Lecture 14 - Self-Esteem, Respect, and Honor
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
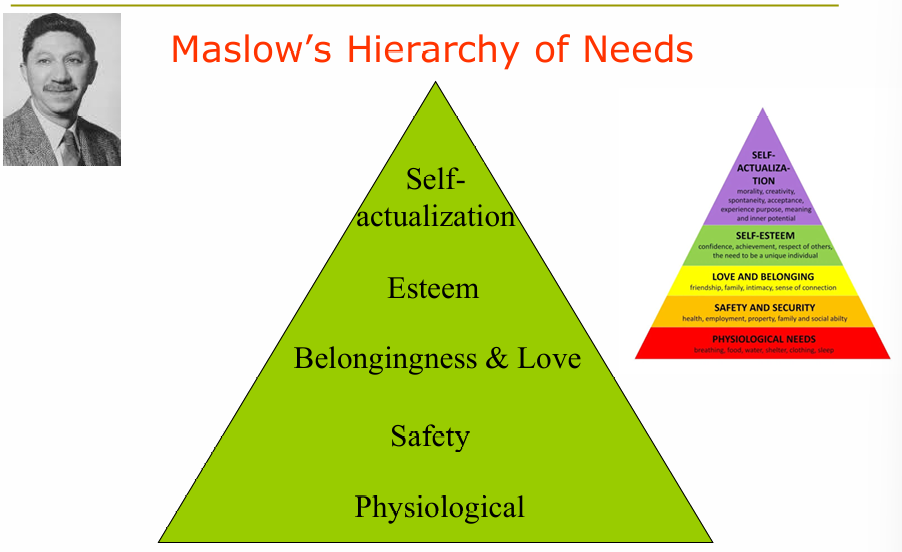
what is maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
what are the origins of the modern view of self-esteem?
“the single most important key to human motivation is self esteem.” - Nathaniel Branden
“In order to deal with reality successfully - to pursue and achieve the values which his life requires - man needs self-esteem; he needs to be confident of his efficacy and worth.” Ayn Rand
“The man who does not value himself, cannot value anything or anyone.”
what is the self-enhancing bias?
self-enhancing bias: most people show unrealistic optimism. They are “better than average”
They believe that:
good things are more likely to happen to them than a similar “average” person
bad things are less likely to happen to them than a similar “average” person
what are some popular beliefs about self-esteem?
how was this studied and what were the conclusions of that study?
popular belief
low self-esteem is associated with . .
low academic achievement
aggression
baumeister study
the relationship between self-esteem and educational achievement is very weak (r = .1)
causality in the opposite direction (achievement promotes SE, rather than SE promotes achievement)
SE interventions may actually hurt learning by providing false or non-diagnostic feedback
what are some potential costs of self-esteem?
high SE is often associated with negative behavior (aggression, bullying, sense of entitlement, self-centeredness, etc)
is it true SE or just narcissism?
or “posturing”? just talk? braggadocio?
future research is needed!
what is the Rosenberg self-esteem scale? what were its findings?
most popular measure of self-esteem
Items:
I take a positive attitude toward myself
On the whole, I am satisfied with myself
First Study: 1967 - 1994
65,965 students
large increases in self-esteem over time
goes against the generational stereotype of Boomers as confident and GenX as down on themselves
how has self-esteem changed from 1998 to 2007?
increase in SE across the board (middle, HS, and college)
what is an alternative explanation for the generational changes in self-esteem?
one alternative account of generational changes is that people simply learned to be more positive when talking about themselves
mental health seems to be getting worse (in self-reports and in admissions for self-harm)
what are some cultural differences in the definition of self? (More specifically, focusing on Western and non-Western.)
Western View
individualist cultures
people have an independent, context-free view of the self
non-Western View
collectivist cultures
people have an interdependent, contextual view of the self
what is the twenty statements test?
twenty answers to the question “who am I?”
cross cultural comparisons reveal differences in relative frequency of response categories
psychological attributes (funny, outgoing, silly)
physical attributes (tall)
preferences / interests (i like soccer)
goals (i want to get an A in this class)
attitudes (I am racist and sexist)
activities (I am unemployed af)
social roles (I am a student)
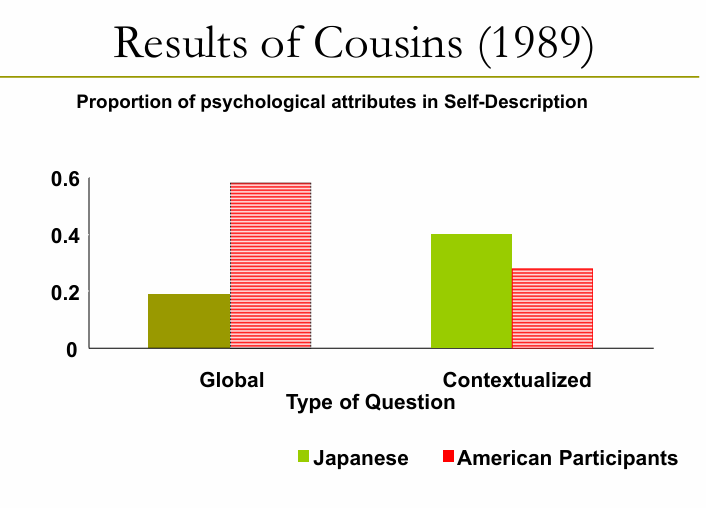
Describe the “who are you” in different cultures study?
what were the results?
Background: US and Japanese participants responded to “Who am I” questions
Two Types:
Global (“Who am I?”)
Contextualized (Who am i in school? work?)
Results:
Western cultures emphasize the importance of stable, cross-situational, internal, psychological traits
Non-western cultures emphasize the importance of flexibility in context
how has culture of honor differed in the south versus the north?
North
culture of dignity
each individual at birth possess an intrinsic value at least theoretically equal to that of every other person
driven by internal standards, conscience, norms
characteristic emotion is guilt, rather than
shamedignity cannot be taken away by others
thus is relatively impervious to insults
South
culture of honor
respect and reputation is key
especially a reputation for reciprocity. pay back the good things and the bad things
honor can be taken away by others and is thus susceptible to attack, especially by insults (disrespect)
insults must be directly paid back by victim — not a third party or the state
characteristic emotion is shame
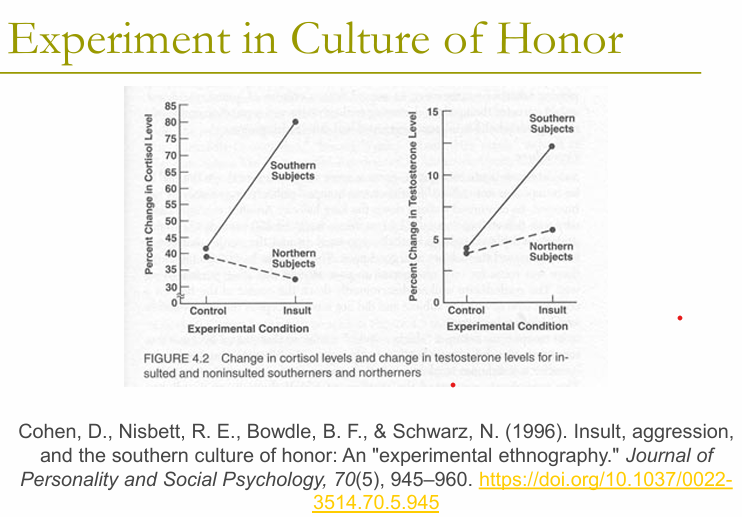
how has the culture of honor been studied?
how were the results different in measurements between southerners and northerners
Background:
Northerners and southerners put through fake test and were disrespected by a confederate
Measures: cortisol, testosterone, self-reports
Results:
southern subjects’ change in cortisol > northern subjects
southern subjects change in testosterone > northern subjects