Gas Permeable Corneal Lens Design and Fitting
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3 material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Name some benefits of GP lenses
better quality of vision
safety
comfort
value
durability
can be used for irregular cornea diseases
myopia progression
ortho K
Who would benefit from a corneal and scleral GP?
pt with an irregular cornea (keratoconus, scars, and post transplant)
IMPORTANT: What is the percentage of GP’s prescribed out of all CL?
11% of all CLs are GPs (46% spherical)
IMPORTANT: Who can use GPs?
all age groups
infants/ toddlers- larger, more flexible, SiHy for EW (mostly EW GP corneal lenses)
children: high astigmatism and refractive amblyopia
teens: watch out for sports due to debris trapping of GPs and dislodging
YA, middle adults, elderly, aphakic individuals
What are some disadvantages of GPs?
disease transmission
time-consuming fitting process
can be blurry at first
What are some advantages of GPs?
fewer reorders
fewer pt revisits
pts get final lenses more quickly
What happens at the diagnostic fitting?
place the diagnostic lens on the pts eyes
evaluate the fluorescein pattern and fit of each lens
order the lens based on info gathered about best-fit
Do you need collected data before ordering a GP?
yes, the GPs are ordered based on collected data only
What data is needed to order a GP?
keratometry and refraction is required
other data can be used (topography, pupil size, lid tension, etc.)
review: What is the empirical fitting?
use refraction and keratometry (also can use HVID)
no lens is placed on the eye initially but the contact is dispensed at a later appointment
Who should you try to AVOID doing empirical fittings of GPs on?
keratoconus
irregular corneas
Why should you avoid using empirical fitting of GPs on keratoconus and irregular cornea patients?
performance of these lenses can be unpredictable so you want to borrow a fitting set from a GP lab.
What are the disadvantages of empirical fitting?
required more in-office visits
The empirically ordered lens will be close, but a reorder is often done
What are advantages of empirical fittings?
saves time sometimes
the lab selects the lens
pts prescription is the first lens you put on them
some companies actually encourage it for their GPs
if a pt only relays at the end of the exam they want contacts, its also beneficial
IMPORTANT: How should GPs be stored (long term)?
store them DRY because if we store them wet for a long time the solution will dry out and lead to a BASE CURVE CHANGE (warpage)!
How do you present corneal GPs to patients?
explain their condition
introduce GP lenses (‘awareness vs pain) (gas-perm v hard)
explain the benefits of GPs
briefly confront comfort
IMPORTANT: How can we make the initial fitting experience more comfortable for the patient? What are the advantages of doing that?
use a topical anesthetic and allow them to gradually experience lens awareness (15-20 mins) and the advantage is that it gives you time to evaluate the fluorescein pattern
IMPORTANT: Disadvantages of topical anesthetic
more staining from topical anesthetic use
may mislead the patient
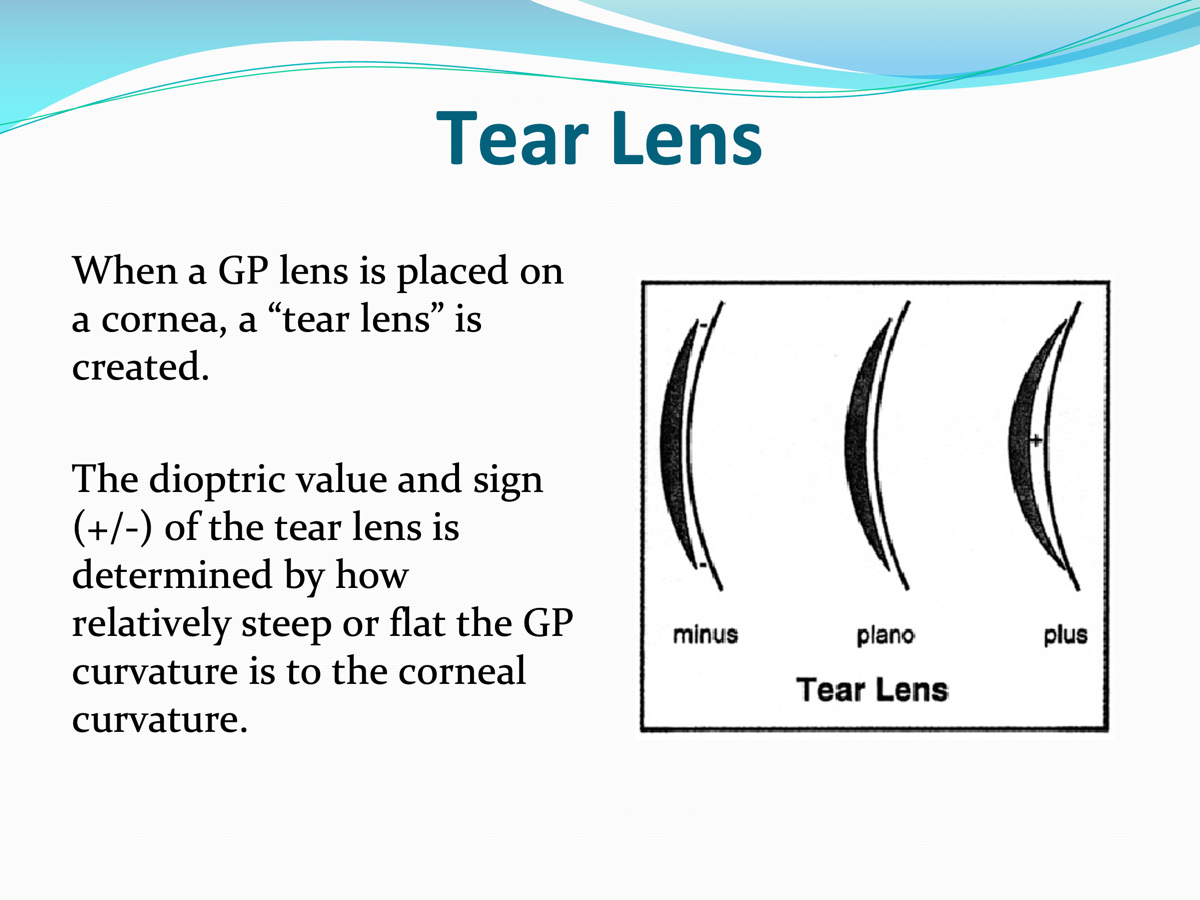
When a GP lens is placed on the cornea, what is created?
a tear lens
IMPORTANT: How is the tear lens determined?
the dioptric value and sign (±) is determined by how steep or flat the GP curvature is to the corneal curvature
IMPORTANT: What is SAM/FAP for?
The tear lens is created from the GP lens placement and what power must be added or subtracted to compensate for it
IMPORTANT: What is SAM/FAP?
STEEPER ADD MINUS
FLATTER ADD PLUS
IMPORTANT: Why do we add minus when the BCR is steeper than the cornea?
when the BCR is steeper a + tear lens is created and a - power must be added to compensate for it
IMPORTANT: Why do we add plus when the BCR is flatter than the cornea?
The BCR is FLATTER and a minus tear lens is created, so we add PLUS power to compensate for it
For a spectacle Rx: +3.00D and Keratometry: 43.25 D, what tear lens is created if you add 42.75D BCR GP lens on the eye? What contact lens power is needed to compensate?
-0.50D
+3.50
For a spectacle Rx: +3.00D and Keratometry: 43.25 D, what tear lens is created if you add 43.50 D BCR GP lens on the eye? What contact lens power is needed to compensate?
+0.25
+2.75
IMPORTANT: How do you calculate residual astigmatism?
CRA = TRA - ΔK
CRA = calculated residual astigmatism
TRA = total refractive astigmatism (@ corneal plane)
ΔK= central anterior corneal toricity
If the corneal Plane Rx: -3.00-1.25 x 180 and Keratometry: 42.75 @ 180; 44.00 @ 090. What tear lens is created if you place a 42.75D BCR GP lens on this eye? How would this affect your initial power selection?
plano and -1.25
the power selection is -3.00 D
If the corneal Plane Rx: -3.00-1.25 x 180 and Keratometry: 42.75 @ 180; 44.00 @ 090. What tear lens is created if you place a 42.25D BCR GP lens on this eye? How would this affect your initial power selection?
-0.50 and -1.75
-2.50
IMPORTANT: How do you do CRA for the pts whose refractive astigmatism and corneal astigmatism have similar axes?
CRA= TRA - ΔK
IMPORTANT: For patients whose refractive astigmatism and corneal astigmatism are 90 degrees apart
CRA= TRA + ΔK
What is the ideal pt for a spherical GP lens?
a pt with
-0.75 x WTR corneal astigmatism
-0.75 x WTR refractive astigmatism
similar axes
Why is that the ideal patient?
-0.75 x WTR corneal astigmatism
-0.75 x WTR refractive astigmatism
similar axes
movement would be up and down (along the steepest corneal meridian) using the flattest as a fulcrum
A -1.00 DS GP contact lens with a BCR of 44.25 D would correct both meridians! and Refractive astigmatism is corrected by the tear lens
How does a GP lens want to move ATR astigmatic cornea?
in the path of least resistance
nasal or temporal
with the blink (leading to decentration complications)
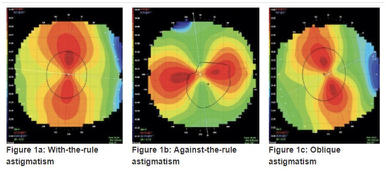
Which corneal astigmatism is preferable for a spherical GP lens?
WTR is preferred over ATR for a spherical GP lens
ATR can be fitted, just be aware of the movement (lateral(horizontal))
What are if the keratometry readings are spherical?
there is no corneal meridian to serve as a fulcrum (prop) and the lens can move all over
mainly displacing superior-temporally after the blink leading to GLARE complaints
also tucking under the upper lid to help keep it centered
IMPORTANT: What if the keratometry readings show high astigmatism?
it is acceptable to use spherical/aspheric GP lenses up to about 2 D of corneal astigmatism
around 2 D or more of corneal astigmatism the lens can rock too much and become uncomfortable
potential for FLEXURE
so consider a GP with a toric back surface
IMPORTANT: When would you consider using an aspheric back surface on a corneal, single vision, GP lens and why?
good for patients with 1.00-2.00 D of corneal astigmatism, because it’s a little more forgiving in the periphery at the 3 and 9 o’clock.
What are the two main corneal GP philosophies?
Lid attachment (larger >9.5 mm and fit flatter)
interpalpebral (smaller <9.5 mm and fit steeper)
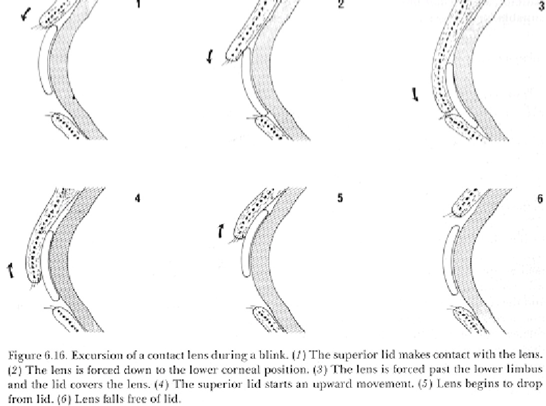
How do you decide between interpalpebral and lid-attachment?
let the lid be your guide (esp. upper lid)
What is the average fissure width?
9-11mm
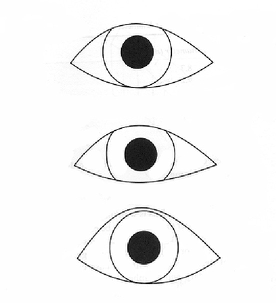
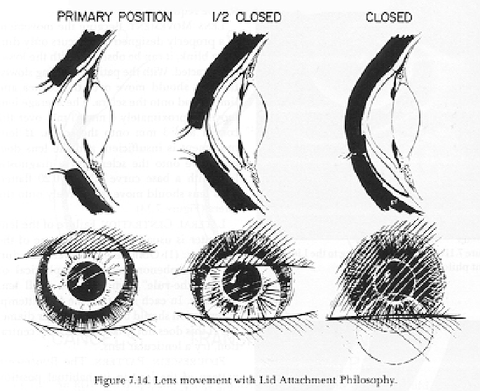
IMPORTANT: If the upper lid covers the superior cornea from 10-2 o’clock and the fissure width is normal, how should you fit the lens? (top picture)
lid attachment fit
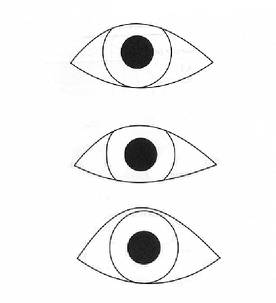
IMPORTANT: if there is a a narrow palpebral fissure, how should you fit the lens? (middle picture)
interpalpebral fit

A patient comes in looking like the lowest picture, their upper lid is at or above the limbus, how should you fit the lens?
interpalpebral fit because it won’t get lid attached.
What are some other reasons why one would choose lid attachment over interpalpebral fit?
lid attachment is more comfortable and tucked under the upper lid leading to less contact of the upper lid and lens edge
less corneal disruption at 3 and 9 o’clock
What does lid attached lenses cause more than smaller lenses?
corneal molding and distortion
What must the relationship between the OZD and pupil size be?
the OZD MUST be LARGER than the pupil size in DIM light. if not the pts will return and complain of flare at night and in dark environments
check pupil size and compare it to OZD
check for lens decentration (if not centered on the cornea pt will experience flare when the OZD nears the pupillary margin)
What is the center of gravity?
property that treats an object as though all of its weight were concentrated at one point
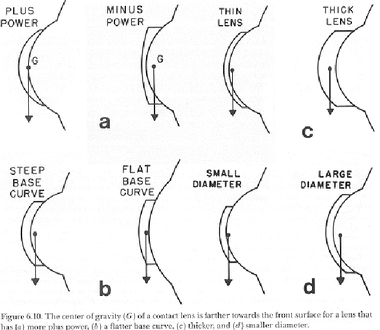
What is the exact position of the COG dependent on?
diameter
power
BCR
lens thickness
Where is the COG?
anterior surface or somewhere inside the lens
If the COG is anterior the lens has a higher tendency to
drop
If the COG is posterior the lens has a higher tendency to
to adhere (stick)
The COG can be moved anteriorly with smaller or larger diameter lenses?
smaller and this results in a lower lens position
The COG can be moved posteriorly with smaller or larger diameter lenses?
larger resulting in a higher lens position
Why do plus lenses tend to drop after the blink?
they are thicker and have a higher mass and lead to inferior decentration
What do minus lenses tend to do after a blink?
they are thinner and lower in mass than plus lenses so they stay with the upper lid (lid attached) or get pushed inferiorly when the upper lid hits the thick lens edge
The current trend is to fit larger OADs (9.6 mm or larger) to optimize initial comfort, where does the improved comfort come from?
less lens movement
less lid/lens interaction
good centration
What is the diameter selection OAD/OZD consideration?
The OAD should be 1.4 mm larger than the OZD to give room for application of peripheral curves (0.7 mm on each side)
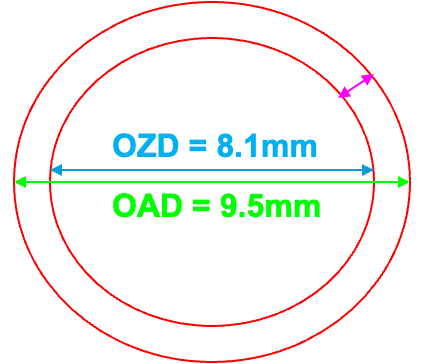
If the OZD of 8.1 is desired, what should the OAD ordered be?
9.5 mm
What do you change the OAD/OZD by for a clinically significant difference in fit?
Change the OAD/OZD by at least 0.3mm for a clinically significant difference in fit.
What is the BCR primary purpose?
to optimize the fitting relationship of contact lens to cornea
What are some factors affecting the BCR?
corneal curvature
desired lens to cornea relationship
observed fluorescein pattern
How do you convert D to mm?
337.5 (337.5/D=mm) or (337.5/mm = D)
What is the Base curve selection equation?
Initial BCR = Mean K - 0.50D
Why do we use -0.50 D?
adjustments for corneal asphericity by going flatter
When do we consider a bitoric?
if >2.00 D of corneal astigmatism
Find the initial base curve selection.
42.50 @ 162; 43.50 @ 072 (1.00D)
Mean K = (42.50 + 43.50) ÷ 2 = 86.00 ÷ 2 = 43.00D
Initial BCR = 43.00 - 0.50 = 42.50D (on “K”)
When fitting a spherical GP, we refer to fitting of the lens in relation to the
flatter k reading or “K”
larger lid attached = steeper lens
smaller interpalpebral lens = slightly flat lens
For every 0.5 mm change in the OZD; the BCR should adjust by?
0.25 mm
Increase the diameter by 0.50 mm, then
flatten the BCR by 0.25 mm
decrease the diameter by 0.50 mm, then
steepen the BCR by 0.25 mm
What do you change the BCR by to have a significant effect on the lens?
0.50 D
What is tricurve vs tetracurve?
tricurve is two peripheral curves while tetracurve is three peripheral curves
tricurve: Base Curve Radius, Secondary Curve Radius, and Peripheral Curve Radius
tetracurve: Base Curve Radius, Secondary Curve Radius, Intermediate Curve Radius and Peripheral Curve Radius
Which one do you select a smaller OAD for? Tricurve or Tetracurve
tricurve
__________ is always larger than edge clearance, why?
Edge lift is always larger than edge clearance because the cornea is aspheric.
lift = lens
clearance = cornea
What is the appropriate amount of AEL?
0.10-0.12 mm which results in 0.50 mm wide band of fluorescein around the lens periphery.
How do you increase the edge lift of a lens?
flatten the peripheral curve radius
increase the peripheral curve width
What has more of an effect on the edge of lift?
Changing the PCW or PCR has more of an effect on edge lift than changing the secondary or intermediate curves.
IMPORTANT: In order to make a clinically significant change what do we change the PCR and PCW by?
PCR by at least 1.0 mm
PCW by at least 0.2 mm
What are consequences of too little edge lift?
difficult to remove the lens
trapping of debris
increase risk of cornea adherence
VLK 3 and 9 o’clock staining
If you have too much edge lift you may see?
3 and 9 o’clock staining ‘wicking of tears at lens edge, decreased blink rate
lens decentration
dislodging
decrease in comfort
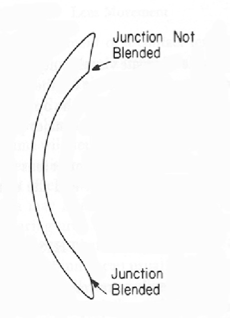
IMPORTANT: What is a blend?
allows more tear flow and gets rid of a sharp edge (causes metabolic debris, prevent tear flow, be uncomfortable)
IMPORTANT: What is the minimum blend that can be ordered to enhance debris removal?
Medium (B)
IMPORTANT: what is the blend ordered most of the time?
heavy (C) blend is mostly ordered
A thin lens is more likely to
position superiorly
warp
flex
a thick lens is more likely to
decenter inferiorly
lead to complications (injection, corneal desiccation, variable vision)
How do you decrease the risk of flexure?
At least a 0.03mm change in center thickness should to be made for a clinically significant change.
What has more of an effect on mass than O2?
in GPs, center thickness has more of an effect on mass than O2, so a thicker lens will decrease O2 by about 1% but more mass 24%
If you have a patient complaining of discomfort with GP lenses and you can’t figure out why, what may be the solution?
edge polishing (edge design and shape) may be the primary variable affecting comfort and lens positioning
IMPORTANT:
Edge thickness and center thickness are approximately equal at -2.00 D (standard lens design).
a minus lenticular can be added to do what to edge thickness?
increase edge thickness
A minus lenticular design is recommended with minus powers between -1.50 and plano and on all plus powers.
When should a plus lenticular be considered?
for a minus lens power of -5.00 D or greater
decreases edge thickness and minimizes inferior decentration
IMPORTANT: What is plasma treatment?
A Super cleaning of the lens surface! using radio waves and oxygen increasing the attraction of liquids. Making lens more wettable, improving comfort, and reducing fogging. Do not use GP polish, anything abrasive or alcohol based
only on new lenses
ships wet this time ;)
last 6 months

What is tangible Hydra-PEG?
polymer coating for CL
improves wettability, lubricity, water retention, minimizes protein and lipid deposits
no alcohol or abrasive cleaners or tap water

What is needed by the lab to order a lens?
lens type
BCR
power
What is the ultimate goal in ordering a lens?
moves vertically with a blink
centers after a blink
not harmful to the cornea
comfortable
good vision
What is the lacrimal lens equation?
CLP = CPR - OR - LLP
CLP = Contact Lens Power
CPR = Corneal Plane of Refraction
OR = Over-Refraction
LLP = Lacrimal Lens Power
Is PMMA good for a GP?
no, its not O2 permeable and can cause edema
refit with a low-Dk FSA material allowing for more gradual corneal rehab process and pts will be less likely to damage the lens when cleaning
What is the most popular spherical GP design at NSUOCO?
megathin Essilor