APES Midterm Study Guide
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
terrestrial (land) biomes
includes rainforests, tiagas, temperate deciduous forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundras
aquatic biomes
major biomes include rivers, lakes, and wetlands (all freshwater) and ocean zones
what defines biomes
annual temp. and avg. precipitation
threats to terrestrial biomes
warming climate causes biomes to shift locations
littoral zone
shallow water with emergent plants
limnetic zone
where light can reach, no rooted plants only phytoplankton
profundal zone
too deep for sunlight (no phots.)
benthic zone
murky bottom where inverts (bugs) live, nutrient-rich sediments
coral reef zone
warm shallow waters beyond the shoreline; most diverse biome on earth
intertidal zones
narrow bands of coastline between high and low ride, organisms must be adapted to survive crashing waves and direct sunlight
open ocean
low productivity/area as only algae and phytoplankton can survive in most of the ocean
threats to aquatic biomes
overfishing, pollution from runoff, and deforestation allowing more sediment to erode into bodies of water
carbon cycle
movement of molecules that contain carbon (CO2, glucose, CH4) between reservoirs
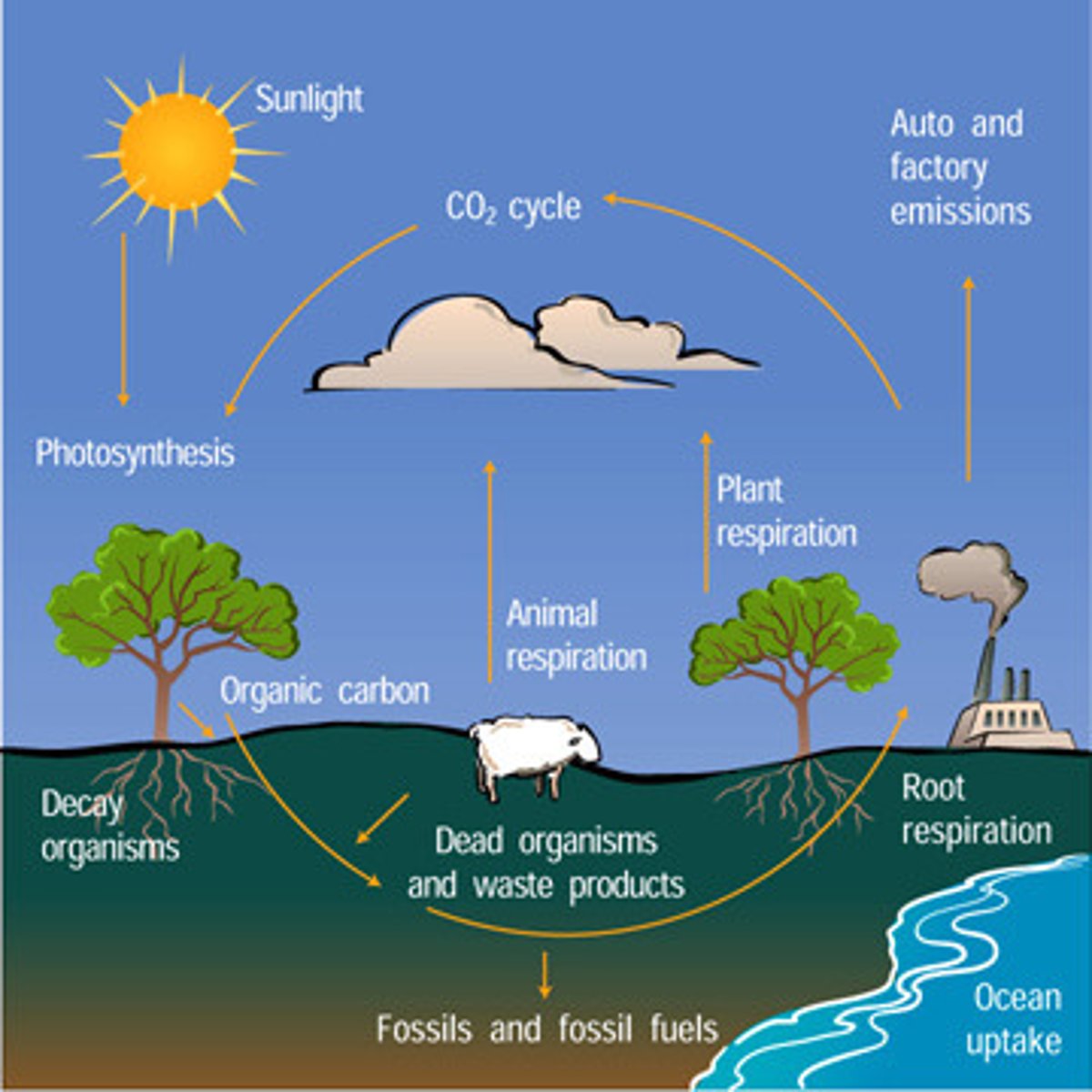
carbon sink
reservoir that takes in more carbon than it releases (ex. ocean, plants, forests, photosynthesis)
carbon source
reservoir that releases more carbon than it takes in (ex. fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, cellular respiration)
nitrogen cycle
movement of N containing molecules between reservoirs
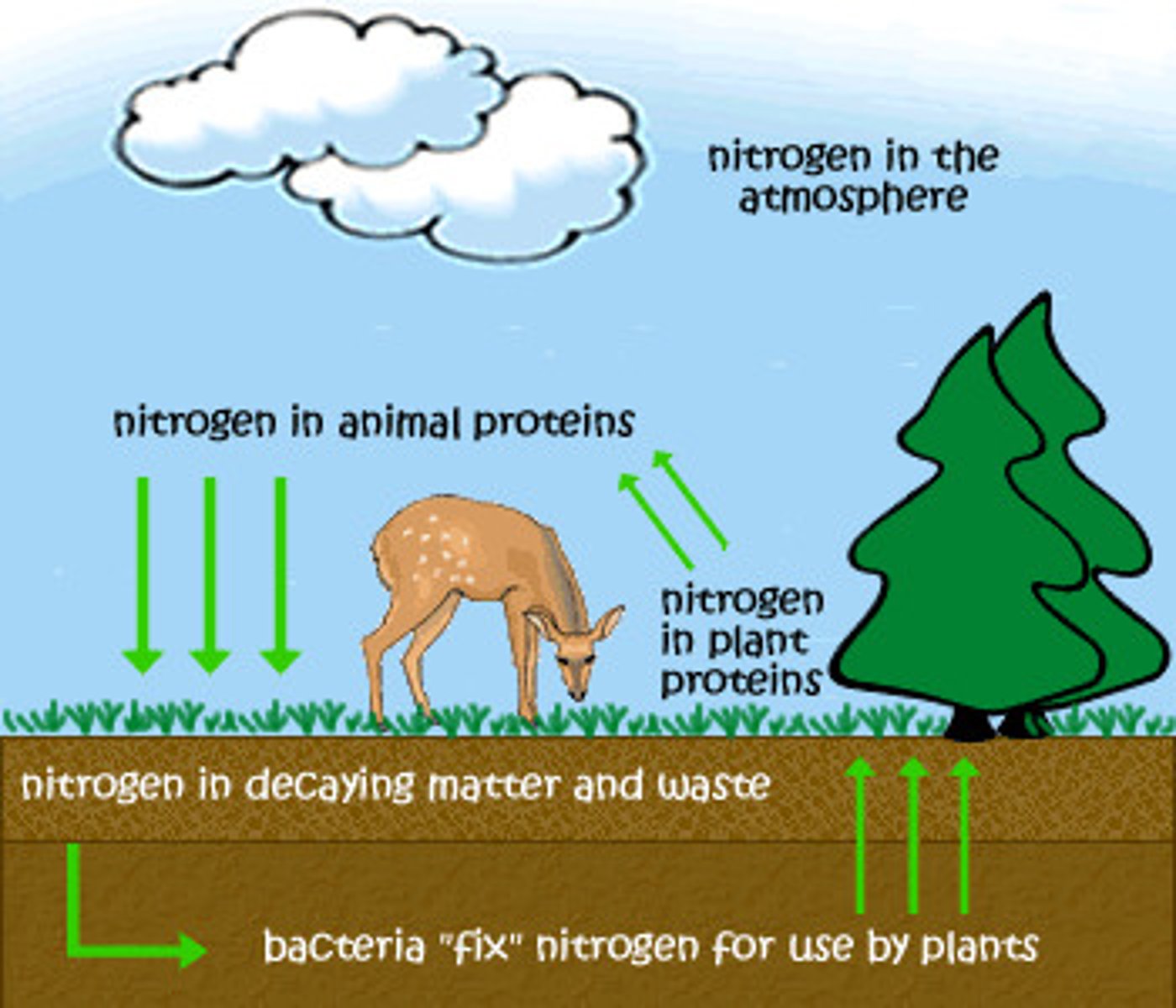
nitrogen fixation
process of N2 gas being converted into useable ammonia or nitrate
assimilation
plants and animals taking in N and incorporating it into their body
ammonification
decomposers convert waste back into ammonia and return it to the soil
nitrification
conversion of ammonium into nitrate by soil bacteria
denitrification
conversion of N into gas and return to the atmostphere
phosphorus cycle
movement of P atoms and molecules between reservoirs
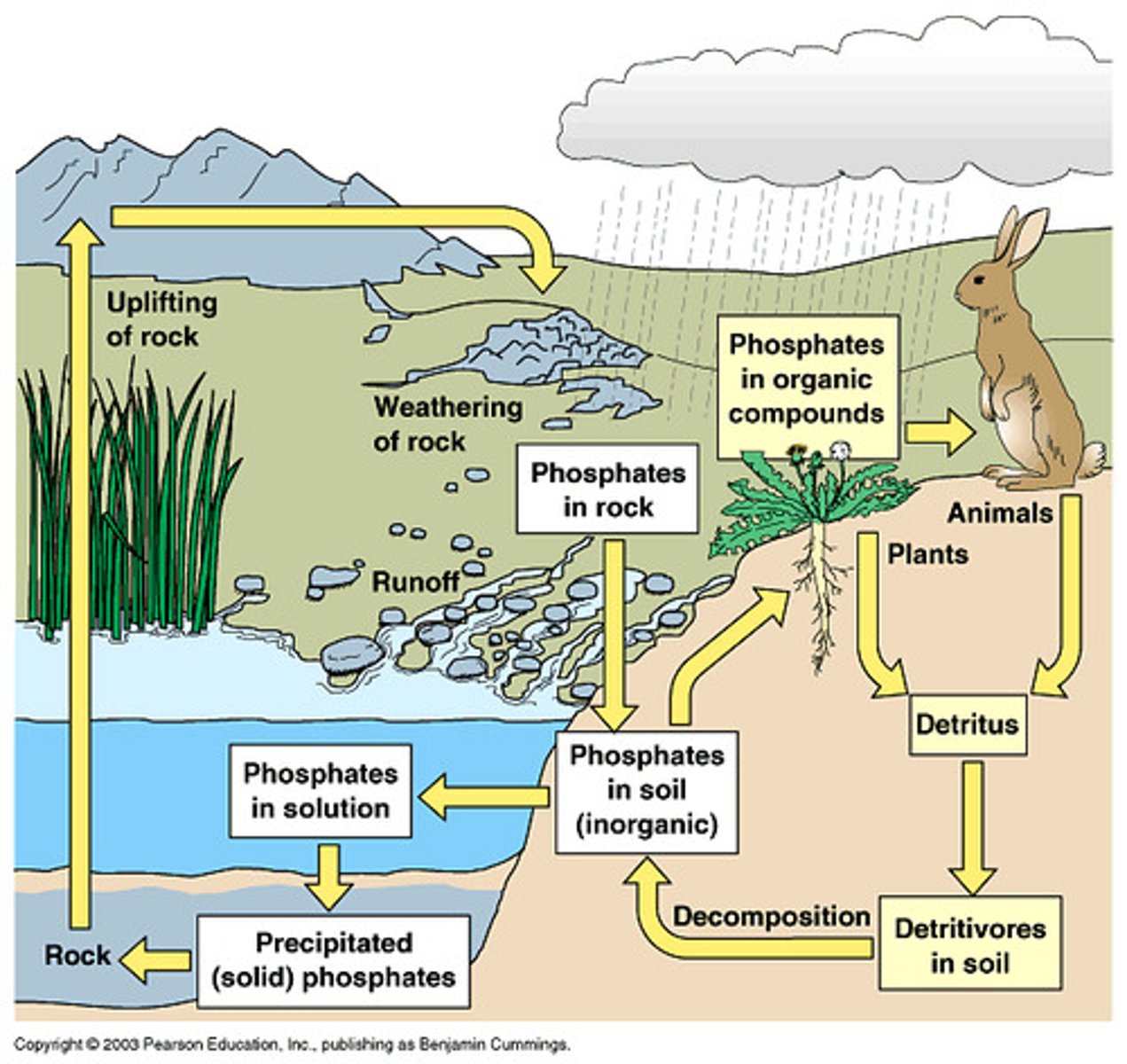
phosphorus sources
weathering of rock, wind and rain break down rock and phosphate is released and dissolved into water
assimilation and excretion/decomposition
P is absorbed by plant roots; animals assimilated by eating plants
hydrologic (water) cycle
movement of H2O (in different states) between reservoirs, energy from sun drives the H2O cycle, reservoirs include ocean, groundwater, and atmostphere
transpiration
water leaving a surface of a body of water
runoff and infiltration
precipitation (rain) either flows over earth's surface into a body of water (runoff) or trickles through soil down into groundwater aquifers (infiltration/percolation)
ecology
relations of organisms to one another and their physical surroundings
photosynthesis
plants, algae, phytoplankton, carbon sink because it removes carbon from atmosphere and stores carbon in glucose molecules
cellular respiration
done by plants and animals to release stored energy, uses O2 to break glucose down and release energy, carbon source because it releases CO2 into the atmosphere
trophic cascades
triggered when a top predator is added or removed from the ecosystem and causes population changes within the ecosystem because of it
biotic factors
everything living in an ecosystem (animals, plants)
abiotic factors
non-living things in an ecosystem (water, air, rocks)
10% rule
in trophic pyramids only about 10% of the energy from one level makes it to the next level; the other 90% is used by the organism and lost as heat
net primary productivity
also known as NPP; the amount of energy (biomass) leftover for consumers after plants have used some for respiration
gross primary productivity
also known as GPP; the total amount of sun energy that plants capture and convert (compare to total paycheck without taxes)
species richness
the total number of different species found in an ecosystem
eveness
a measure of how all the individual organisms in an ecosystem are balanced between the different species
higher biodiversity
usually caused by a higher ecosystem/population health
interspecific competition
occurs between individuals of the different species
intraspecific competition
occurs between individuals of the same species
predator adpations
could include sharp teeth, claws, quick moving
prey adaptations
camouflage, mimicry, defensive structures such as shells
mutualism
relationship that benefits both organisms
commensalism
relationship that benefits one organism and doesn't impact the other
parasitism
one organism lives on and feeds off another organism
primary succession
starts from bare rock in an area with no soil. Moss and lichen spores carried by wind grow directly on rocks, common on volcanoes and glacier retreats
secondary succession
starts from already established soil, in an area where a disturbance (fire/tornado) occurred
invasive species
animals or plants from another region that don't belong in their new environment
keystone species
strongly interacting species that have a large impact on their ecosystems relative to their abundance
generalist species
a species able to thrive in a wide variety of environmental conditions and use a variety of resources
specialist species
can only live in specific habitats, and eat specific food sources
rule of 70
the time it takes (in years) for a population to double is equal to 70 divided by the growth rate (doubling time)
k-selected species
have a high survivorship early in mid life due to high parental care, high survivorship in mid life due to large size and defensive behavior, rapid decrease in survivorship in late life due to old age, mostly mammals, have few offspring, slow pop. growth
r-selected species
have many offspring with little to no parental care, shorter lifespan, generally reproduce many times throughout lifespan, includes insects, fish, plants
density-dependent factors
factors that influence pop. growth based on the size of the population (ex. food, competition, habitat, water)
density-independent factors
factors that influence pop. growth (ex. natural disasters)
carrying capacity
the maximum number of individuals in a population that an ecosystem can support (based on line of resources)
demographic transition
a model showing how a nation's population, birth, and death rate are historically correlated when transitioning from agrarian to industrialized
watersheds
all of the land that drains into a specific body of water (river, lake, etc.), divided by ridges of land; vegetation, soil composition, and slope play a large role in how watersheds drain
human impacts on watersheds
nutrient pollution causes eutrophication (algae blooms): runoff causes excess nutrients to end up in water; endocrine disrupters (from sewage treatments), sediment pollution increases turbidity
O-horizon
organic; plant roots, dead leaves, and animal waste on top of soil, provided nutrients and limits H2O loss
A-horizon
topsoil, layer of hummus (decomposed organic matter) and minerals, most biological activity happens here (earthworms, soil microbes)
B-horizon
subsoil, lighter layer below topsoil, mostly made of minerals, with little to no organic matter, contains some nutrients
soil formation (from below)
weathering of parent material produces smaller, and smaller fragments that make up geological part of soil, sand, silt, and clay
soil formation (from above)
breakdown of organic matter, adds hummus to soil, erosion deposits soil particles from other areas adding to soil
sand
largest particles, highest porosity and permeability
silt
in between clay and sand
clay
smallest particle size, lowest porosity and least permeable
divergent plate boundary
plates move away from each other, rising magma plumes force plates apart, forms mid-oceanic ridges, volcanoes, seafloor spreading and rift valleys
convergent plate boundary
plates move towards each other, leads to subduction (one plate being forced beneath another), forms mountains, islands arcs, earthquakes, and volcanoes
transform boundary
plates slide past each other in opposite directions, forms earthquakes
windward side
warm, moist air from ocean hits "windward" side of the mountain, rises, cools (condensing H2O vapor and causing rain) this leads to lush, green vegetation in the area
leeward side
dry air descends down "leeward" side of mountain, leads to air (dry) desert conditions
troposphere
change (weather), most dense layer, contains most of the atmosphere's gas molecules, temp. decreases as air gets further from warmth of earth's surface
stratosphere
less dense, ozone layer is found here, absorbs UV-B and UV-C rays, temp increases because top layer is warmed by UV rays
mesophere
middle, very low density, temp decreases because density decreases leaving fewer molecules to absorb sun
thermosphere
therm = hottest temp, absorbs harmful x-rays and UV radiation, northern lights appear here, temp increases due to highly energetic solar radiation
exosphere
outermost layer that merges with space, exit, no relationship between temp and altitude
el nino
caused by weakened trade winds that then reverse (west to east), warms equator current and brings heat and percip. to Americas, cooler drier upwelling off SA coast, high pressure in west pacific, low pressure in east specific
la nina
caused by stronger that normal trade winds (winds still blow east to west), increased upwelling off SA, cooler conditions, extra good fisheries, warmer and rainier than normal in Australia and SE asia
tragedy of the commons
individuals will use shared/public resources (must be public resource) in their own self interest, degrading (or overuse, deplete, or use up) them. Examples include overgrazing, overfishing, water and air pollution, overuse of groundwater
solutions for tragedy of the commons
private land ownership (individual or gov.), fees or taxes for use (ex. permits for grazing, logging, or fishing), taxes and fines
surface mining
removal of overburden to access ore near surface, methods include open pit, strip mining, mountaintop removal (which is especially damaging), and placer. Causes erosion, habitat loss, stream turbidity, increases particulate matter in air
mine reclamation
the process of restoring land to the original state after mining has finished; fill in empty mine, restore contours and land, return topsoil, remove tailings, replant native plants
acid mine drainage
one environmental impact of mining; rainwater reacts with sulfur-containing rock to form toxic sulfuric acid, lowers pH of water, making toxic metals like mercury and aluminum more soluble in water sources (this kills aquatic org.)
clearcutting
cutting down all the trees in a specific area, usually so the land can be used for agriculture
soil erosion
caused by loss of stabilizing structure, removes soil and nutrients
increased soil and stream temp
loss of tree shade causes temp to increase, warm water = less oxygen
flooding and landslides
caused by logging machinery compacts soil, increased sun dries soil, decreased water holding capacity
CAFO
concentrated animal feeding operation; create massive amounts of waste that must be stored in manure lagoons that can be flooded by heavy rain and contaminate nearby water
monocropping
growing one single species of crop, this increases soil erosion (crops are harvested all at once and soil is left bare) and decreases habitat diversity for species in the area
tiling
mixing and breaking up soil with machines, increases erosion by loosening topsoil, loss of organic matter and topsoil nutrients overtime, increases pollutants and sediments in nearby water
slash and burn
clearing land for agriculture by cutting trees and burning them, has the same negative impacts as clearcutting and releases CO2 into the air
free range grazing
alternative to CAFOs; positives: no need for antibiotics, doesn't require production of corn feed for animals, waste is dispersed over land naturally; negatives: more expensive to consumer
overgrazing
can cause desertification: soil is so compacted it can't hold water, can be solved by rotational grazing