Lesson 50: Intro to Fluid therapy
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What are the names of the 3 fluid compartments?
Intracellular
Interstitial
Intravascular (plasma)
What is the predominant force that determines fluid movement from the intracellular to the interstitial space?
Osmotic forces
What are the two main starling forces that move fluid between the interstitial and intravascular compartments?
Hydrostatic pressure
Oncotic pressure
What is the modified starling hypothesis?
That there is additional pressure due to the endothelial glycocalyx
What regulates the transvascular fluid movement, vasomotor tone, coagulation, and inflammation.
The glycocalyx
What membrane interacts with plasma proteins, and keeps larger molecular like albumin and red blood cells in the intravascular space, based on weight, electric charge, and concentration?
The glycocalyx
what happens if the the glycocalyx is damaged?
Ablumin, RBCs leak into interstitium, pro-coagulation
What are the goals of fluid therapy?
Replenish normal intake if the patient isn’t eating or drinking
Replenish excessive ongoing losses
Replenish hydration if dehydrated
Replenish volume if hypovolemic
What is the normal amount of fluid the body loses per day?
40-60 ml/kd/day
What is the amount of fluid that is lost to be considered excessive ongoing losses?
~50 ml/kg/day
What is it called when the interstitial deficit ± intracellular deficit if very severe?
Dehydration
Persistant dehydration via increased losses, decreased intake, or both can result in what?
Hypovolemia
If there is an intravascular deficit from dehydration it can result in what?
Hypovolemia
What fluid compartment is deficient if the patient is dehydrated?
Interstitial
What fluid compartment is deficient if the patient is hypovolemic?
Intravascular
What are the physical exam parameters to identify dehydration/hypovolemia?
Hydration parameters
Perfusion parameters
What are the indirect measures to identify dehydration/hypovolemia?
Urine output/USG
Lab parameters such as PCV/TS, lactate, and sodium
Which type of physical parameter measures Mucus membrane moisture level, Skin turgor, Eyes, Demeanor, Urine concentration, PCV/TS?
Hydration parameter
What does the Hydration parameters measure?
Interstitial/intracellular volume status
What does perfusion parameters measure?
Intravascular volume status
Which type of physical parameter measures Mucous membrane color, CRT, HR, Pulse quality, BP, Extremity temp, urine output?
Perfusion parameters
What is another name for decreased perfusion called?
Shock
What is the most common problem that causes a decrease in perfusion?
hypovolemia
What are other examples that can cause shock/decreased perfusion?
Sepsis and Heart failure
What are the ways to assess mucus membranes?
Color
Moisture/tacky
CRT
What is the normal mucus membrane assessment?
Color: Pink
Moisture: moist
CRT: 1-2 sec
What is an abnormal mucus membrane assessment?
Color: Pale
Moisture: tacky
CRT: <1 or > 3
If a patient has pink, tacky mucus membranes, with a CRT of 2 seconds they are?
Dehydrated
If a patient has pale, moist mucus membranes, with a CRT of 3 sec they are?
Hypovolemic
Where do you assess skin tenting/turgor?
Neck/shoulder and eyelid in foals
Prolonged skin tent is a sign of what?
Dehydration
What are factors that can affect skin tenting?
Age
Nutrition status
Increased HR is a sign of what?
Decreased perfusion
Review: What is the equation for CO?
CO= HR X SV
If CO is low…
HR compensates by increasing
If SV is low…
HR compensates by increasing
What are other factors that can increase HR other than CO and SV?
Pain/fear
Compensation only last so long → low HR
Cats quickly go from High to low HR
Decreased strength of Pulse and low BP are signs of what?
Low perfusion
What does cold extremities indicate?
Sign of poor perfusion
What does no urine output indicate?
patient is not perfusing kidneys
What does concentrated urine indicate?
Dehydration, appropriate response
What does dilute urine with dehydration indicate?
Kidney disease/injury
Which species can you palpate the bladder in?
Cats
If the jugular fill in horses is delayed what does this indicate?
Hypovolemic
Sunken eyes are a sign of severe dehydration in which species?
Ruminants and Small aminals
Sunken eyes are not a sign of severe dehydration in which species?
Horses
In small animals dehydration can be estimated from physical findings. What percentage of dehydration indicates hypovolemia?
>10%

Is the Frenchie de

Is Bella dehydrated, hypovolemic, or both?
Dehydrated
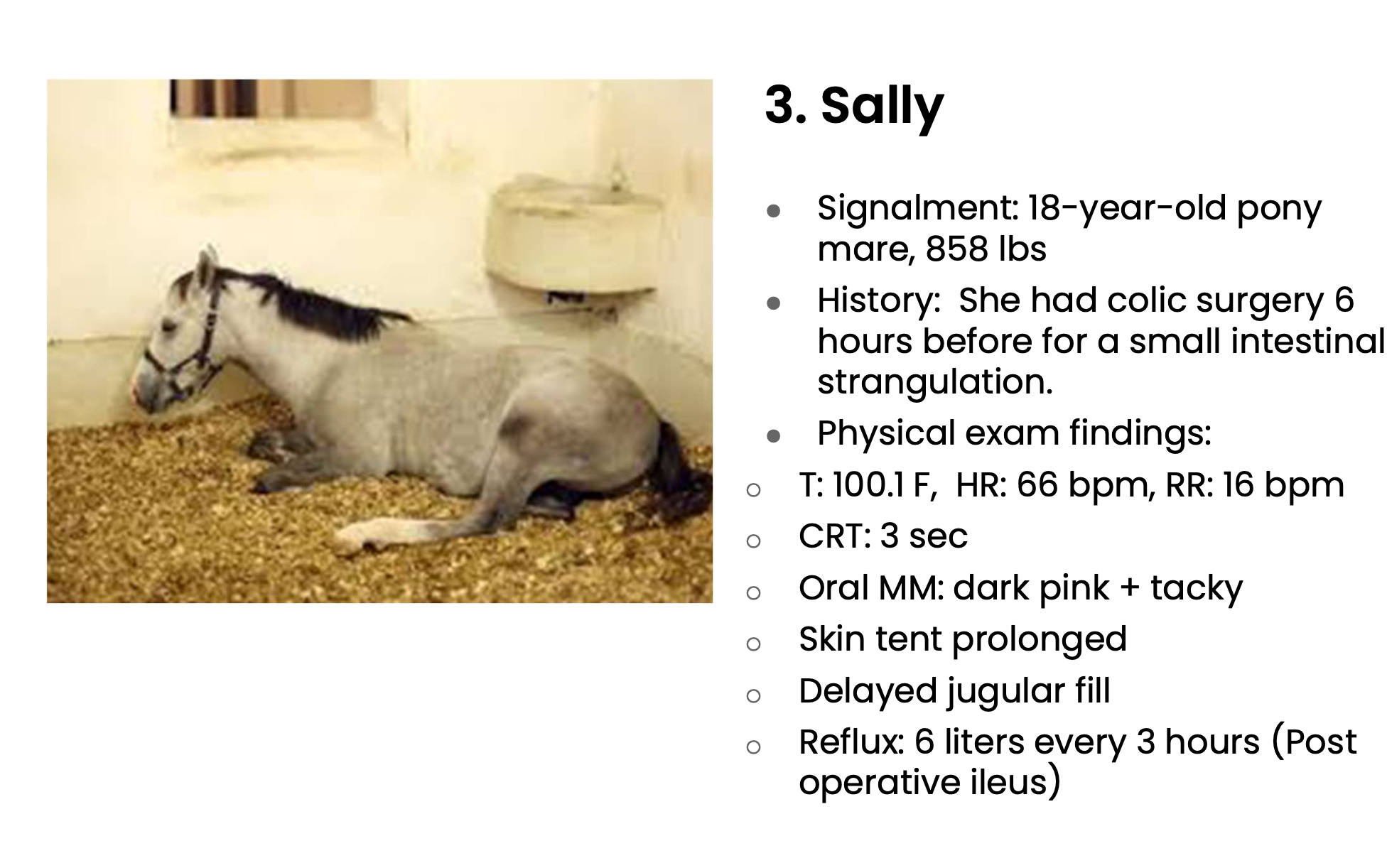
Is Sally dehydrated, hypovolemic, or both?
Both

Is Beau dehydrated hypovolemic or both
both

Is Ramon dehydrated, hypovolemic, or both
Dehydrated