lecture homeostasis
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
define homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment
positive feedback
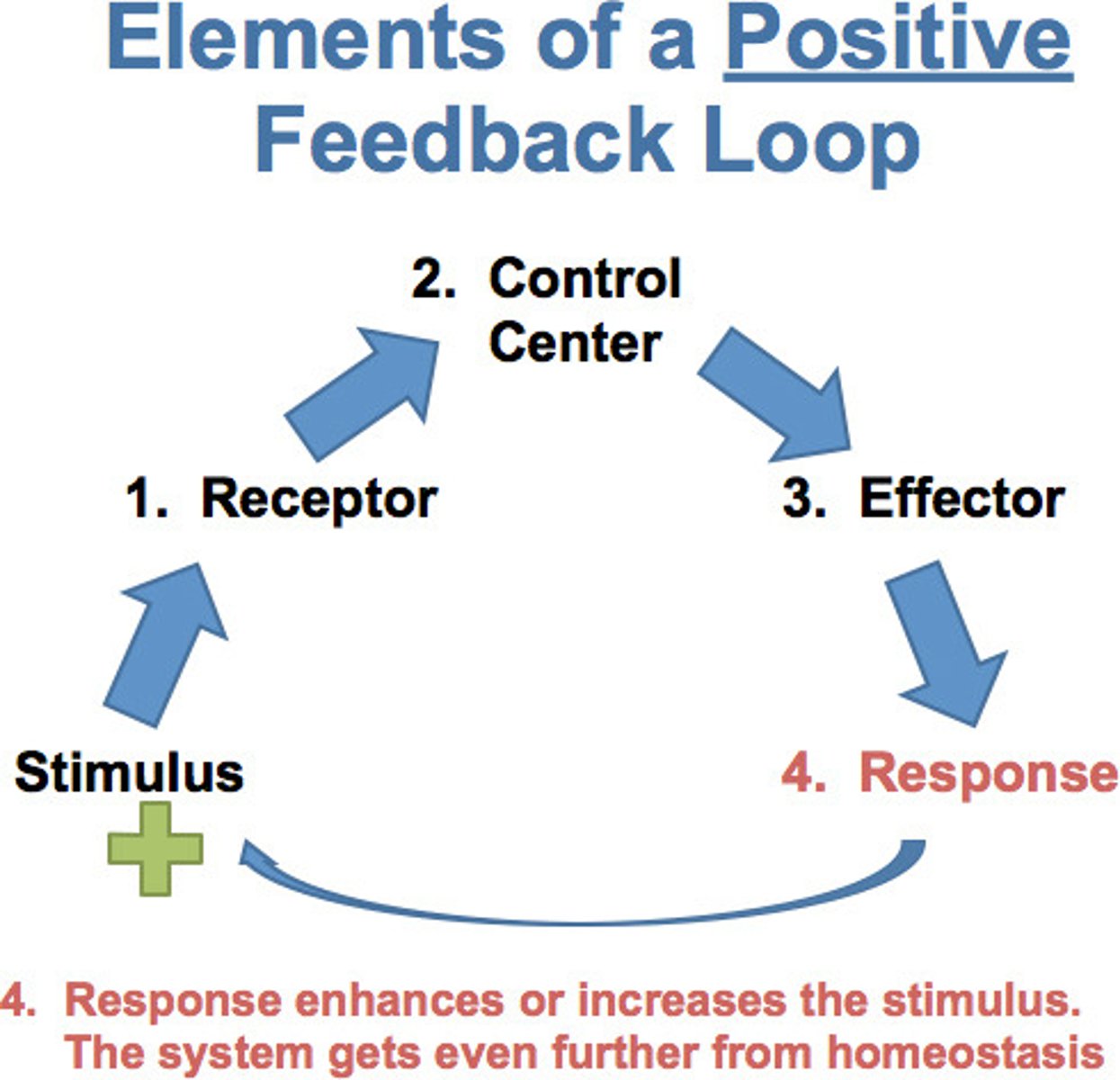
Feedback that tends to magnify a process or increase its output.
negative feedback
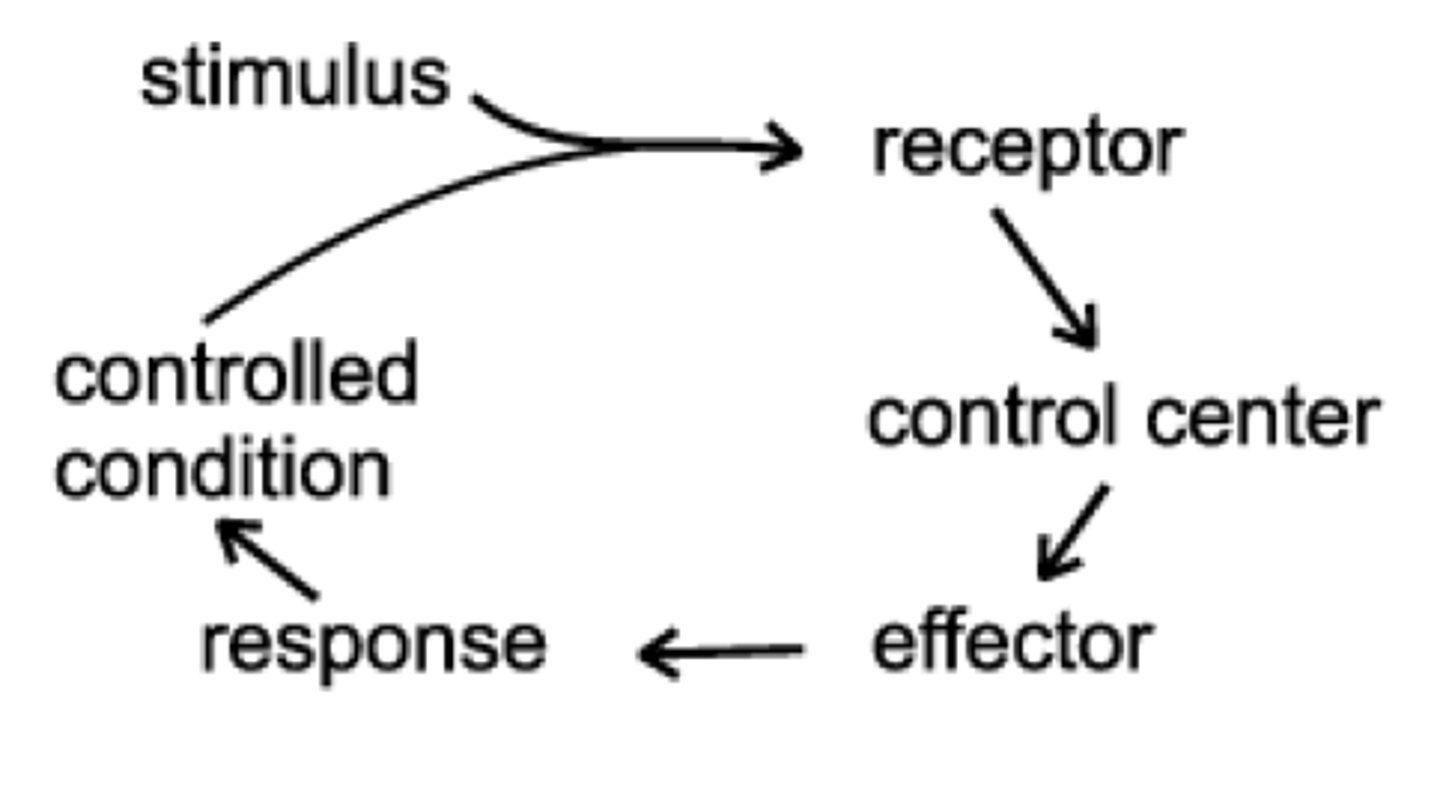
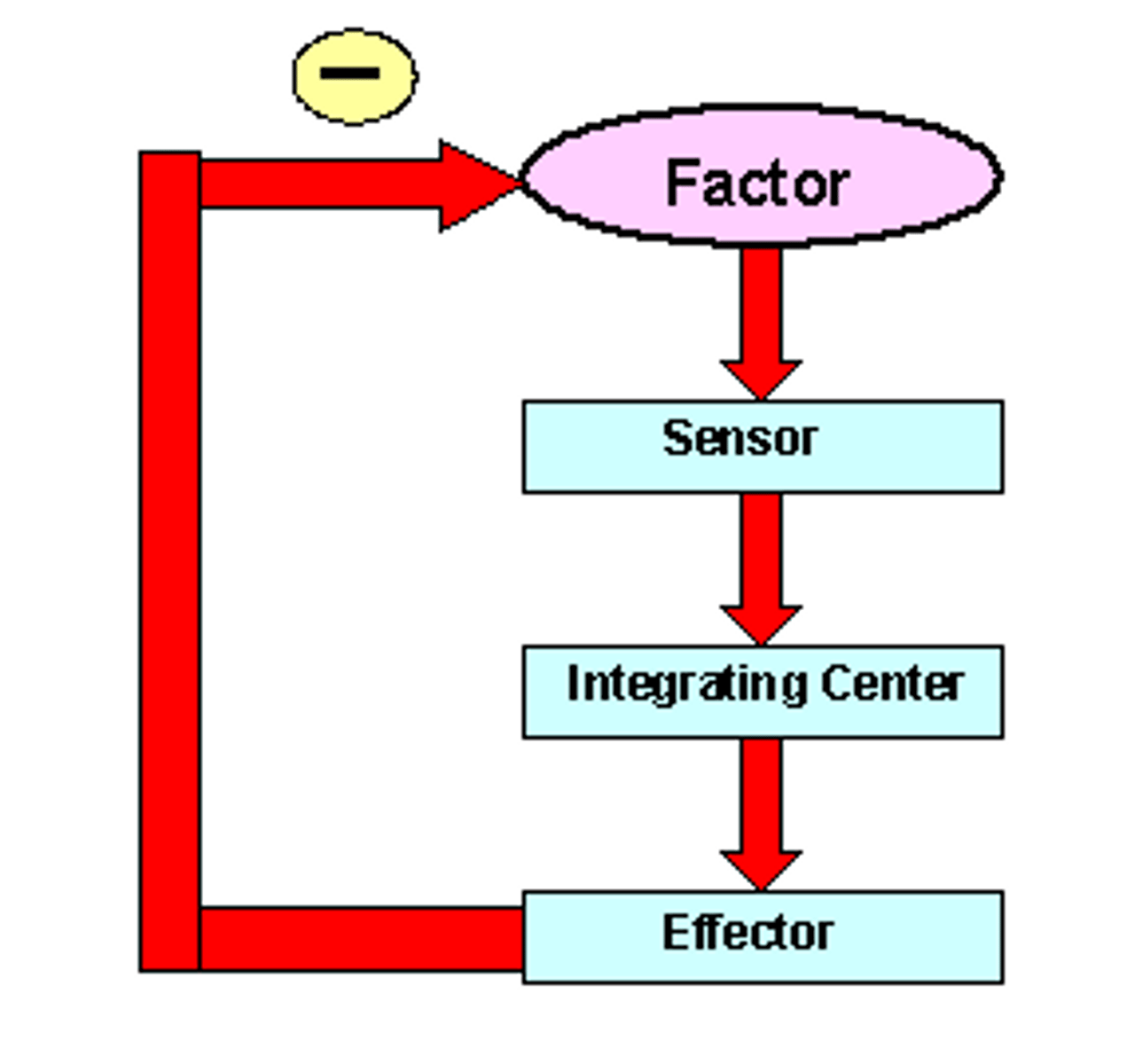
A type of regulation that responds to a change in conditions by initiating responses that will counteract the change. Maintains a steady state.
Homeostatic inbalances result in?
1. Disorder: Any abnormality of structure or function
2. Illness characterized by signs and symptoms
set point
the point at which one's body tries maintain
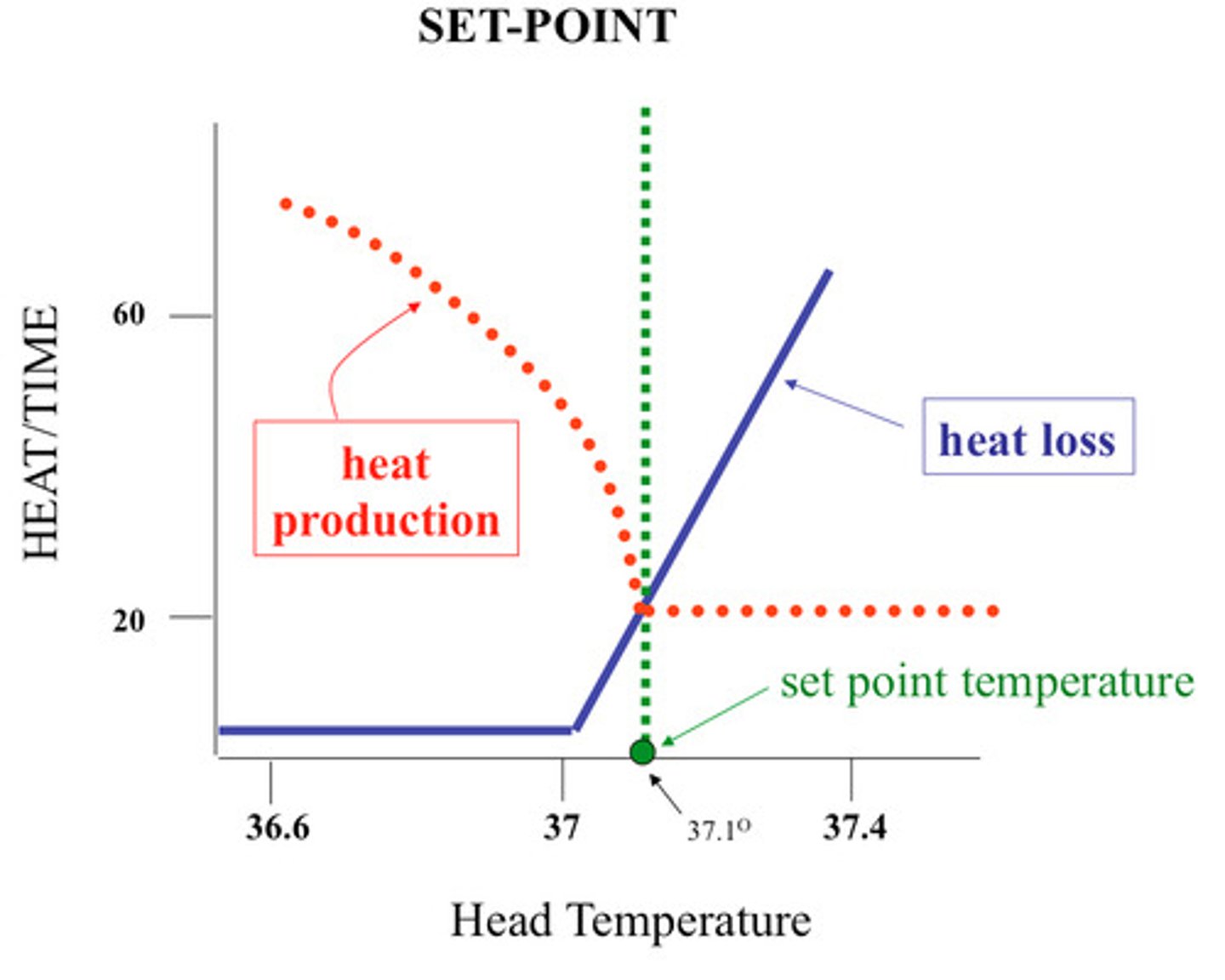
normal range
range of values around the set point that do not cause a reaction by the control center
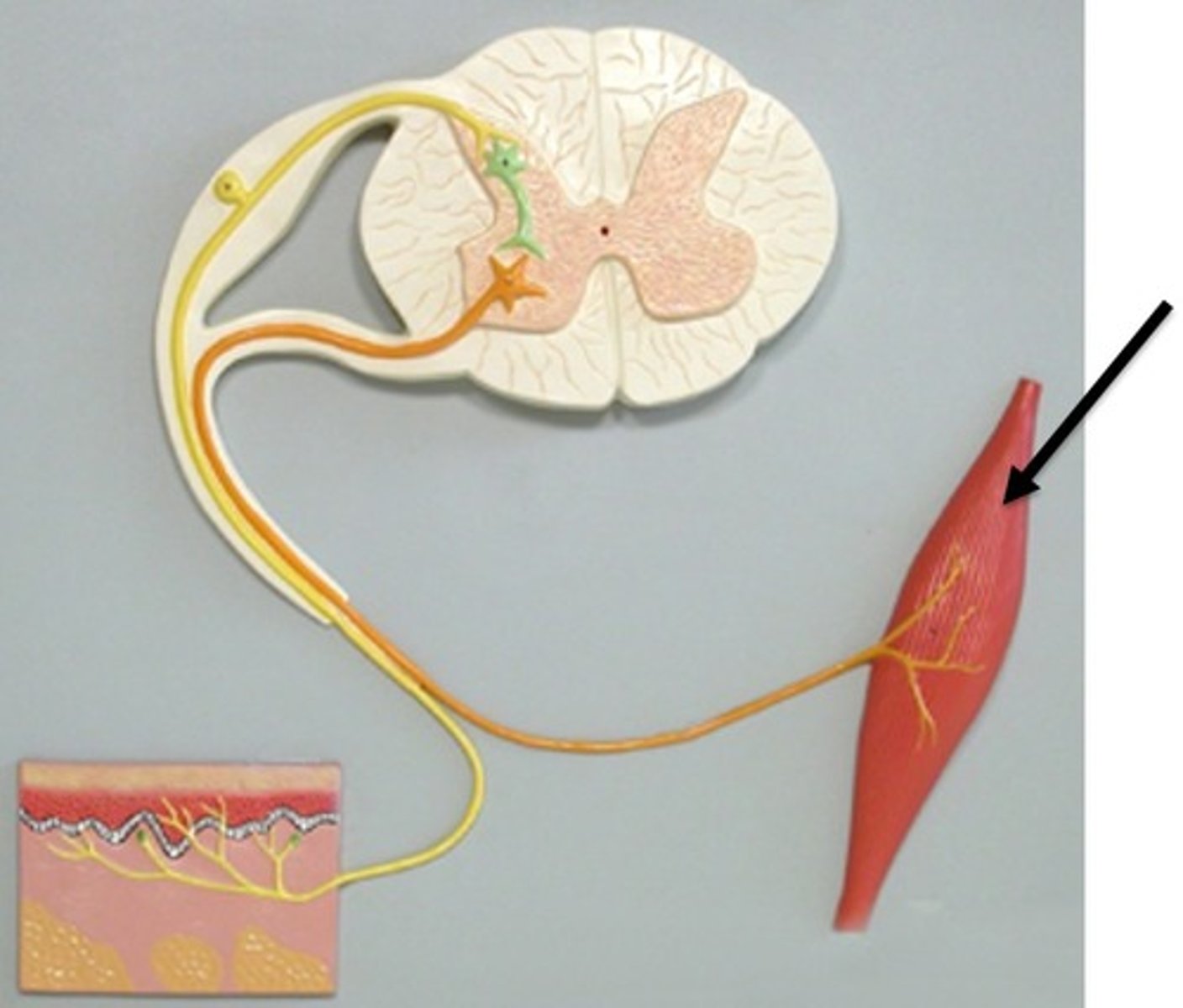
effectors
cause responses that alter conditions in the internal environment
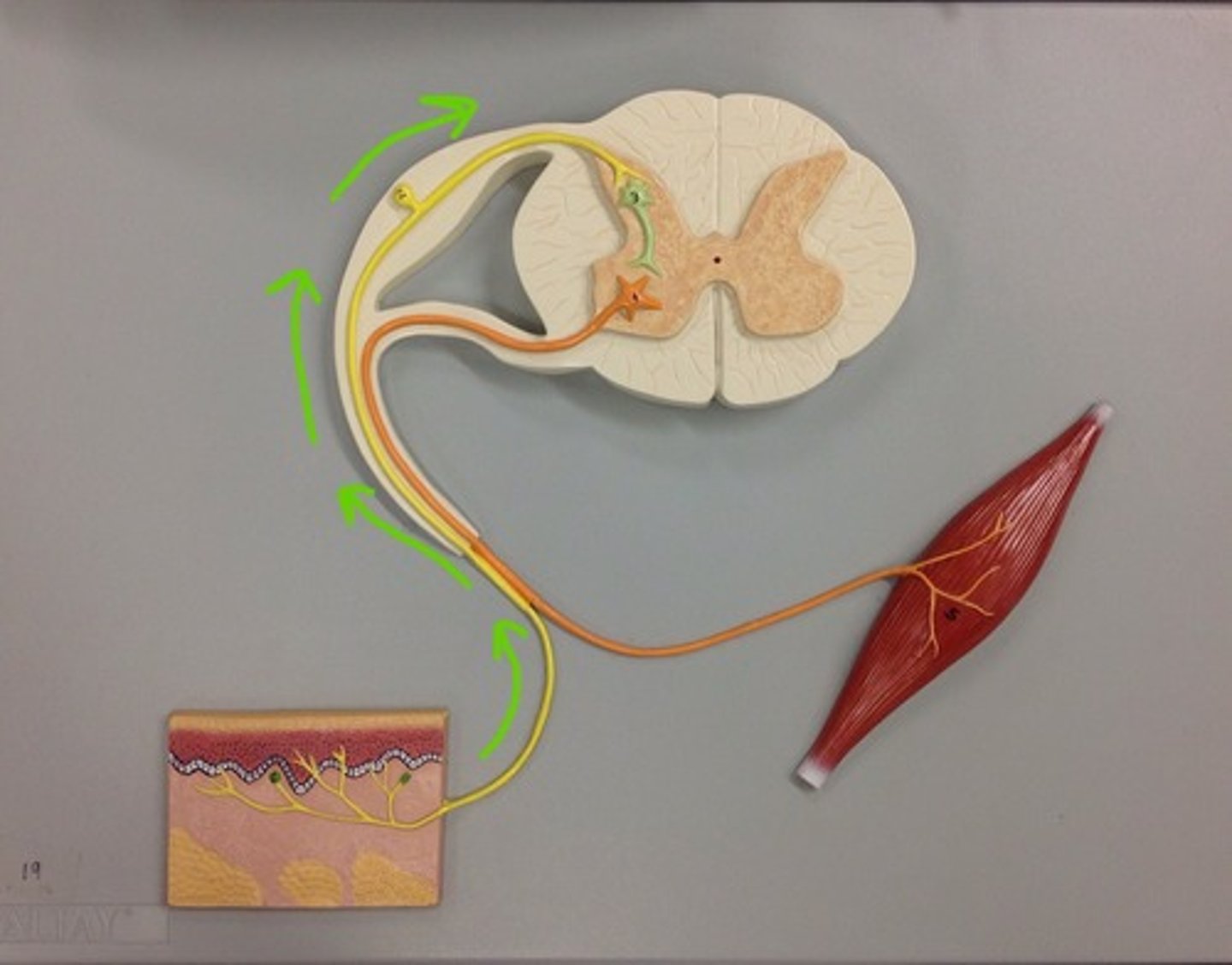
affector
a neuron that transmits sensory information
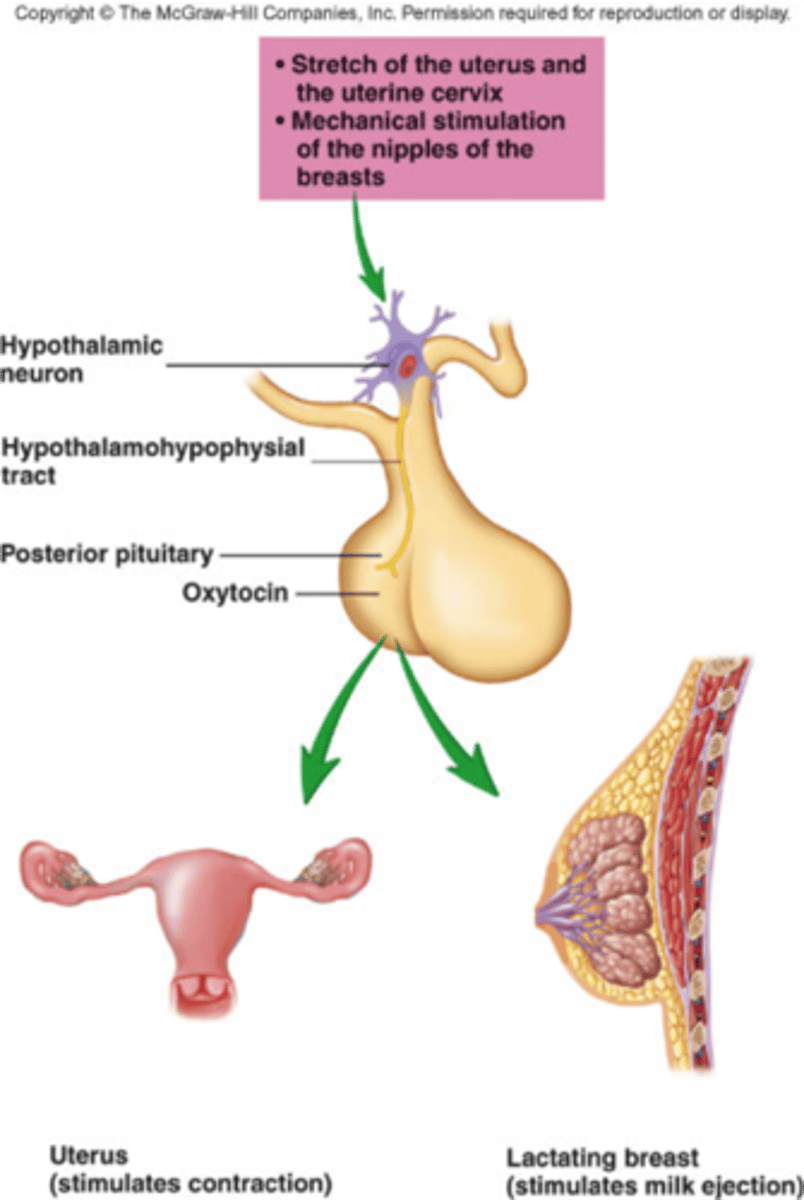
explain positive feedback loop of childbirth
When the fetus stimulates the placenta to make prostaglandins, the prostaglandins stimulate the placenta smooth muscle to contract, contractions push the baby's head against the cervical opening at the base of the uterus, activating pressure receptors, engaging a nerve cell based process, releasing oxytocin from the posterior pituitary, stimulating more contractions, pushing the baby's head more strongly against the cervical opening. Overall, increasing cervical pressure increases activation of pressure receptors, increases stimulation of uterine contractions through prostaglandin production from placenta and oxytocin from posterior pituitary. Diagram for this in notes.
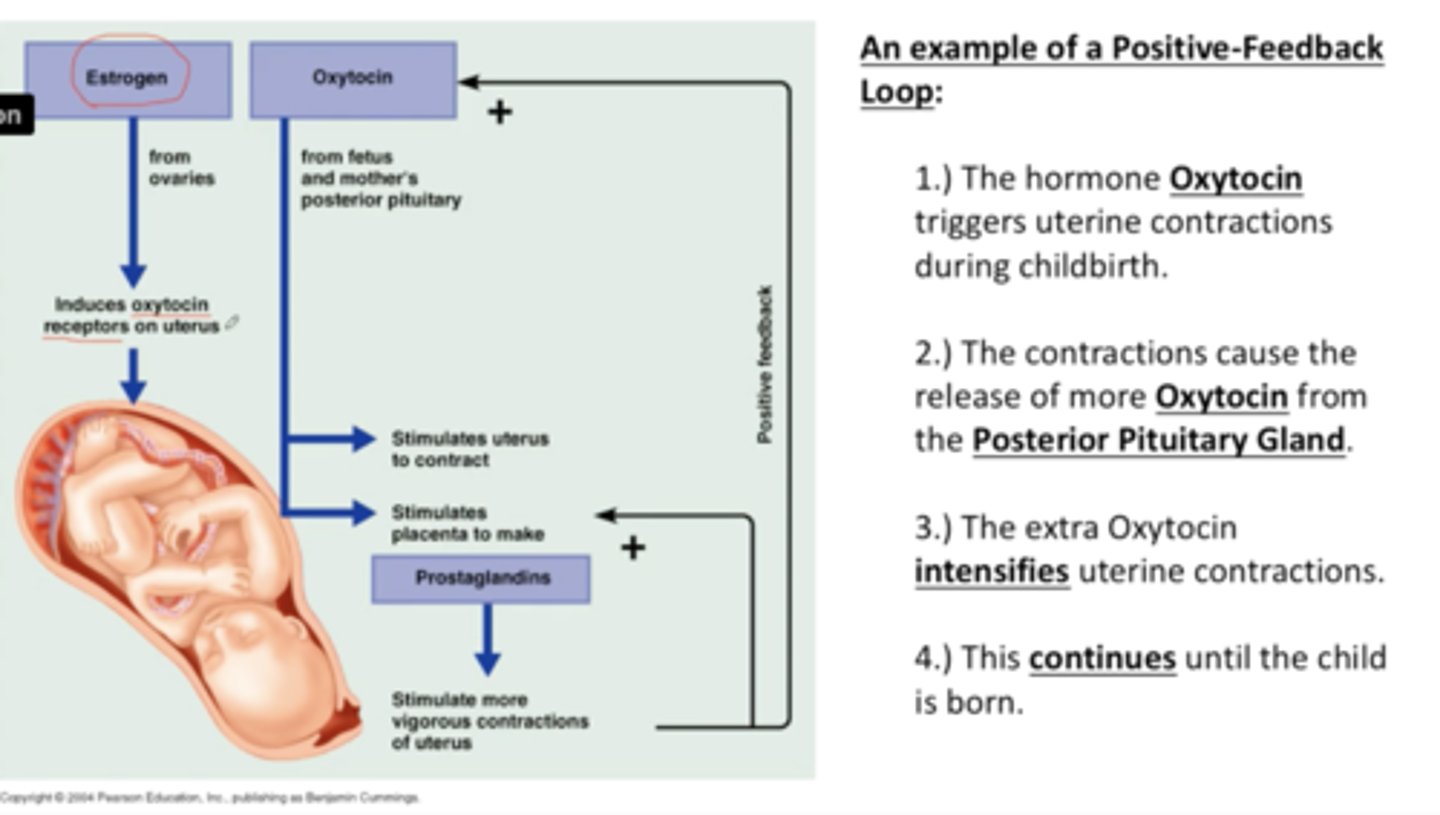
pitocin
Hormone, induces labor
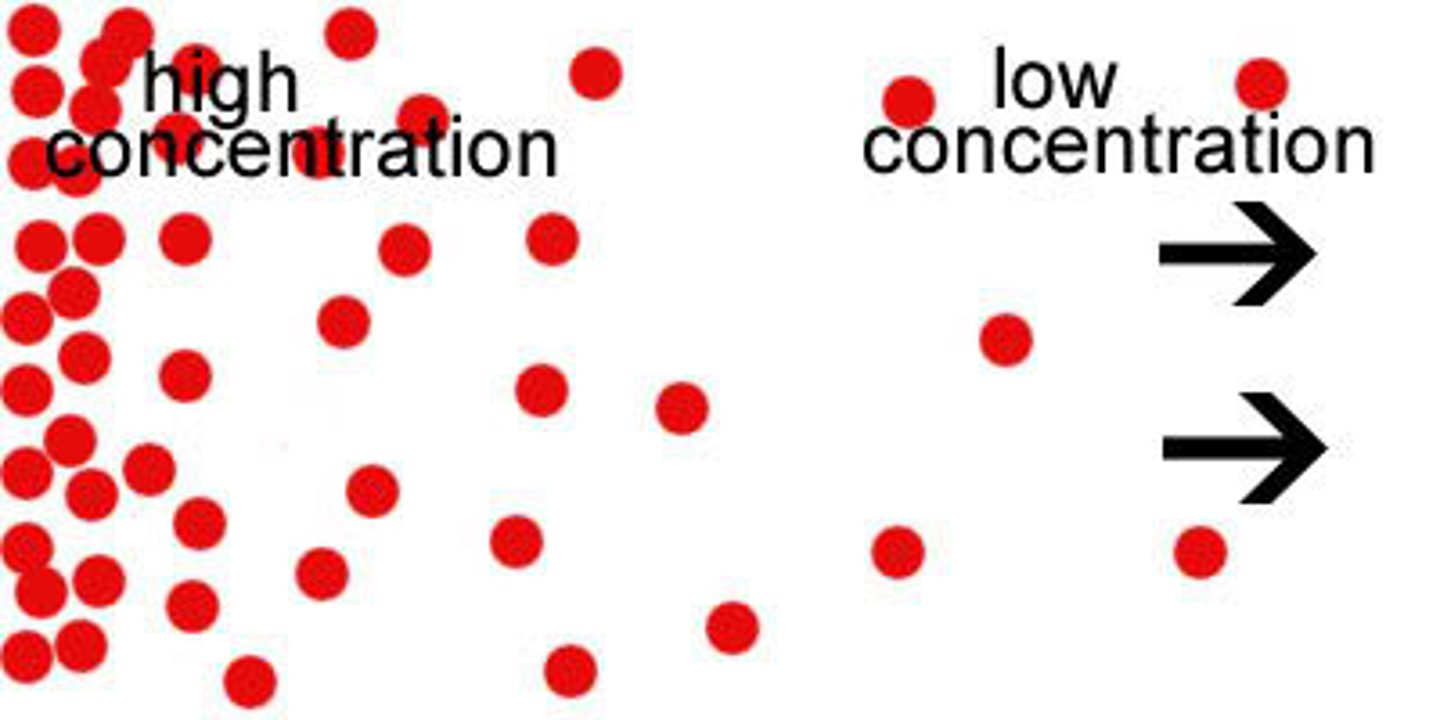
concentration, thermal or pressure gradient
different values in two different loctions
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.

Independent variables in the homeostasis lab
exercise or no exercise
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the variable that may change in response to manipulations of the independent variable.

what was the dependent variables in the homeostasis lab
changes in carbon dioxide and oxygen
Was CO2 consumed or produces in cell respiration
produced
Is oxygen consumed or produced in cell respiration
consumed
When graphing your data in the homeostasis lab was the change in oxygen
positive or negative
negative ( consumed )
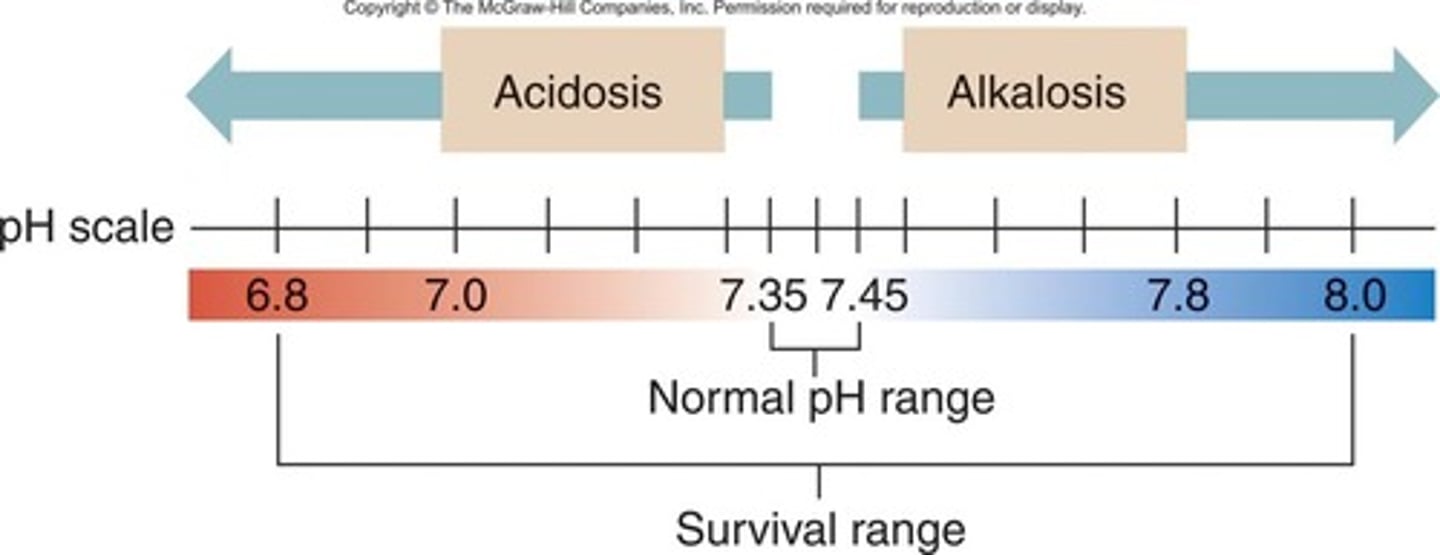
the homeostatic set point for the bodies pH is
7.4
When CO2 mixed with water what is produced
carbonic acid
What happens to the pH as more carbon dioxide is produced by the body
becomes more acidic
How does the body maintain pH by controllng CO2 levels in the body
breathe out more ( increase respiration )
Where are the pH detectors in the blood located
carotid arteries
10 minutes after exercise what happens to the CO2 production levels
less CO2 is produced, respiration slows
10 minutes after exercise what happens to the O2 consumption
less oxygen is consumed , respiration slows
Which of the four tests is best to use to detect glucose?
Benedict's Test
What color change occurs in the benedict indicator in the presence of glucose ( blue no glucose )
orange / red
What indicator is used to test for starch
IKI ( iodide potassium Iodine ) turns from brown to black or violet
When blood glucose is high , what hormone is produced
insulin
What organ produces insulin
pancreas
What effect does insulin have on glucose
lowers blood sugar by increasing uptake by cells and causes the liver to convert blood sugar to glycogen
what hormone is released when the blood sugar is low
glucagon
What organ secrete glucagon
pancreas
what effect does glucagon have on blood sugar
increases blood sugar by breaking down glycogen into glucose