promoting health and preventing illness
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
block two week 3 socpop
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
disease prevention
Actions aimed to:
Eradicate, eliminate, or minimise disease
Minimise subsequent disability
If eradication is not feasible:
Aim to slow disease progression
health promotion
Process of enabling people to:
Increase control over their health
Increase control over determinants of health
Focuses on:
Improving quality of life
Mental and spiritual wellbeing
Health viewed as a positive and inclusive concept
levels of prevention (Leavell and Clark)
Primordial prevention
Primary prevention
Secondary prevention
Tertiary prevention
cardiovascular disease progression and prevention types
Healthy state
Development of risk factors:
Hypertension
Diabetes
Arterial wall stress → damage
Cholesterol deposition → atherosclerosis
Coronary artery stenosis
Myocardial infarction
Risk of recurrent myocardial infarction
tertiary prevention
Treating established disease
Preventing complications and disability
tertiary prevention in CV disease
Preventing long-term breathlessness post-MI
Reducing risk of recurrent MI
Cardiac rehabilitation
Angioplasty and stent
Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
secondary prevention
Detecting disease early before symptoms (preclinical disease)
Preventing progression to clinical disease
examples of secondary prevention
Risk scoring (e.g. QRISK3)
Identifying high-risk individuals
Aggressive management of risk factors
Education
primary prevention
Preventing disease before it occurs
Addressing known risk factors
primary prevention in CV disease
Managing hypertension
Managing diabetes
Reducing cholesterol
Lifestyle education
primordial prevention
Preventing the development of risk factors
Keeping healthy people healthy
primordial prevention examples
Addressing socioeconomic deprivation
Health education
Promoting healthy lifestyles
levels of prevention in asthma
primordial:
Prevent uptake of smoking in society
Smoking cessation support for future parents
primary:
Smoking cessation in parents
secondary:
Identifying allergen sensitisation
Monitoring children with family history of atopy
tertiary:
Preventing severe asthma exacerbations
Regular asthma reviews
Escalation up asthma treatment ladder
high risk approach to prevention
Targets individuals above a defined risk threshold
Example: treating people with high blood pressure only
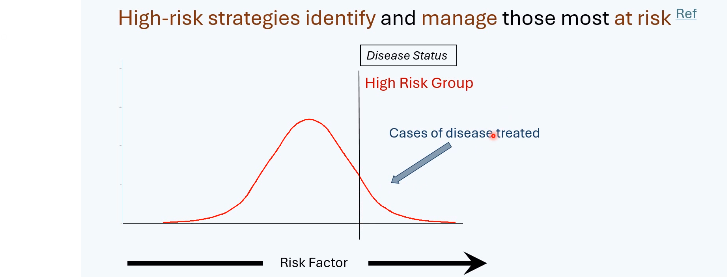
advantages to high risk approach
Large benefit to treated individuals
Cost-effective
High motivation for patients and clinicians
limitations to high risk approach
Requires screening or case finding
Does not address underlying causes
New cases continue to develop
population approach
Targets entire population
Shifts risk factor distribution
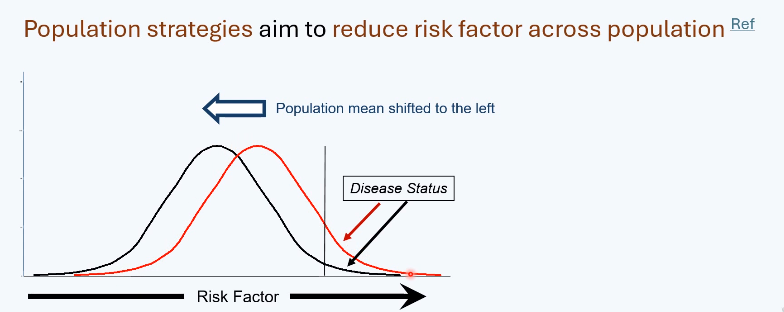
advantages to the population approach
Reduces prevalence and incidence
Larger population-level impact
limitations to the population approach
Low motivation for individuals and clinicians
Treats people who may never benefit
May penalise already healthy individuals
prevention paradox
Population-level interventions prevent more cases overall
Even though individual benefit may be small
Particularly relevant for widespread risk factors
examples of prevention paradox
Mild hypertension affects many people
Severe hypertension affects few
Targeting mild hypertension population-wide prevents more heart disease overall
upstream approaches
aims to prevent root causes that have broad health consequences such as the wider determinants of health
e.g: reduce poverty and unemployment, water fluoridation
downstream approaches
prevention through dealing with lifestyles and adverse health behaviours, and the consequences of poor health
e.g: smoking cessation and indoor ban, weight management
Beattie’s model of health promotion
