aldehydes and ketones
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What can a primary alcohol form when oxidized?
It can be distilled and form An aldehyde
Or a carboxylic acid
What can a secondary alcohol form when oxidized?
A ketone
What can a tertiary alcohol form when oxidized?
Not
What oxidizing agents can be used to oxidize alcohols?
Acidified dichromate
Potassium permanganate
What test can you use to determine if a solution contains an aldehyde or ketone?
Tollens Silver mirror test or Fehlings
Positive test for Fehlings
Brick red precipitate, aldehyde is present
What is the Positive result for Tollens reagent (Silver mirror test)
Silver mirror forms or black precipitate (silver oxide) forms
Aldehyde is present
Why must you rinse out the test tube immediately after doing the Tollens reagent test?
Because the product can explode
Compare the nucleophilic addition in aldehydes and ketones
Addition of the C=O bond
They are attacked by nucleophiles at the positive carbon centre
What reagents can be used in nucleophilic addition of carbonyl compounds?
KCN(aq) or NaCN
To form the -CN nucleophile
Draw the mechanism for the nucleophilic addition of propanal
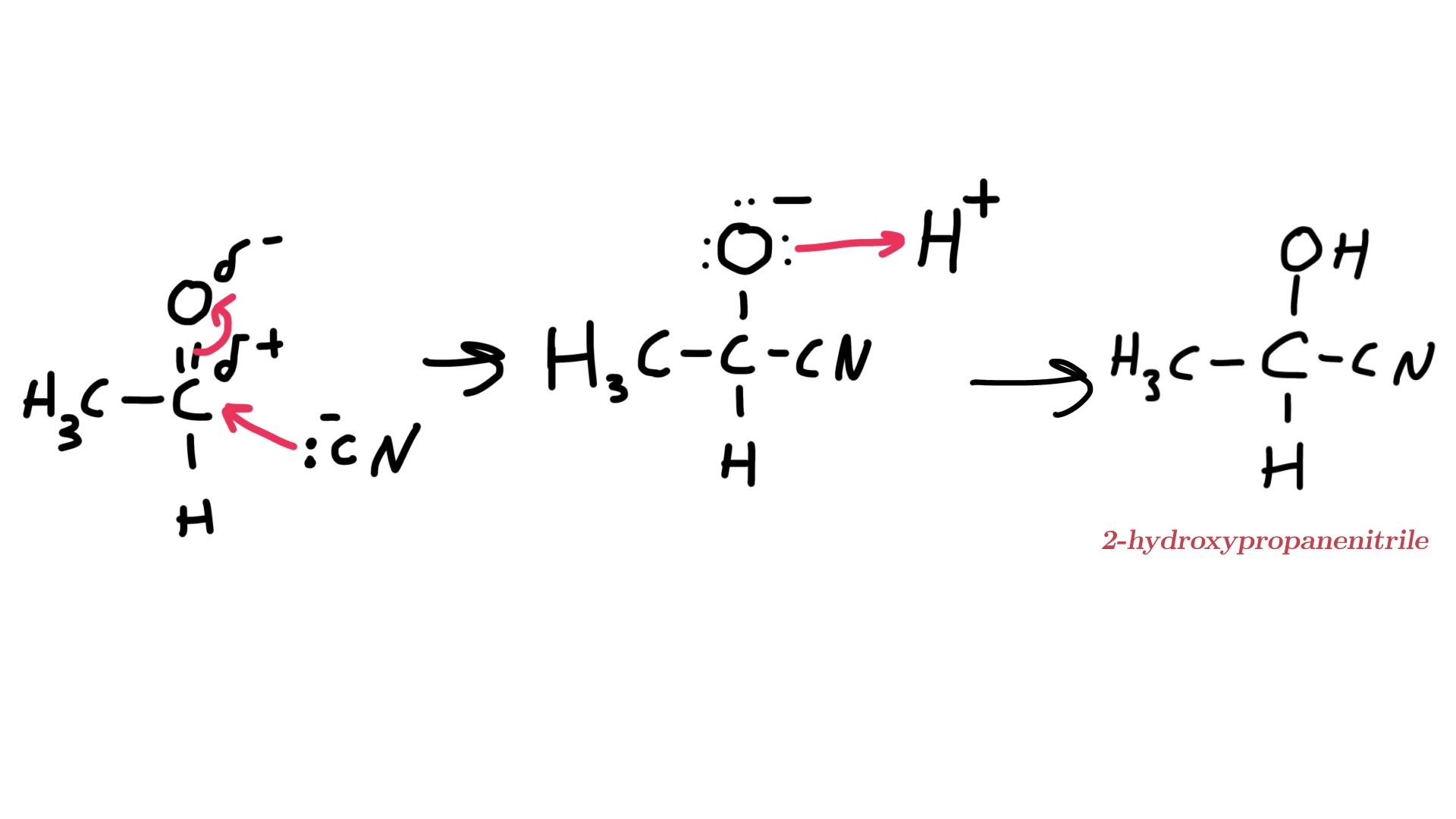
What are Allene’s attacked by in nucleophilic addition?
Electrophiles
Draw and explain the structure of a Carbonyl group
Polar bonds due to the difference in electronegativity between the carbon and oxygen atom.
Planar shape
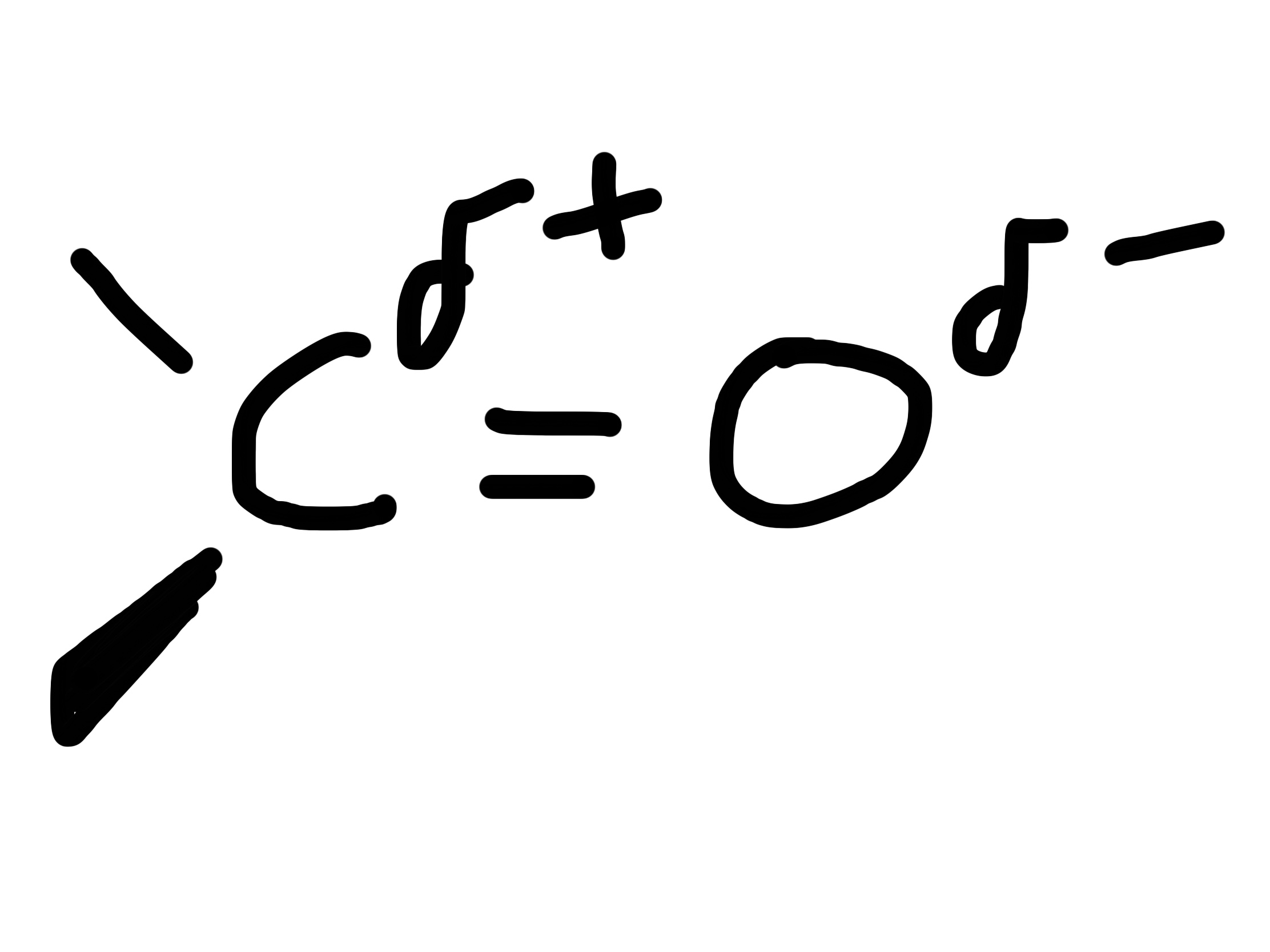
Explain how in nucleophilic addition to compind with carbonyl groups can result in optical isomers
Due the carbonyl group having a planar shape
Nucleophilic attack can happen on the top or bottom
Resulting in 2 optical isomers that can form
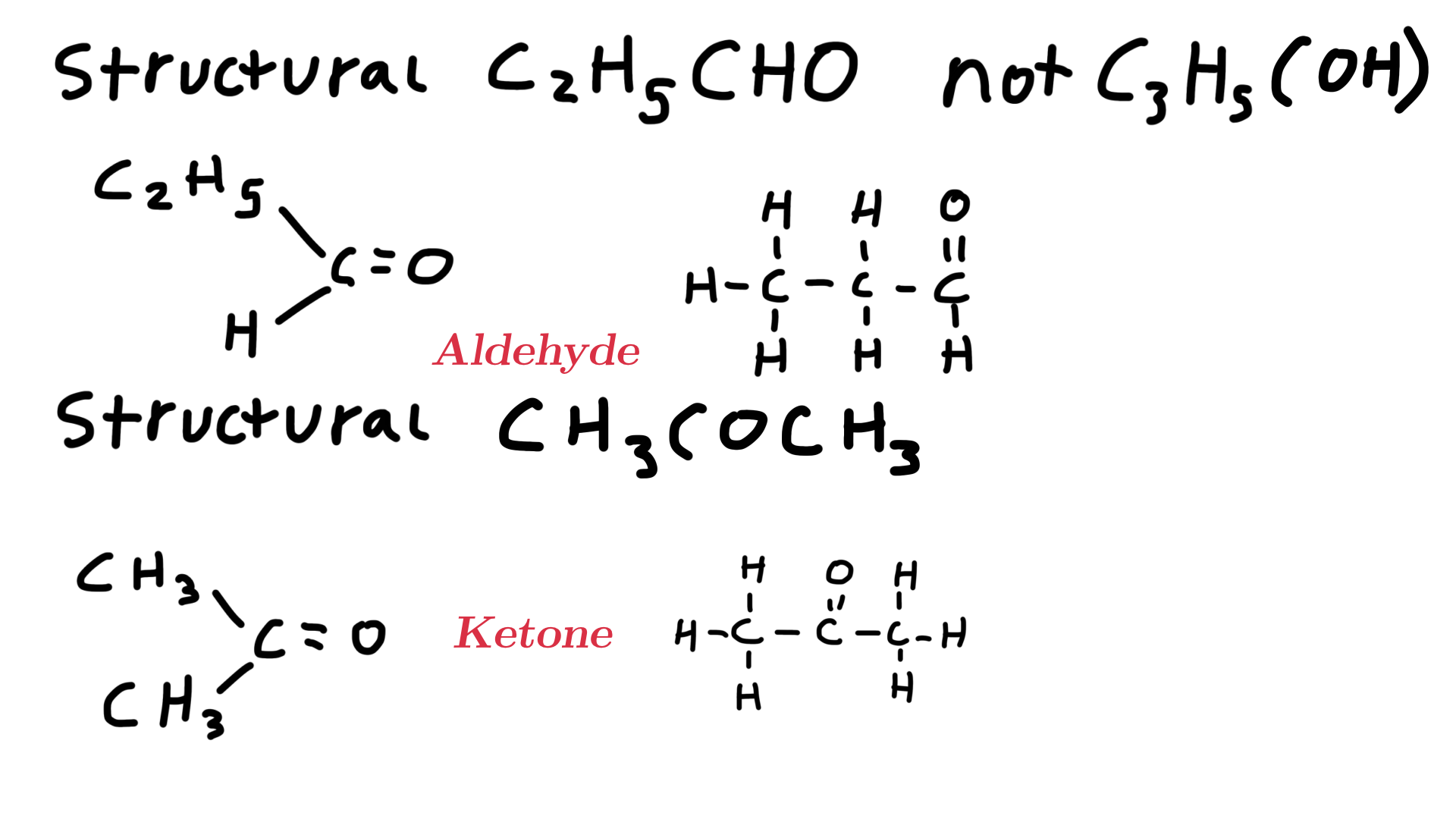
Describe the structure of an Aldehyde
One H attached to Carbonyl group
Describe the structure of a Ketone
2 carbon atoms attached to carbonyl group
State the structural formula of C3H6O and the displayed formulas it can have and state the functional groups
Explain why when comparing different carbonyl compounds that the comparisons of their MR should be relative?
The bigger the size of the compunds
The stronger the van dear waals forces
So the intermolecular forces are greater and more energy is needed to overcome them
Which is more soluble? An alkane, alcohol or ketone?
If it’s water it is alcohol due to it having a high boiling point, it can hydrogen bonding, and the OH bond is polar
If it is organic solvent it is Alkane because the solvent is non-polar and Alkanes are non-polar