ClinicalPsych
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
1
New cards
Multiple relationships
Only allowed to have 1 relationship with your client therapist-client.
if you do have social event with the person - do not talk with them about this thing; check frequency of event,
if you do have social event with the person - do not talk with them about this thing; check frequency of event,
2
New cards
break confidentiality
3 times you have to break it: - harm to a child involved (verbal abuse counts) - if you are going to hurt yourself or someone else - legal court order (an official proclamation by a judge (or panel of judges) that defines the legal relationships between the parties to a hearing, a trial, an appeal or other court proceedings.)
3
New cards
if not fully licensed
‘You should tell your clients: I’m not fully licensed yet, however I have a supervisor who is helping me with this case. ‘
4
New cards
Informed consent
a) telling them **about confidentiality** b) what you **are taking notes** of c) writing the progress notes. you write generically, if smn gets your notes, they do not reveal any personal information d)should inform on what kind of expertise they have e)**the length of the therapy** f)who you contact in case of emergency. g) you have to tell your clients they can quit any time
5
New cards
supervisor responsibilities
if anything goes wrong it’s on the supervisor. You are responsible for what your student is doing
6
New cards
competence, what to work on?
work in area you have an expertise on it. get trained, if you are taking case you have not worked with. Get a supervisor.
7
New cards
Therapeutic approaches: Short-term Psychodynamic Principles:
\- grounded in psychodynamic principles - Freud
\- transference based on the idea is to analyze the relationship I have with the clinet.
You should find out why they are transfering aything to your relationships.
\- transference based on the idea is to analyze the relationship I have with the clinet.
You should find out why they are transfering aything to your relationships.
8
New cards
phases of short-term pscyhodynamic approach
**Why are we interacting this way? What does it tell us about this person**
1\. developing positive transfering relationships 2. analyzing transference relationships 3. terminating therapy, dealin with loss
1\. developing positive transfering relationships 2. analyzing transference relationships 3. terminating therapy, dealin with loss
9
New cards
Process-expiriential
Fritz Pertz
Fritz Pertz
**process-focused therapy**
\- based in client-centered and existential therapies - experience emotions - personal choice and discovery - believe in catharsis. no empirical support of that - exploration of emotional experience
“whatever you feel right now - feel genuine emotion. bereal“
No contact with the therapist
\*\* potentially harmful
\- based in client-centered and existential therapies - experience emotions - personal choice and discovery - believe in catharsis. no empirical support of that - exploration of emotional experience
“whatever you feel right now - feel genuine emotion. bereal“
No contact with the therapist
\*\* potentially harmful
10
New cards
Humanistic
content focus
\- Rogerian - unconditional positive regard
\- client is feeling cared for
\- client feels comfortable
\- therapist talks less
\- provides a ‘corrective emotional support’
- Therapist has to really care about their clients, geuinaly empathsizing.
This safe emotional, non-judgmental setting. that connection by itself is curing for the person
\- Doesn’t have a lot of empirical support
- unconditional positive regard
\
*supportive therapy*
\- Rogerian - unconditional positive regard
\- client is feeling cared for
\- client feels comfortable
\- therapist talks less
\- provides a ‘corrective emotional support’
- Therapist has to really care about their clients, geuinaly empathsizing.
This safe emotional, non-judgmental setting. that connection by itself is curing for the person
\- Doesn’t have a lot of empirical support
- unconditional positive regard
\
*supportive therapy*
11
New cards
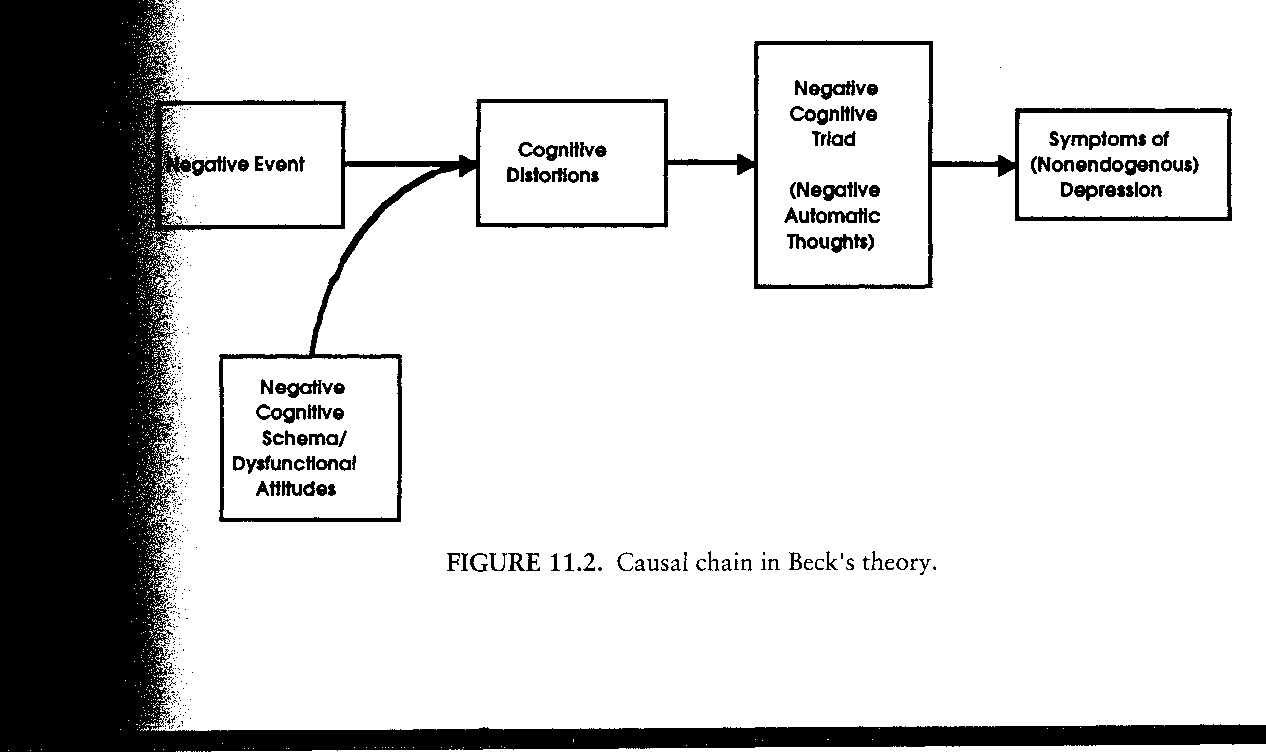
CBT
the most studied, most empirically-supported treatment - derived from Beck’s theory - negative thinking patterns cause psychopathology - therapist has a very active role - identyfying and disouting negative thoughts Youn act this way, because of your thouhghts. You tell people the whole model You should have a lot of skills to keep going, we are going to learn it together.
12
New cards
phases of cbt
\- assessment, socialization, goals Here is how I see in this thoery< here is what I think, our theory. - intervention phase - termination phase - booster sesssion If the person gets stucked
13
New cards
process of cbt
Psychologist:
1. cathces the ‘emotion‘ the client reported
2. why? what cognitive schemas underlie this emotion
3. educate
\
Realistic: super negative thought - moderately negative
\
never -probably, low
1. cathces the ‘emotion‘ the client reported
2. why? what cognitive schemas underlie this emotion
3. educate
\
Realistic: super negative thought - moderately negative
\
never -probably, low
14
New cards
how to research?
1. identify a target
2. choose a theory
3. identify a group (risk factors based on the theory)
4. Intervention (fix #3)
5. Design a study (test if #4 works)
15
New cards
mediator
* mechanisms that explain things
* negative thoughts in Beck’s cognitive theory
* negative thoughts in Beck’s cognitive theory
16
New cards
moderator
* interactions
* smth is most likely to happenn
* cog/ vulnerability in
* depends, combines, interacts
* smth is most likely to happenn
* cog/ vulnerability in
* depends, combines, interacts
17
New cards
depression - example
step 1. depression
step 2. beck’s theory
step 3. the high-risk group
major stessful life events + tendency to cog. vulnerability ( we would target this)
\
Dysfunctional Attitude Scale (self-report vul. measure)
* pick people who score ij the 90th percentile on the DAS
step 4. design intervention
get rid of the risk factor: intervention to help people think differently about stress events
step 5. design a study
day 1. measure symptoms of depression
* history of depression at the baseline
* random assignment
* intevrention to experimental group
* same set of tests
* after 2 years
* measure symptoms of depression again
step 2. beck’s theory
step 3. the high-risk group
major stessful life events + tendency to cog. vulnerability ( we would target this)
\
Dysfunctional Attitude Scale (self-report vul. measure)
* pick people who score ij the 90th percentile on the DAS
step 4. design intervention
get rid of the risk factor: intervention to help people think differently about stress events
step 5. design a study
day 1. measure symptoms of depression
* history of depression at the baseline
* random assignment
* intevrention to experimental group
* same set of tests
* after 2 years
* measure symptoms of depression again
18
New cards
Anxiety disorder stduy
* CBT over other treatment
* those who got appropriate treatment:
* fewer sessions
* less anxiety
* lower relapse rate
* those who got appropriate treatment:
* fewer sessions
* less anxiety
* lower relapse rate
19
New cards
Depression
* general facts
* general facts
General facts:
* the most common disorder
* cause of disability
* cost 83 billions of dollars
* recurrent, lethal
* surges during ages 15-20
* gender difference (more women)
* the most common disorder
* cause of disability
* cost 83 billions of dollars
* recurrent, lethal
* surges during ages 15-20
* gender difference (more women)
20
New cards
Depresision
* theory
* theory
Cognitive: beck’s theory of depression
* negative conditions, views of self at the core of depression
Interpersonal:
* difficulties in communication and dysfunctional relationships at the core
behavioral:
* approach system problem
* negative conditions, views of self at the core of depression
Interpersonal:
* difficulties in communication and dysfunctional relationships at the core
behavioral:
* approach system problem
21
New cards
Treatment
1. Psychotherapy
* psychodynamic (30%)
* interpersonal (50%)
* CBT (50%)
2. Pharmacology
* medication (50%)
* placebo (30%)
\
22
New cards
CBT for depression
* pscyhoeducation
* behavioral activation
* ==identify negative cgonitions==
* ==challenge negative cohnitions==
* ==generate more adaptive cognitions==
==(cognitive restructuring)==
\
\
\*\* the only therapy that prevents relapse
* behavioral activation
* ==identify negative cgonitions==
* ==challenge negative cohnitions==
* ==generate more adaptive cognitions==
==(cognitive restructuring)==
\
\
\*\* the only therapy that prevents relapse
23
New cards
Interpersonal therapy for depression
* assess interpersonal context
* check for the following: greef, role dispute, role transition, interpersonal deficit
* check for the following: greef, role dispute, role transition, interpersonal deficit
24
New cards
Anxiety
general facts
general facts
* not from dsm
* an umbrella term for specific phobias, panic disorder, GAD, PTSD, OCD
* high rate of treatment efficacy
* exposure therapy
* 19% in a given year
* at least 6 month
* comorbid with other disorders
* \
* an umbrella term for specific phobias, panic disorder, GAD, PTSD, OCD
* high rate of treatment efficacy
* exposure therapy
* 19% in a given year
* at least 6 month
* comorbid with other disorders
* \
25
New cards
burning-out
using evidence-based therapies help to burn-out less to therpaists
26
New cards
27
New cards
the explination of anxiety
* the core - exxagerated apprasial of threat and danger
* more likely to see situations as dangerous
* begin to avoid situations
* repeated reinforcement for avoidance + generalization of the pther situations
* more likely to see situations as dangerous
* begin to avoid situations
* repeated reinforcement for avoidance + generalization of the pther situations
28
New cards
Anxiety treatment:
cognitive
cognitive
\-psychoeducation about anxiety
\- change thinking patterns that support fears
‘anxiety will not hurt you‘, ‘the problem is not anxiety, the problem is it comes when it;s unneccessary‘
\- change thinking patterns that support fears
‘anxiety will not hurt you‘, ‘the problem is not anxiety, the problem is it comes when it;s unneccessary‘
29
New cards
behavioral
* exposure: imaginal and in vivo (in reality)
* intensive/flooding
* systematic desensitization/ graduated
(gradually - by stages)
* equally effective but flooding is harder
! you should tell clients what is going to be happening
\
* intensive/flooding
* systematic desensitization/ graduated
(gradually - by stages)
* equally effective but flooding is harder
! you should tell clients what is going to be happening
\
30
New cards
keys to exposure therapy
1. provide pateint with skills to deal with heightened emotions (deep breathing, cognitive soothing)
2. **continue exposure trial till the anxiety get reduced. never stop before it comes down**
3. talk about every homework you’ve assigned
4. humor encouraged, interpersonal skills to help people do it
5. not using AVOIDANCE, not talking about other things
\
31
New cards
Eating disorders
Anorexia nervosa
Anorexia nervosa
* low body weight
* disturbed body image
* restricting & binging/purging type
* less than 1%
* life threatening
* difficult to treat
* disturbed body image
* restricting & binging/purging type
* less than 1%
* life threatening
* difficult to treat
32
New cards
bulimia nervosa
* binge eating
* compensatory behaviors
* disturbed body image
* normal weight range
* 2 types (purging, non-purging)
* compensatory behaviors
* disturbed body image
* normal weight range
* 2 types (purging, non-purging)
33
New cards
Binge eating disorder
no compensatory behaviors
34
New cards
PICA
eating non-food substances
35
New cards
why do eating disorders appear?
* unrelaistic beliefs about beauty, body weight, body shape
* perfectionism, self-esteem, body image
* perfectionism, self-esteem, body image
36
New cards
treatment for eating disorders
CBT
* identify patterns of problematic eating behaviors
* thoughts and feelings associated with episodes
* cognitive restucturing
* identify patterns of problematic eating behaviors
* thoughts and feelings associated with episodes
* cognitive restucturing
37
New cards
Substance use
20% -men, 5% - women
abuse - recurrent use, despite problems
dependence - meet all criteria for abuse + tolerance to substance, withdrawal, troubles controlling drinking
abuse - recurrent use, despite problems
dependence - meet all criteria for abuse + tolerance to substance, withdrawal, troubles controlling drinking
38
New cards
‘etiology‘
* negative affect, inhibition
* impact on executive functions
* genetics
* impact on executive functions
* genetics
39
New cards
Treatment
* quite a few ESTs: a lot of things swork
* CBT - to occasional drinking
* 12 steps, aa total abstanence
* CBT - to occasional drinking
* 12 steps, aa total abstanence
40
New cards
CBT for substance abuse
1) motivation to change
2) drinking goals
3) initiation of abstinence
4) functional analysis (what triggers the person to drink)
5) coping strategies
6) family involvement
7) long-term maintanence
2) drinking goals
3) initiation of abstinence
4) functional analysis (what triggers the person to drink)
5) coping strategies
6) family involvement
7) long-term maintanence
41
New cards
Personality disorders: Borderline personality disorder
2% of adults
20% od psychiatric hospitalizatiosn
severe mood swings
unstable relationships
self-insurance
risk
20% od psychiatric hospitalizatiosn
severe mood swings
unstable relationships
self-insurance
risk
42
New cards
Treatment for borderline
* Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
\- basic capacities
\- posttraumatic stress reduction
\- increasing respect for self
\- attaining capacity for joy (anhedonia)
* Interpersonal reconstructive therapy
\- personality disorders are a gift of love
\- identify patterns, understand where they are, why they are no longeruseful
\- basic capacities
\- posttraumatic stress reduction
\- increasing respect for self
\- attaining capacity for joy (anhedonia)
* Interpersonal reconstructive therapy
\- personality disorders are a gift of love
\- identify patterns, understand where they are, why they are no longeruseful
43
New cards
Controversies in adults treatment:\`
trauma witnessed
trauma witnessed
* good empirical support for cognitive-behavioral therapy - exposure (imaginal) - cognitive (modify dysfunctional beliefs about danger)
* Reliving the trauma
* EMDR - the most controversial treatment - commercial success - imaginal representation while making side-to-side eye movements - clients asked to express negative conditions and then more positive ones (’reprocessing’)
* Reliving the trauma
* EMDR - the most controversial treatment - commercial success - imaginal representation while making side-to-side eye movements - clients asked to express negative conditions and then more positive ones (’reprocessing’)
44
New cards
Controversies of EMDR
* why does it work?
* eye movements ‘unlock’ the pathological condition
* pathology is ‘dysfunctionally stored information that can ’
The research:
1. solid enough to earn 2nd on APA Guidelines
2. eye movements and other methods of lateral sttimulation are unnecessary for clinical improvement
3. any measurable change is likel
McNally
* what is effective in EMDR is not new and what is not effective
* taker smth that works, add a twist and cathcy story, and then marked it.
* eye movements ‘unlock’ the pathological condition
* pathology is ‘dysfunctionally stored information that can ’
The research:
1. solid enough to earn 2nd on APA Guidelines
2. eye movements and other methods of lateral sttimulation are unnecessary for clinical improvement
3. any measurable change is likel
McNally
* what is effective in EMDR is not new and what is not effective
* taker smth that works, add a twist and cathcy story, and then marked it.
45
New cards
Crtitcal Incident Stress Debriefing
\- intended to prevent the development of disorders following trauma
\- **assumptions: exposure to trauma is a sufficient precursor for psychopathology**
\- conducted in groups, is administered withih 24/72 hours after the event
- usualy lasts 2-3 hours
\- intro of debriefing, statements of facts, disclosure of thoughts and emotions, specification of possible sxs, and education about consequences of trauma
ReSEArCH: Firefighters engaged in body recovery - statistical significant - 3 years later - **debriefing slightly worse on various measures** - those with initial high level of sx stayed simptomatic if had debriefing, but recovered if not
* psychological debriefing is ineffective and has adverse long-term effects. It is not as appropriate treatment for trauma victims.
\- **assumptions: exposure to trauma is a sufficient precursor for psychopathology**
\- conducted in groups, is administered withih 24/72 hours after the event
- usualy lasts 2-3 hours
\- intro of debriefing, statements of facts, disclosure of thoughts and emotions, specification of possible sxs, and education about consequences of trauma
ReSEArCH: Firefighters engaged in body recovery - statistical significant - 3 years later - **debriefing slightly worse on various measures** - those with initial high level of sx stayed simptomatic if had debriefing, but recovered if not
* psychological debriefing is ineffective and has adverse long-term effects. It is not as appropriate treatment for trauma victims.
46
New cards
Controversial treatment to Substance Use
1. **antabuse antidipsotropcics** - meds that induce unpleasant reactions following ingestionon alcohol.
* conditioning, pair in aversive experience with the act of drinking
* little efficacy
2. **Project Drug Abuse and Resistence Education**
* 50% of local school
* uses **informed police officers to teach about negative aspects of substance use and positive aspects of healthy lifestyles**
* 1 hour session/17 weeks
* must be based on science.
* doesn’t work
47
New cards
Antidepressants, controversies
* it’s hard to beat the placebo for depression
* pain killers can’t beat the placebo effect anymore.
Kirsch
* strong positive response
* a significant portion of the positive response observed in individuals with depression when receiving placebos can be attributed to a non-active or inert treatment (such as a sugar pill) rather than the specific properties of the treatment itself.
* Hopelesness is at the core of depression. It is an expectancy that life will not improve and there is nothing that can be done about it
* **Placebos instill an expectancy for improvement which addresses a core feature of depression.**
* pain killers can’t beat the placebo effect anymore.
Kirsch
* strong positive response
* a significant portion of the positive response observed in individuals with depression when receiving placebos can be attributed to a non-active or inert treatment (such as a sugar pill) rather than the specific properties of the treatment itself.
* Hopelesness is at the core of depression. It is an expectancy that life will not improve and there is nothing that can be done about it
* **Placebos instill an expectancy for improvement which addresses a core feature of depression.**
48
New cards
Giant & dwarf
* the pre-post effect for adm - 1.5 (large size) - placebo - also large - 75% of the effect of ADM is duplicated by placebo
\
* there is a correlation of .85 for the effectiveness of prozac and the percentage of participants reporting side effects
* It’s doing something with my body, it’s going to do something with my psyche too
* Total effect size is the combination of non-specific and specific effects
\
* there is a correlation of .85 for the effectiveness of prozac and the percentage of participants reporting side effects
* It’s doing something with my body, it’s going to do something with my psyche too
* Total effect size is the combination of non-specific and specific effects
49
New cards
Controversial treatment of depression
* serotonin-depression hterapy SSRI works well, no evidence for the chemical imbalance
* CBT: don’t know why it works
* Herbal - in the form of tea - some benefit for people with mild to moderate depression
\
\
!Total effect size is the combination of non-specific and specific effects
* CBT: don’t know why it works
* Herbal - in the form of tea - some benefit for people with mild to moderate depression
\
\
!Total effect size is the combination of non-specific and specific effects
50
New cards
Ginko BIloba
\- modest efficacy for dementia Alzheimer
- slow down aging
- slow down aging
51
New cards
Criteria for selecting treatment
1. reatment should be statistically significantly superior to the comparison groups described
2. Research must have sufficient statistical power to detect moderate differences
3. Treatment must have been conducted ○ Treatment manual - therapists don’t like to use it however it is very efficient ○ Popper - treated for specific problems, with reliable and valid inclusion criteria ○ Reliable and valid outcome measure ○ Appropriate data analysis ● Superiority of treatment in at least 2 independent research settings. Superior to pill, psychological placebo or to another treatment
52
New cards
3 levels within prevention
○ Universal ○ Selective ○ Indicative
53
New cards
Universal prevention intervention
%%targeted at entire communities regardless of risk.%%
Example - a series of commercials on educational topics in San Francisco. Everybody saw the commercial - community. %%These almost always look like they don’t work. Statistical problem - hard to find statistical significance because in the sample vast majority of people do not have the disorder%%
Example - a series of commercials on educational topics in San Francisco. Everybody saw the commercial - community. %%These almost always look like they don’t work. Statistical problem - hard to find statistical significance because in the sample vast majority of people do not have the disorder%%
54
New cards
Selected prevention intervention
targets high risk groups. They are chosen because they %%possess factors that put them at risk%% for psychopathology. You can show if the prevention worked or not
55
New cards
Indicated prevention intervention
targeted at people %%with early signs and symptoms of disorder%% but have not had a full diagnosis yet.
56
New cards
How do you conduct prevention intervention research?
a. Identify the target - what do you want to prevent (depression etc)
b. Choose a theory (for selective one)
c. Identify the high-risk group - based on theory because they have a specific thing.
d. Design the intervention - creating activities, tasks, etc. to fix what people in the third point have
e. Design the study
b. Choose a theory (for selective one)
c. Identify the high-risk group - based on theory because they have a specific thing.
d. Design the intervention - creating activities, tasks, etc. to fix what people in the third point have
e. Design the study
57
New cards
Treament for kids, adolescents.
who is our client?
who is our client?
* Kids rarely refer themselves
○ Only a small proportion of kids get the help they need
○ Parent-therapist vs youth-therapist relationship
○ Legal issues and confidentiality
○ Only a small proportion of kids get the help they need
○ Parent-therapist vs youth-therapist relationship
○ Legal issues and confidentiality
58
New cards
Psychopathology and kids’ life
Most forms of psychopathology affects following
■ Memory
■ Concentration
■ Sleep
■ Behavioral problem
■ Energy
■ School absence
■ Stress
■ Peer relationships
■ Decision-making
■ Attention
■ Parental issues
■ Memory
■ Concentration
■ Sleep
■ Behavioral problem
■ Energy
■ School absence
■ Stress
■ Peer relationships
■ Decision-making
■ Attention
■ Parental issues
59
New cards
What makes something psychopathology? Symptoms above are random symptoms
%%works with kids, too%%
■ Syndrome
■ Duration
■ Persistence
■ Context
■ Impairment
■ It’s about extremes, need to know norms
■ Syndrome
■ Duration
■ Persistence
■ Context
■ Impairment
■ It’s about extremes, need to know norms
60
New cards
difference in treatment between kids, adults
* 4 meta-analysis
* we do more behavior stuff than cognitive ones so results are better for behavioral treatments
* we do more behavior stuff than cognitive ones so results are better for behavioral treatments
61
New cards
Empirically supported treatments (EST) for kids
Autism - ABA (applied behavior therapy) and communication training
■ ADHD - behavioral parent training, Behaviour modification in classroom
■ Anxiety and depression - CBT, CBT including parents
■ Disruptive behavior disorders - parent management training
■ ADHD - behavioral parent training, Behaviour modification in classroom
■ Anxiety and depression - CBT, CBT including parents
■ Disruptive behavior disorders - parent management training
62
New cards
Parent management training
* Child behavior can be changed by %%modifying the child’s social environment%% rather than directly working with the child
* In families with aggressive children, child learns coercive (примусовий) ways to get what they want
* *Basic learning examples - parents reward child for whining or aggression by providing attention or giving in and the child rewards parents by ceasing the aversive behavior*
* 4-8 weeks for young mildly oppositional kids
* 12-25 weeks for clinically referred kids with conduct disorder
* In families with aggressive children, child learns coercive (примусовий) ways to get what they want
* *Basic learning examples - parents reward child for whining or aggression by providing attention or giving in and the child rewards parents by ceasing the aversive behavior*
* 4-8 weeks for young mildly oppositional kids
* 12-25 weeks for clinically referred kids with conduct disorder
63
New cards
depression in adolescent - CBT for adolescence by peter lewinsohn
Group formal with 6-8 adolescents
16 two hour sessions over 8 weeks
Psychoeducation
CBT
Parents involved
16 two hour sessions over 8 weeks
Psychoeducation
CBT
Parents involved
64
New cards
HYPE Checklist
Psychotherapy HYPE checklist
a. Substantial exaggeration of claims of treatment effectiveness
b. Conveying of powerful and %%unfounded expectancy effects%%
c. Excessive appeal to authorities or “gurus”
d. Heavy reliance on endorsements from presumed experts
*продукт схвалений експертами*
e. Use of a slick sales pitch and the use of extensive promotional efforts, including sale of paraphernalia (еквіпмент для конкретної активності)
\-adepts agree that they will not share treatment protocols with others.
f. Establishment of accreditation and credentialing procedures
g. Tendency of treatment followers to insulate themselves from criticism
*-відгороджуються від критиків*
h. Extensive use of “psychobabble” - *psychological verbiage that sounds scientific but in fact contains little or no content, to market their treatment approach*
i. Extensive use of “neurobabble”: *naïve biological reductionism to promote their treatment*
j. Tendency of advocates to be defensive and dismissive of critics; selective reporting of contradictory findings, such as the results of dismantling studies
k. Extensive reliance on anecdotal evidence
l. Claims that treatment “fits all” - NO Boundary conditions
m. Claims that treatment is “evidence-based” on the basis of informal clinical observations
n. Inadequate empirical support: %%Limited reports or omission of treatment outcome information, such as patient selection criteria, drop-out rates,%% and follow-up data.
o. No proposed scientific basis for change mechanisms; proposed theoretical treatment mechanism lacks “connectivity” with extant science
p. Repeated use of implausible ad hoc maneuvers to explain away negative findings
q. Comparison of treatment %%with weak and “intent to fail” treatment groups,%% or with only partial (incomplete) treatment conditions
r. Failure to consider or acknowledge potential allegiance and decline effects
s. Failure to consider differential credibility checks across treatment groups; failure to consider the role of non-specific factors, such as the therapeutic alliance
a. Substantial exaggeration of claims of treatment effectiveness
b. Conveying of powerful and %%unfounded expectancy effects%%
c. Excessive appeal to authorities or “gurus”
d. Heavy reliance on endorsements from presumed experts
*продукт схвалений експертами*
e. Use of a slick sales pitch and the use of extensive promotional efforts, including sale of paraphernalia (еквіпмент для конкретної активності)
\-adepts agree that they will not share treatment protocols with others.
f. Establishment of accreditation and credentialing procedures
g. Tendency of treatment followers to insulate themselves from criticism
*-відгороджуються від критиків*
h. Extensive use of “psychobabble” - *psychological verbiage that sounds scientific but in fact contains little or no content, to market their treatment approach*
i. Extensive use of “neurobabble”: *naïve biological reductionism to promote their treatment*
j. Tendency of advocates to be defensive and dismissive of critics; selective reporting of contradictory findings, such as the results of dismantling studies
k. Extensive reliance on anecdotal evidence
l. Claims that treatment “fits all” - NO Boundary conditions
m. Claims that treatment is “evidence-based” on the basis of informal clinical observations
n. Inadequate empirical support: %%Limited reports or omission of treatment outcome information, such as patient selection criteria, drop-out rates,%% and follow-up data.
o. No proposed scientific basis for change mechanisms; proposed theoretical treatment mechanism lacks “connectivity” with extant science
p. Repeated use of implausible ad hoc maneuvers to explain away negative findings
q. Comparison of treatment %%with weak and “intent to fail” treatment groups,%% or with only partial (incomplete) treatment conditions
r. Failure to consider or acknowledge potential allegiance and decline effects
s. Failure to consider differential credibility checks across treatment groups; failure to consider the role of non-specific factors, such as the therapeutic alliance
65
New cards
Autism - controversies
* Under a big umbrella now so difficult to diagnose
* Rates have gone up now
* ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis)
*observe and record various behaviors and their antecedents ( what was before) and consequences. quantify and analyze the patterns*
* precise quantification and analysis of behavior and learning patterns and conditions that serve to elicit and maintain them
*що викликає та що підтримує таку поведінку*
* Tons of research showing it works with language, social and intellectual functioning.
* Difference between enjoyable activity and effective intervention
* Rates have gone up now
* ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis)
*observe and record various behaviors and their antecedents ( what was before) and consequences. quantify and analyze the patterns*
* precise quantification and analysis of behavior and learning patterns and conditions that serve to elicit and maintain them
*що викликає та що підтримує таку поведінку*
* Tons of research showing it works with language, social and intellectual functioning.
* Difference between enjoyable activity and effective intervention
66
New cards
what aorks with autism?
* Parent training
* Behavior modification (classroom)
* Stimulant modification
* Behavior modification (classroom)
* Stimulant modification
67
New cards
ADHD
* associated with disruptive parenting
* modification of parenting helps with ADHD
* Should not prescribe stimulants for kids under 6
* Effects only lasts while meds are in the system 3-8 hours
* Meds reduce symptoms but do not improve academic or social skills
* Mild side effects
* Potential loss of self-efficacy
* Combining meds and behavior worked better
* modification of parenting helps with ADHD
* Should not prescribe stimulants for kids under 6
* Effects only lasts while meds are in the system 3-8 hours
* Meds reduce symptoms but do not improve academic or social skills
* Mild side effects
* Potential loss of self-efficacy
* Combining meds and behavior worked better
68
New cards
Evaluating psychotherapy
Research is the only way to evaluate psychotherapy ● Moves field forward ● Can’t rely on clinical experience ● 3 things to think about: Client, Treatment
● In clinical areas experiments are called RCTs
● Psychotherapy is effective after all the experiments
● In clinical areas experiments are called RCTs
● Psychotherapy is effective after all the experiments
69
New cards
Paul Meehl about Psychotherapy
Ultimate question - what treatment, by whom, is most effective for this individual with that specific problem with what specific problem under which set of circumstances and how does it come about - Paul Meehl
● We know what treatment for that problem
● We know what treatment for that problem
70
New cards
DODO BIrd
All txs are equally effective - dodo bird hypothesis. They all are the same because we do not know how they work and all do the same things
\
Efficacy driven by common factors ● There are specific txs for specific disorders ● Txs aren’t equal, some have harms ● Hence this verdict is not supported ● Common factors only explain a small proportion of outcomes. May not even precede outcome
\
Efficacy driven by common factors ● There are specific txs for specific disorders ● Txs aren’t equal, some have harms ● Hence this verdict is not supported ● Common factors only explain a small proportion of outcomes. May not even precede outcome