Biomolecules & Chemistry
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/141
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
1
New cards
Compounds
2 or more elements chemically combined (bonded) in a definite ratio
2
New cards
Organic Compounds
- contain carbon and hydrogen (sometimes oxygen)
- ALWAYS covalent bonds
- form large/complex molecules
- make up & made by living things
- main nutrients of life: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), nucleic acids, and proteins
- ALWAYS covalent bonds
- form large/complex molecules
- make up & made by living things
- main nutrients of life: carbohydrates, lipids (fats), nucleic acids, and proteins
3
New cards
Inorganic Compounds
- do not contain carbon & hydrogenTOGETHER
- ionic or covalent
- not large/complex
- ionic or covalent
- not large/complex
4
New cards
Carbon
- small
- 4 valence electrons = 4 covalent bonds
- limitless sizes and arrangements of organic molecules (especially when carbon bonds to itself)
- 4 valence electrons = 4 covalent bonds
- limitless sizes and arrangements of organic molecules (especially when carbon bonds to itself)
5
New cards
Hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen, contain a lot of energy because of all the bonds, ALWAYS nonpolar/hydrophobic (will not dissolve in water of form hydrogen bonds)
6
New cards
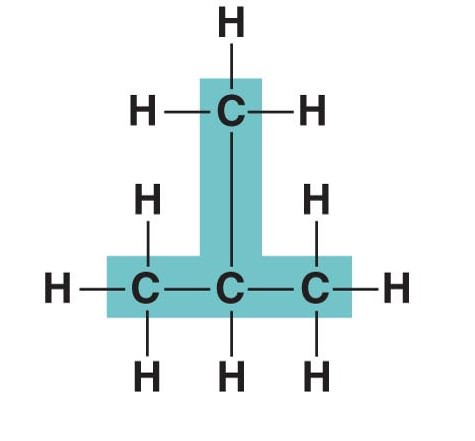
Carbon skeleton
The chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule
7
New cards
Functional Groups
Attached to the carbon skeleton and are groups of atoms that participate in chemical reactions and give the molecule its overall properties
8
New cards
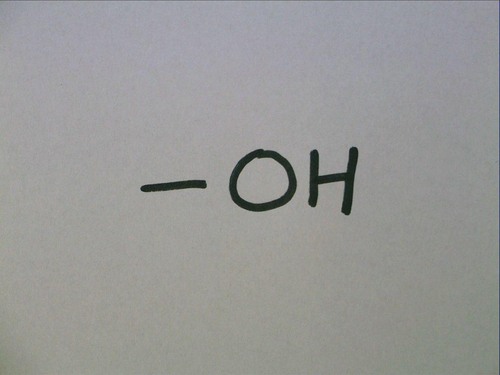
Hydroxyl group
polar and allows H-bonding in that region (O is electronegative)
9
New cards
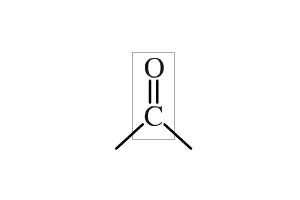
Carbonyl group
aldehydes & ketones (found in sugars)
10
New cards
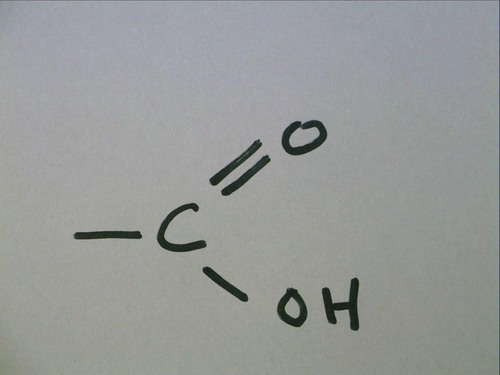
Carboxyl group
organic acid (carbonyl + hydroxyl)
11
New cards
Amino group
acts as a base
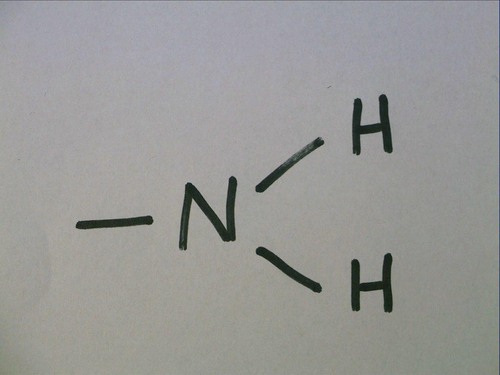
12
New cards
Phosphate group
will make hydrogen bonds (polar), very electronegative, found in energy molecule ATP
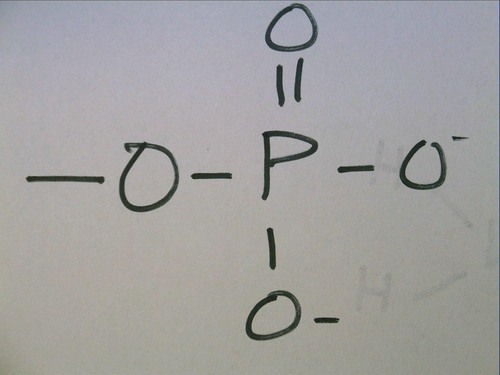
13
New cards
Chemical energy is a molecule stored in
chemical bonds (so more bonds in carbon = more stored energy)
14
New cards
Energy is released (not absorbed) from a molecule by
breaking the bonds (unlike water, covalent bonds are broken through chemical reactions)
15
New cards
The body's number one nutrient to use for energy is
carbohydrates
16
New cards
When carbohydrate molecules are all used up, the body will break the bonds contained in
lipids (fats)
17
New cards
Calorie
A measure of energy content in food
- carbs & proteins have 4 calories per gram
- lipids have 9 calories per gram
- 3500 calories to gain 1 pound or burn 3500 calories to lose 1 pound
- carbs & proteins have 4 calories per gram
- lipids have 9 calories per gram
- 3500 calories to gain 1 pound or burn 3500 calories to lose 1 pound
18
New cards
Nutrients of life
Chemicals in food that the body requires for energy, growth, repair, and maintenance
19
New cards
Monomers to polymers
synthesis
20
New cards
Polymers to monomers
hydrolysis
21
New cards
(def.) Dehydration synthesis reactions
Remove a water molecule forming a new bond
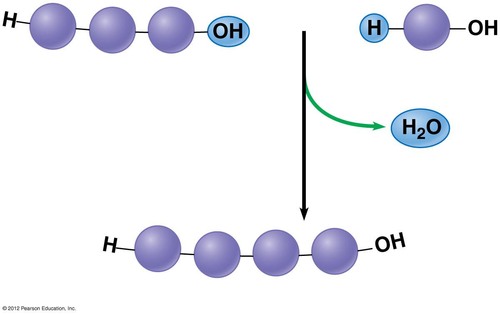
22
New cards
Hydrolysis
Adds a water molecule to break a bond
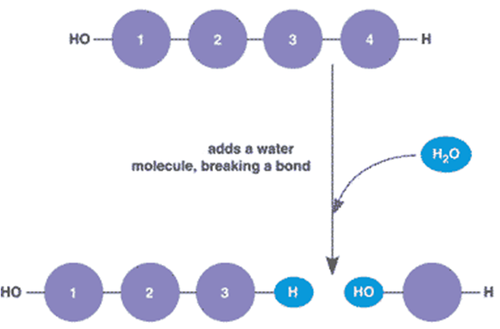
23
New cards
Isomers
Compounds with the same chemical formula, but different structural formulas
- glucose, fructose, galactose = C6H12O6
- glucose, fructose, galactose = C6H12O6
24
New cards
Carbohydrates
- contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen ONLY
- monomer = monosaccharide
- 2H: 1O
- "ose"
- monomer = monosaccharide
- 2H: 1O
- "ose"
25
New cards
Carbohydrates function: useable energy
- immediate energy goes into bloodstream, comes from simple sugars (monosaccharides and disaccharides)
- stored energy (long chains of glucose), comes from starches (polysaccharides):
- humans = glycogen (animal starch); stored in liver and muscle
- plants = starch/amylose (vegetables, grains, pasta, potato, bread, rice)
- stored energy (long chains of glucose), comes from starches (polysaccharides):
- humans = glycogen (animal starch); stored in liver and muscle
- plants = starch/amylose (vegetables, grains, pasta, potato, bread, rice)
26
New cards
Carbohydrates function: structural carbohydrates
- NOT USED FOR ENERGY
- cellulose: structural polysaccharide, found in plant cell walls and gives plants a boxy, rigid structure, not digestible (bread, cereal, veggies) = fiber helps in digestion, lowers bad cholesterol, regulate blood sugar levels
- cellulose: structural polysaccharide, found in plant cell walls and gives plants a boxy, rigid structure, not digestible (bread, cereal, veggies) = fiber helps in digestion, lowers bad cholesterol, regulate blood sugar levels
27
New cards
Monosaccharides are
simple or single sugars (monomers in sugar polymers like glucose fructose and galactose)
28
New cards
Glucose
#1 energy source for most organisms - 6 rings
29
New cards
Fructose
sweetest monosaccharide (honey, flower nectar, fruits) - 5 rings
30
New cards
Galactose
found combines with glucose to make lactose (milk sugar) - 6 rings
31
New cards
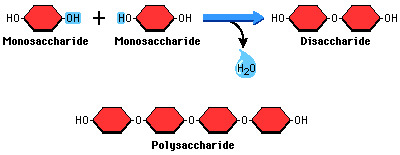
Disacharrides are
two sugars joined by an o-glycosidic bond = sucrose, maltose, lactose
32
New cards
Dehydration synthesis reactions
build disaccharides by removing a water molecule to put monomers together
33
New cards
Glucose + Glucose =
Maltose (seeds)
34
New cards
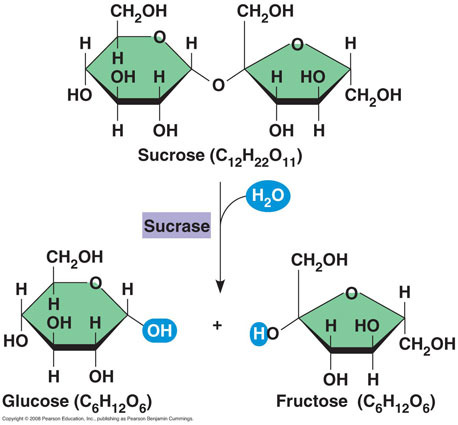
Glucose + Fructose
Sucrose (table sugar)
35
New cards
Galactose + Glucose
Lactose (milk sugar)
36
New cards
Hydrolysis reactions
break down disaccharides by adding water back to break it and restore 2 monosaccharides
37
New cards
Polysaccharides are
many monosaccharides together (hundreds of glucose monomers)
38
New cards
Polysaccharides are made by
dehydration synthesis
39
New cards
Polysaccharides are broken down by
hydrolysis
40
New cards
(Polysaccharide) plant starch/amylose
stores sugar used for energy, chains of glucose monomers coil up in water making them insoluble and good for storage, straight chains
41
New cards
(Polysaccharide) animal starch/glycogen
stores sugar in liver and muscle (long term energy), in animals glucose is stored as glycogen, insoluble in water BUT glycogen chains are longer and highly branches
42
New cards
(Polysaccharide) cellulose
not used for energy, found in plant cell walls (fiber), no enzyme (amylase) to break down bonds between glucose subunits in structural polysaccharides
43
New cards
Lipids (fats)
- contain carbon, hydrogen, and very little oxygen
- do not dissolve in water they are nonpolar molecules
- do not dissolve in water they are nonpolar molecules
44
New cards
Hydrophobic
water fearing
45
New cards
Hydrophilic
water loving
46
New cards
(Lipids) triglycerides (fats & oils; dietary fats)
- stored energy, heat insulation/padding (body fat is stored under the skin but over the muscle: adipose tissue)
47
New cards
(Lipids) phospholipids
- cell membrane structure
48
New cards
(Lipids) steroid hormones (made from cholesterol)
- hormones send chemical systems in the body (cortisone, testosterone, estrogen, growth hormone)
49
New cards
(Lipids) waxes
- protective coating from water that prevents dehydration (surface of leaves & fruits, inside ears)
50
New cards
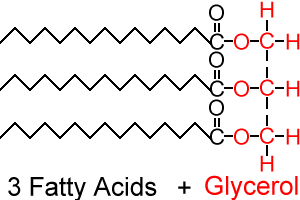
Lipids (monomers)
3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol
51
New cards
Fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group which makes it an organic acid
52
New cards
Fatty acids, nucleic acids, and amino acids all have
carboxyl groups
53
New cards
Triglycerides are made by
dehydration synthesis
54
New cards
Glycerol C3H8O3
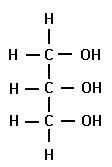
55
New cards
Triglycerides have more bonds and more energy
so fats have more calories
56
New cards
Triglycerides are broken down by
hydrolysis
57
New cards
Do fats or carbohydrates store more energy?
fats because the molecules have more bonds
58
New cards
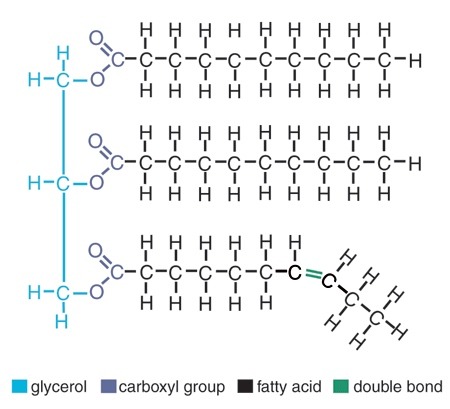
Saturated fatty acids
have all SINGLE carbon bonds (not including carboxyl group), saturated with hydrogen atoms, solid at room temp., animal sources: butter, lard, meat, fat, eggs, cream, cheese
59
New cards
Unsaturated fatty acid
one or more double bonds, unsaturated with hydrogen, kink prevents molecule from packing tightly, liquid at room temp., plant sources (vegetables oils, nut oil, omega-3 fatty acids, fish oil)
60
New cards
Monounsaturated
one double bond
61
New cards
Polyunsaturated
two or more double bonds
62
New cards
Hydrogenation
process that turns unsaturated oil more saturated by adding hydrogen and removing some of the double bonds (for better texture, taste, longer shelf life), forms trans-fats
63
New cards
Trans-fats
the trans bond (when hydrogens are on opposite sides) makes it solid and acts like it is saturated because stable structure making it difficult to digest which clogs arteries
64
New cards
Hydrogenation process adds
hydrogens to "cis" double bonds
65
New cards
Which is healthier, saturated or unsaturated?
Unsaturated fats (oils) lower bad cholesterol levels, metabolized faster due to bent structure, don't leave fatty streaks (plaque) in arteries because they are liquid
66
New cards
Atherosclerosis
hardening of the arteries from accumulation of cholesterol & saturated fats over time = narrowing arteries lead to hypertension (high blood pressure) and cardiovascular disease, heart attack, stroke
67
New cards
Proteins
- contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (sometimes sulfur)
- each amino acid has 4 groups surrounding a central carbon
- R group/variable side chain: gives the amino acid its chemical properties
- one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape
- unique 3D shape determined by order of amino acids
- make up our entire structure and physical traits but also allow all metabolic functions to occur in all cells
- each amino acid has 4 groups surrounding a central carbon
- R group/variable side chain: gives the amino acid its chemical properties
- one or more polypeptide chains folded into a highly specific 3D shape
- unique 3D shape determined by order of amino acids
- make up our entire structure and physical traits but also allow all metabolic functions to occur in all cells
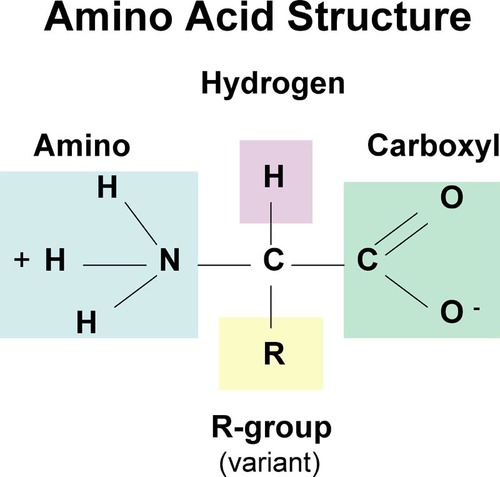
68
New cards
Proteins (monomers)
20 amino acids
69
New cards
Amino acids are put together by
dehydration synthesis
70
New cards
Amino Acid + Amino Acid ---> Dipeptide + H2O
Building of Protein molecules with Dehydration Synthesis
71
New cards
Peptide bond
A covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid & the amino group of the next amino acid (carbon double bonded to oxygen and nitrogen next to it)
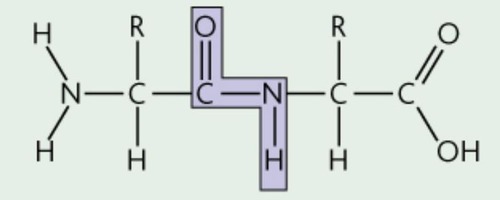
72
New cards
To add more amino acids
more dehydration synthesis reactions must occur
73
New cards
Dipeptide
Two amino acids bonded together
74
New cards
To break down a polypeptide or dipeptide
hydrolysis occurs
75
New cards
When more amino acids are added to a dipeptide
a polypeptide chain is formed
76
New cards
How does a polypeptide become a functional protein?
1. at least 50 amino acids
2. a specific shape/confirmation determined by structures
2. a specific shape/confirmation determined by structures
77
New cards
Primary (1°) structure
a specific sequence of amino acids determined by order of nucleotides in DNA - stabilized by peptide bonds, can't be denatured, NO SHAPE
78
New cards
Secondary (2°) structure
Polypeptide is coiled into a helix or folded into a pleated sheet - stabilized by hydrogen bonds (between amino and carboxyl groups of amino acids)
79
New cards
Tertiary (3°) structure
overall 3D shape results from interactions among R groups (all types of bonds: ionic, covalent, H-bond) proteins = globules,responsibleforfinalshape
80
New cards
Quaternary (4°) structure
proteins that contain 2 or more polypeptide chains (ex. hemoglobin has 4 polypeptides with an iron atom in each center)
81
New cards
If a protein changes shape and can no longer function, it is
denatured
82
New cards
Enzymes must keep their shape
to perform their functions
83
New cards
Temperature (human body temp = 37C)
- too hot can permanently denature a protein
- too cold can slow down function protein, but is usually reversible
- too cold can slow down function protein, but is usually reversible
84
New cards
Changes in pH
- proteins usually have an optimum pH where it functions best
85
New cards
Salts
- ions/charges attract parts of the protein, pulling it out of shape
86
New cards
Denaturing
- primary sequence is not affected by denaturing
- peptide bonds don't break
- peptide bonds don't break
87
New cards
Functions of proteins are determined by their
shape; form = function
88
New cards
Enzymes (organic catalysts)
- start and speed up chemical reactions
- not used up in reaction
- recycled and used over and over again
- each reaction requires a different enzyme
- not used up in reaction
- recycled and used over and over again
- each reaction requires a different enzyme
89
New cards
Motor/contractile proteins
Muscle (actin & myosin), movement of cilia & flagella
90
New cards
Immune defense
Antibodies are special proteins made by white blood cells that inactivate and destroy viruses and bacteria - specific for specific pathogens
91
New cards
Transport proteins
Carry molecules into or out of cell membrane or throughout the body (ex. hemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that carry oxygen to all cells)
92
New cards
Structural proteins
collagen (skin, wounds, tendons), keratin (hair, nails)
93
New cards
Storage proteins
not for energy to burn (ex. casein, protein of milk, is major source of amino acids for baby mammals)
94
New cards
Hormones/signaling (chemical messengers)
allows coordination of an organism's activity
- insulin regulates sugar in bloodstream
- receptors built into membrane of all cells which detect signaling molecules released by other cells (neurotransmitters, hormones)
- insulin regulates sugar in bloodstream
- receptors built into membrane of all cells which detect signaling molecules released by other cells (neurotransmitters, hormones)
95
New cards
Nucleic acids
- contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
- blueprints for proteins
- blueprints for proteins
96
New cards
Monomer of nucleic acid is
nucleotide
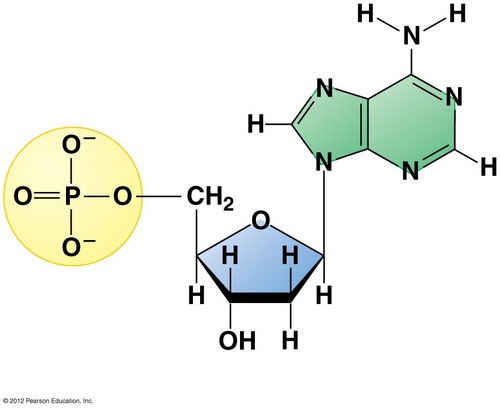
97
New cards
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
- universal genetic code for all living things (all physically traits and metabolic functions)
- codes for sequence of amino acids (proteins)
- EVERYTHING (even prokaryotes) have DNA
- codes for sequence of amino acids (proteins)
- EVERYTHING (even prokaryotes) have DNA
98
New cards
Gene
a specific order of nucleotides which codes for a specific order of amino acids, found on physical structures (chromosomes)
99
New cards
Genome
all of the genes that make up an organism
100
New cards
Every 3 nucleotides (CODON) code for
1 amino acid