ap env science
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
stupid dumb test friday
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
genetic diversity
Describes the amount of diversity within in the gene pool of a species.
species diversity
Describes the amount of diverse types of species in one area
habitat diversity
Describes the amount of different types of habitats within an ecosystem, or the world.
thrive in varied environments
generalist species
broad diet and resource use
generalist species
adapt well to environmental changes
generalist species
need specific conditions to survive
specialist species
narrow diet and resource use
specialist species
vulnerable to environmental changes
specialist species
provisioning
refers to the ecosystem services that provide resources humans can use, like food, water, timber, and medicines
"regulating" ecosystem services
processes that help control natural systems
Anthropogenic activity
refers to human actions or processes that impact the environment.
Which of the following affects a species' ecological tolerance?
Temperature and precipitation, competition within the species, habitat availability, or food resource availability.
What happens when an environmental disturbance shifts habitat conditions outside the range of tolerance of a species?
the species can move to a new habitat, the local population of the species move out, genetic diversity can help the species adapt to the new conditions
Which of the following is the best example of an exclusively natural (non-anthropogenic) ecosystem disturbance?
tornadoes
Which of the following DOES NOT contribute global to sea level rise?
increasing global temperature leading to more frequent precipitation
keystone species
a species that has a major impact on its ecosystem. if removed, can impact the rest of the animals
pioneer species
species to colonize ungrowing / disturbed environments ( like after a wildfire ) .
climax species
plants and animals that characterize the final, stable community of an ecosystem at the end of ecological succession.
indictator species
species who give early warning signs of damage or danger to a community
a non-native species that, when introduced to a new environment, can cause harm to the ecosystem, economy, or human health.
invasive species
These species are suited to their environment and help keep the ecosystem stable. In this community, there are many different species, and the ecosystem stays mostly the same until a major disturbance happens.
climax species
These species are sensitive to changes in environmental conditions, so they act like a "biological warning system." If they thrive, the ecosystem is likely healthy; if they decline or disappear, it can signal pollution, climate change, or other environmental problems.
indicator species
These species often outcompete native species for resources like food and habitat, leading to declines in native populations.
invasive species
These species are strong and can survive in harsh conditions, helping to create soil and make the environment more suitable for other species to move in later. They "pave the way" for other plants and animals in the ecosystem.
pioneer species
Even though they may not be the most abundant, their presence is important for maintaining the balance and health of the environment. If they’re removed, it can cause dramatic changes, often leading to the collapse of the ecosystem.
keystone species
Which of the following is NOT a key characteristic of keystone species?
they have large population sizes
How do lichen & mosses initiate primary succession?
they secrete acids onto rocks, leading to chemical weathering
Which of the following is NOT a key characteristic of pioneer species?
high soil nutrient requirements
Which of the following is an example of a climax species?
maple trees, oak trees
Which of the following is an example of a pioneer species?
lichen, mosses
Which of the following is an example of a keystone species?
sea otters, wolves
Which of the following is an of a indicator species?
mayflies, lichens?/
Which of the following is NOT one of the three levels of biodiversity?
Richness
what does biodiversity literally mean
life - range of different things
Habitat loss is the number one cause of organism extinction.
With no habitat there is no food or shelter for many plants and animals
bottleneck effect
when a population size is decreased because of environment/humans, leading to less genetic diversity making it harder to adapt
species richness
the number of different species in an area
species evenness
relative abundance of each species
ecosystem loss
urbanization, glacier receding, mining, deforestation
species loss
invasive species, hunting, monocropping
genetic loss
geneticially modified organisms ( gmo ), inbreeding
regulating
nature controls things like air quality, climate, and water (e.g., trees clean the air)
provisioning
Nature gives us resources like food, water, and raw materials (e.g., fish, crops, wood).
cultural
Nature offers experiences that benefit people emotionally or spiritually (e.g., parks, hiking, sacred places).
supporting
Nature maintains essential processes, like soil formation and nutrient cycling, that allow other services to exist.
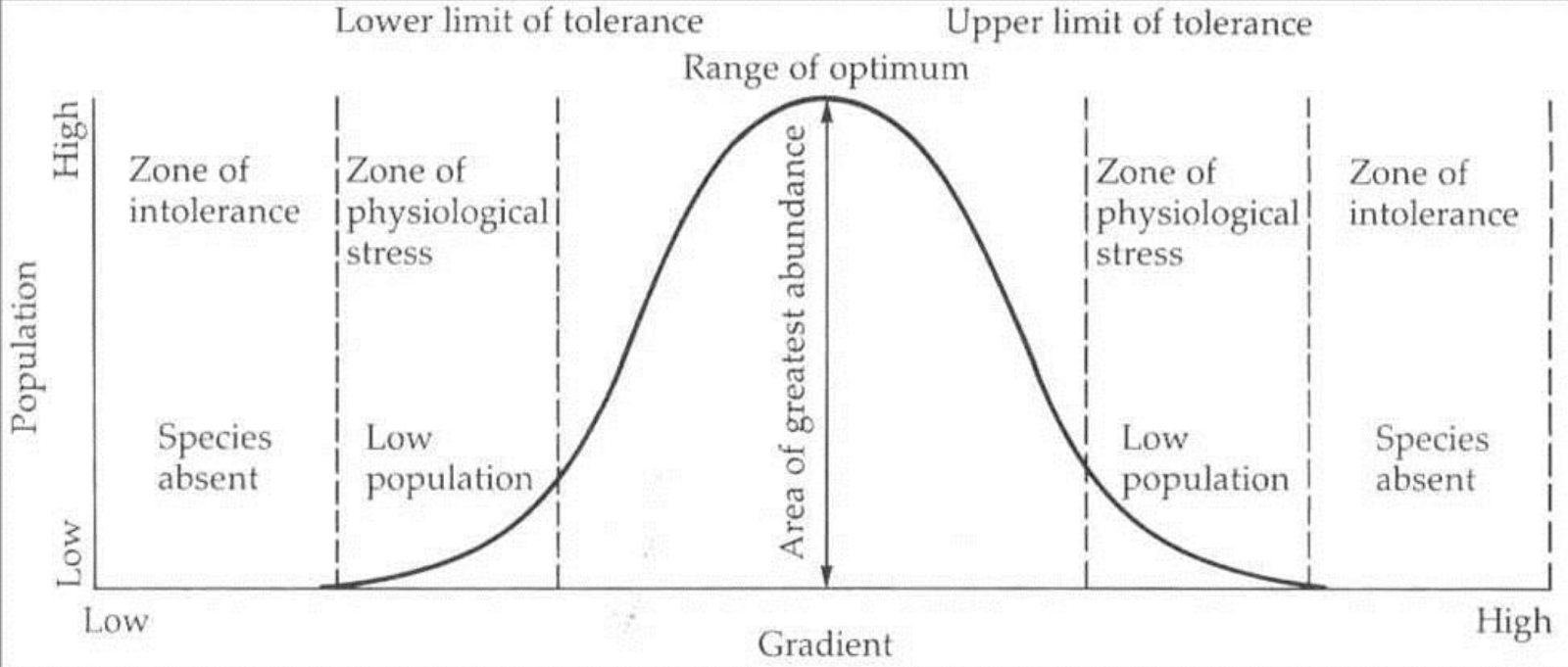
what goes first and fifth in range of tolerance
intolerance/death
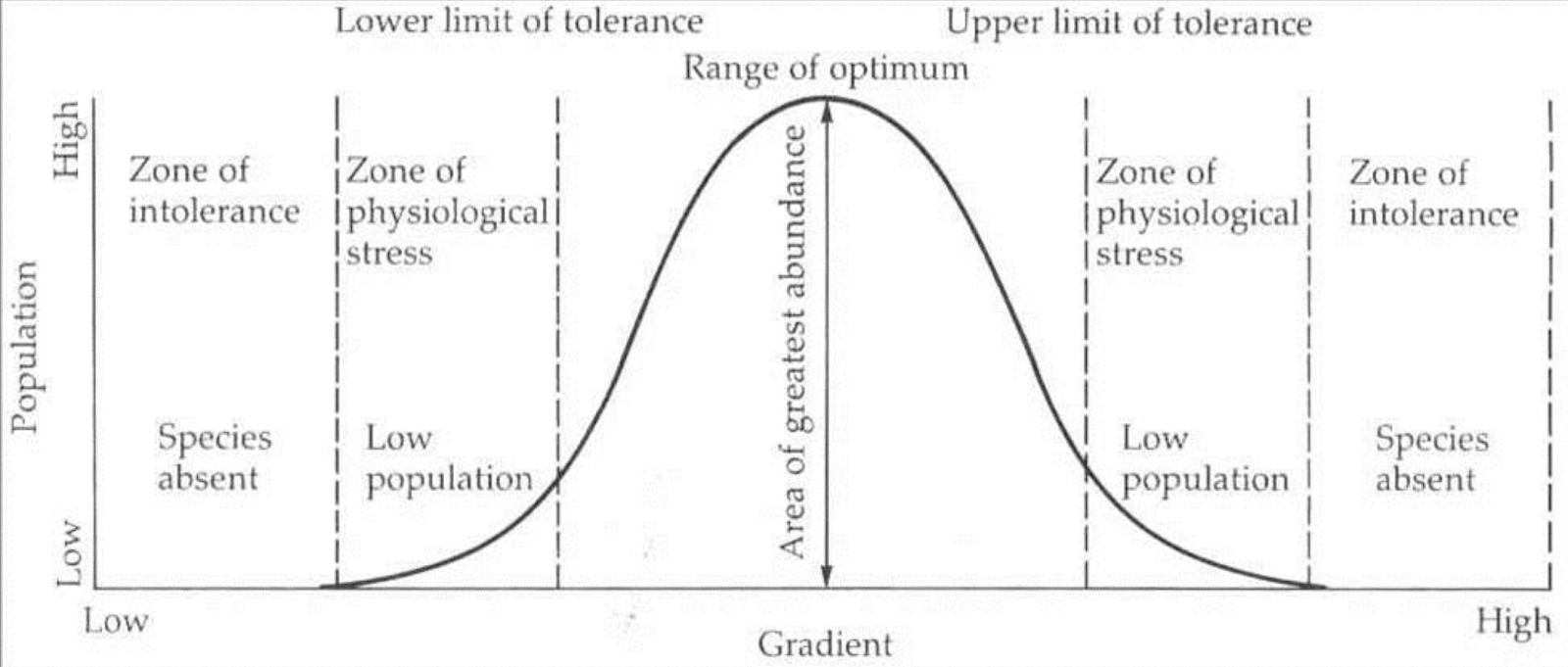
what goes second and fourth in range of tolerance
zone of stress
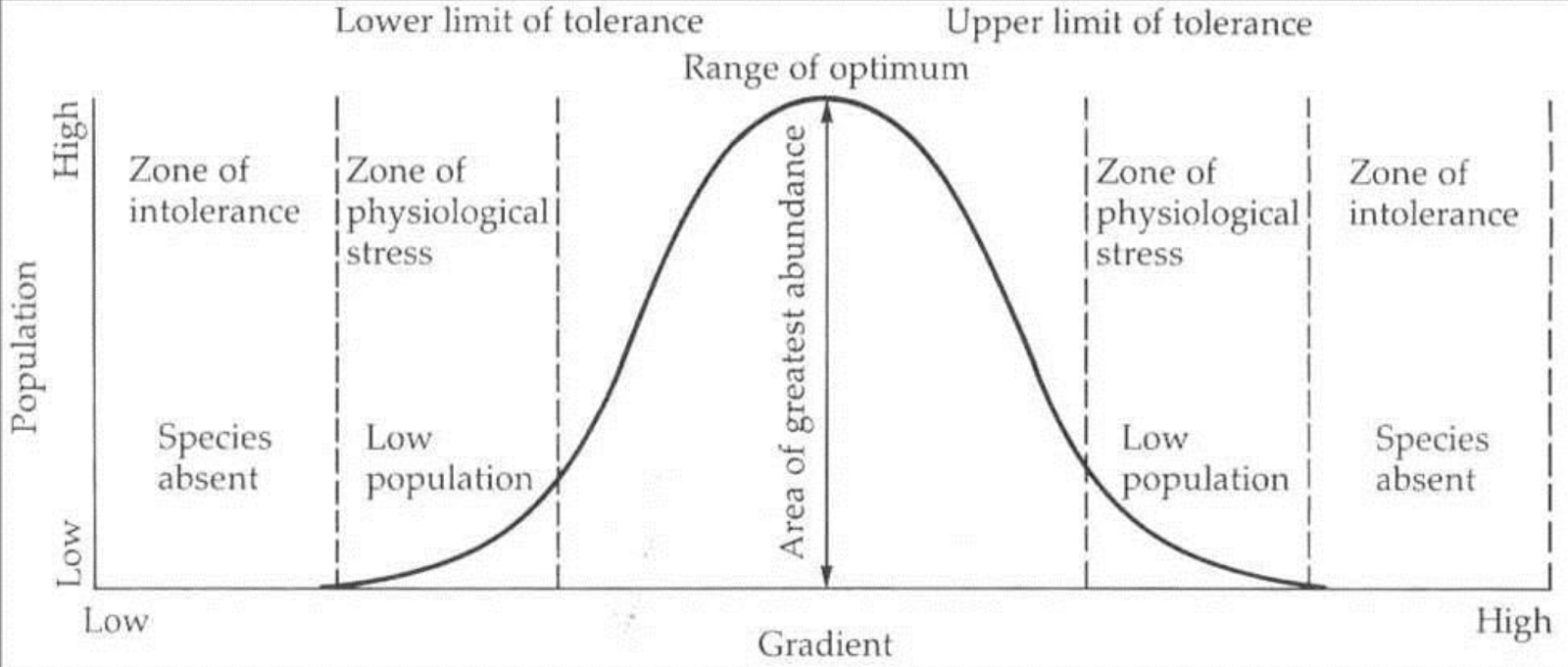
what goes in the third/middle in range of tolerance
optimum range
Periodic
Happens at regular intervals (e.g., seasonal flooding in river systems).
Episodic
Occurs occasionally but not regularly (e.g., volcanic eruptions).
Random
Unpredictable and happens without warning (e.g., a lightning strike causing a wildfire).
primary secession
Starts on bare land with no soil, like after a volcanic eruption or glacier retreat. Life gradually builds up from scratch, starting with pioneer species like lichens.
secondary secession
Happens in areas where an ecosystem has been disturbed but soil and some life remain, like after a forest fire or hurricane. The recovery is faster because life doesn’t need to start from scratch.
what substrate does primary sucession start on?
on rocks with no soils
what substrate does secondary sucession start on?
soil
stages of sucession
rock with no soil/soil, pioneer species ( small little plants / flowers ), intermediate species ( shrubs, small trees ), climax communty ( big ahh trees like oaktree )
resistance
ability to remain unchanged when subjected to disturbance
resillience
ability/rare of a ecosyystem to recover from a disturbance and to return to normal state
what makes modern damily change with anthropogenic causes different from previous natural change
frequency and intensity