Leuture 5 DNA discovery and structure
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:55 AM on 3/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
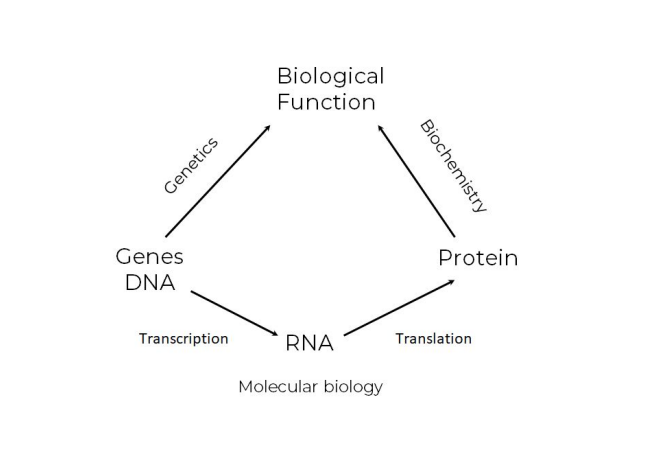
What is the Biological Function
3
New cards
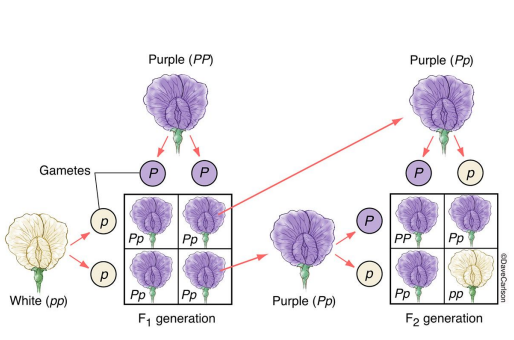
Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) revealed that….
heredity is the result of discrete units of inheritance.
* Traits are not blended - can either have mom or Dad traits can be pasted down generation from generation
* Traits are not blended - can either have mom or Dad traits can be pasted down generation from generation
4
New cards
Wilhelm Ludvig Johannsen coined the term gene to refer the …
not or particle of inheritance
* Phenotype - Trait expressed by gene
* Genotype - collection of genes that code for phenotype
* Phenotype - Trait expressed by gene
* Genotype - collection of genes that code for phenotype
5
New cards
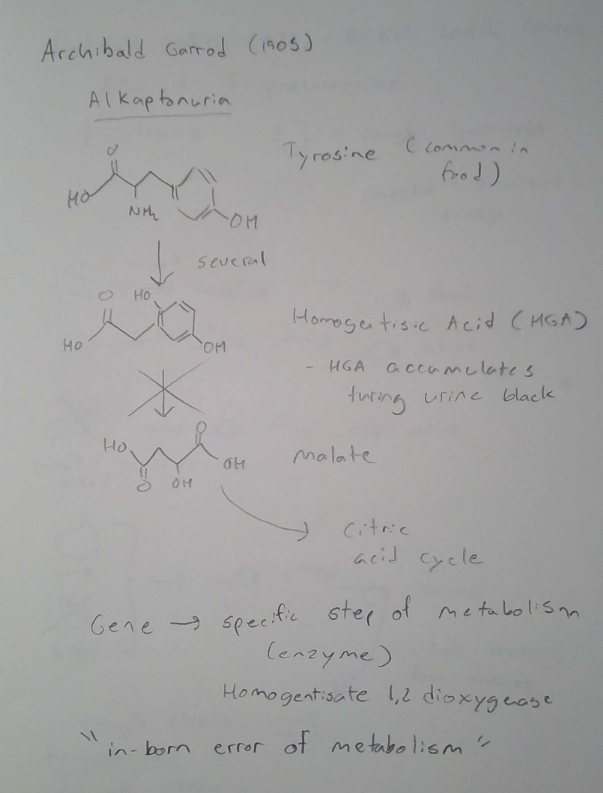
Archibald Garred
Identifies alkaptonuria as a heritable geneticc disease that follows Mendel’s law
6
New cards
Alkaptonuria
* black urine - inborn error of metabolism used of pedigree
7
New cards
What is the Biochemical basis of hereditary?
8
New cards
Majority of death resulted from secondary infections of…
Streptococcus pneumoniae
9
New cards
What are the two strains of streptococcus pneumoniae
* Rough Colony (R)
* Smooth Colony (S)
* Smooth Colony (S)
10
New cards
What is the R strain
benign (lacks a protective capsule, recognized and destroyed by host’s immune system)
11
New cards
S-strain
Is virulent (polysaccharide capsule prevents detection by host’ immune system)
12
New cards
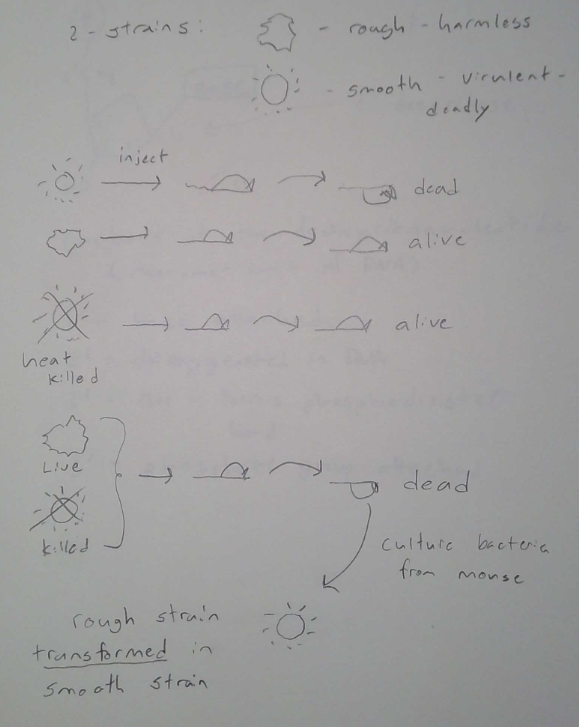
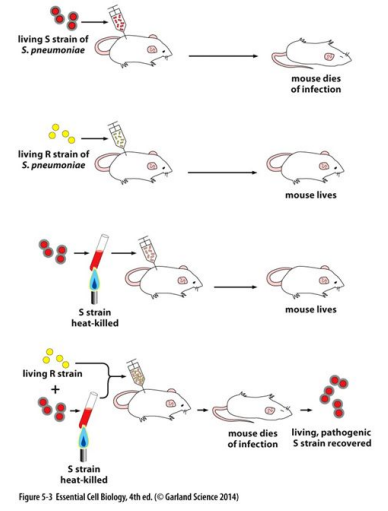
Fredirck Griffith (1928) discovered that the ..
dead virulent strain of S. pneumonia (S-strain) could transform the harmless form (R-strain) into the virulent form.
13
New cards
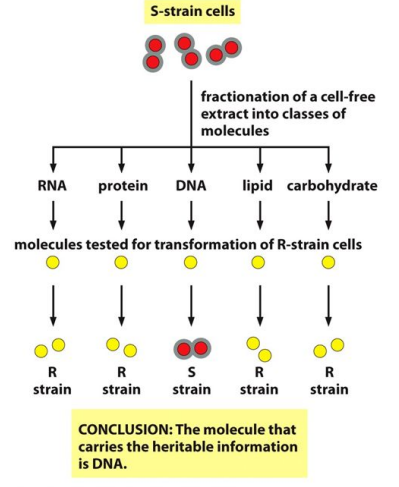
Avery, and McCarty and Mcleod discovered that…
R-strains could be transformed with DNA extracts from dead S-strains
14
New cards
Conclusion
the molecule that carries the heritable information is DNA
15
New cards
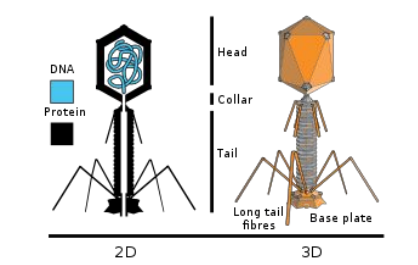
Bacteriophage are?
They consist of two component
They consist of two component
* Class of Viruses that infect bacteria
* Requires bacterial host for replication
\
* DNA Genome
* Protein Capsid
* Requires bacterial host for replication
\
* DNA Genome
* Protein Capsid
16
New cards
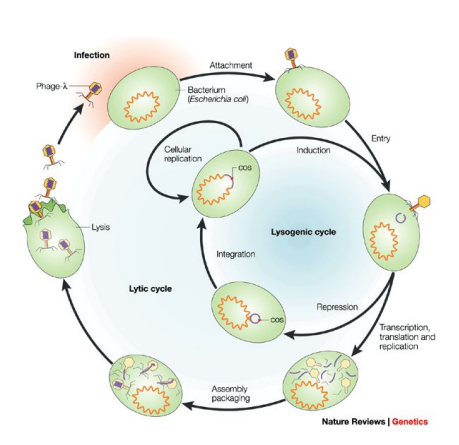
Bacteriophage life cycle
The genetic information required for viral replication must be contained in either the DNA or the proteins
17
New cards
Hershey and chase (1952)
Labeled Bacteriophage with radioactive elements
Labeled Bacteriophage with radioactive elements
* Phosphorous of DNA
* The sulfur of Amino Acids - Cysteine and methionine
\
* Traced the transfer of those elements to the infected bacteria
* The sulfur of Amino Acids - Cysteine and methionine
\
* Traced the transfer of those elements to the infected bacteria
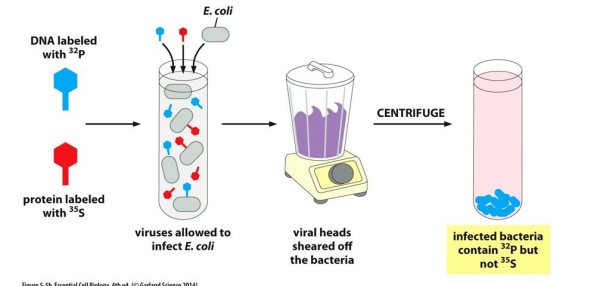
18
New cards
Hershey and Chase confirmed What?
Experiment DNA and Protein/sulfur put in viruses that allowed to infect E.coil- blender shear off viral heads off bacter- infected bacteria contained 35P not S35
19
New cards
Nucleotides
A nucleotide consist of a nitrogen-containing base, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups
\
Carbons of the deoxyribonucleotide (monomer unit of DNA)
\
Carbons of the deoxyribonucleotide (monomer unit of DNA)
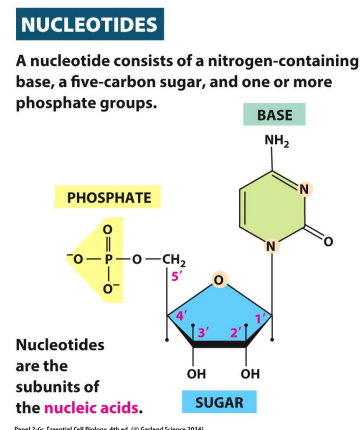
20
New cards
1’
Base attached
21
New cards
2’
Deoxygenated in DNA
22
New cards
3’
OH - forms phosphodiester bond
23
New cards
5’
Phosphate group attached
24
New cards
What are the Nucleotide bases
What are Pyrimidine and Purine bases
What are Pyrimidine and Purine bases
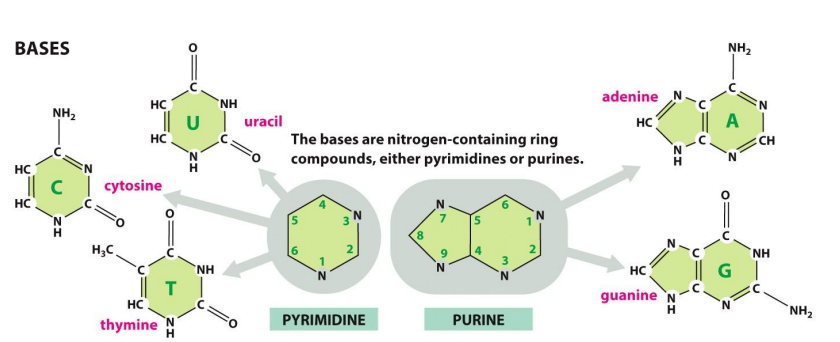
25
New cards
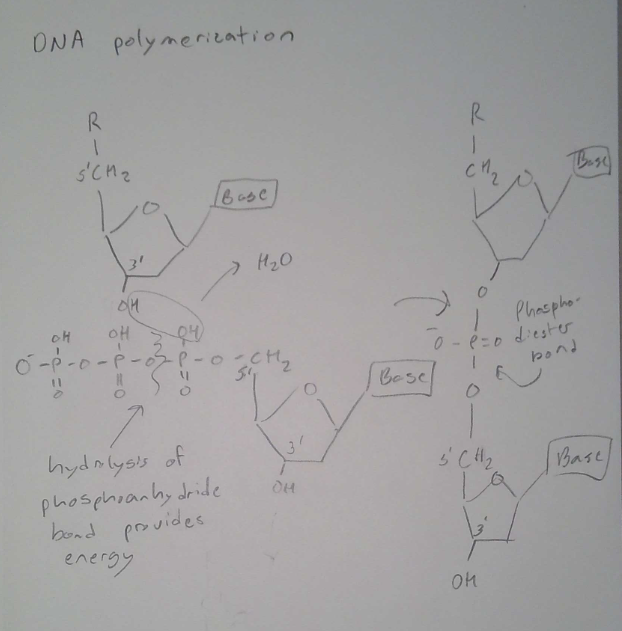
DNA Polymerization
* Hydrolysis of Phosphor anhydride bond provide energy
* Creates favorable reaction - high energy → Low energy
* Creates favorable reaction - high energy → Low energy
26
New cards
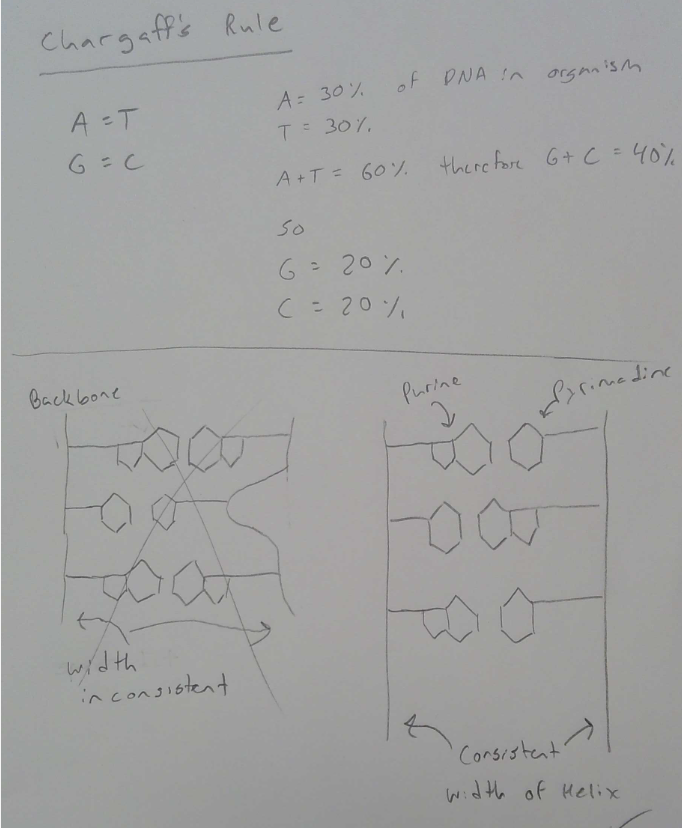
Erwin Chargaff do?
Nucleotide occur in predictable ratios in living things
27
New cards
What is Chargaff's Rule?
A = T
G = C
G = C
28
New cards
Discovery of the structure of DNA - Watson, Crick, Wilkins, and Franklin
29
New cards
Discovery of structure of DNA - Watson, Crick, Franklin, and Wilkins
* Double helix with Bases pointing inward
* Complementary base-pairing between purine and pyrimidine explain Chargaff’s rule
* Complementary base-pairing between purine and pyrimidine explain Chargaff’s rule
30
New cards
Complementary base-pairing of DNA makes it possible to faithfully replicate of genetic material
* Each strand serves as a template to make a new double helix - semi-conservative replication.

31
New cards
Part 2 - DNA and Chromatin Structure
32
New cards
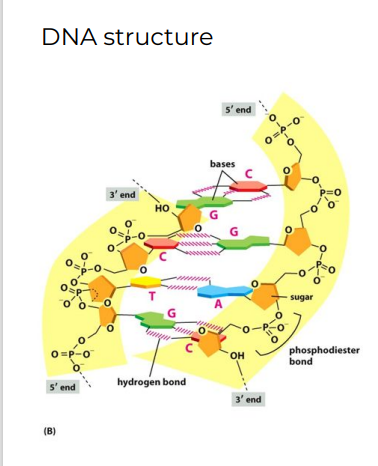
DNA Structure backbone is assembled via condensation reactions forming…
Phosphodiester bonds
33
New cards
Nucleotides are connected 5’ to 3’ and strands are..
\
one strand and the other…
\
one strand and the other…
* antiparallel
\
* One strand runs 5’ to 3’
* Other runs 3’ to 5’
\
* One strand runs 5’ to 3’
* Other runs 3’ to 5’
34
New cards
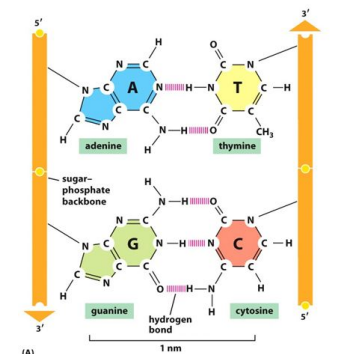
DNA Structure is held together by…
Hydrogen bonds between bases
35
New cards
G to C bonds are… than A to T
Stronger
36
New cards
Increasing the GC content increases the … of DNA
Stability
37
New cards
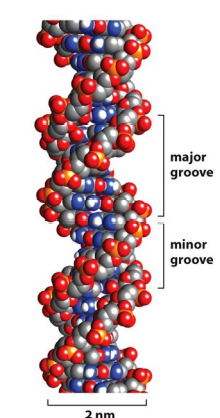
The DNA Helix has two grooves
* Major groove - 22 A wide - primary site of sequence specific binding of protein
* Minor groove - 12 A wide - primary non-specific binding of proteins
* Minor groove - 12 A wide - primary non-specific binding of proteins
38
New cards
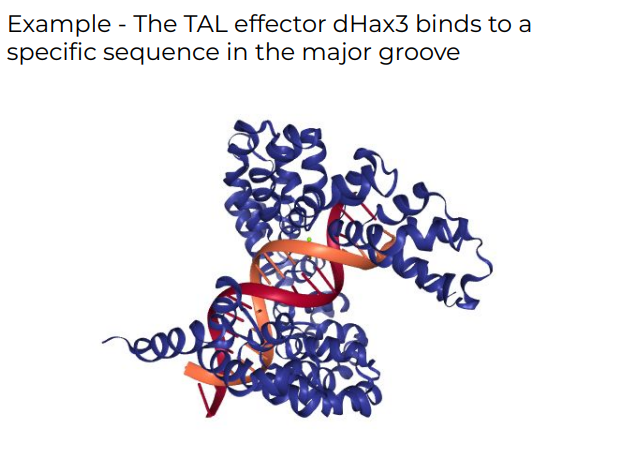
39
New cards
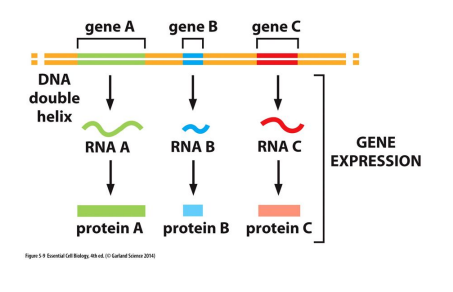
Major DNA sequence features (2)
* Genome
* Gene
* Gene
40
New cards
Genome?
The complete DNA sequence of an organism
41
New cards
Gene
Portion of the genome transcribed to RNA and usually translated into a protein
42
New cards
Genes are read (transcribed) …..from either strand of the double helix
5’ to 3’
43
New cards
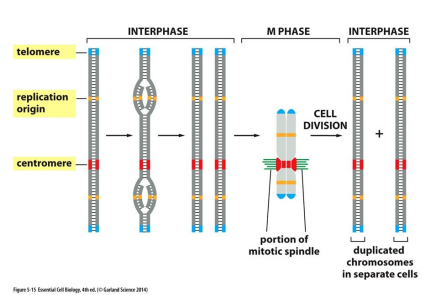
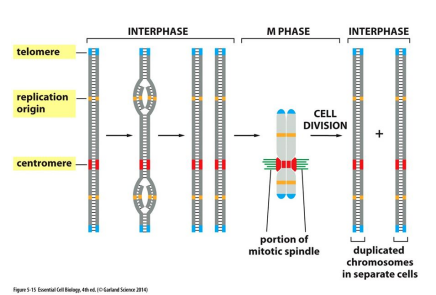
Replication Origin
Special sequence where the replication of DNA begins
44
New cards
Centromere
A special sequence that attaches to mitotic spindle and allows chromosome separation in mitosis
45
New cards
Telomere
Repetitive sequences at the ends of Chromosomes that protect from degradation and/or fusion with other chromosomes
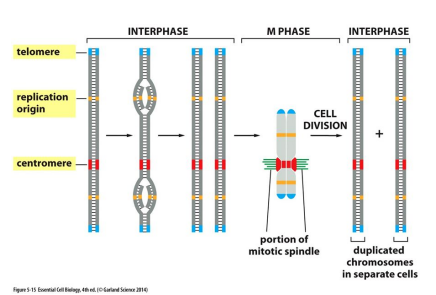
46
New cards
The Problem with DNA is that it’s Thin and Extremely long molecule.
* Each cell in your body has 2 meters of DNA
47
New cards
How does DNA fit in the cell?
DNA is packed with proteins into a complex called chromatin
48
New cards
Histone proteins are major elements of…
chromatin
49
New cards
Histone protein come together in an …. complex which DNA wraps around.
Octomer
50
New cards
Nucleosome?
The histone + DNA Complex
51
New cards
Histones proteins are…. charged and attract the …. charged DNA
Positively charged
Negatively charged
Negatively charged
52
New cards
Decondense Chromatin appears like …..
DNA wraps around nucleosome ….times …bp
DNA wraps around nucleosome ….times …bp
Beads on a string
\
1\.7 times (147 basepairs)
\
1\.7 times (147 basepairs)
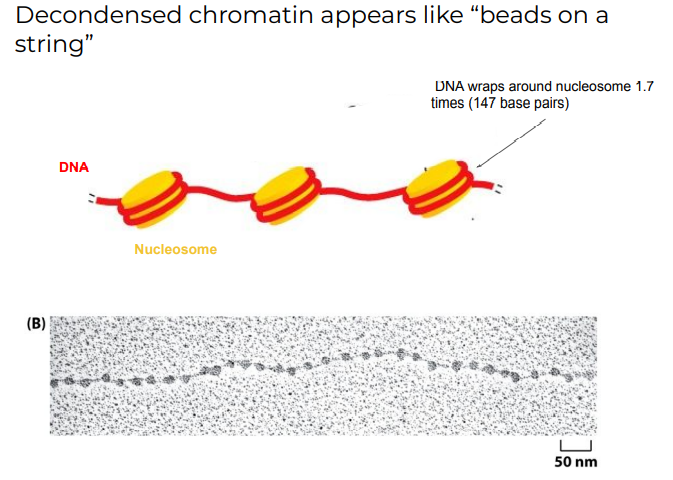
53
New cards
Another histone protein…. can …
H1 can link histones together and help condense the chromatin fibers
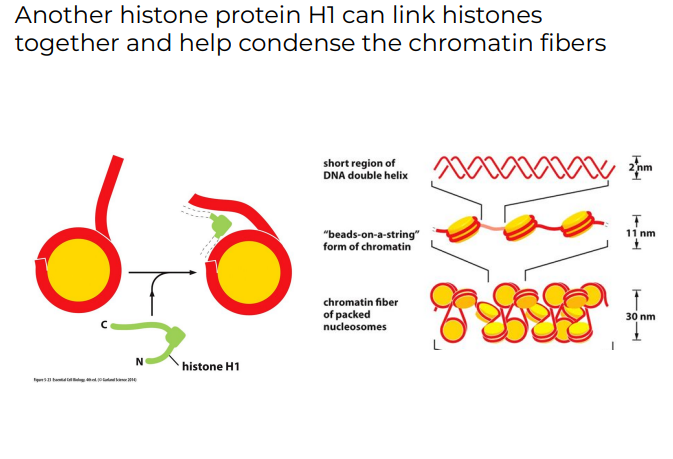
54
New cards
Chromatin fibers are … into loops by …
Folded
CTFC proteins
CTFC proteins
55
New cards
What do CTFC do?
Pull loop through until it reaches a specific sequence
* Matches Specific DNA Sequences
* Chromosome loop-forming clamp proteins
* Matches Specific DNA Sequences
* Chromosome loop-forming clamp proteins
56
New cards
What is the Result of this?
Each DNA molecule has been packaged into a Mitotic chromosome that is 10,000-fold shorter than its fully extended length
\
* Fully condense at Meta-phase of cell cycle
\
* Fully condense at Meta-phase of cell cycle
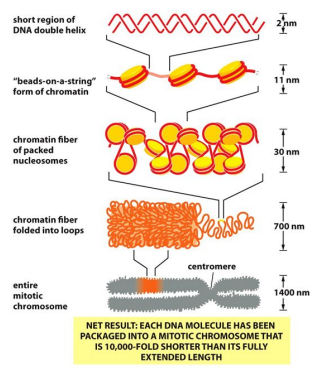
57
New cards
DNA in Eukaryote cells is organized into ..
Chromosomes
58
New cards
What is a chromosome
Complex of DNA (One continuous helix) and many proteins
59
New cards
In human chromosomes are paired …
Homologous chromosomes, one from each parent
60
New cards
Chromosomes take on different conformations through the cell cycle
Interphase, meta phase, interphase
61
New cards
In interphase, when cell is not dividing,..
different chromosomes reside in distinct territories within the nucleus.
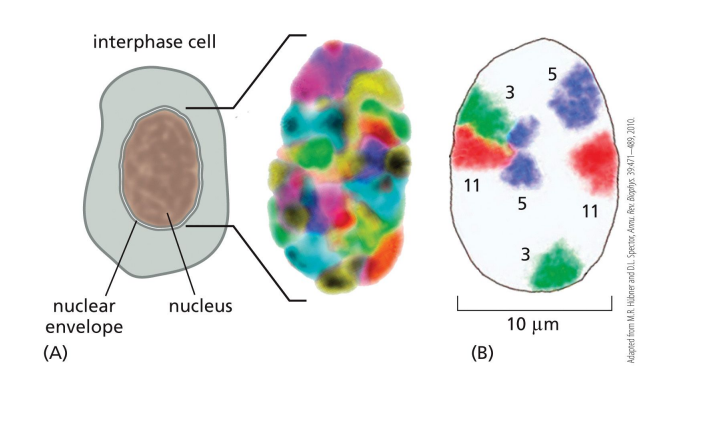
62
New cards
Nucleus chromatin is found in two forms
* Heterochromatin
* Euchromatin
* Euchromatin
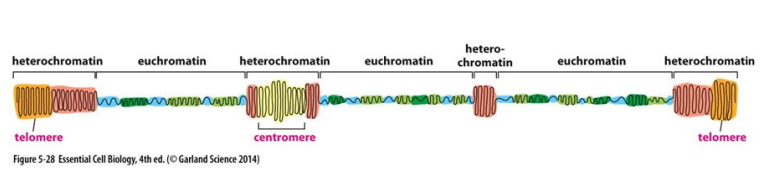
63
New cards
Heterochromatin
That is condensed and not transcriptionally active by telomere and centromere.
64
New cards
Euchromatin
That is loose and transcriptionally active
65
New cards
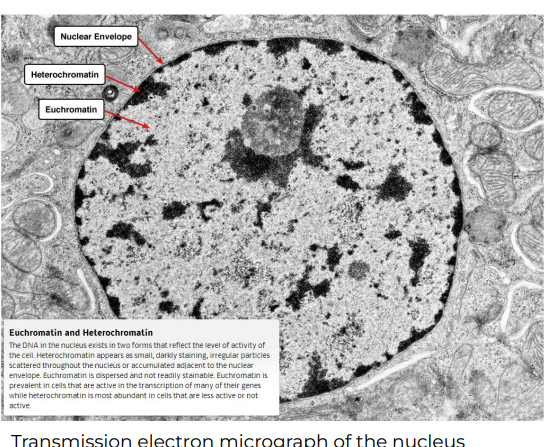
\
66
New cards
Chromatin conformation and composition is dynamic and modified for specific biological function
67
New cards
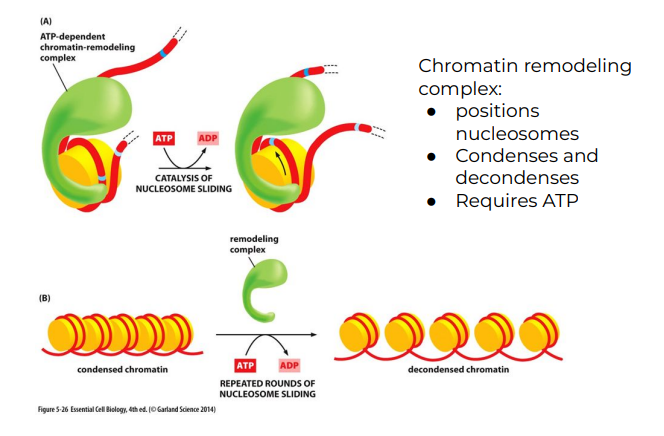
Chromatin remodeling complex (3)
* Positions nucleosomes
* Condenses and decondense
* Requires ATP
* Condenses and decondense
* Requires ATP
68
New cards
The Histone proteins have….terminal tails that are…
N-terminal tails that are modified to mark regions of genome for transcriptional activation or silencing
69
New cards
What are the 5 Levels of DNA
1. Double helix
2. Beads on a string - DNA wraps around Histone 1.7 times 147bp creating nucleosome
3. Chromatin fibers are made with Histone HI
4. Chromatin fiber loops with CTFC - pull loop through until it reaches a specific sequence
5. Folded loops are fully condensed at meta-phase of cell cycle
70
New cards


71
New cards
