Chemistry - Unit 6 - Covalent Bonding
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What elements (IE and IE) are likley to form a covalent bond?
Elements with high EN and high IE are likely to gain electrons and not likley to lose electrons. When they combine, EN is not strong nough to pull electrons off (other has high IN) so they SHARE electrons (covalent bonds)
What are the steps to drawing a covalent compound?
1)Determine the total number of valence electrons (add/remove correct number if it is an ion)
2)Put the least electronegative element that isn't H in the center (central atom)
3)Place other atoms (terminal atoms) symmetrically around the central atom
4)Connect all terminal atoms to the central atom with a single bond (2 v.e. each)
5)Add remaining v.e. to terminal atoms until they have 8 (full octet)
6)Place any remaining v.e. on the central atom and (if necessary) use lone pair v.e. To create double or triple bonds so all atoms have an octet
What are single, double, and triple covalent bonds? How many electrons do each share and what is the strength of each?
Single (one bonding pair)- 2 electrons shared, weakest
Double (two bonding pairs) - 4 electrons shared, middle strength
Triple (three bonding pairs)- 6 electrons shared, strongest
Polarity
How charge is distributed
Even in a covalent bond the electrons can be pulled more towards one atom than the other because of differences in electronegativity.
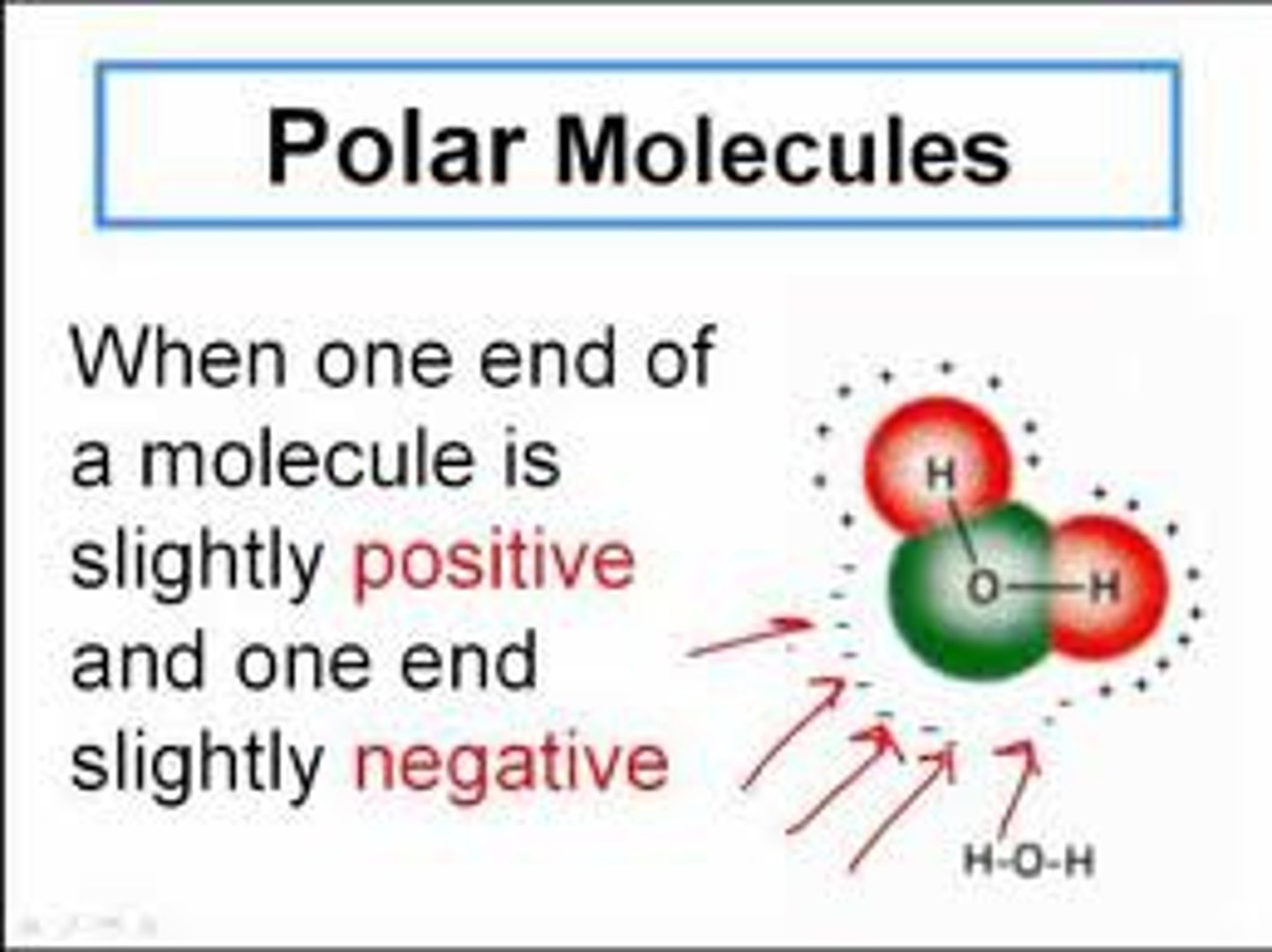
Polar
charge is distributed unequally/asymmetrically
Nonpolar
charge is distributed equally/symmetrically
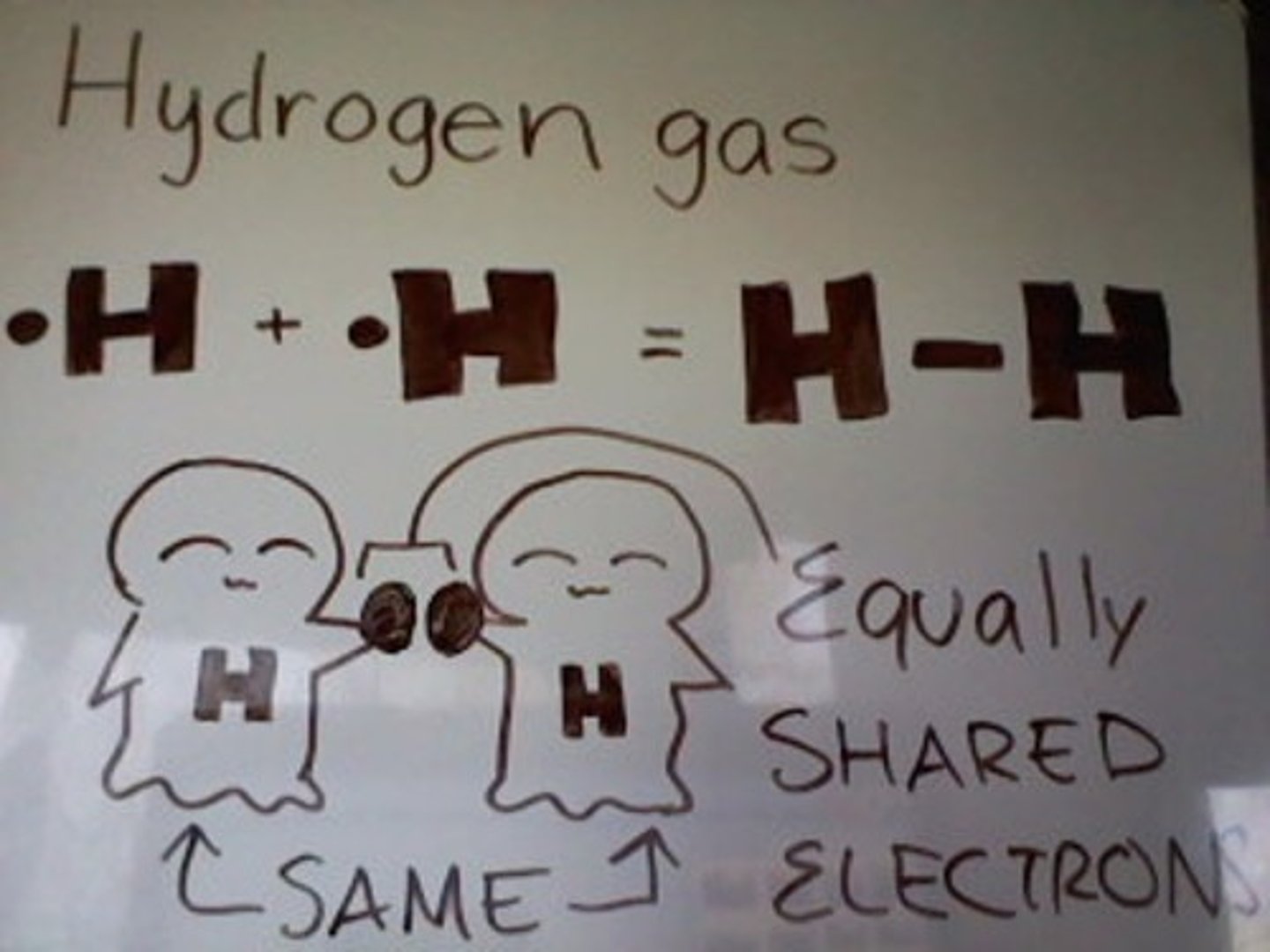
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
when e- are shared equally
<0.4 E.N. difference
C-H bonds are nonpolar
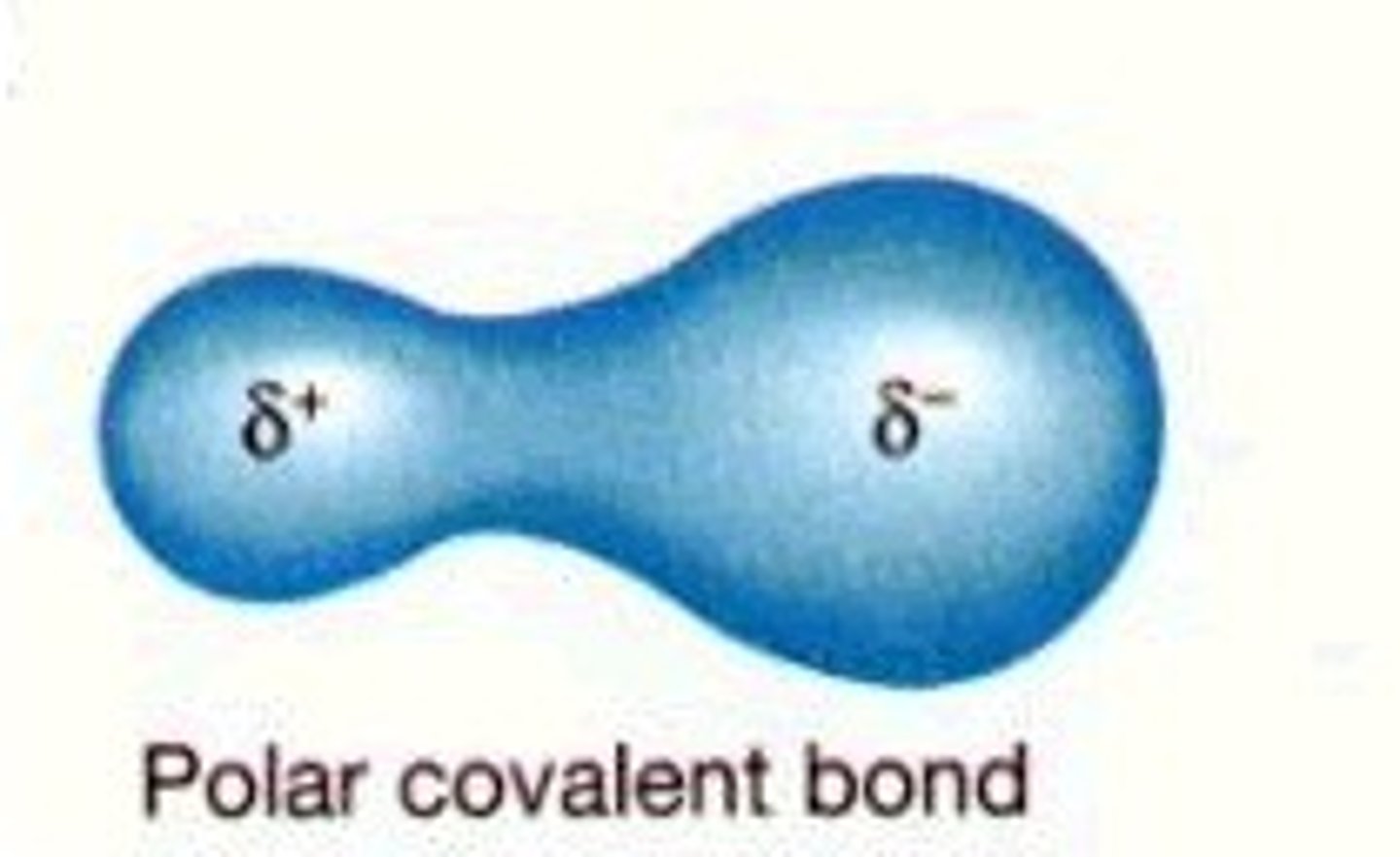
Polar Covalent Bond
when e- are NOT shared equally
0.4 - 1.8 E.N. difference
Ionic Bond v. Polar Bond
Ionic: when one atom (high EN) takes e- from another atom (low IE), Greater than 1.8 E.N. difference, between a metal and a non metal
Covalent: when two atoms have high EN and high IE that there is not a large enough difference so electrons want to stay on both atoms so electrons are SHARED to complete both atom's octet. Between nonmetals.
Ionic Bond
Ionic: when one atom (high EN) takes e- from another atom (low IE), Greater than 1.8 E.N. difference, between a metal and a non metal
Ionic v Covalent v Metal
Ionic: metal and nonmetal
Covalent: 2 nonmetals
Metal: 2 metals
Drawing Arrows (rules)
In polar covalent bond you can either draw a polarity arrow
Or draw a partial negative and partial positive chargeto show where the electrons are
Molecular Polarity
-Molecules are polar if charge (EN difference) is distributed unequally around the central atom (H2O)
-Molecules are nonpolar if charge (EN difference) is distributed equally around the central atom (CO2)
Remember SNAP
Symmetric (around the central atom)
Nonpolar
Asymmetric (around the central atom)
Polar
What is SNAP
Symmetric (around the central atom)
Nonpolar
Asymmetric (around the central atom)
Polar
Do polar and nonpolar molecules mix? What type of molecules mix?
Polar and nonpolar molecules do not mix
Like mixes with like (polar with polar, nonpolar with nonpolar)
Metals: solid vs liquid state
Metals atoms in the solid and liquid state are held together by the attraction between the "sea of valence electrons" and the positive metal cations.
The mobile electrons (mobile charge) allows electrical current to pass through metal.
Ionic Compounds: Solid vs Aqueous
Cations and anions in solid Ionic compounds are held together and in place by the attraction between opposite charges.
When dissolved in water, polar water molecules are able to separate the ions because of the attraction between opposite charges.
partial positive charge on H attracted to Cl anion
partial negative charge on O attracted to Na cation
What is needed in order for something to conduct electricity?
Must have mobile charge, ions or electrons
Ionic conductivity, solubility, and melting point
Not conductive in solid form, soluble in water, high melting and boiling point
Metallic conductivity, solublity, and melting point
Conductive, insoluble in water, high melting points
Covalent conductivity, solubility, and melting point
Not conductive, insoluble in water, low melting points
In terms of EN what's the difference between polar and non polar BONDS?
Non polar- equal EN less then .5 EN difference
Polar - different EN more then .5 EN difference
hydrogen and oxygen are ____
Non polar
Requirements for polar
Any lone pairs in the central atom.
-UNEQUAL distribution of charge
What atom goes in the middle of Lewis structures?
Least electronegative (Central atom)
What can obscure the symmetry of a molecule?
Valance electrons on the central atom
Arrows point to ————
More electronegativity
For conductivity of electricity you need —- so ionic is only conductive in water
Moving electrobs
Is water polar or non polar and why?
Central atom has a lone pair so the two hydrogens are offset and the molecule is POLAR
Partial charges
-elements with stronger EN have negative partial charge becuase they are pull electrons closer to them (More electrons = negative charge)
-elements with lower EN have positive partial charge becuase they have a weaker pull to electrons (Less electrons = positive charge)
-This seperation in charges is call a DIPOLE moment
Covalent V Ionic Bonding
Ionic = difference in electronegativity is over 1.7 so electrons are FULLY exchanged, only one element has one full shell, they are held together by electostatic forces, conductive. Requires one metal and one nonmetal.
Covalent = differrence in electronegativity is less than 1.7 so electrons are SHARED (becuase its so close they must satsify both shells), both elements have full shells, not conductive, happens between nonmetals