1.30 Speckle Tracking Echocardiography Strain Imaging
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is strain echo?
The assessment of the contractility of LV wall motion.
What are the primary uses of strain echo?
Ischemic heart disease
Cardiomyopathies (all)
Valvular heart disease
Diastolic function
Myocardial dysfunction in patients with cardiotoxicity undergoing chemotherapy
When was 2-D strain first introduced (year)?
2004.
What is tracked in strain echo?
The distances between the speckles are tracked frame to frame over the cardiac cycle and provides information about myocardial deformation.
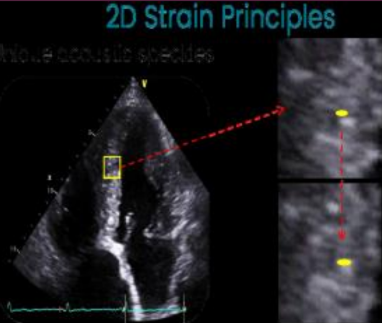
In simple terms, strain is the difference of end diastolic and end…?
systolic length.
LV contractility consists of what three things?
Thickening
Shortening
Twisting (rotation and torsion)
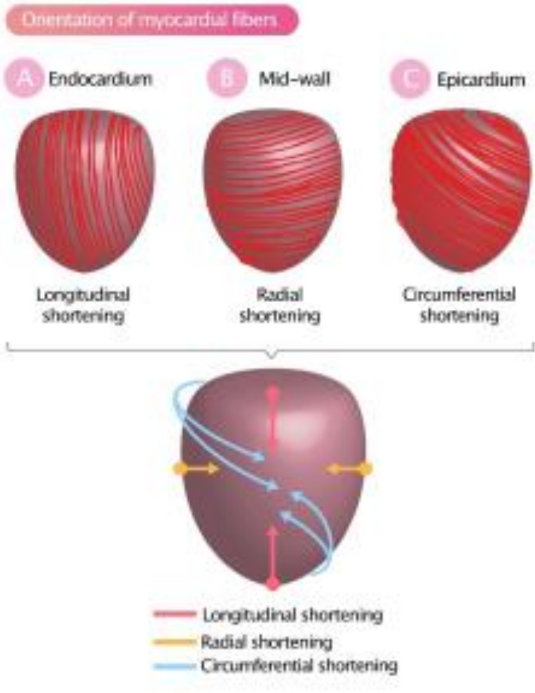
What does strain mean?
Stretching or deformation by the application of force (in the heart’s case, contraction).
What is the formula for strain?
(L1-L0)/L0 × 100 (with L1 = length at a given point in time, and L0 = baseline length)
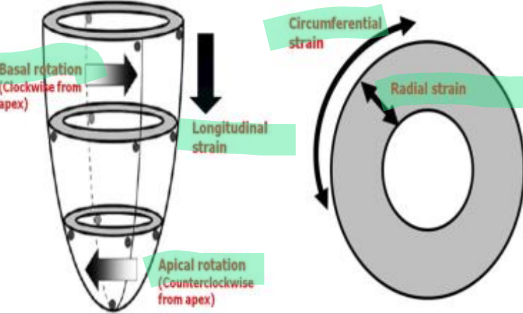
What are the different types of strain of the LV?
Longitudinal strain (LS)
Circumferential strain (CS)
Basal rotation (clockwise from apex)
Apical rotation (counterclockwise from apex)
Radial strain (RS)
With strain echo, what type of strain is assessed?
Longitudinal strain.
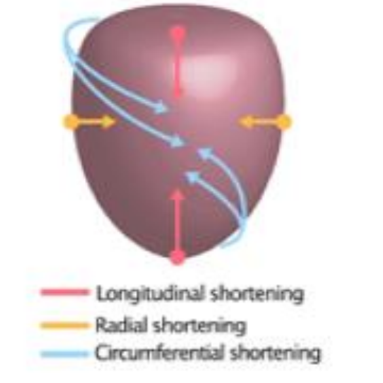
What is longitudinal strain?
Refers to the shortening or the lengthening of the myocardium from the base to apex.
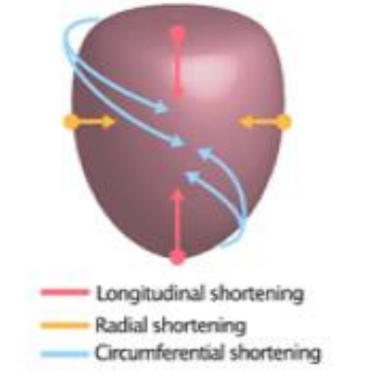
What is circumferential strain?
The reduction of the circumference of the LV cavity.
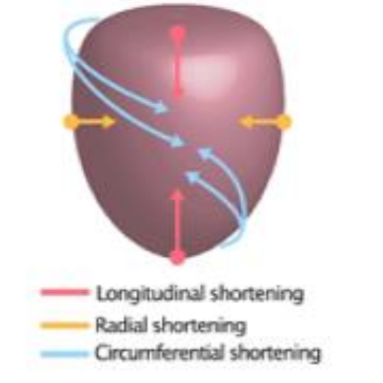
What is radial strain?
The measurement of LV wall thickening during systole.
True or False: Today, global longitudinal strain (GLS) is the most validated and clinically used application.
True.
What does GLS stand for?
Global longitudinal strain.
Do all machines have the same strain software?
No. Each machine does strain differently, and has different values for what is considered normal and abnormal wall motion. When assessing a patient on various occasions for strain, it is important to keep using the same vendor (same brand) of machine that was used to perform their previous echos.
What views of the LV are required for strain?
A4, A2, and A3.
What Doppler is required for the use of strain?
A5 CW of the LVOT/Ao, with the CLOSING CLICK of the aorta!
When visualizing the LV, it is important to keep what in mind?
The frame rate (40-80, anything higher is even better), the depth (including the valve apparatus), the sector width (including only the LV), and the focus must be set at mid or basal level (mid is preferred).
What are some contractions to strain?
Heart rhythm abnormalities (ie. arrhythmias)
Bones
Breathing (ie lungs - suspend breathing for the time that image acquiring is done)
How many beats per loop is required for strain?
Ideally 3 beats, but 2 beats can work as well.
How is measurement of strain performed?
Some vendors will have three points, each at the valve annulus and the apex, some will have lines for you to trace the endocardium, and some will have dots along the whole interface of the myocardium.
Strain echo may be influenced by what factors?
Racial/ethnic/international differences
Age
Sex
Hemodynamic factors
Cardiovascular risk factors
Medications
Dialysis
Pregnancy
Endurance athletes
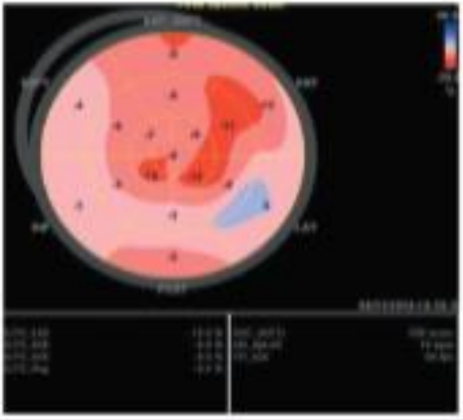
Red is considered what in terms of the wall motion with strain?
Good!
Pink is considered what in terms of the wall motion with strain?
Okay function.
White is considered what in terms of the wall motion with strain?
Bad function.
Blue is considered what in terms of the wall motion with strain?
BAD BAD function (moving further away instead of shortening in systole).
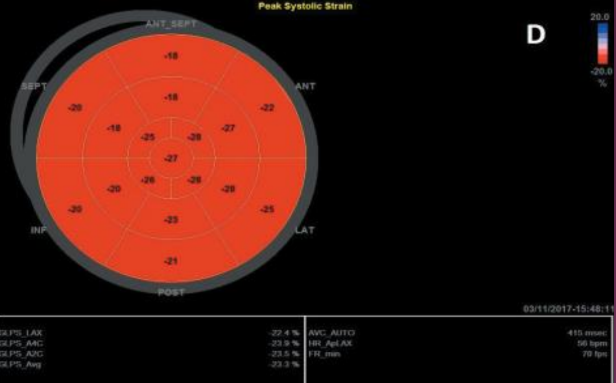
What is the typical negative percentage in change of the walls?
-18 to -20% is good. Anything higher is really good. Anything lower than -16% indicates an issue.
The redder and more negative a GLS value, the better or worse?
The better.
Degree of hypokinesis is indicated with what?
A value less than -16% (ie. -10%) (Light pink)
Degree of akinesis is indicated by what value?
Zero (white).
Degree of dyskinesis is identified by what?
Blue colour or a positive percentage (ie. 6%)
What does a normal GLS look like?
What does GLS look like with hypertension?
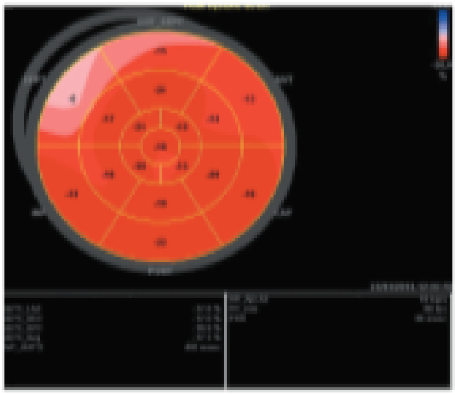
What does GLS look like with apical hypertrophic cardiomyopathy?
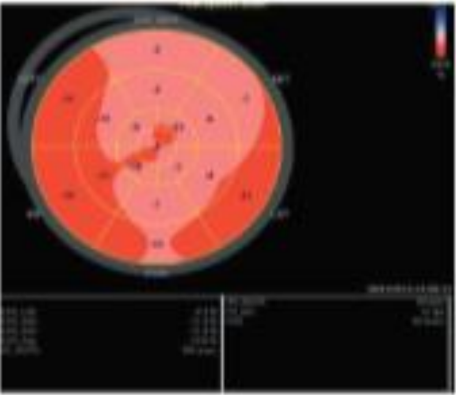
What does GLS look like with amyloidosis?
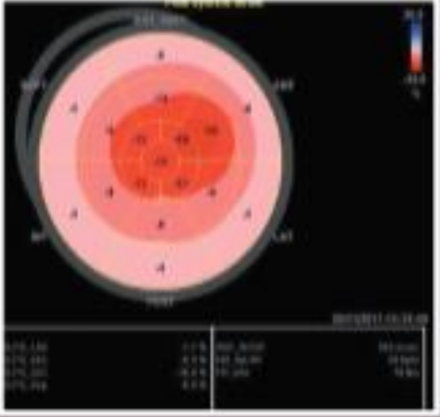
What does GLS look like on a oncology patient (if the medications affect the heart)?