Medical Parasitology medical Part 1
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Type of parasites
Endoparasites: live inside it's host “infection”
Ectoparasite: live outer surface of host “infestation”
Obligate parasite : depends on host for nourishment, reproduction, habitat & survival
Facultative parasite: capable of leading both free-living without host & parasitic existence
Accidental/incidental parasite: establishes itself in host where it doesn't ordinarily live
Erratic/aberrant parasite: wanders into organ in not usually found
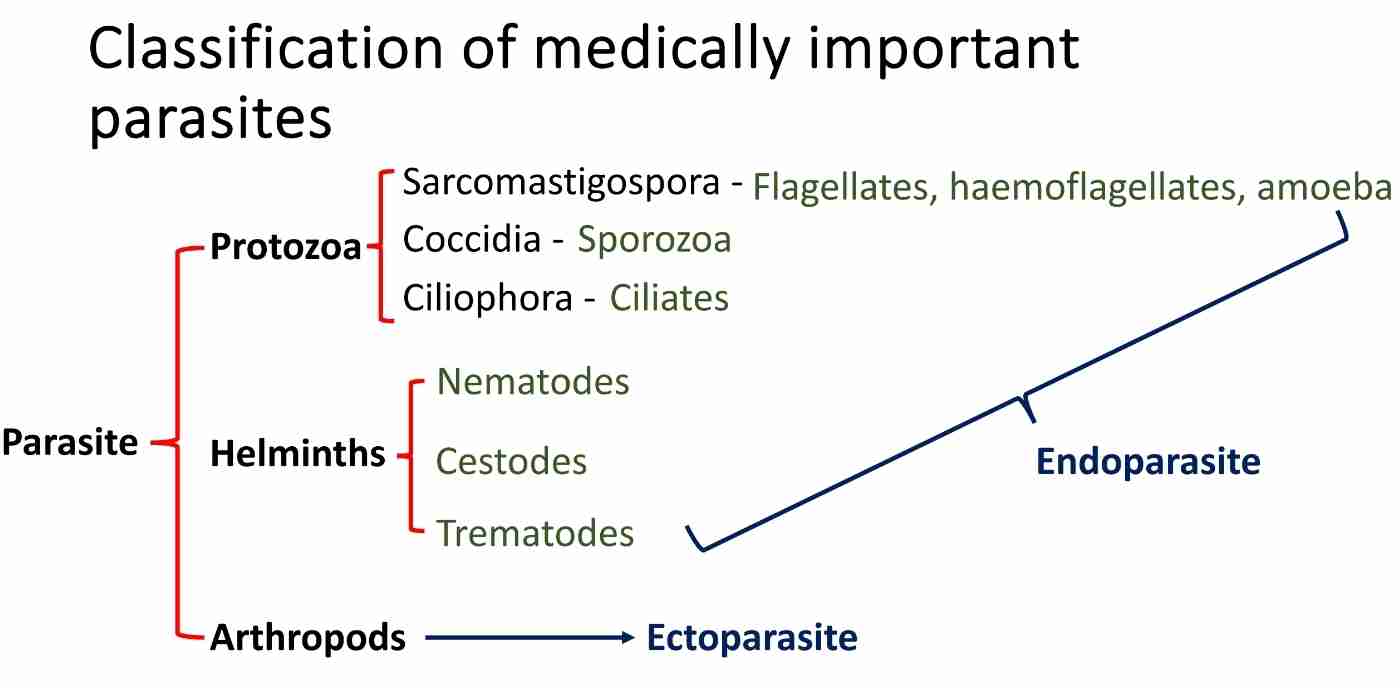
Medically important parasites
Parasite
Protozoa
Sarcomastigospora - flagellates, haemoflagellates & amoeba
Coccidia - sporozoa
Ciliophora - ciliates
Helminths
Nematodes
Cestodes
Trematodes
Arthropods
Ectoparasite
General characteristics of protozoa
Unicellular, eukaryotic organisms
Consists of cytoplasm & membrane-bound nucleus/nuclei
High rates of reproduction:
Asexual (binary fission & schizogony)
Sexually
Size ranges from 1-150 μm (require microscopy for detection)
Basic characteristics of flagellates & haemoflagellates
Move by flagellum/flagella
Reproduce by binary fission
Haemoflagellates posses unique organelle-kinetoplast (contains DNA)
Flagellates transmitted by ingestion of cysts
Basic characteristics of amoeba
Consists of mass cytoplasm
Move by pushing out ectoplasm to form pseudopodia (false feet)
Binary fission
Digested food stored as glycogen &/ chromatid bodies
Form cysts (transmission through this stage)
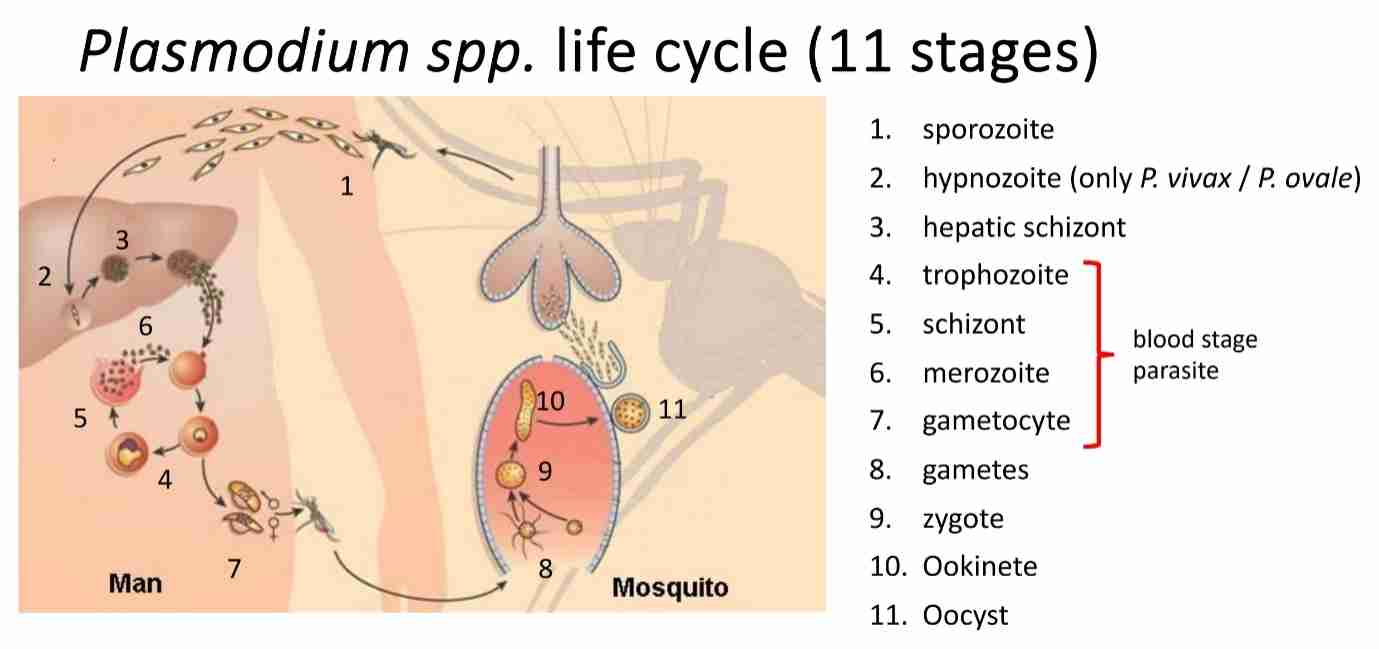
Basic characteristics of sporozoa
No obvious means of locomotion
Complex life cycles
Asexually bu schizogony
Sexually by sporogony
Intestinal coccidia transmitted cysts
Malaria parasites (blood coccidia) transmitted as sporozoites by mosquitoes
Basic characteristics of ciliates
Move by cilia (small hairs cover body)
2 nuclei - macronucleus & micronucleus
Binary fission
Form cysts (transmission through this stage)
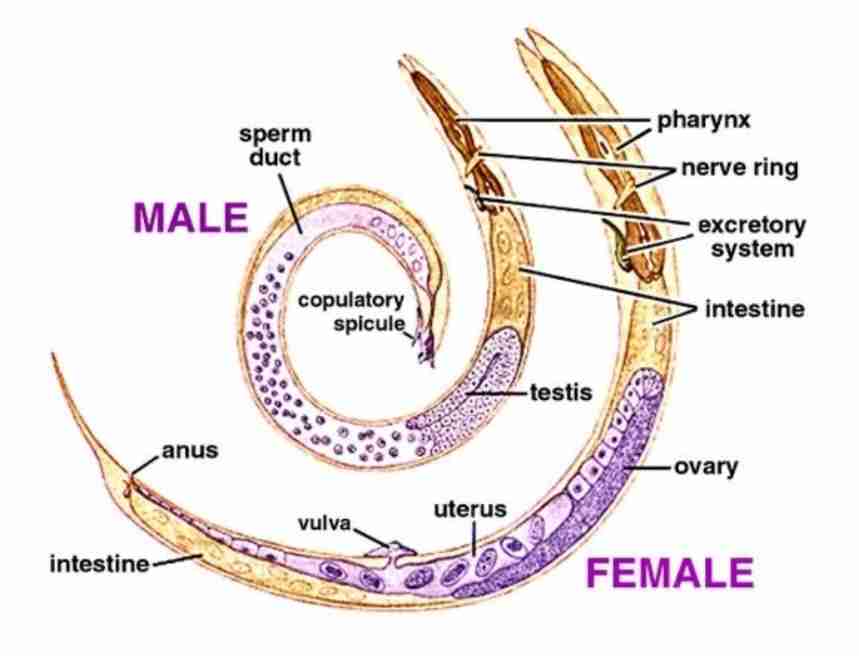
Characteristics of nematodes
Non-segmented cylindrical worms
Mouth surrounded by lips. Some species (hookworm) mouth opens into buccal cavity
Sexes separate (dioecious) : male smaller than female
Female either viviparous (produce larvae)/oviparous (produce eggs)
Live in tissues/intestinal tract
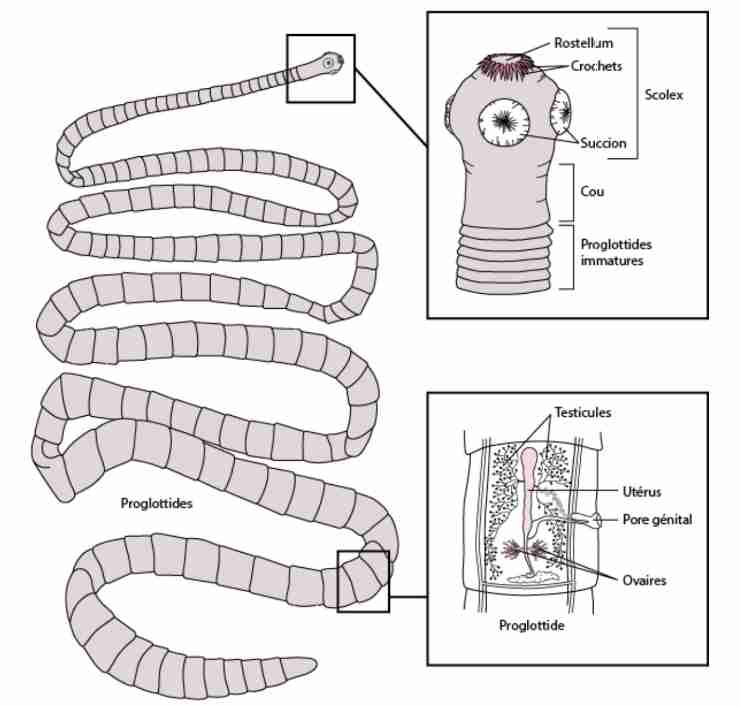
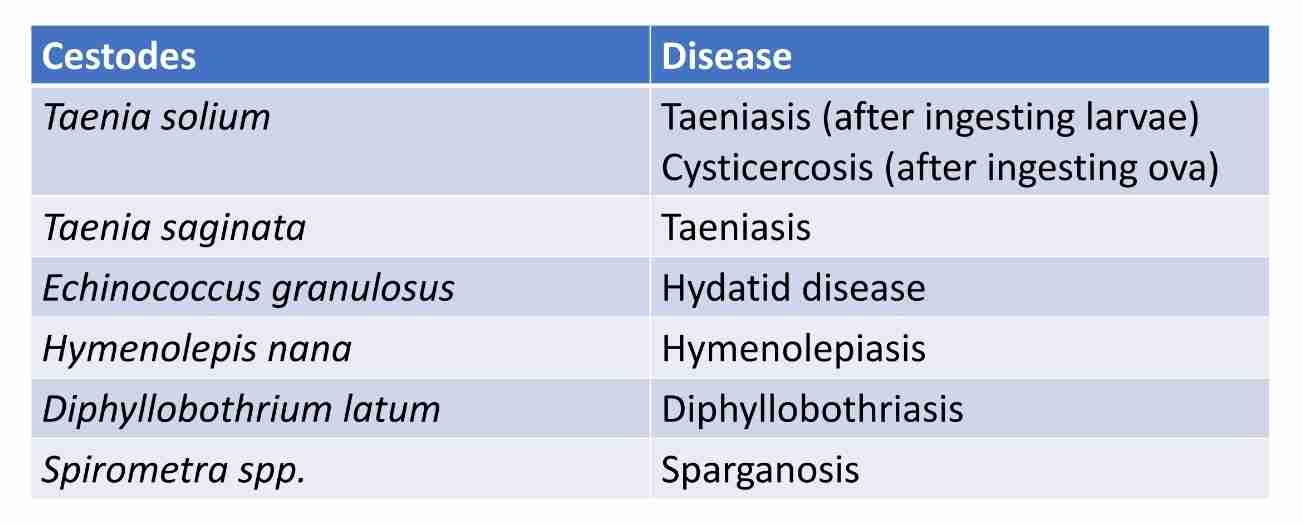
Characteristics of cestodes
Tape-like body
Made up of scolex(head) & proglottid(segments)
Attaches to host by suckers (some species by hooks)
Adult tapeworm live in intestinal tract
Hermaphroditic, with male& female sex organs found in each mature proglottids
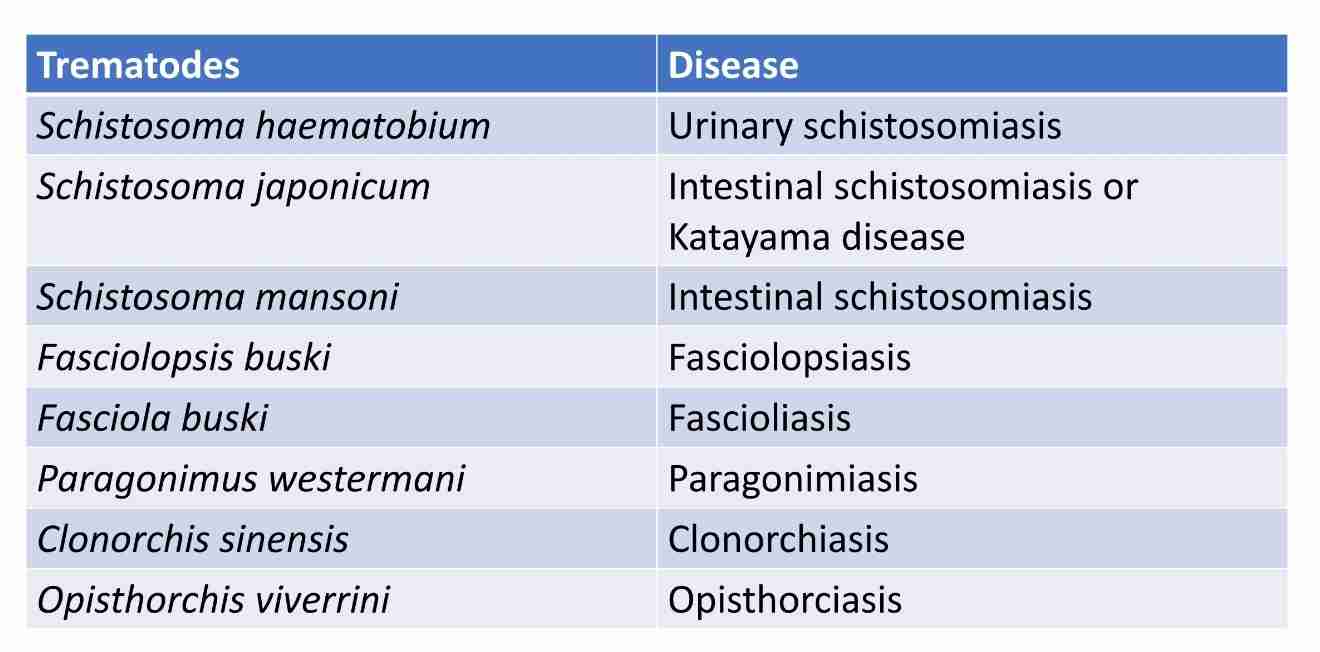
Trematodes of medical importance
Hermaphroditic flukes
Male& female sex organs
Flat, leaf-like worms
Unsegmented
Attch to host by suckers (oral& ventral)
Blood trematodes
Male &female adults (not hermaphroditic)
Adults found in blood
2 generations required to complete life cycle:
Asexual generation - multiplication occurs
Sexual generations - produce eggs
Terminology in Parasitology
Host
Vectors
Life cycle & types of life cycle
Development stages of parasites
Host
Organisms that harbour parasite & provide nutrition & shelter
2 type of host
Definitive host
Intermediate host
Definitive host
Organisms in which sexual reproduction of parasite take place(mosquito for malaria parasites/human for pig tapeworm Taenia solium)
Organisms that mature/most highly developed form of parasite occurs ( human for Trypanosoma cruzi)
Intermediate host
Organisms that support immature/non-productive forms of parasites :
Fish for tapeworm Diphyllobothrium latum
Snail for fluke fasciola hepatica
Rats/birds for protozoa Toxoplasma gondii
Other type of host
Paratenic host
Organisms; parasites doesn't develop further stage but parasite remain alive & capable to infect another susceptible host
Wild boar for lung tapeworm Paragonimus westermani
Reservoir host
Organisms; parasite infect human can live & develop in absence of human host, commonly animals
Potential sources of human infection (zoonosis)
Dogs & rodents for Leishmania donovani
Vectors
Latin; carrier
Organisms; usually arthropods carries infective organism like parasite & virus from one host to another
Types of vectors:
Biological vectors
Parasites undergo multiplication, propagation & development inside arthropod's body
Acquire pathogenic agents through blood meal
Mechanical vectors
Transmit pathogens by their secretion/external surfaces of body
Serve as mere contaminators
Pathogens don't undergo multiplication/development inside their bodies

Life cycle & types of life cycle
Whole process of parasite growing & developing
2 types:
Direct life-cycle
Only one species host necessary to complete development of parasite(no intermediate host)
Protozoa : Giardia lambia
Helminth : Trichuris trichiura
Only require human host through faeco-oral route
Indirect life cycle
2 or more species of host required for parasite to complete development (intermediate & definitive host)
Taenia solium/malaria parasites:
Intermediate host - pig/human
Definitive host - human/mosquito
Development stages of parasites
All parasite pass through series of development stage before the organisms reproduce & new cycle of development begins
2/several development stages : entamoeba histolytica(trophozoite& cyst)
Cryptosporidium parvum :
Infective stage - oocyst in environment
In human - trophozoite, meront, merozoite, gamont & oocyst
Malaria parasite; several development stages
May exhibit different morphological characteristics for different species; trophozoite stage