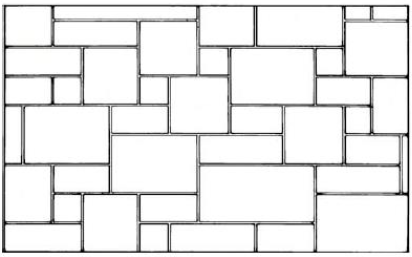
Coursed ashlar