Molecular Genetics Lecture 9 pt. 1 - Detection and quantification of mRNA expression
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Transcriptomics, Techniques used to quantify mRNA expression, Northern blot analysis, RNA in situ hybridization, cDNA synthesis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what is transcriptomics?
study of genome wide mRNA expression of genes
what is useful to identify parts of genes (UTR, promoter, intron, exon) and studying gene functions?
mRNA
what is functional genomics?
study of the function of genes and what biological processes the gene is involved in
what is spatial expression of mRNA mean?
where or what cells/tissues/organs mRNA is expressed
what is temporal expression of mRNA mean?
when or what time, day or life cycle mRNA is expressed
what does quantity mean in regards to measuring mRNA abundance?
how much mRNA is expressed
what are mRNA expression techniques based on?
nucleic acid hybridization
what can form complementary base pairing with the target and help visualize mRNA expression?
labelled probe (RNA, DNA)
what techniques can be used to quantify mRNA expression involving several genes at a time (low throughput)?
northern blot analysis, in situ hybridization, reverse transcription PCR
what techniques can be used to quantify mRNA expression involving thousands of genes at a time (whole genome, high throughput)?
microarray analysis, RNA sequencing techniques
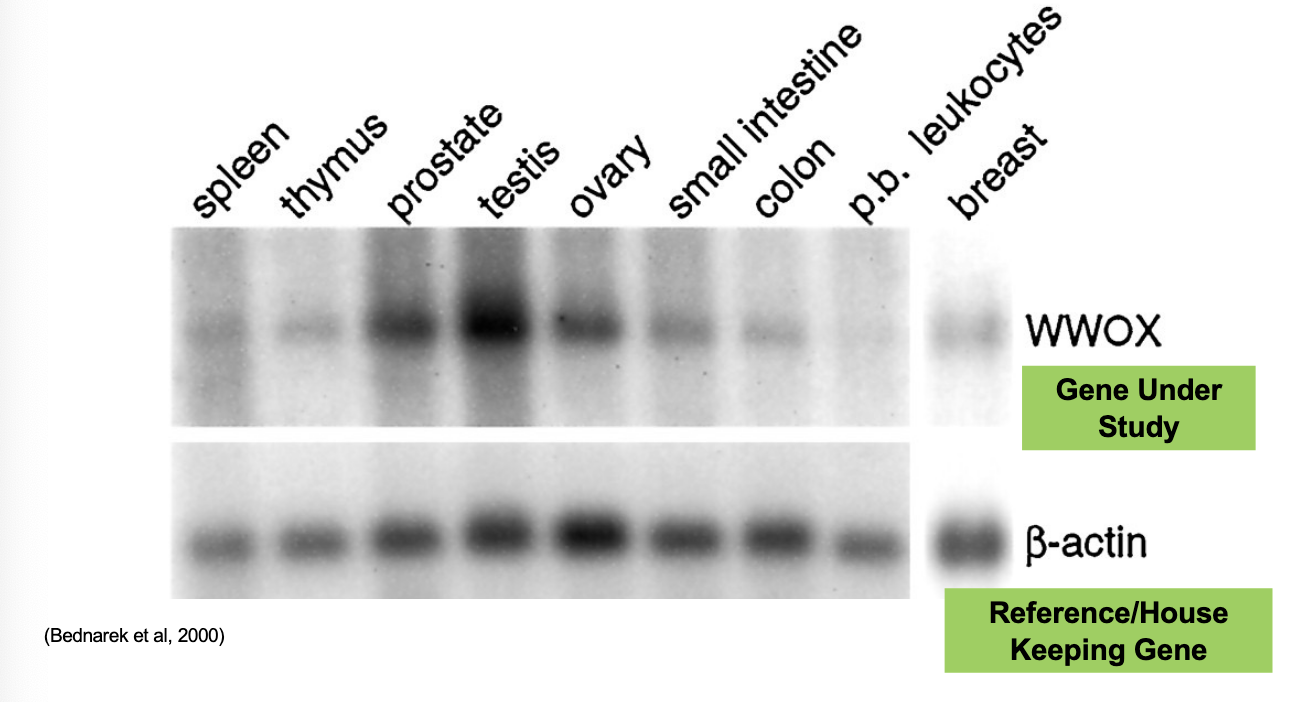
what is northern blot analysis?
modified southern blot technique that uses radioactively labeled DNA probes
what is the first step of northern blot analysis?
isolate total RNA, denature and separate on agarose gel electrophoresis
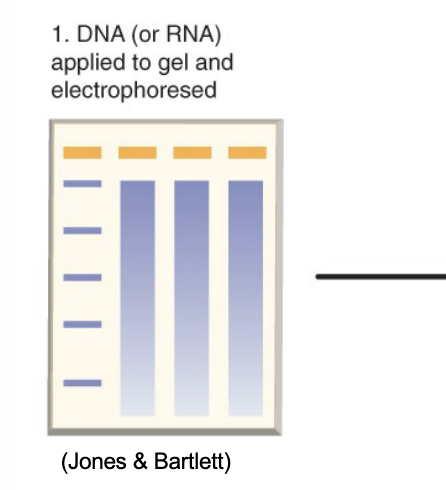
what is the second step of northern blot analysis?
transfer RNA molecules from the gel onto a nitrocellulose or nylon membrane by blotting
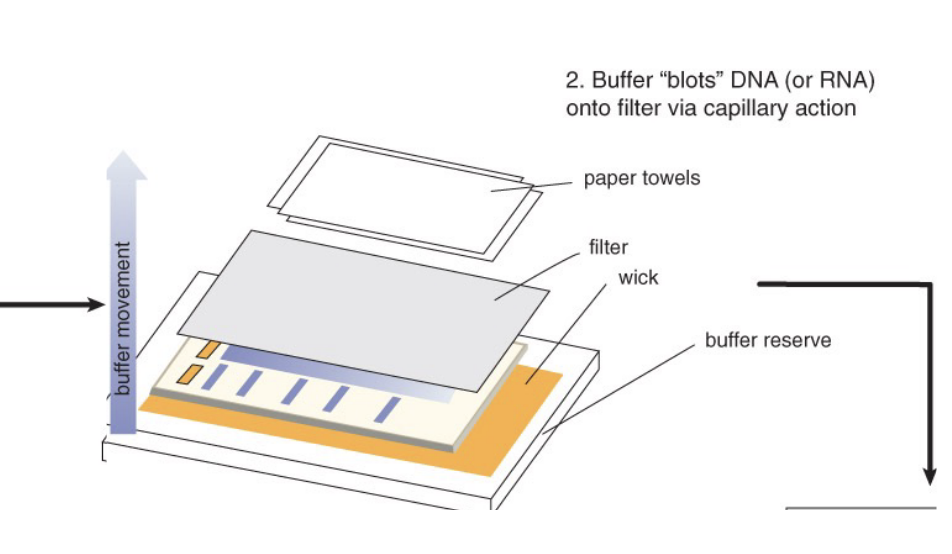
what is the third step of northern blot analysis?
mRNA bound to the membrane is hybridized with a DNA (exon) probe radioactively labeled with 32phosphorus
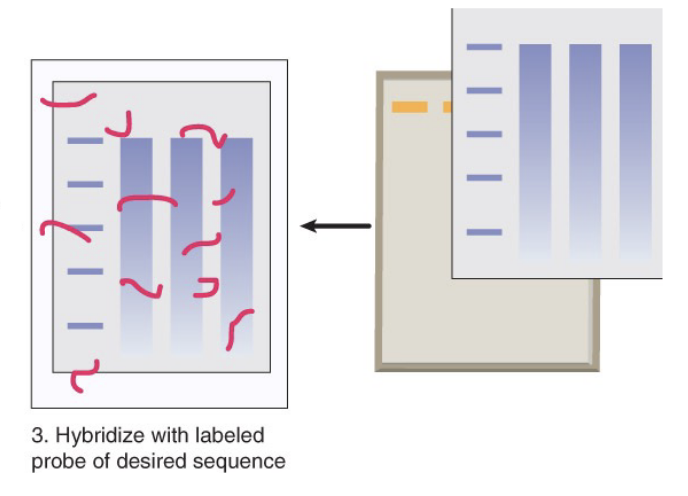
what is the fourth and last step of northern blot analysis?
expose the membrane to x-ray film to visualize the mRNA expression levels of the target gene
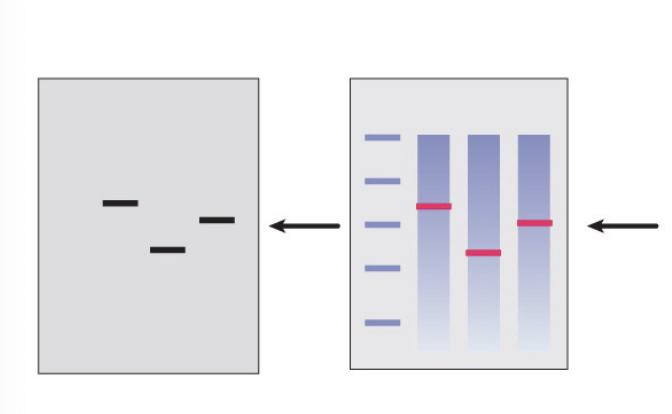
what is the function of a reference/house keeping gene?
used as a normalizer/loading control, positive control
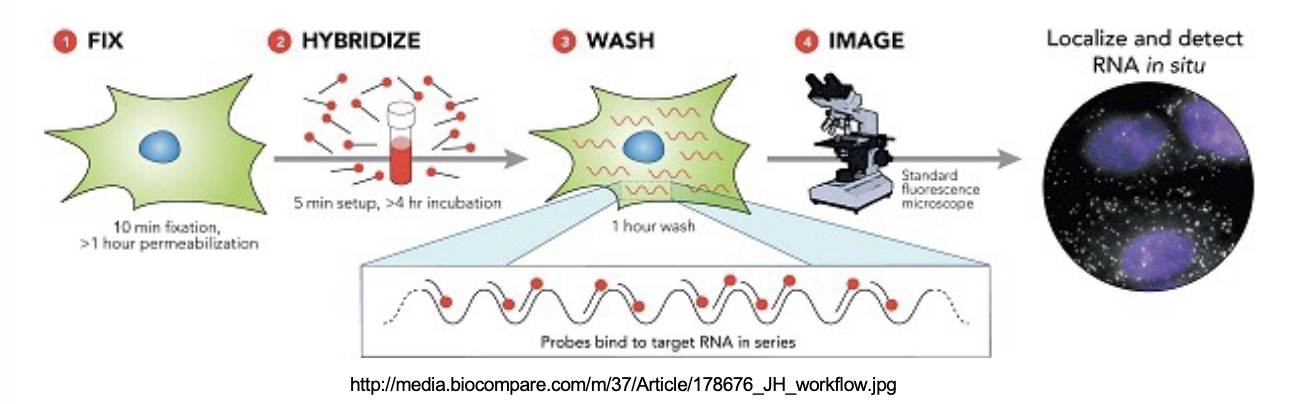
what is mRNA In situ hybridization used for?
used to visualize mRNA expression in specific cells or tissues in its native state
what is the basic process of RNA In situ hybridization?
cells or tissues are immobilized to a microscope slide and labeled probe is hybridized to the slide to visualize probe hybridization to detect mRNA molecules
For RNA in situ hybridization, what is an antisense probe?
complementary and base pairs with mRNA
For RNA in situ hybridization, what is the sense probe?
does not form complementary base pairing with mRNA, negative control
what enzyme is used by RNA viruses (retroviruses) to convert mRNA into DNA to invade bacterial genomes?
reverse transcriptase
how can you use cDNA to understand gene function?
use to identify genes expressed in specific tissue, time or in response to stimuli
RNA is unstable, cannot copy in bacteria and no convenient for manipulations. True or false?
true
what is the function of complementary DNA (cDNA)?
reverse transcribe mRNA to DNA
what is a cDNA library?
a large collection of DNA sequences that are obtained by reverse transcribing mRNA into DNA and cloned into plasmid vectors
_____ _____ is essential to identify the functional elements of genes (exons, UTRs) from genome sequencing and useful in biotechnology.
cDNA library
7 steps of cDNA synthesis from mRNA
extract mRNA from tissue
first strand cDNA synthesis
second strand cDNA synthesis
use DNA ligase to join DNA fragments
clone cDNA fragments into plasmid DNA vector
cDNA library represents mRNA from different tissues/organs
sequence DNA library
in cDNA synthesis from mRNA, ___ ___ ___ nucleotides are added to bind to the poly-A tail by base complementary to serve as a primer
oligo DT (deoxy thymidine)
____ _______ synthesizes the first DNA strand using mRNA as a template during first strand cDNA synthesis from mRNA
reverse transcriptase
In cDNA synthesis from mRNA, partial digestion of RNA is completed by _____ _
RNase H
In cDNA synthesis from mRNA, ___ _________ _ uses short RNA as a primer to synthesize the second strand of DNA.
DNA polymerase I
____ _____ seals the gap and joins DNA fragments in cDNA synthesis from mRNA
DNA ligase
______ ______ can be cloned into plasmid vectors for sequence identification in cDNA synthesis from mRNA
cDNA library