Sec 8.3 & 8.5 SNC 1W1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the astronomical unit (AU)?
Used to measure distances within the Solar System.
equivalent to 150 000 000 km, the average distance between the Sun and Earth.
How far is Neptune from Earth in astronomical units?
29 A.U.
the distance of the nearest star, Proxima Centauri, from Earth
300,000 AU
What is the classification of Pluto and why?
Pluto has been reclassified as a dwarf planet based on its physical properties and motion.
two other dwarf planets besides Pluto
Ceres (part of the Asteroid belt) and Eris (part of the Kuiper belt)
Astronomers suspect there are hundreds more
What are the three types of smaller celestial objects in the Solar System?
Asteroids, meteoroids, and comets.
Asteriods
orbit the sun between orbits of mars and jupiter (asteroid belt)
Small celestial objects made of rock and metal
Meteoroids
chunks of rock and metal
smaller than asteroids
sometimes pulled in by earths gravity, then they burn up in the atmosphere or occasionally impact earths surfaces
Comets
large chunks of ice dust and rock
orbit the sun
100m - 40km
few hundred thousand year orbit
How long does it take Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun?
365.25 days
What direction does the earth revolve around the sun?
Counterclockwise
What causes the apparent motion of the Sun across the sky?
The rotation of Earth on its axis.
How can we describe earth’s orbit?
Like other planets it is Elliptical
Why does the same side of the Moon always face Earth ?
It takes the Moon the same amount of time to complete one
rotation and one revolution.
Why does the earth orbit the sun?
The gravitational force of the sun keeps earth and other planets orbiting
What is gravity/gravitional force
the force of attraction between all objects in the Universe with mass.
The greater the mass of an object, the stronger its gravitational force.
What is the tilt of Earth's rotational axis?
tilted at 23.5° from the vertical.
how does the tilt of the earth relate to the seasons?
We experience summer when Earth’s northern hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun.
During this time, the Sun appears to travel its highest path in the sky, and there are more hours of daylight.
solstices
astronomical events when Earth's axis is most inclined toward or away from the Sun,
occurring June 21 (summer) and December 21 (winter).
equinoxes
days when there are equal hours of daylight and nighttime
occurring March 20 (vernal) and September 20 (autumnal).
What is precession ?
The change in the direction of earths axis over thousands of years.
What star is at earth’s north pole?
Polaris
How many phases does the lunar cycle it have?
The lunar cycle follows a predictable pattern of 8 phases over a period of about 4 weeks.
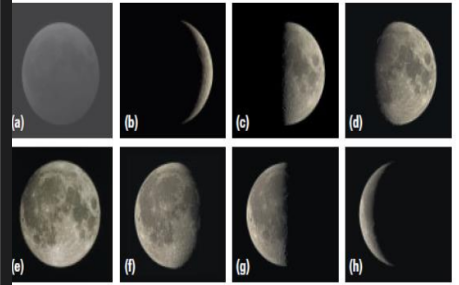
Phases of the moon
a)New moon b)Waxing crescent c)First quarter d)Waxing gibbous e)Full moon f)Waning gibbous g)Third quarter h)waning crescent
Why does the Moon and the Sun appear approximately the same size in the sky?
The Sun has a diameter 400 times greater than the Moon. It is also 400 times farther from Earth than the Moon is.
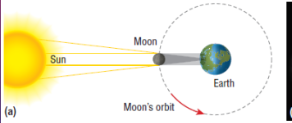
What is a solar eclipse?
the Moon is aligned between Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun from being observed from Earth.
What is a lunar eclipse?
Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon.
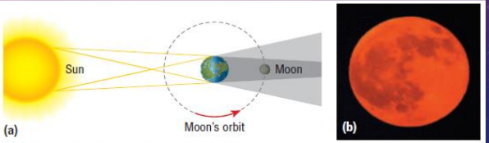
What is a partial lunar eclipse?
only part of the Moon passes through Earth’s shadow,
What causes tides on Earth?
The Moon’s gravitational force pulls Earth and its oceans toward it.
This causes a bulge of water to form on the side of Earth facing the Moon.
As Earth is pulled toward the Moon, a bulge of water also forms on the opposite side of Earth, where the Moon’s gravitational force is weakest.
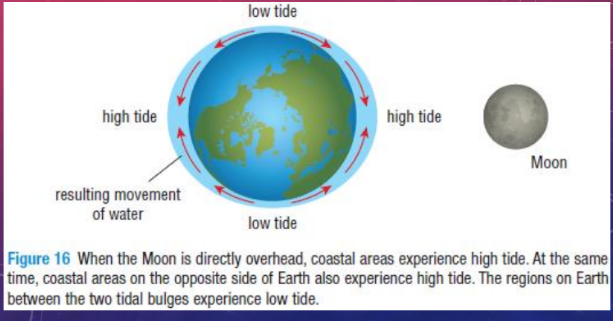
How many high and low tides occur on Earth each day?
There are two high tides and two low tides on Earth each day.
time interval between low and high tide
6 hours