Lab 2 - Introduction to Bacteria and Archaea
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
textbook Ch 24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
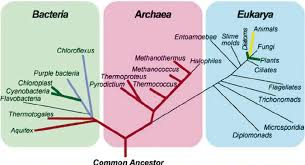
3 domains of life
Bacteria, archaea, eukarya
bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, but they are not each others closest relatives (archaea and eukarya are sister taxa)
microbe
a microscopic organism (of any domain)
polyphyletic
compose the majority of the biodiversity on Earth
prokaryotic vs eukaryotic genome size
eukaryotic genome >> prokaryotic genome
two domain hypothesis
the two domains are bacteria and archaea
eukaryotes are a subgroup of archaea, are sister to some (but not all) archaea
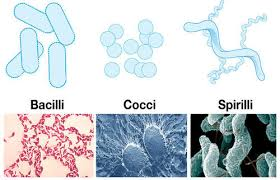
3 common morphologies of bacteria and archaea
coccus (spherical)
bacillus (rod shaped)
helical/spiral (elongated spiral)
how do most bacteria reproductive?
asexually, by binary fission
chromosome is replicated so that the daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent
what three components drive metabolism?
energy source: light (phototrophy) or chemical rxns (chemotrophy)
electron source: inorganic or organic compounds that act as oxidizers
carbon source: inorganic compounds (like CO2) or organic compounds (like sugars)
lithiotrophs vs organotrophs
lithiotrophs: use inorganic electron donors like H2S
organotrophs: use organic electron donors like CH4
autotrophs vs heterotrophs vs carbon fixers
autotrophs: use inorganic carbon (CO2)
heterotrophs: use organic carbon (sugars)
carbon fixers: use CO2 from the atmosphere (like plants)
syntrophic networks
the biochemical reactions driving metabolism are connected/coupled: the products of one group is used by the other
ex. In hot springs, one layer of the biofilm is bacteria that produce CO2 and H2 and the other layer is archaea that uses those products to produce methane
extremophiles vs mesophiles
extremeophiles: thrive at extreme environmental conditions (very hot/cold, very acidic/basic, etc)
mesophiles: live at more normal conditions
vertical transmission
the passing of genes from parents to descendants
lateral gene transfer (LGT)
the mixing of DNA from different lineages
occurs through:
Transformation
Conjugation
Transduction
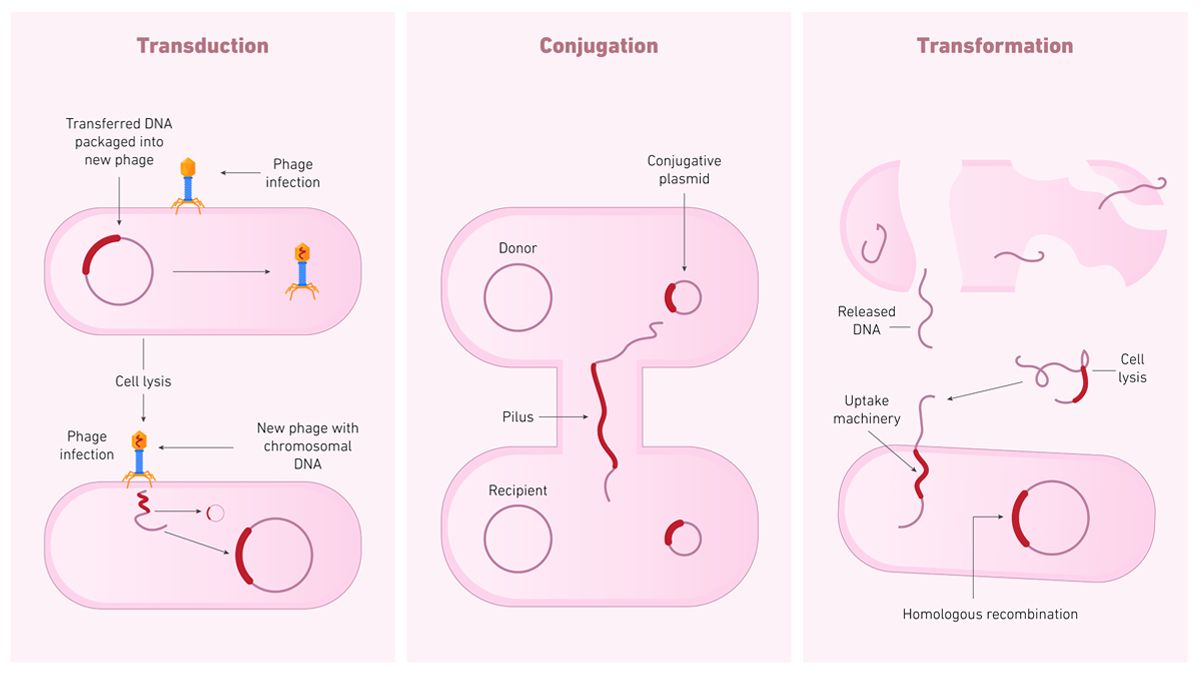
mechanisms of LGT: transformation
DNA foud in the environment is moved into an intact cell via crossing over (replacing a portion of DNA), direct insertion (adding new DNA), or stays as a separate replicating entity (like a plasmsid)
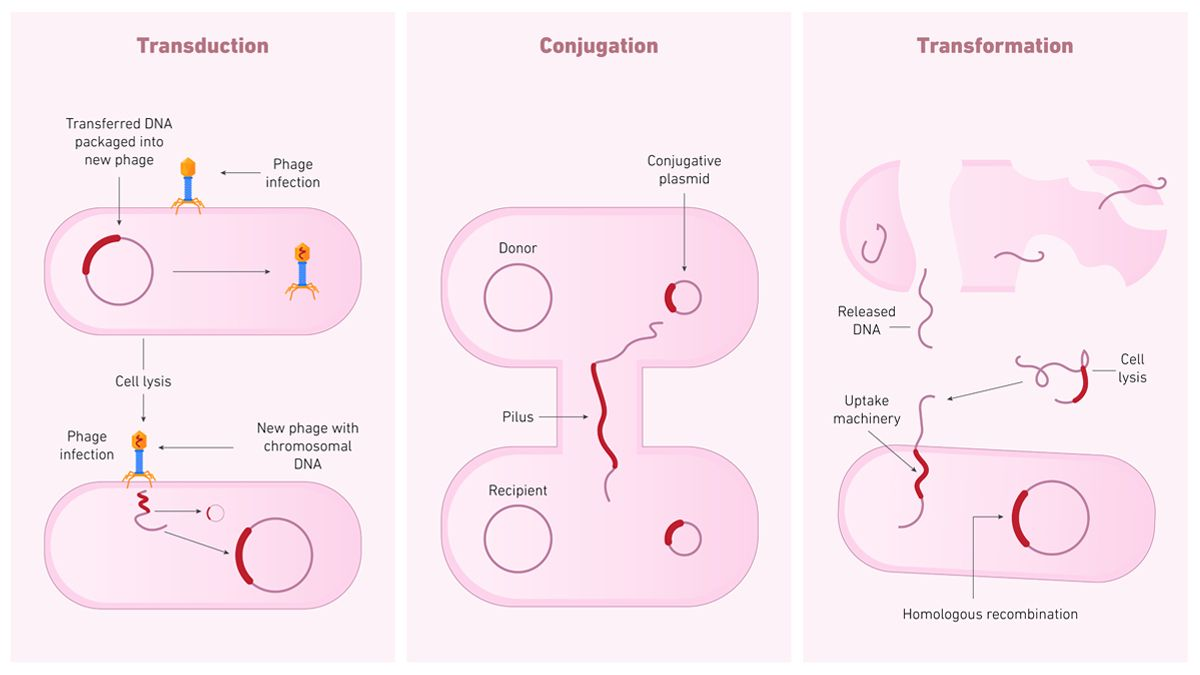
mechanisms of LGT: conjugation
the replication and transfer of a plasmid (a small piece of DNA) between cells via the formation of a sex pilus
does not result in offspring
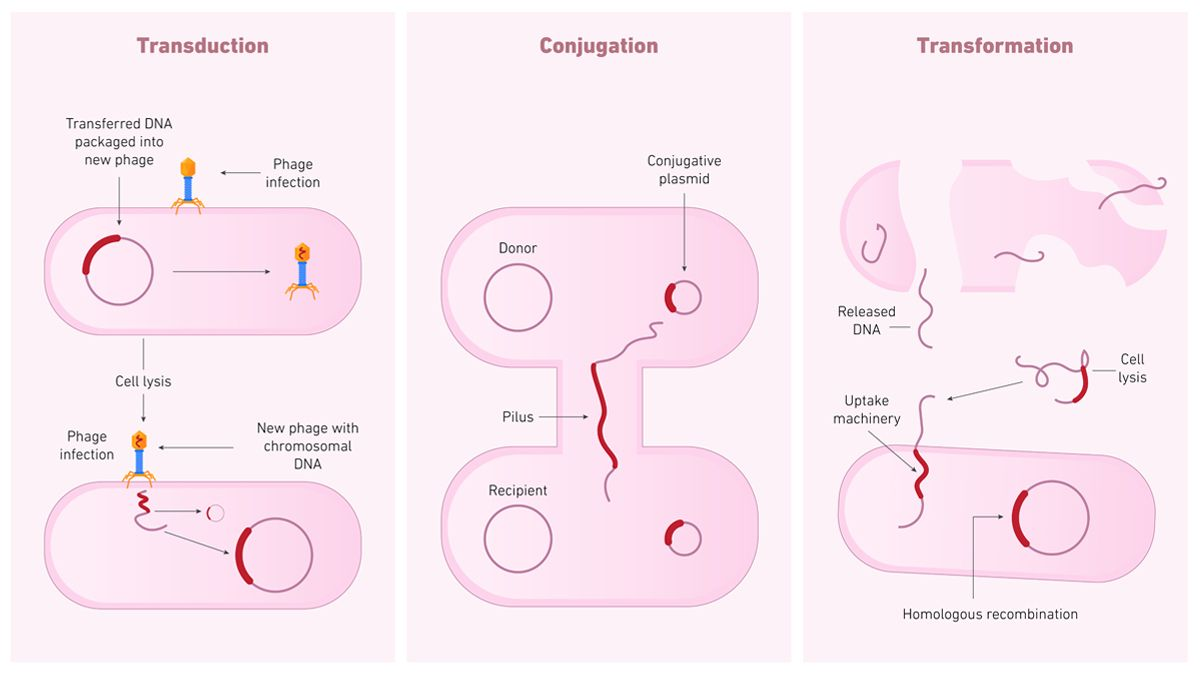
mechanisms of LGT: transduction
the incorporation of DNA into a host through viral particles via incorporation into host’s chromosome or replication as a separate entity
pure culture
a culture that only contains a single species
difficult to grow: must replicate the exact environmental conditions, nutrients, and ecological interdependencies
culture independent DNA studies/metagenomics
extracting genetic material directly from the environment and identifying microbes using their nucleotide sequences
metabolism
the process of acquiring energy, transferring electrons, and transforming carbon compounds into other biomolecules
how do the metabolisms of prokaryotic vs eukaryotic organisms differ?
prokaryotes have a wider range of metabolic processes than eukaryotes
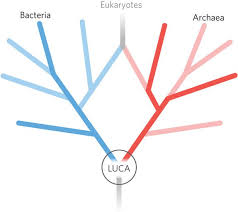
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor
the most recent common ancestor of all life
DNA
central dogma
lipid bilayer membrane
ribosomes
Ether vs ester linkages
ether: branched —> stronger, archaea
ester: unbranched, bacteria and eukarya
peptidoglycan
polymer of amino sugars located either outside the cell wall or between cell membranes
only found in bacteria
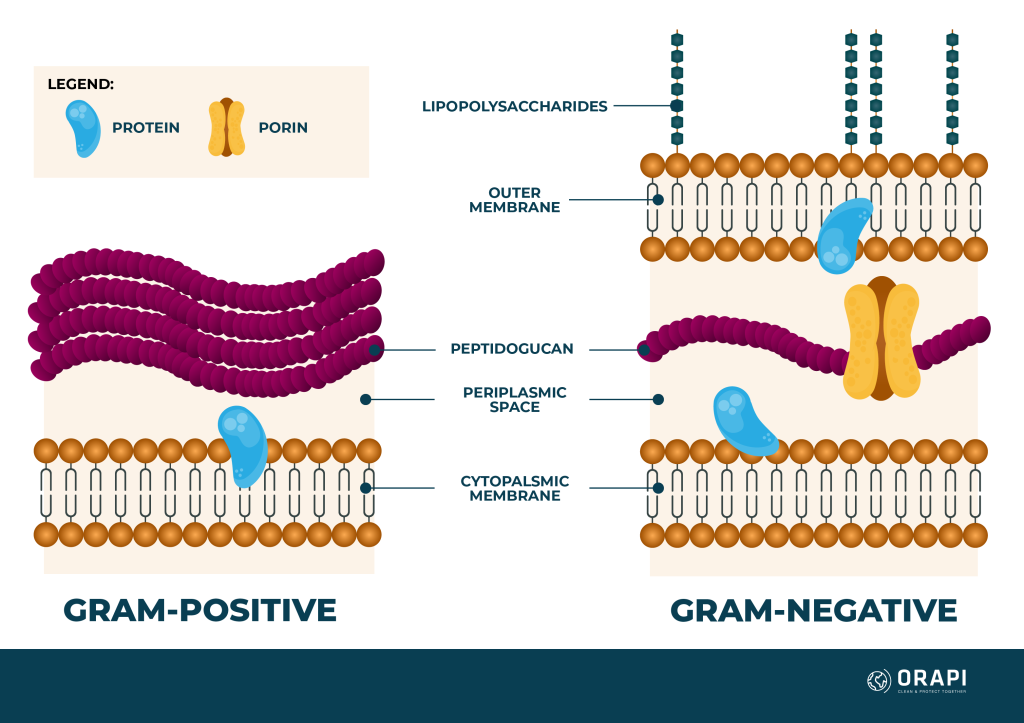
gram positive vs gram negative
+: thick outer layer of peptidoglycan
-: thin layer of peptidoglycan between membranes
Characteristics of ALL prokaryotes
cell membrane
nucleoid
cytoplasm
ribosome
characteristics of SOME prokaryotes
cell wall
internal membranes
flagella and pili
LGT vs sexual reproduction
LGT: unidirectional, involves small portions of genome, can occur over large phylogenetic distances
sexual reproduction: bidirectional, whole genome, between closely related individuals
Plasmids
small circular chromosome separate from main chromosome
characteristics of prokaryotic DNA
circular
haploid
biofilms
groups of bacteria/archaea that secrete an extracellular polymer that binds them together
Quorum sensing
once organisms reach a high enough density, they communicate via chemical signals which activate group behavior genes
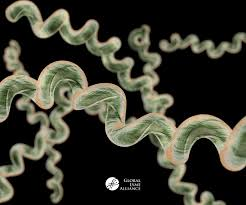
types of bacteria: spirochetes
gram -
motile
axial filaments (modified flagella)
many are pathogenic (ex. Syphilis and Lyme)
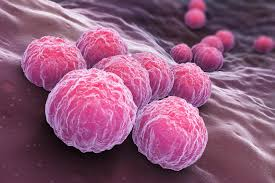
types of bacteria: chlamydias
gram -
cocci/rod
very small
intracellular parasites
STDs, pneumonia
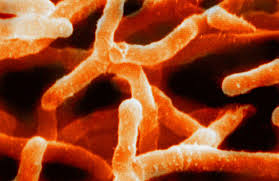
types of bacteria: actinobacteria
more C/G than A/T
branching (often mistaken for fungi)
decomposers, often symbiotic w/ plant roots
used in antibiotics
TB and leprosy
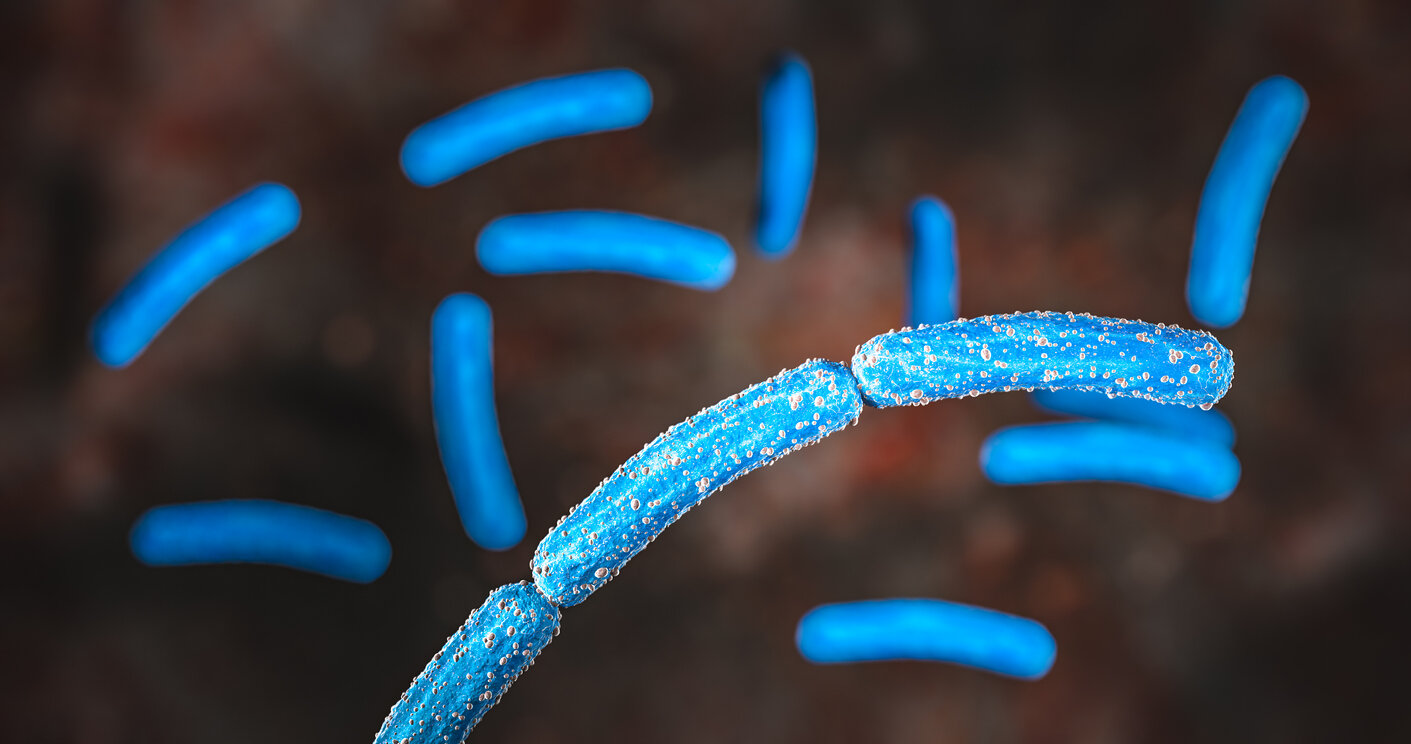
types of bacteria: firmicutes
low C/G to A/T
some produce endospores: resistant seeds that only germinate in ideal conditions
anthrax, MRSA, etc
types of bacteria: cyanobacteria
photolithoautotrophs
fix N
internal membrane for photosynthesis
ancestors of chloroplasts

types of bacteria: proteobacteria
gram -
largest
ancestors of mitochondria
E.coli, plague, etc
what characteristics allow archaea to survive in extreme conditions?
have ether linkage membranes, which are stronger
lipid monolayer is resistant to extreme temps
types of archaea: crenarchaeota
thermophilic and acidophilic
types of archaea: euryarchaeota
methanogens (produce methane by reducing CO2) and/or halophiles (prefer high salt)
types of archaea: asgard archaea
genes are similar to eukaryotic genes
eukaryotes are within asgard
The Great Plate Count Anomaly
there are a lot more cells present in the environment than can be grown in a lab
very hard to grow a pure culture
pathogens
a parasite that causes disease
all are eukarya and bacteria (there are no known pathogenic archaea)
legume/Rhizobium symbiosis
mutualistic relationship where Rhizobium fixes N for the legume and the legume provides Rhizobium with sugar from photosynthesis
water fern symbiosis
mutualistic relationship where Anabaena cyanobacterium fixes N for the water fern (azolla), which provides a protected environment for Anabaena