NSCI 311 cerebrum + cerebral cortex anatomy
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
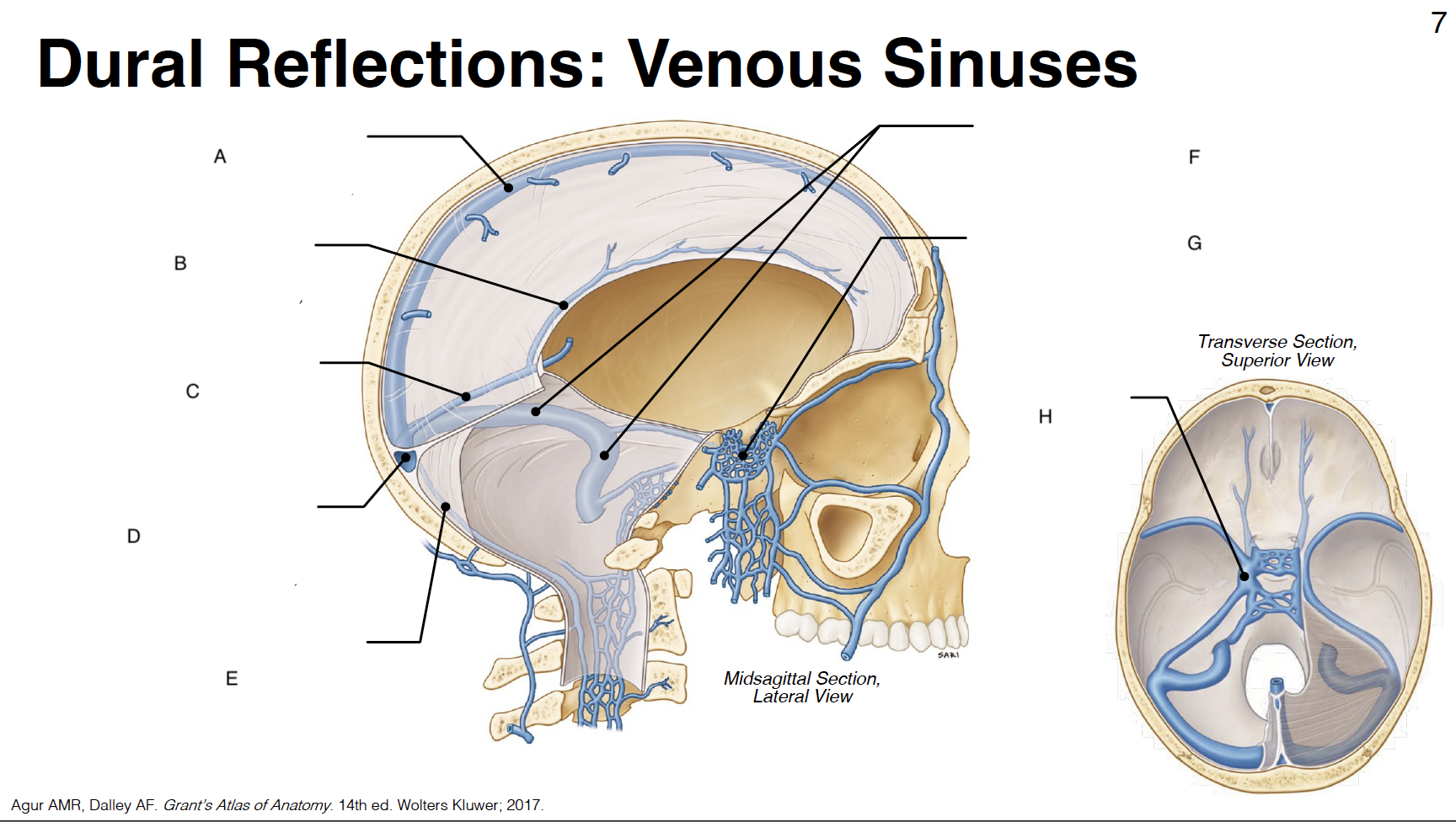
A
Superior sagittal sinus: outer border of falx cerebri (attached)
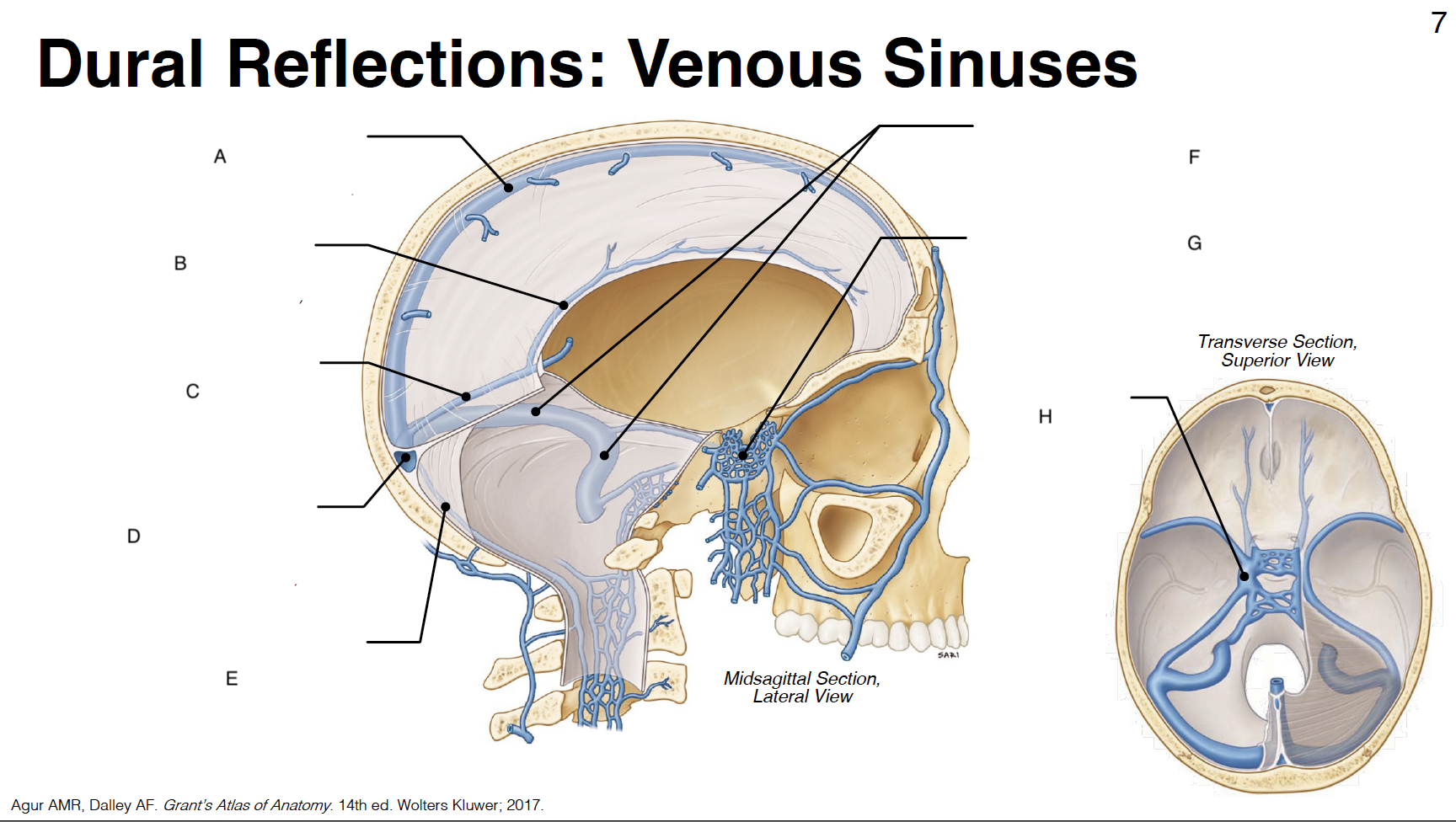
B
inferior sagittal sinus: inner border of falx cerebri (free)
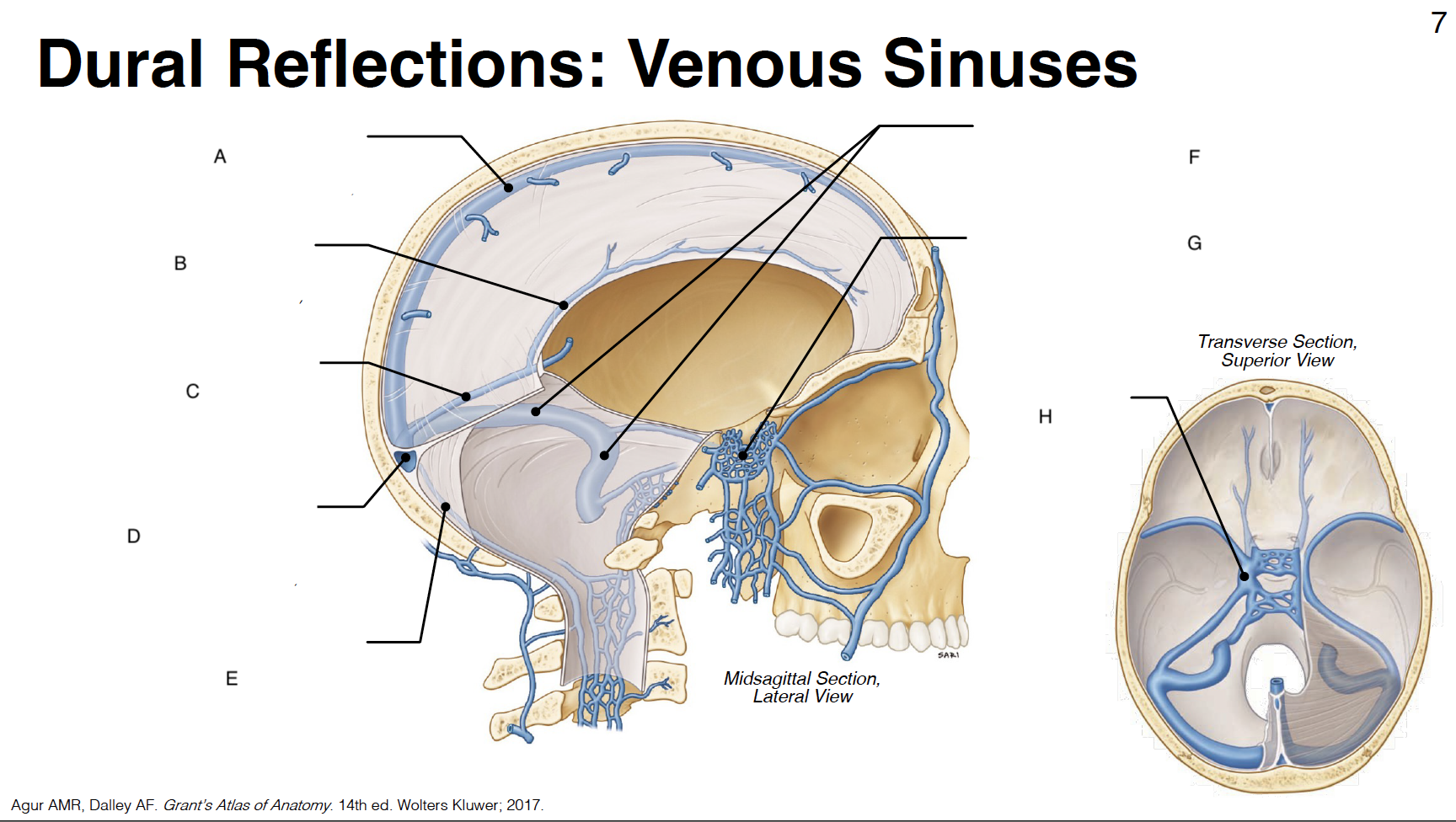
C
straight sinus: junction of falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli
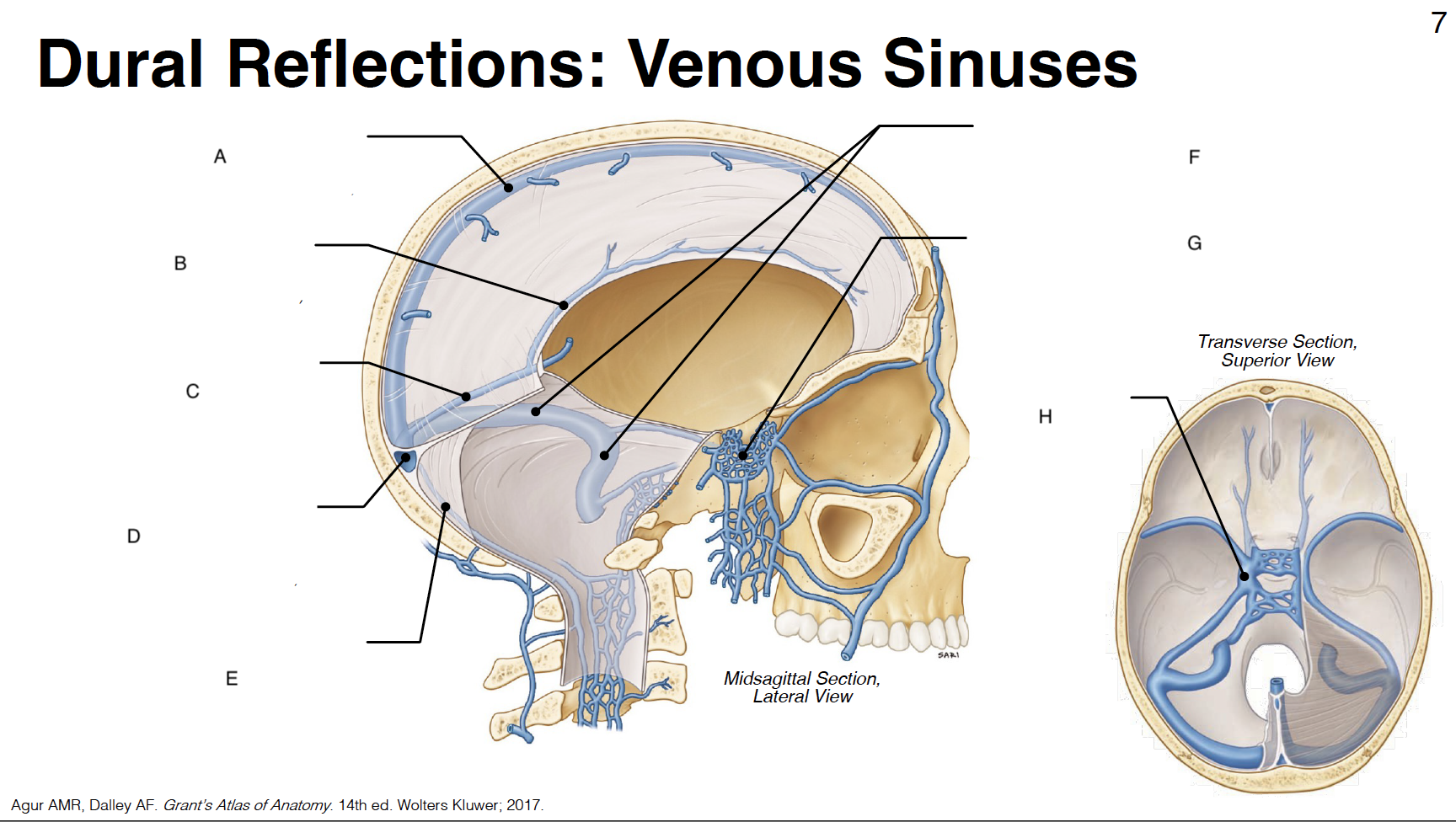
D
confluence of sinuses (where all sinuses come tgt): junction of falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli and falx cerebelli
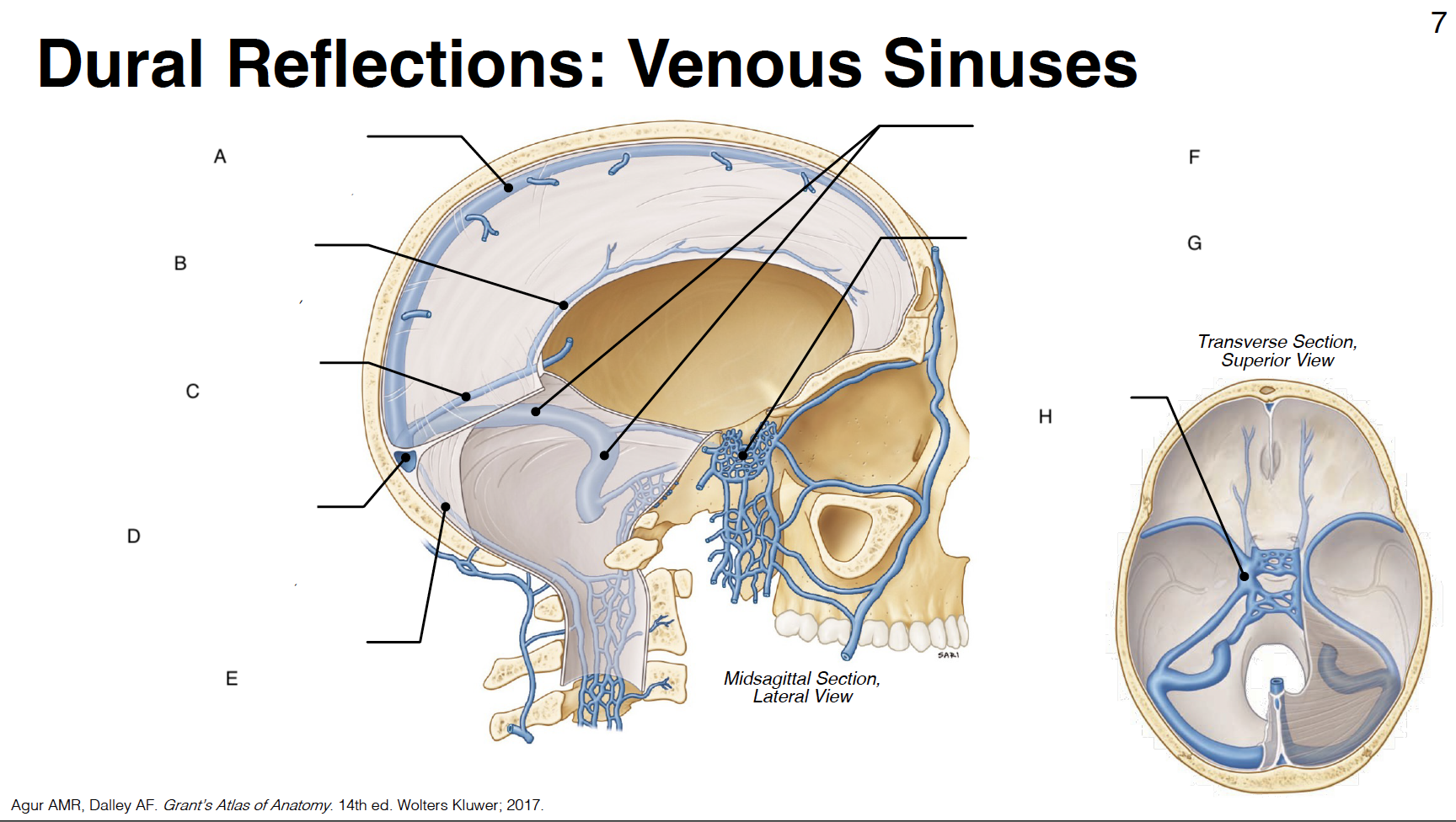
E
occipital sinus: outer border of falx cerebelli (attached)
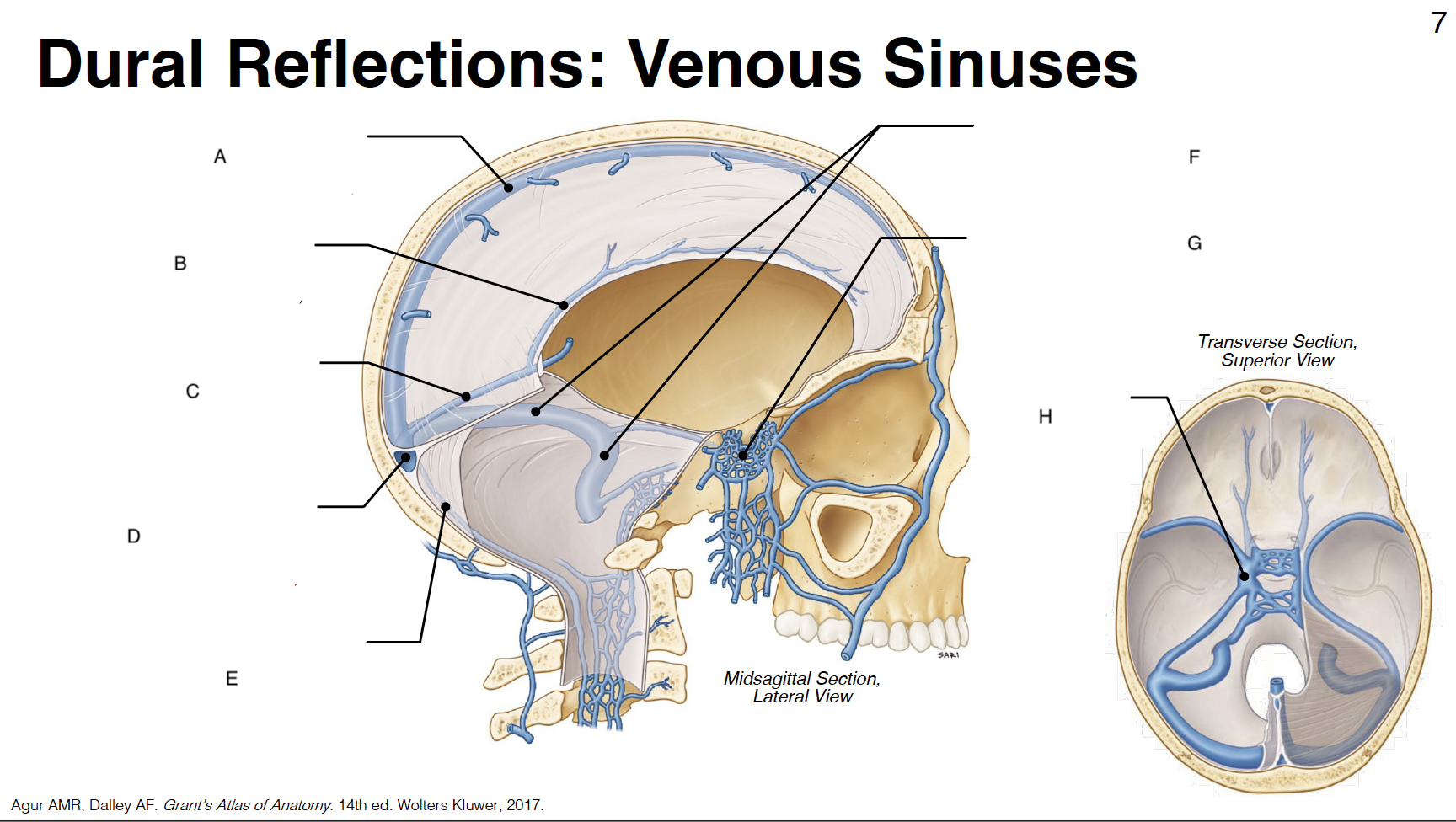
F
transverse sinus and sigmoid sinus: form deep grooves on interior surfaces of occipital, parietal and temporal bones; drain into internal jugular vein IJV)
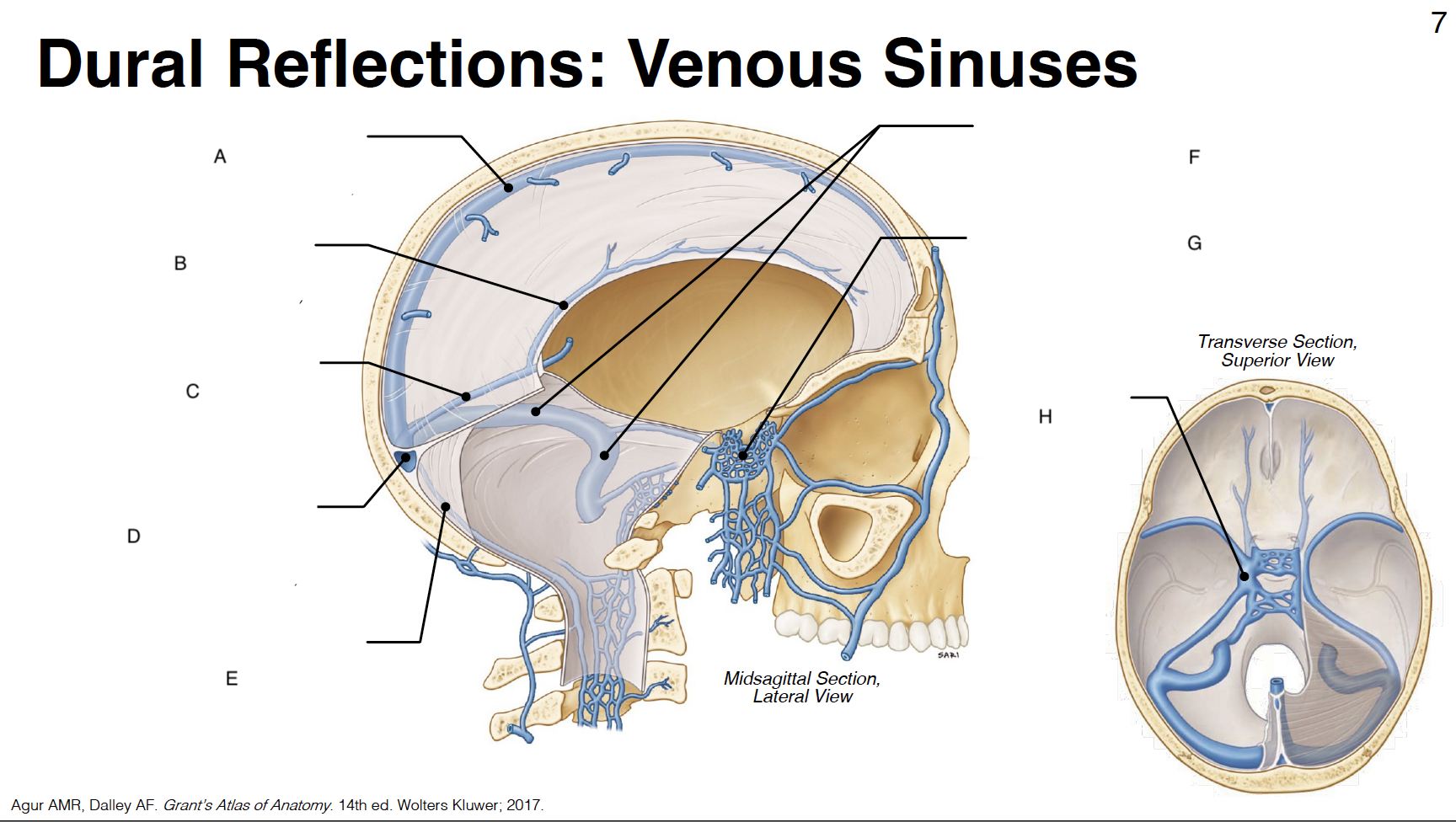
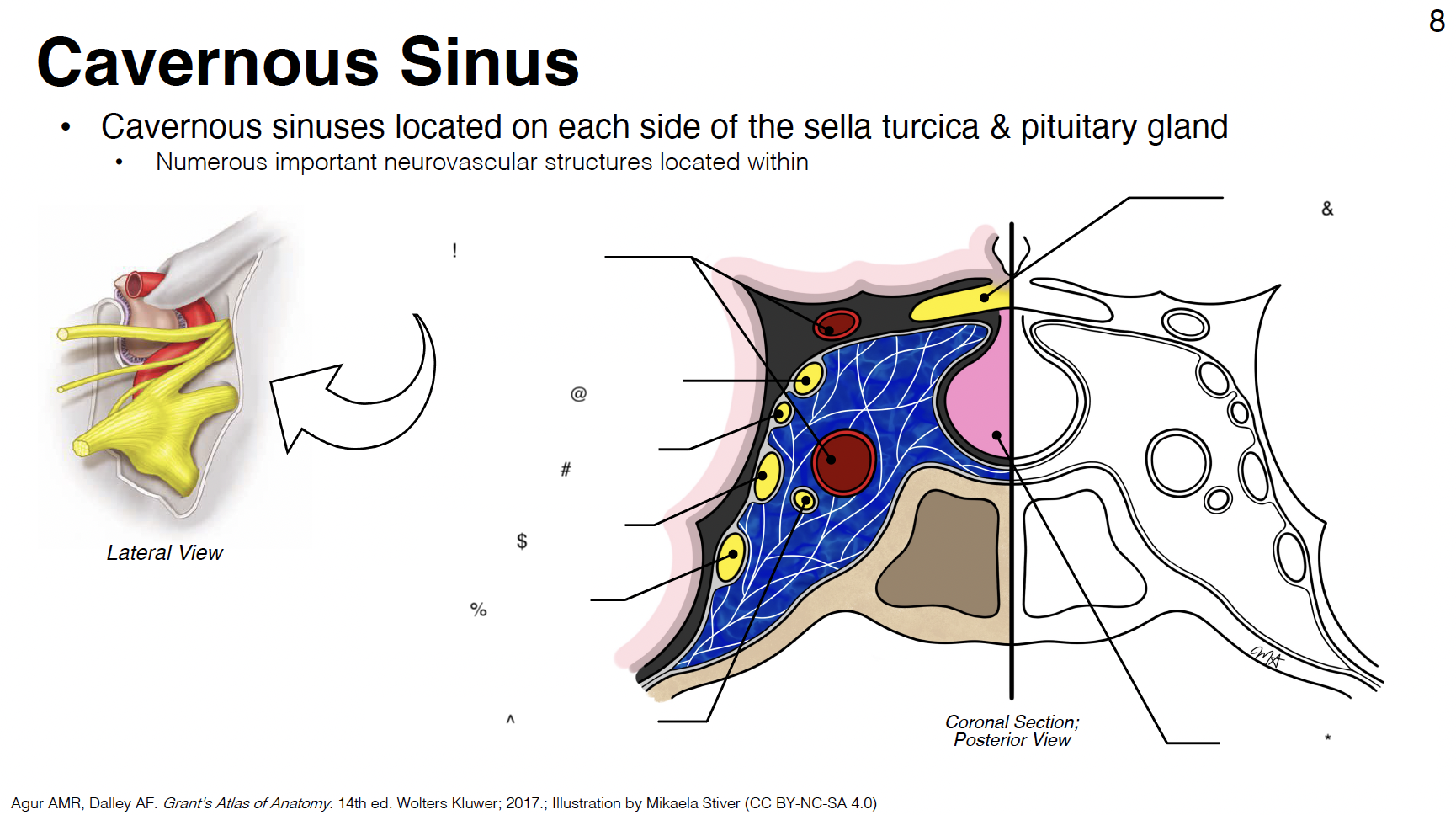
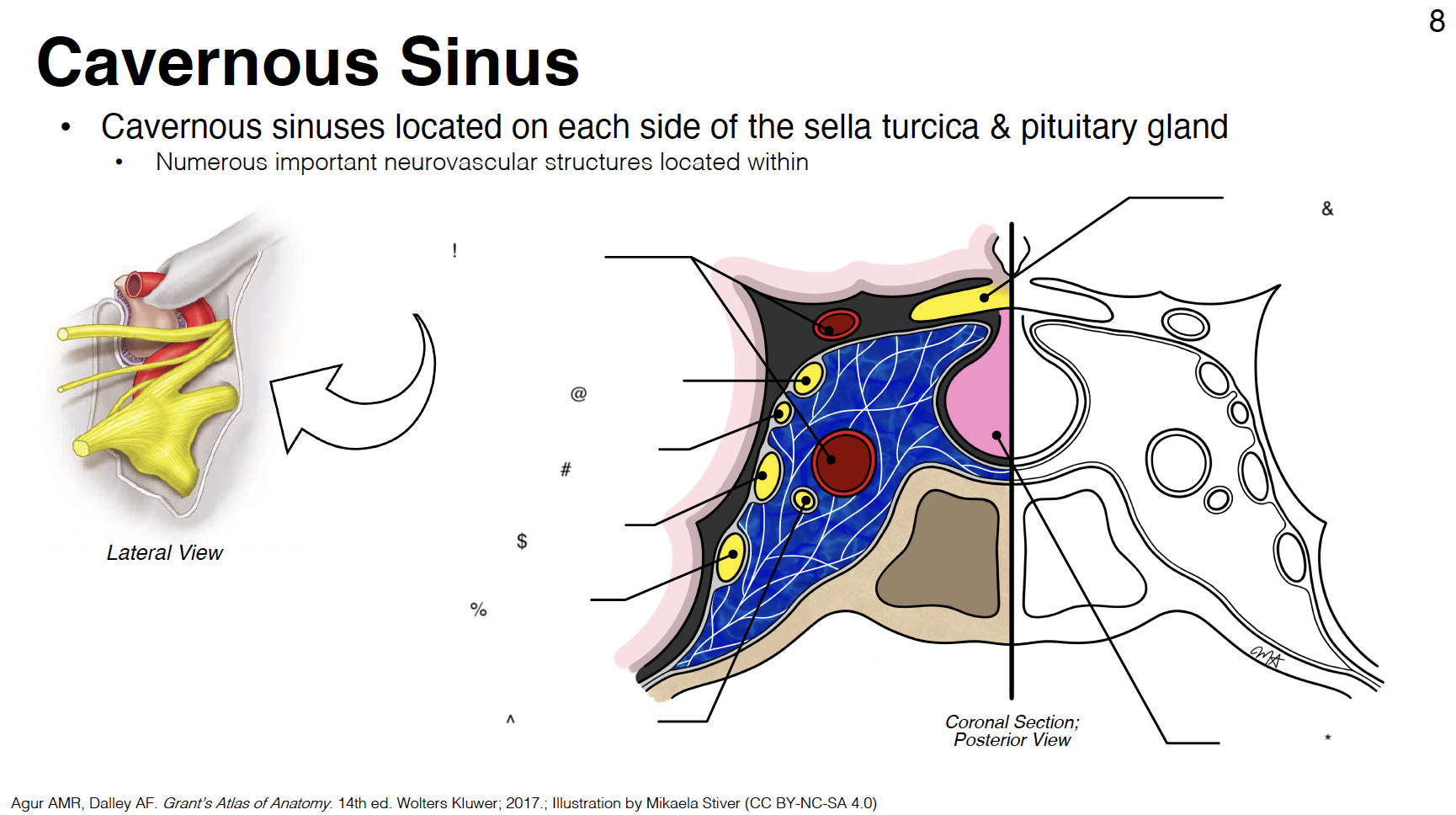
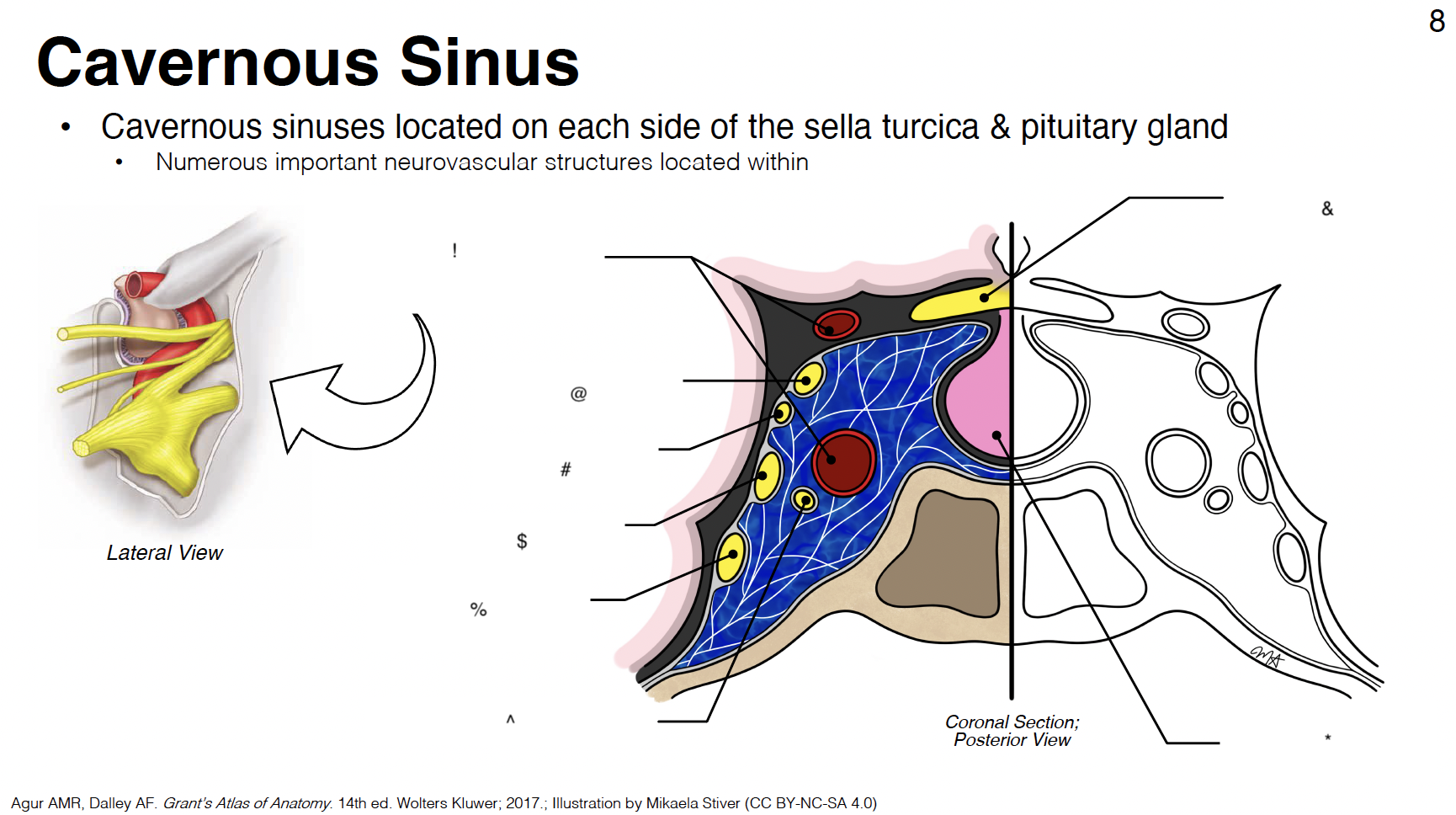
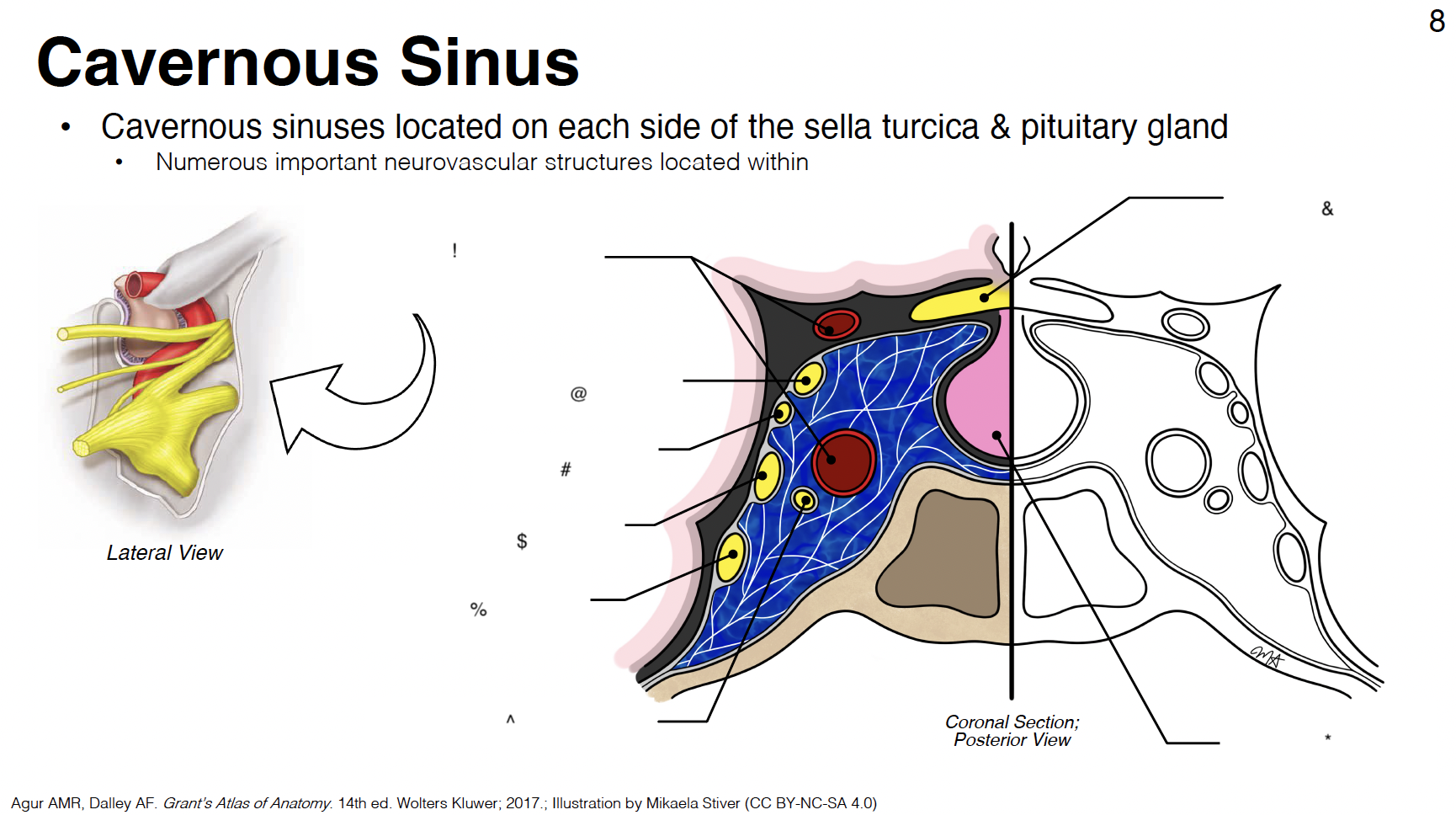
G
cavernous sinus: venous plexus on either side of sella turcica
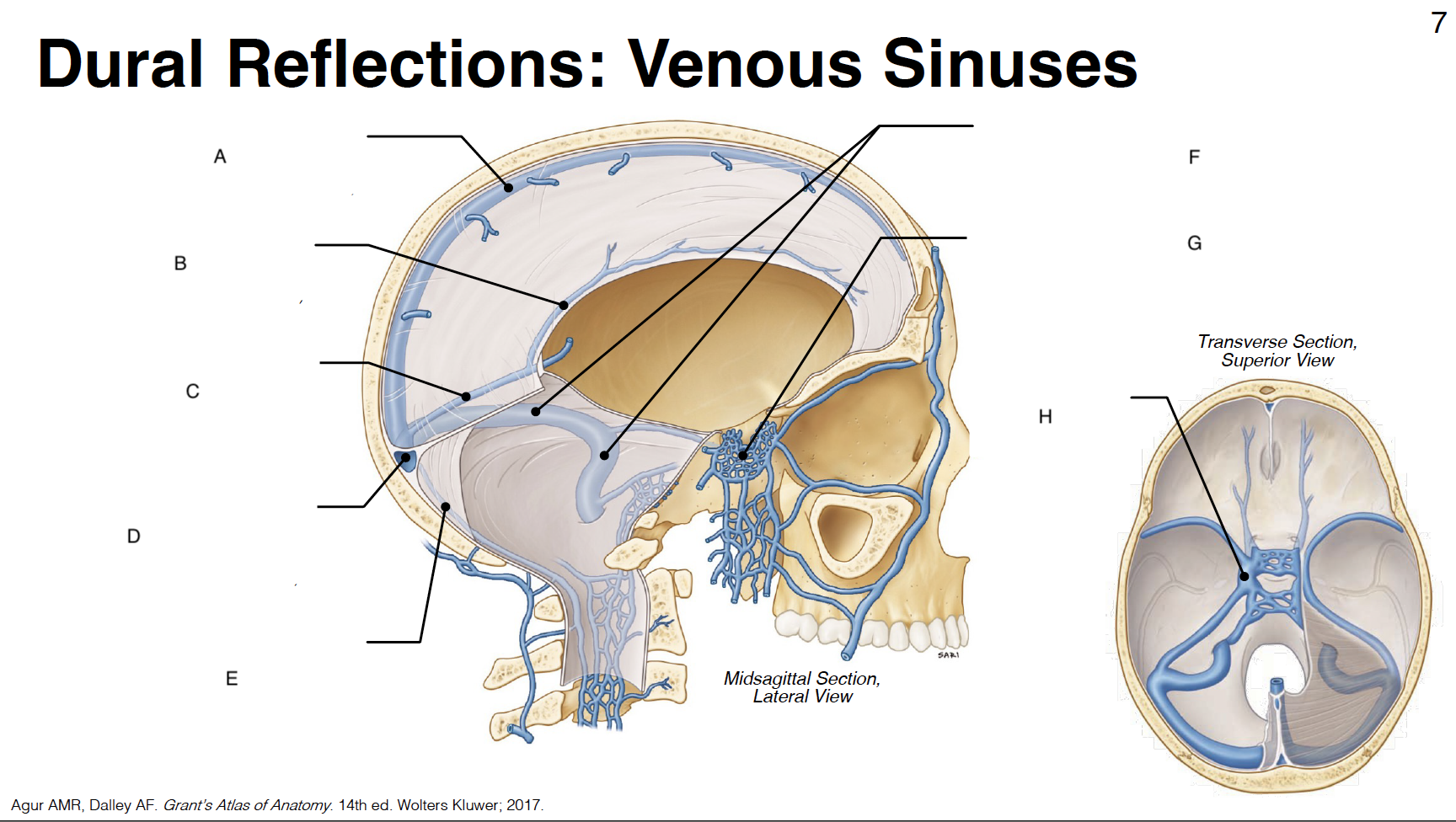
H
Sella turcica: where pituitary gland sits
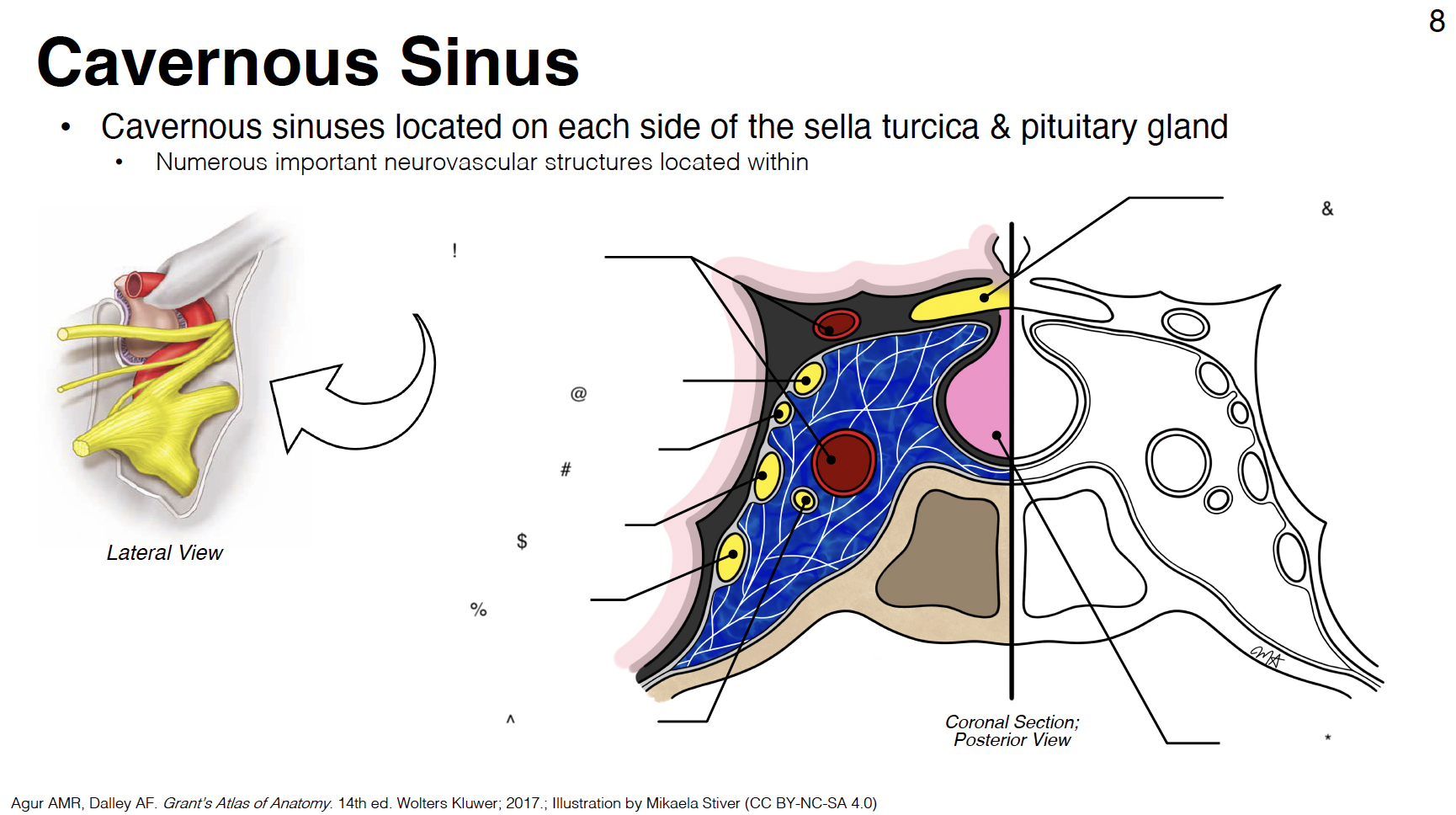
!
internal carotid artery (s-shaped)
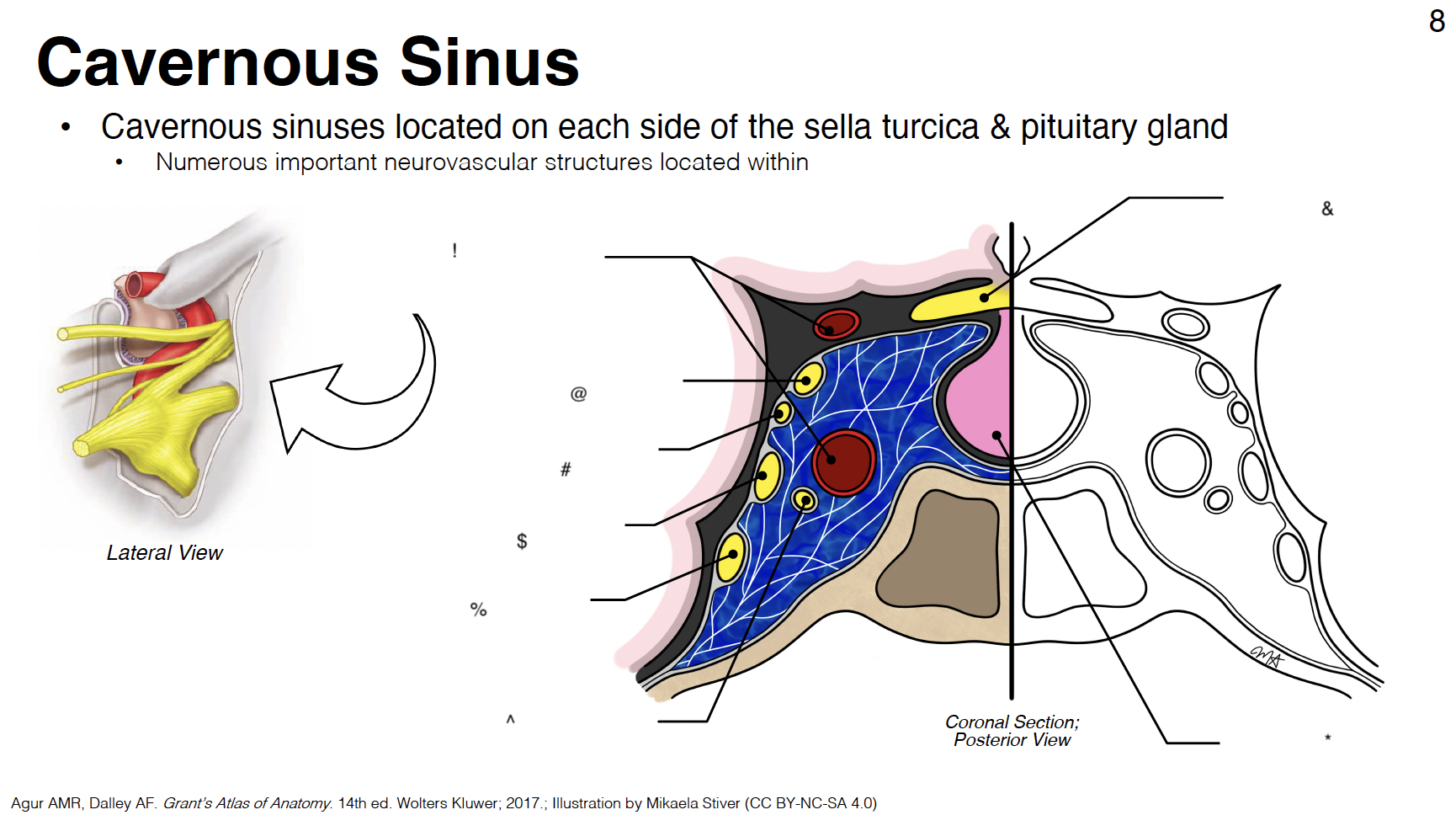
@
CN III: oculomotor
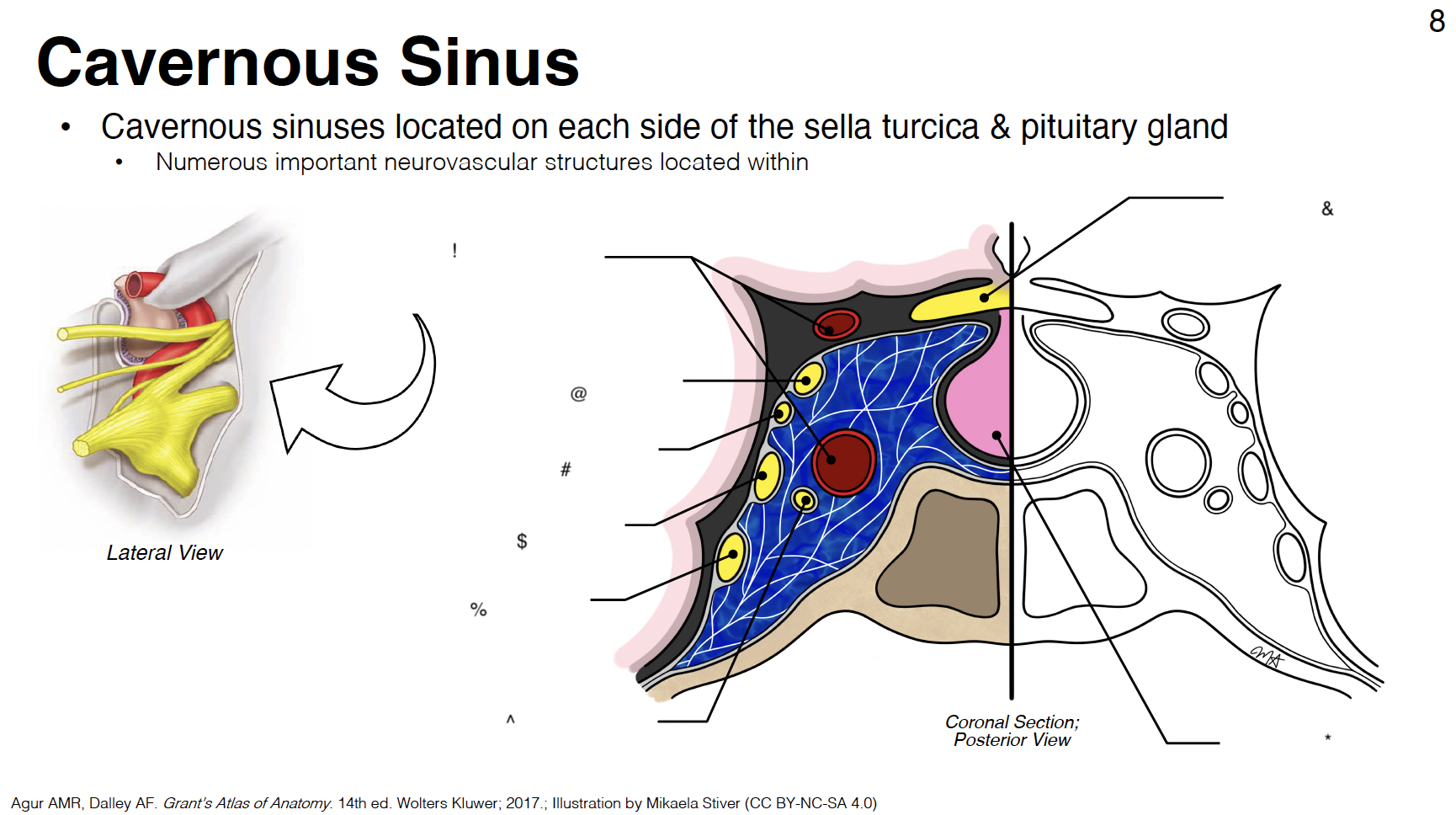
#
CN IV: trochlear
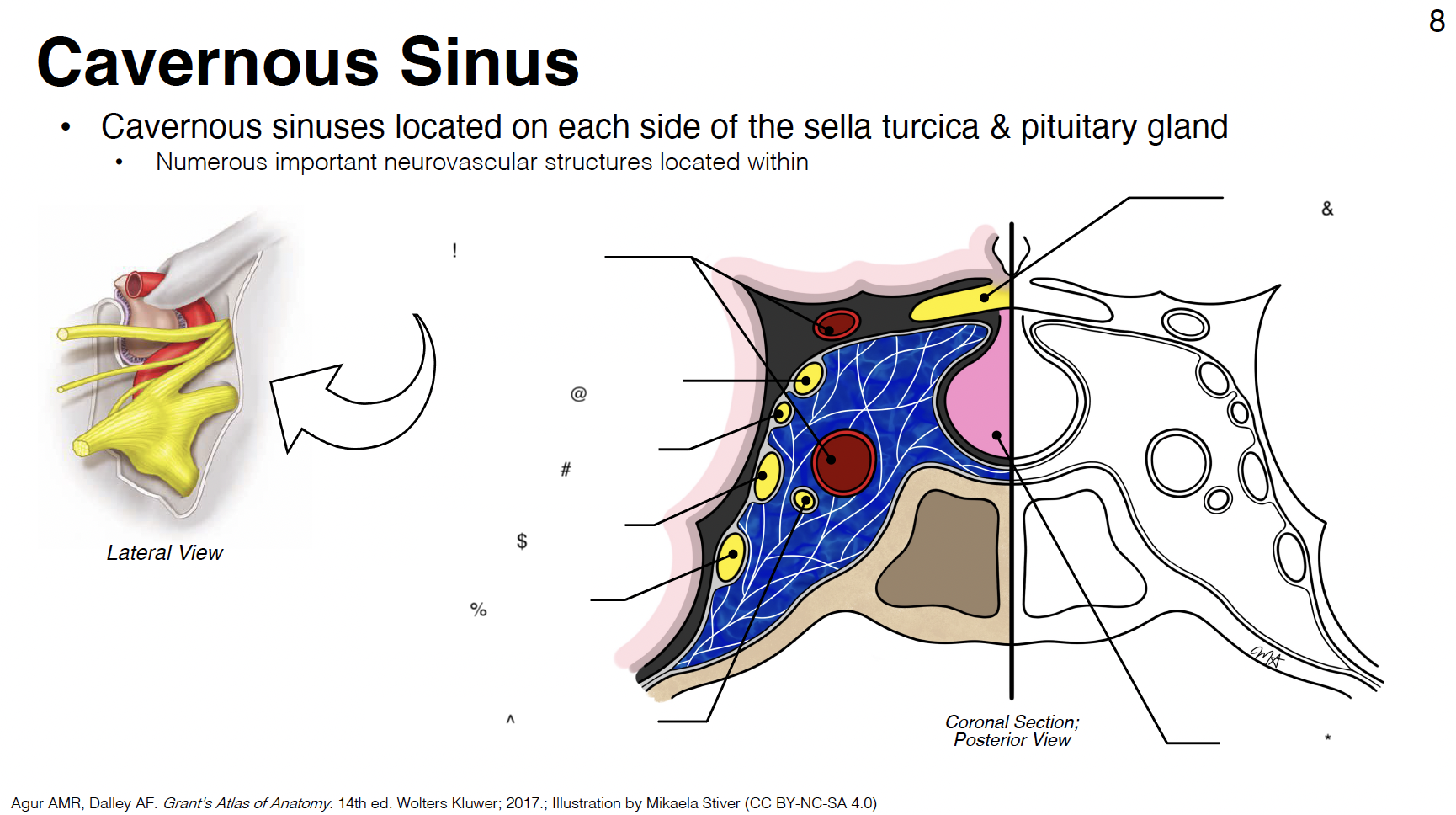
$
CN V1: ophthalmic branch of trigeminal nerve
%
CN V2: maxillary branch of trigeminal nerve
^
CN VI: abducens
&
optic chiasm
*
pituitary gland
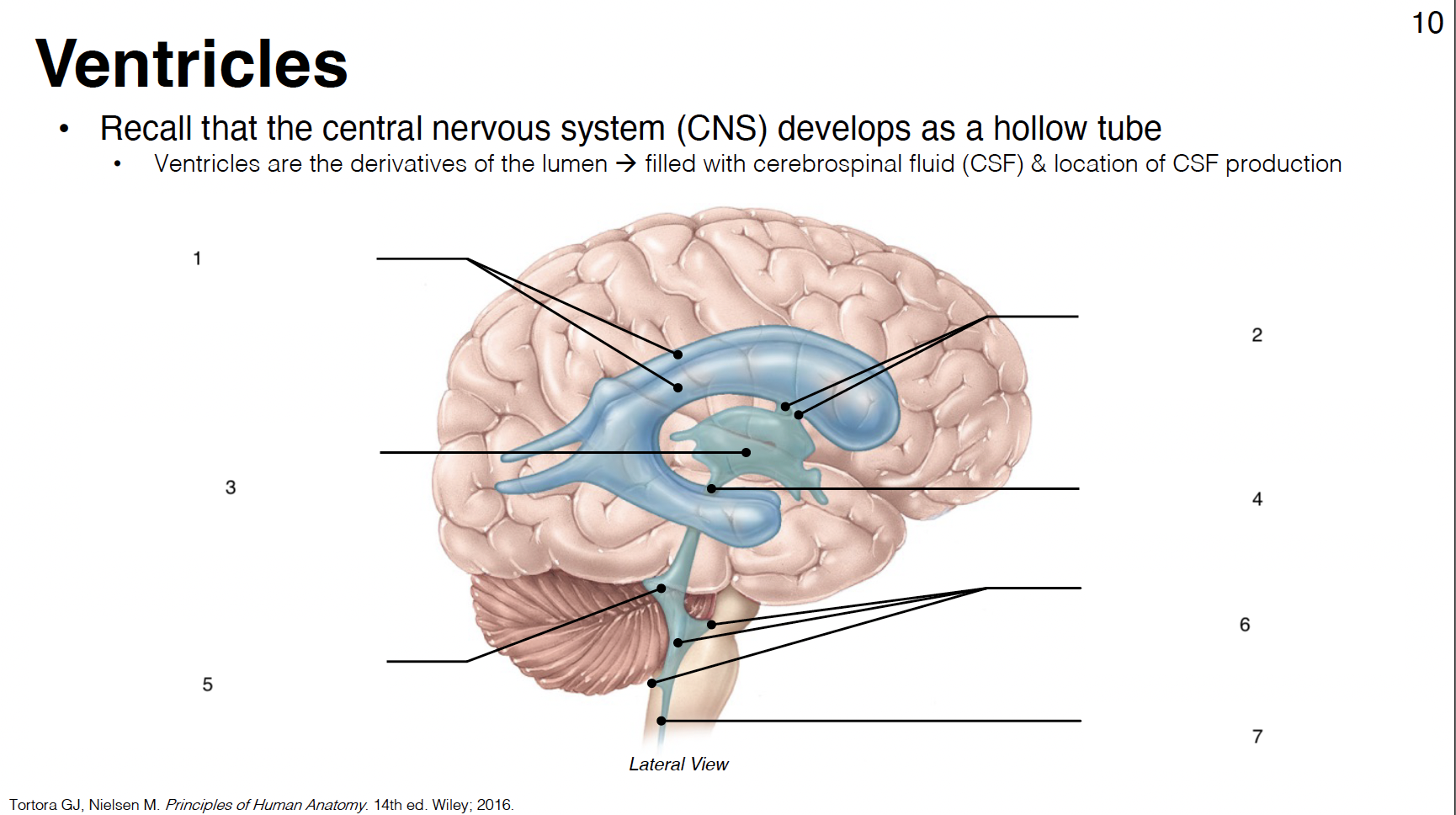
1
lateral ventricles (1st and 2nd in each cerebral hemisphere)
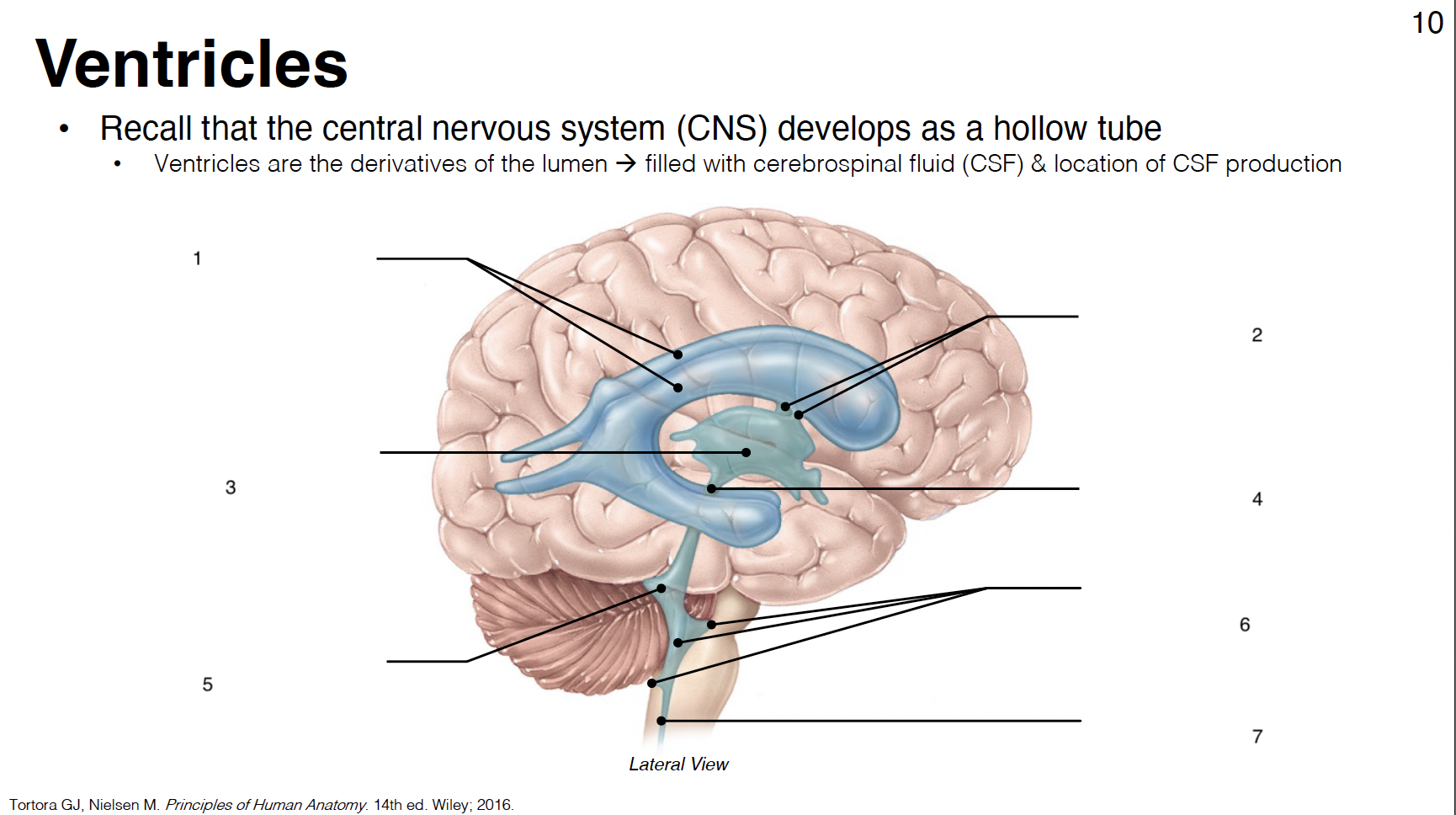
2
interventricular foramina: connect lateral ventricles to 3rd ventricle
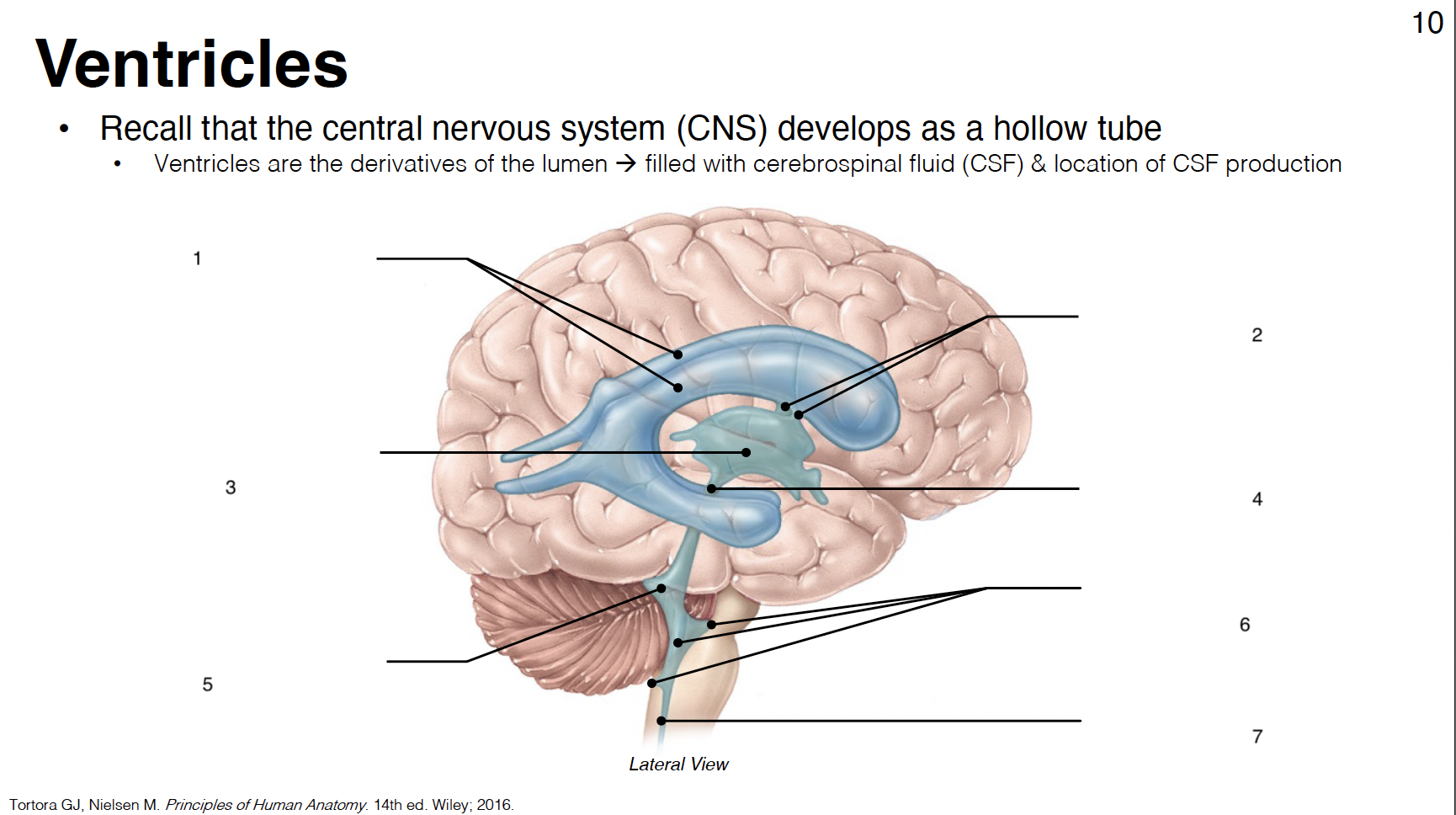
3
3rd ventricle: midline structure between diencephalon on each side
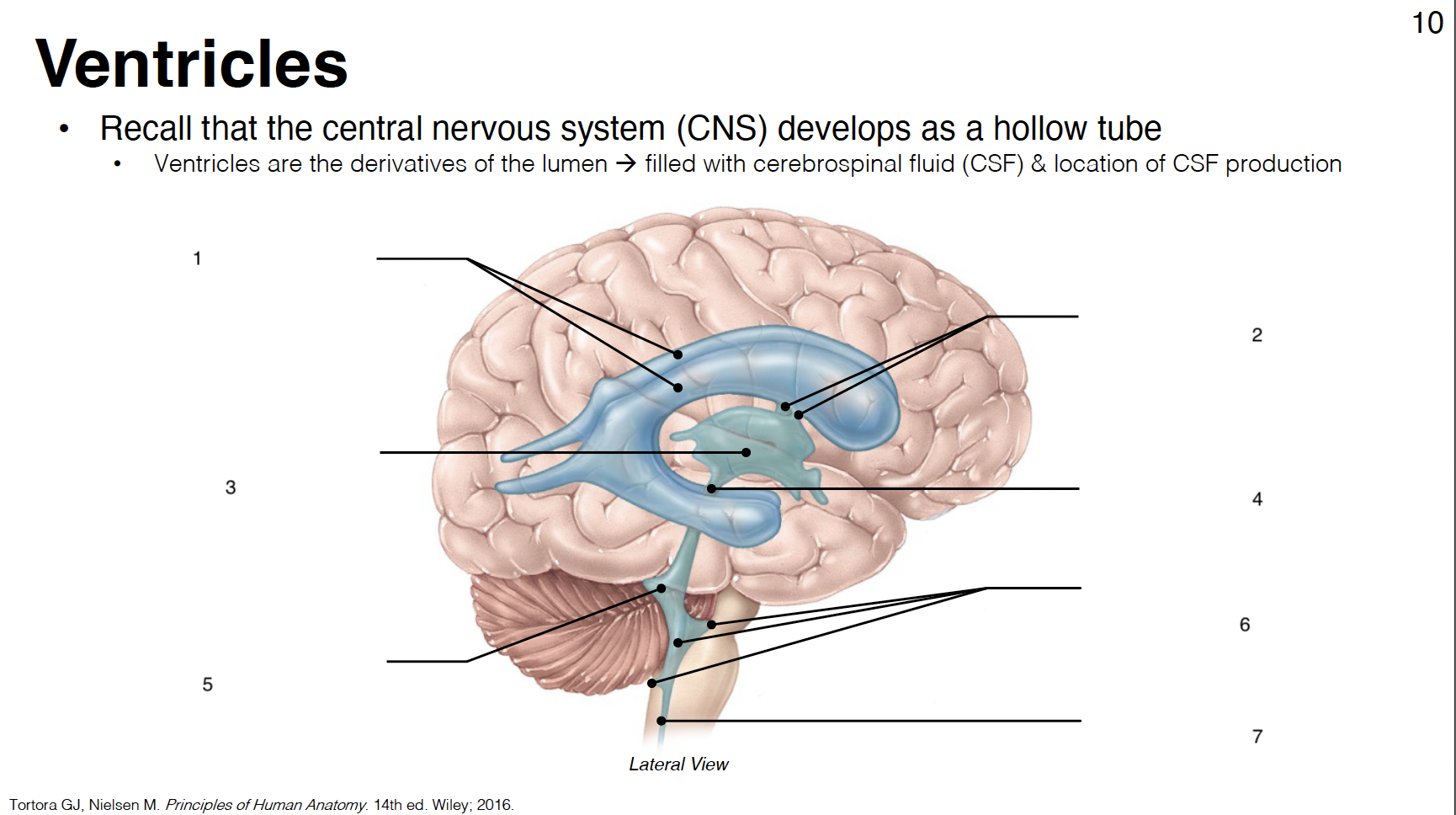
4
cerebral aqueduct: connects 3rd and 4th ventricles
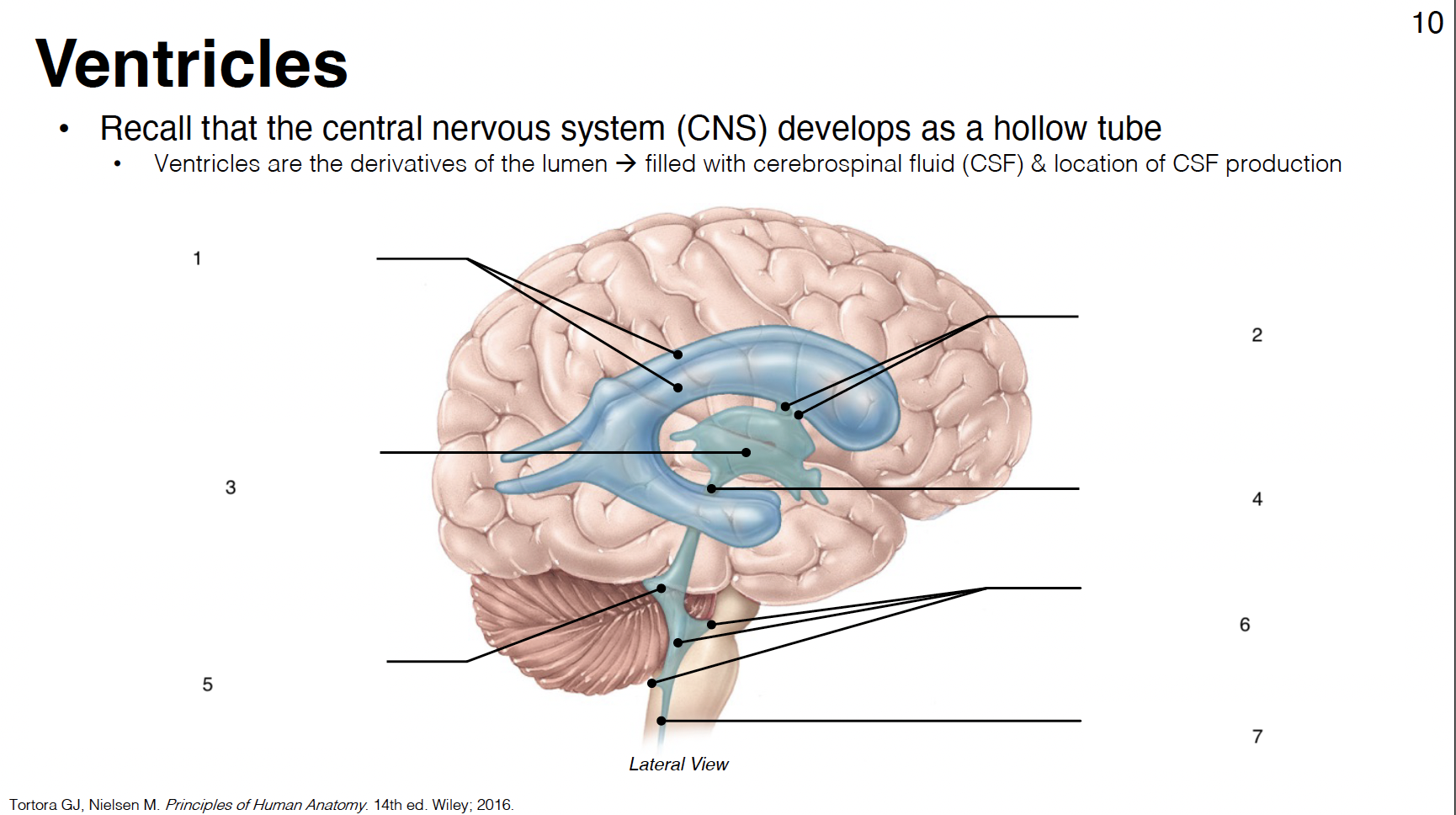
5
4th ventricle: between cerebellum and brainstem
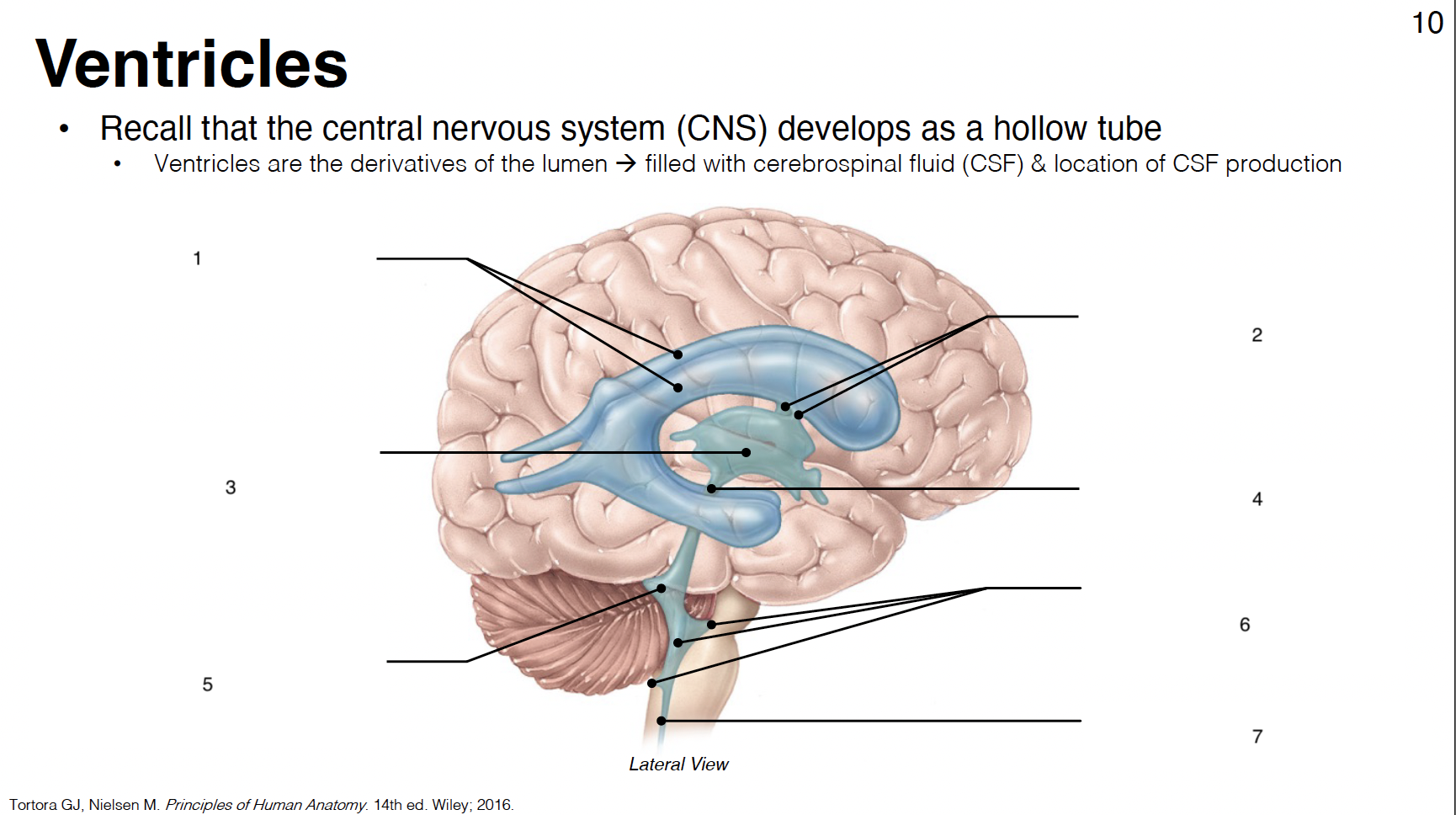
6
lateral apertures (2) and median aperture (1): connect 4th ventricle to subarachnoid space
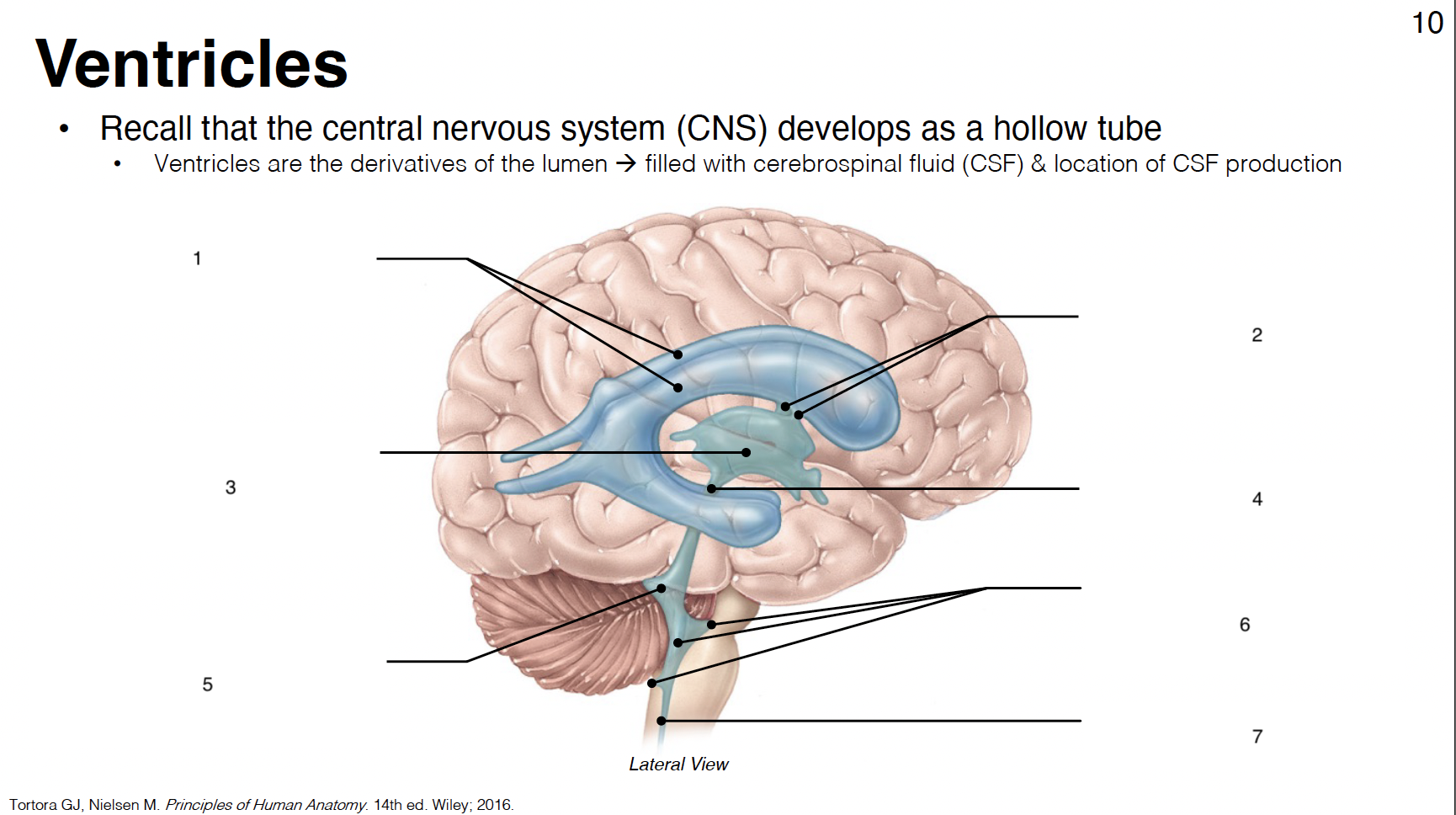
7
central canal: in caudal medulla and SC
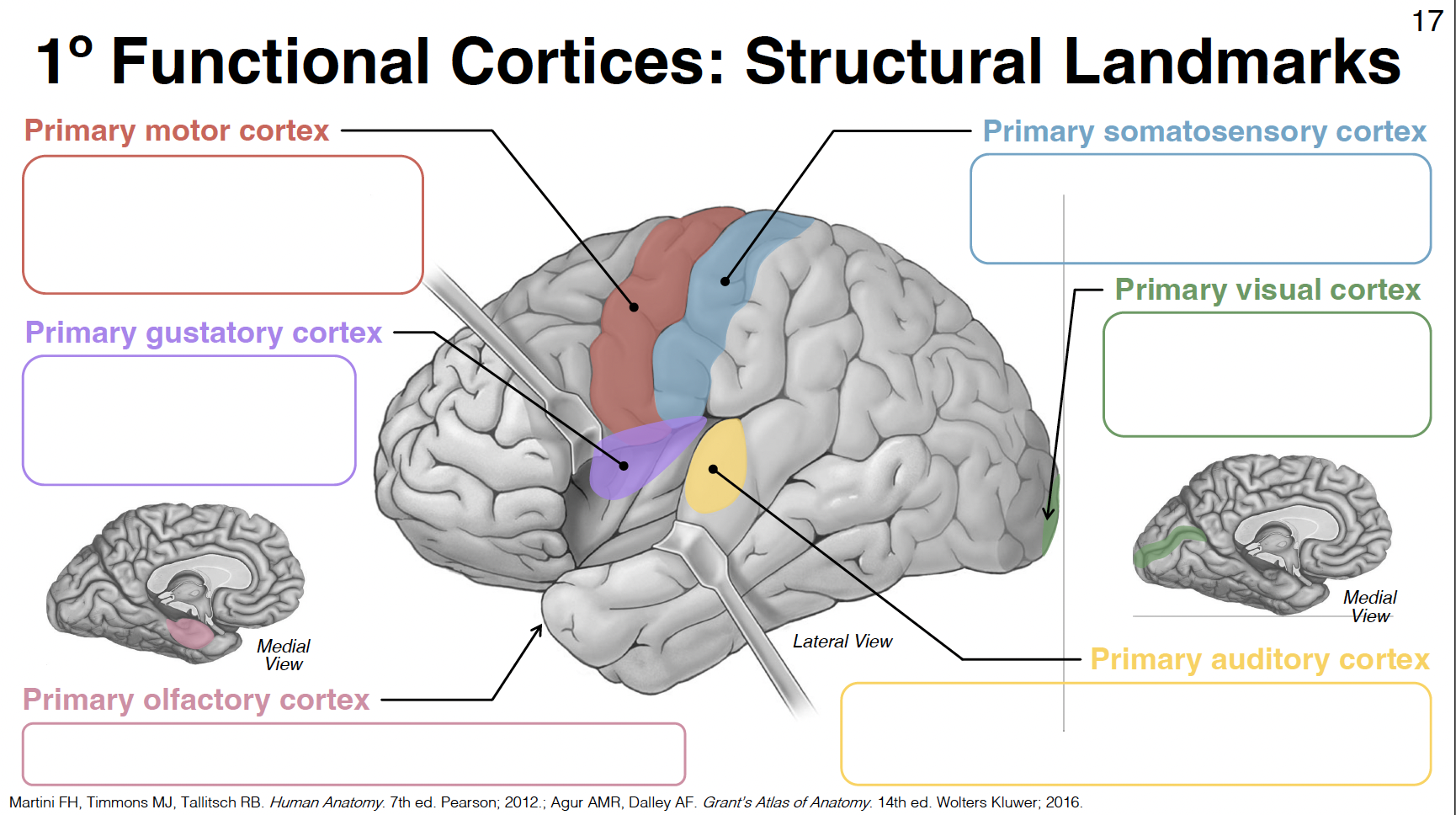
primary motor cortex
pre-central gyrus: between central and pre-central sulcus
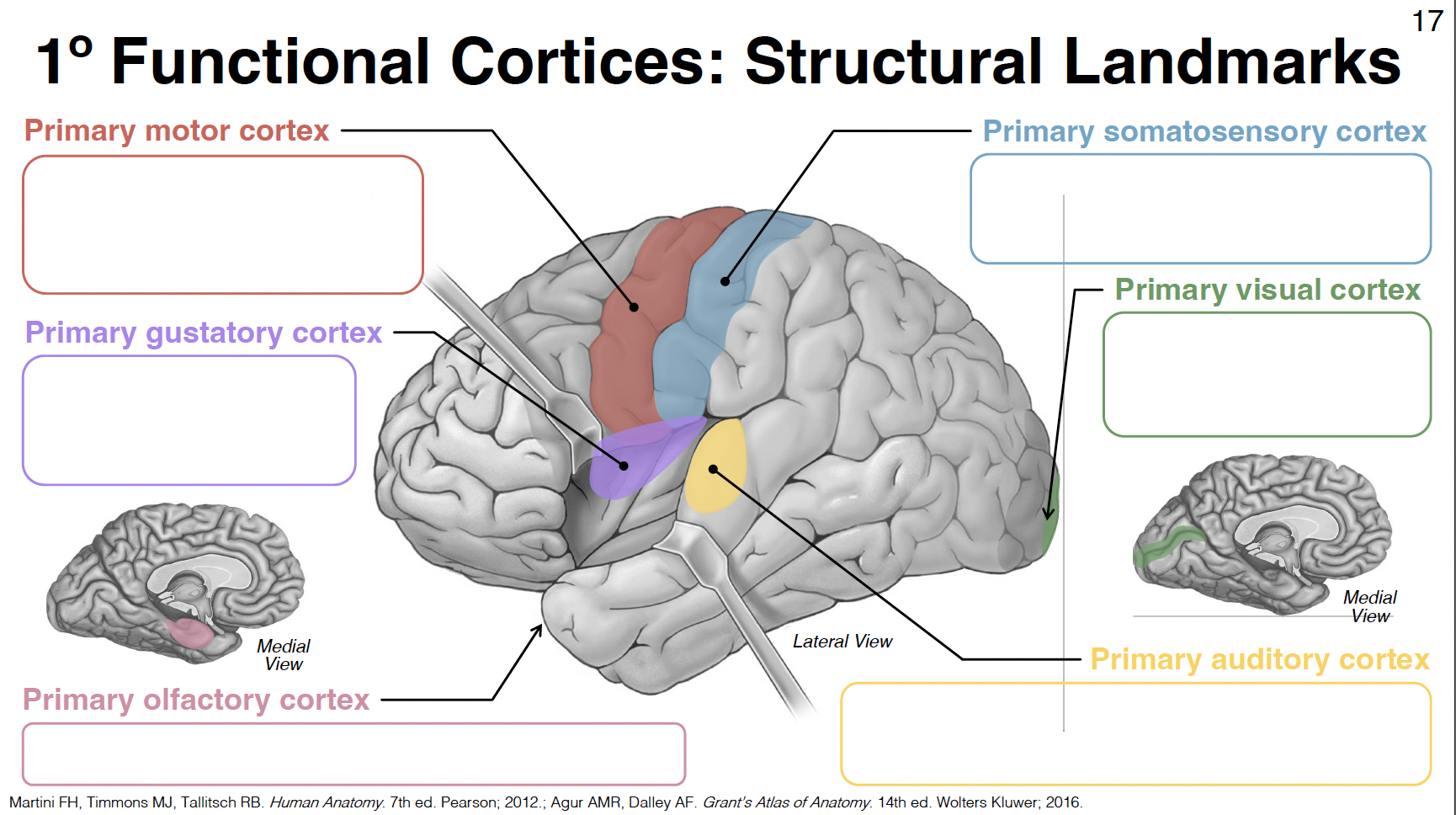
primary gustatory cortex
anterior insula
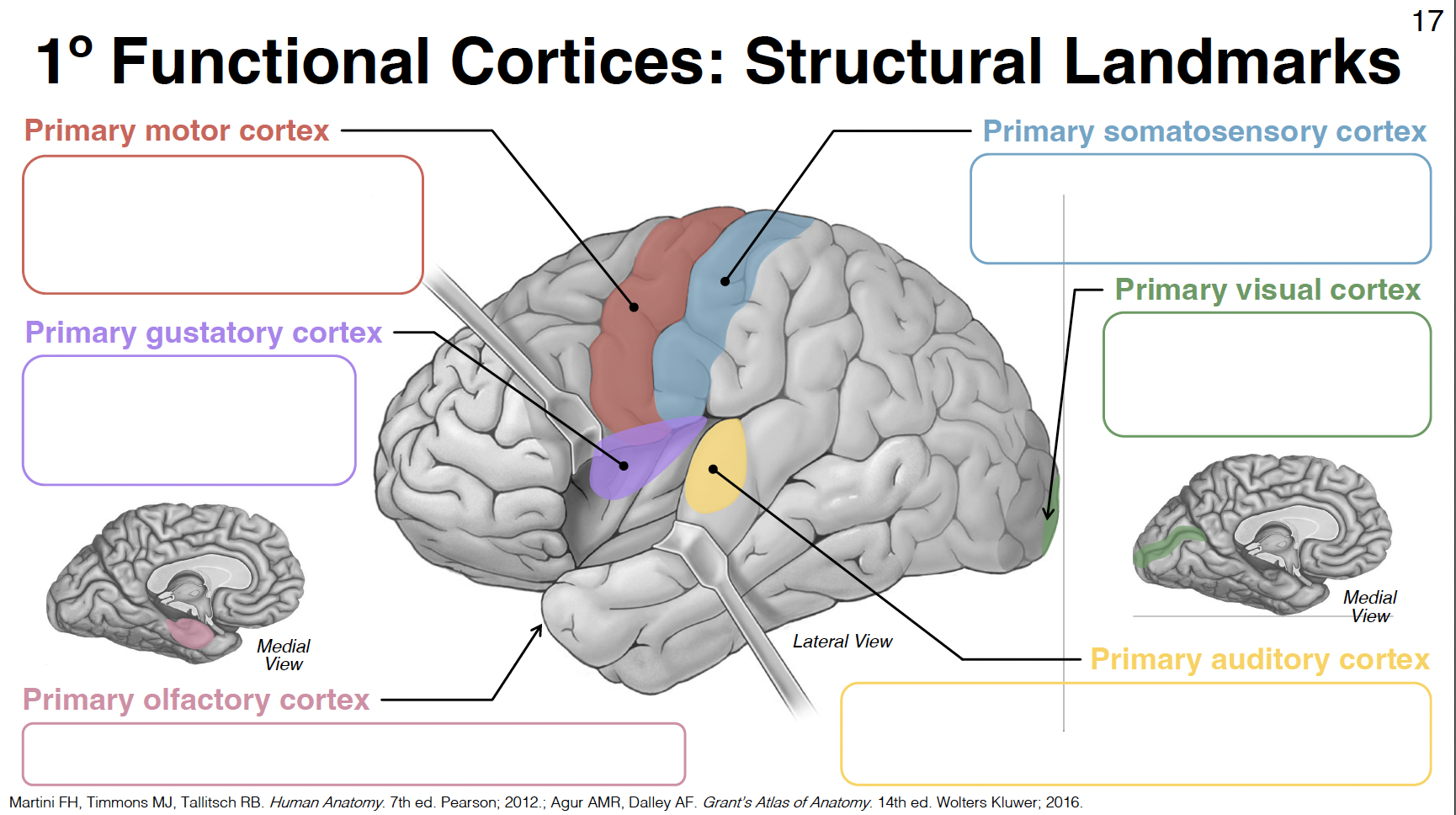
primary olfactory cortex
uncus (close to amygdala) - rostral parahippocampal gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
post-central gyrus: between central and post-central sulcus
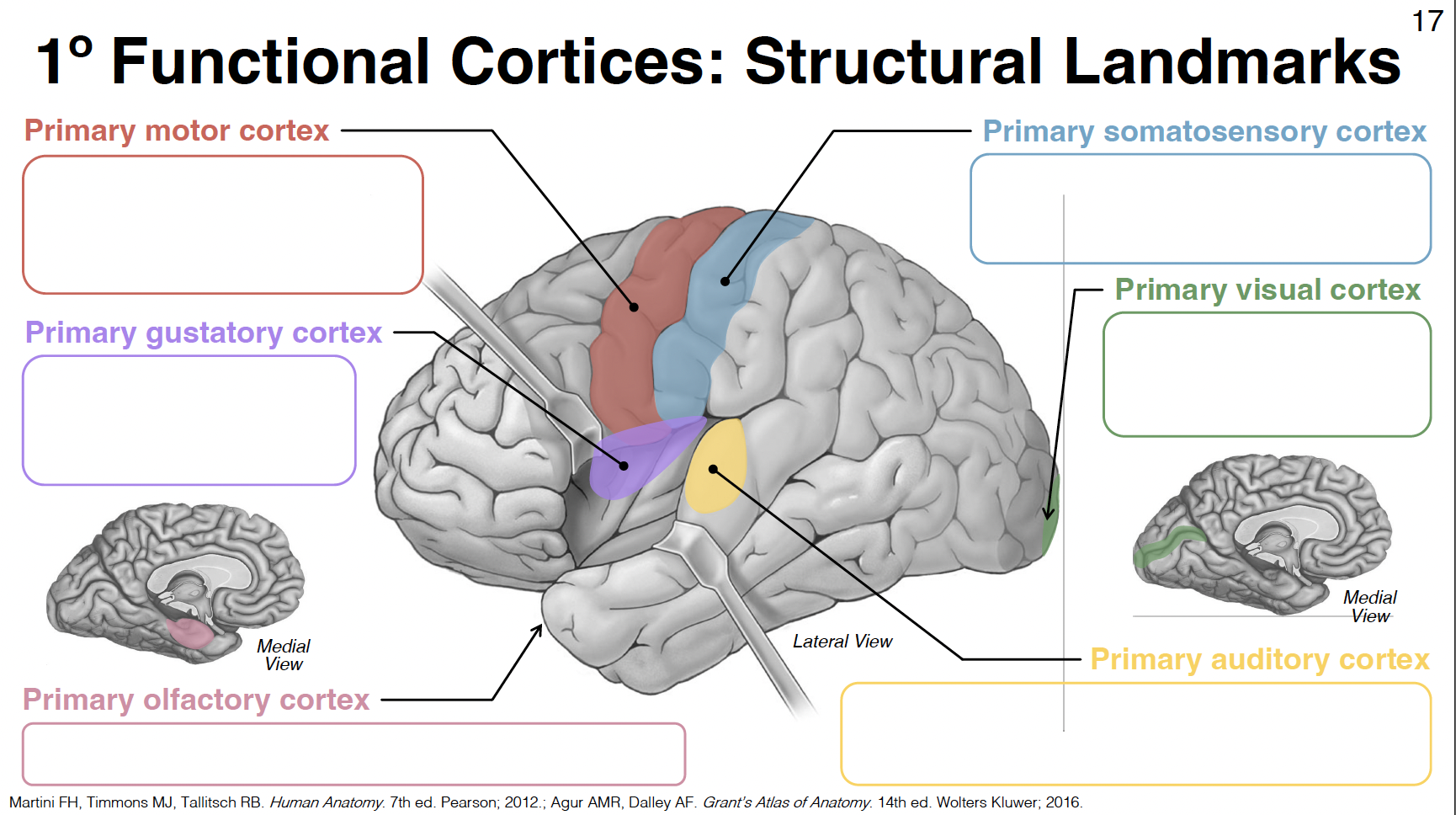
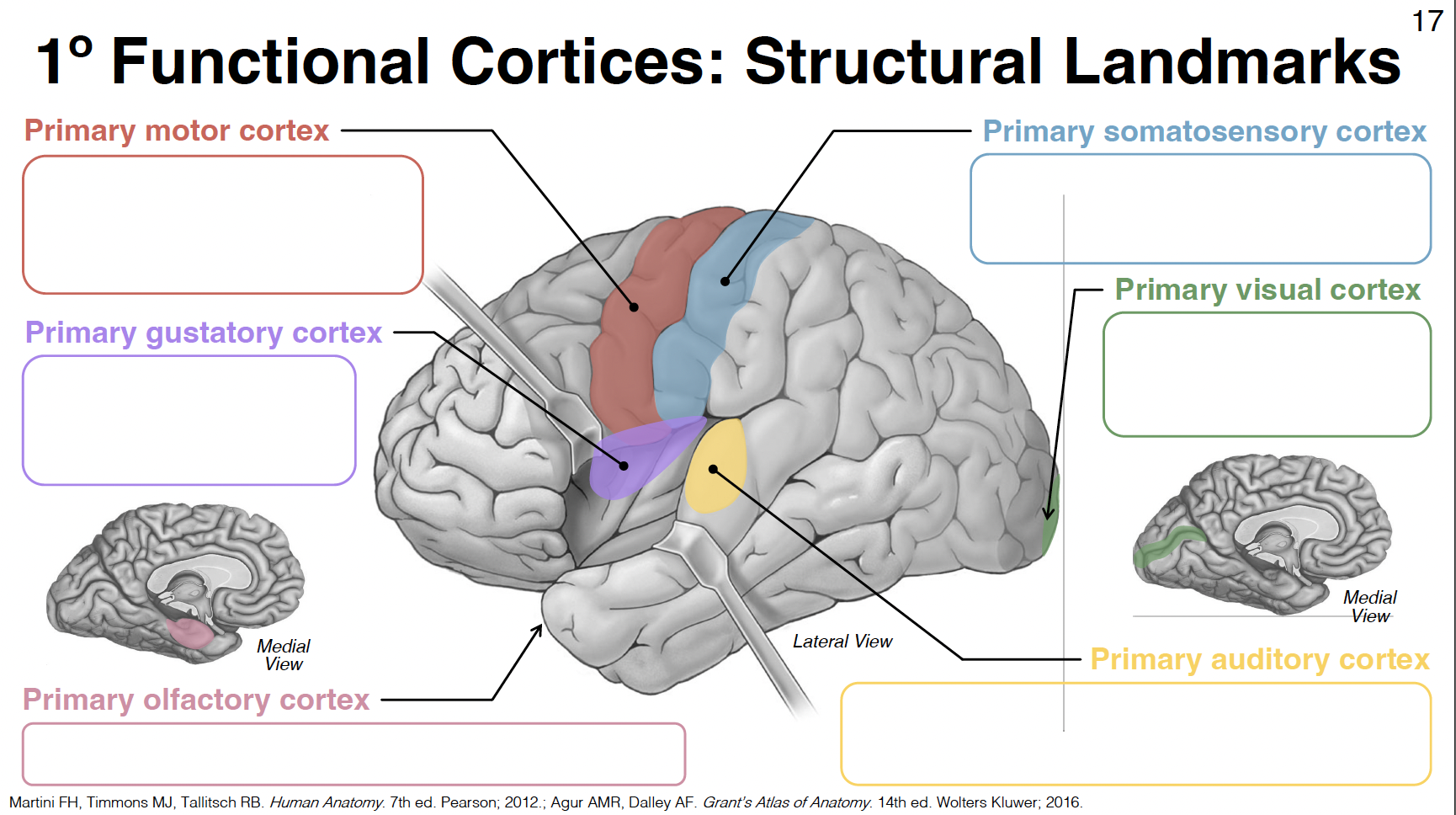
primary visual cortex
in and around calcarine sulcus/fissure
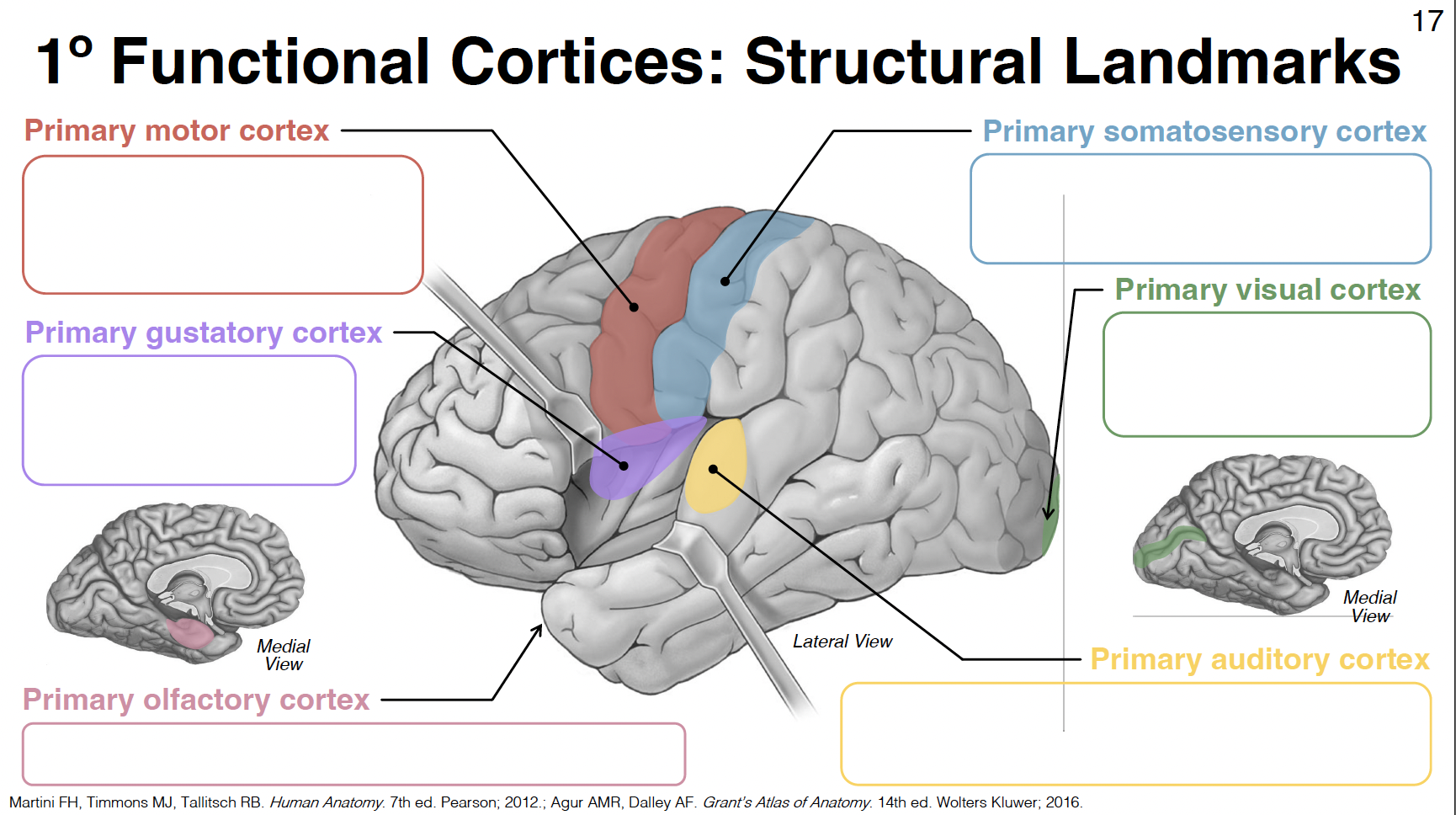
primary auditory cortex
central superior temporal gyrus and transverse temporal gyri (inside lateral fissure)
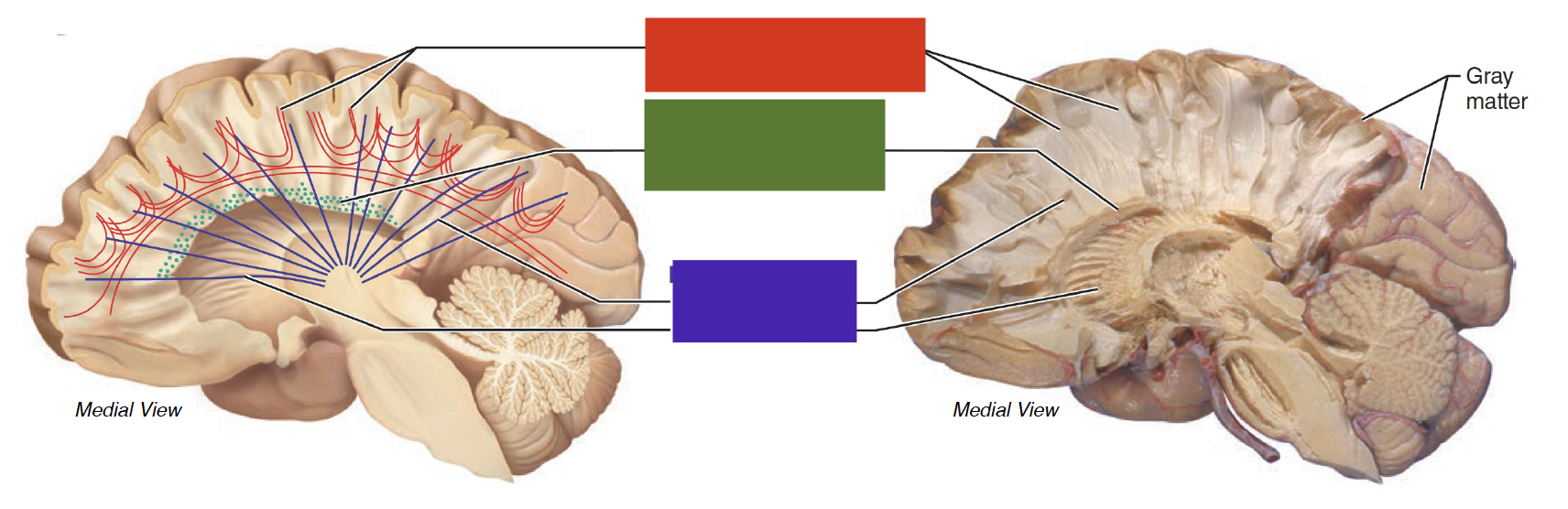
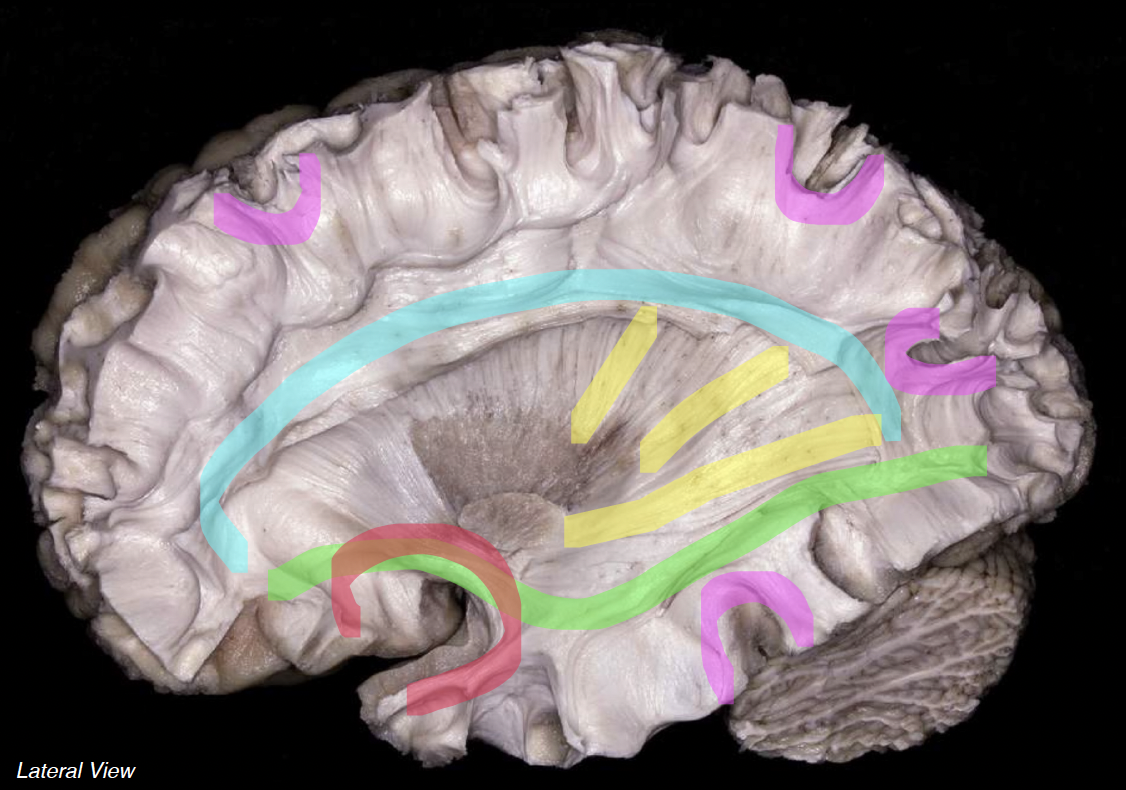
red tract
association fibers: connect areas within the same cerebral hemisphere
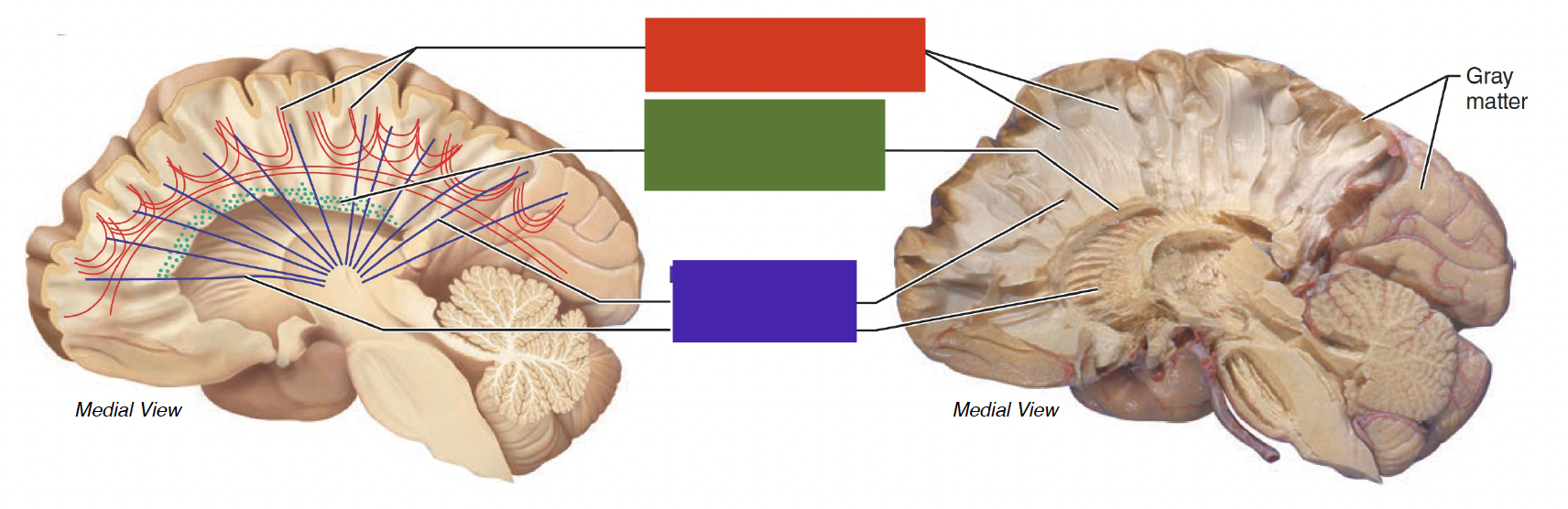
green tract
commissural fibers: corpus callosum
connect areas across hemispheres
signals going thru r mostly inhibitory
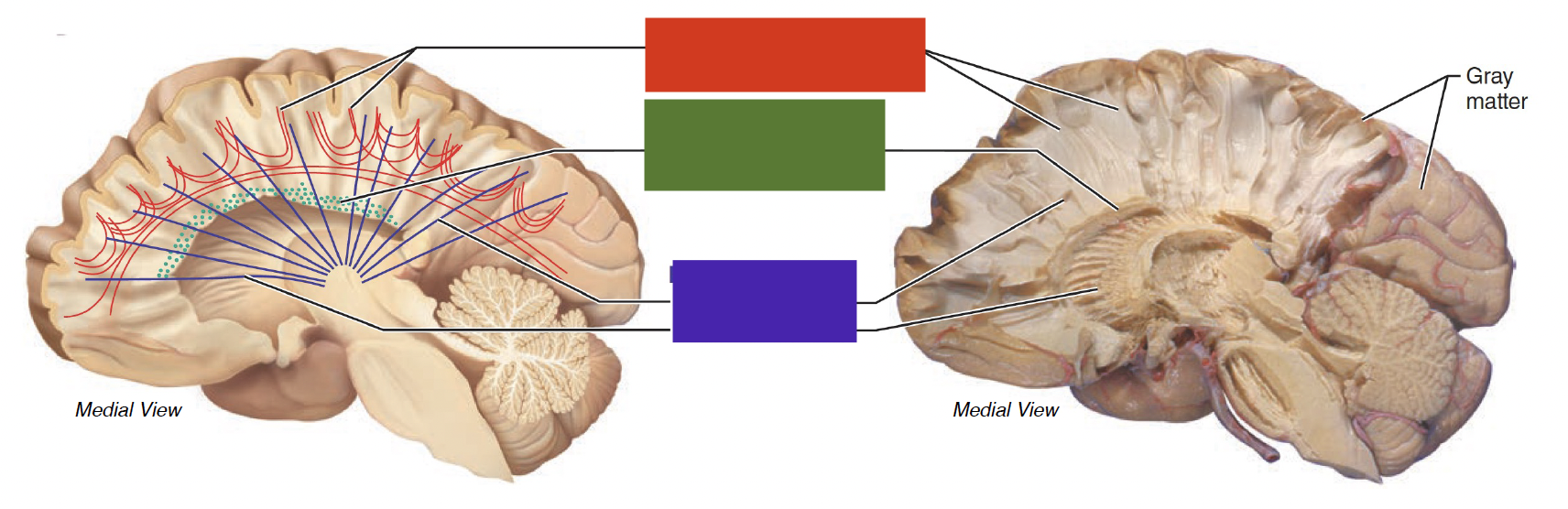
purple tract
projection fibers: corona radiata and internal capsule
connect cerebral cortex and subcortical structures of CNS
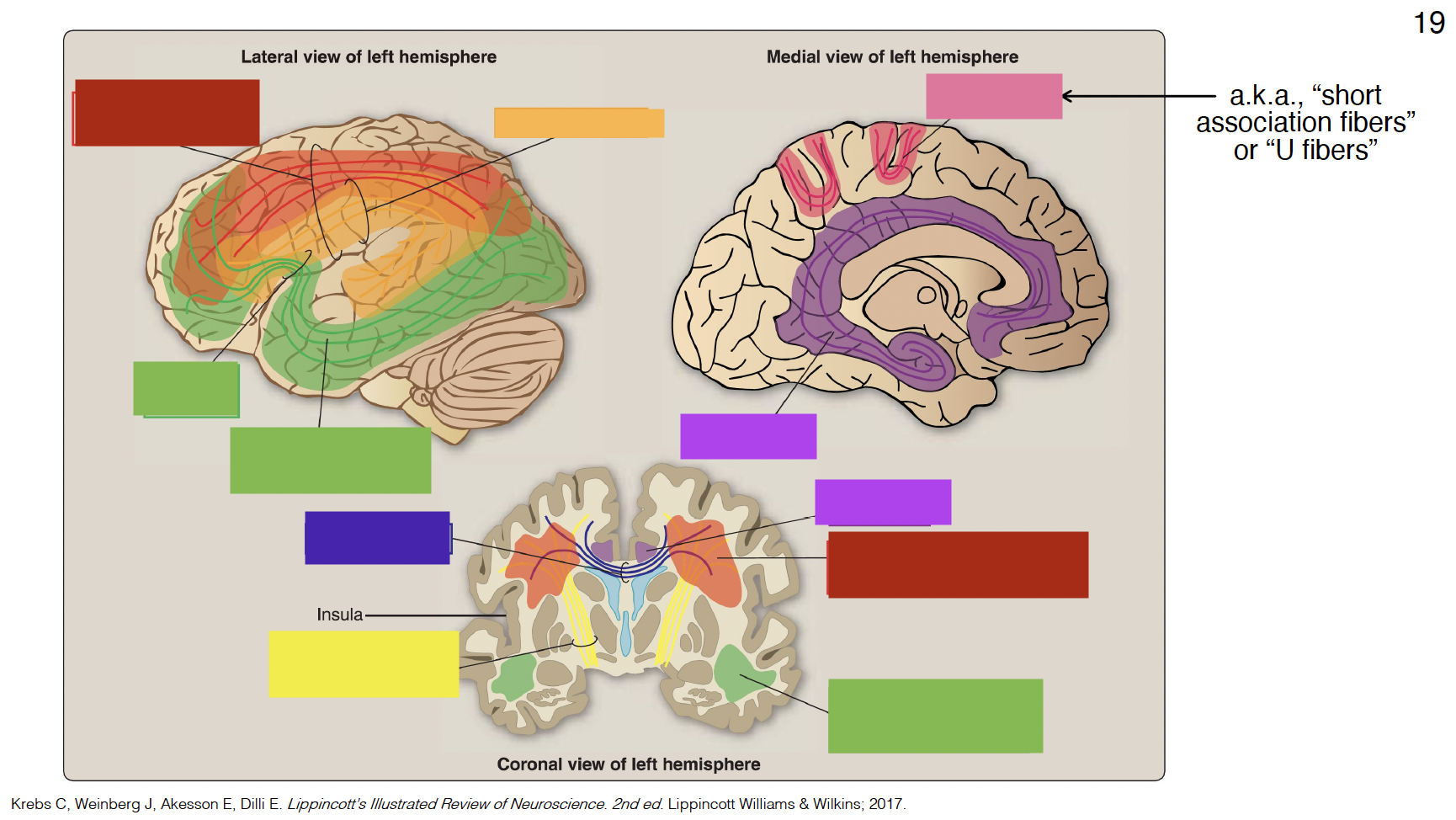
red
superior longitudinal fasciculus
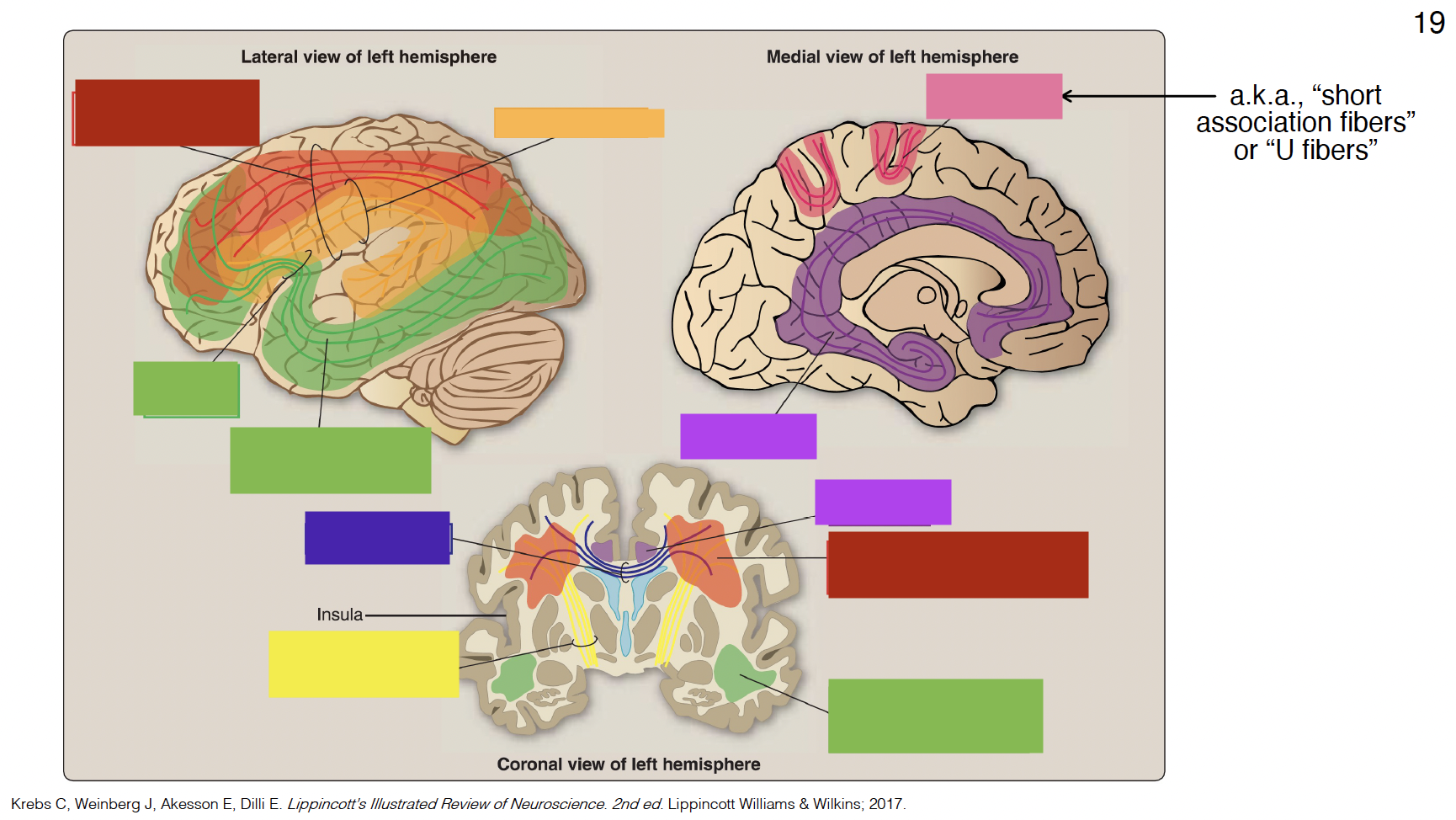
dark yellow
arcuate fasciculus
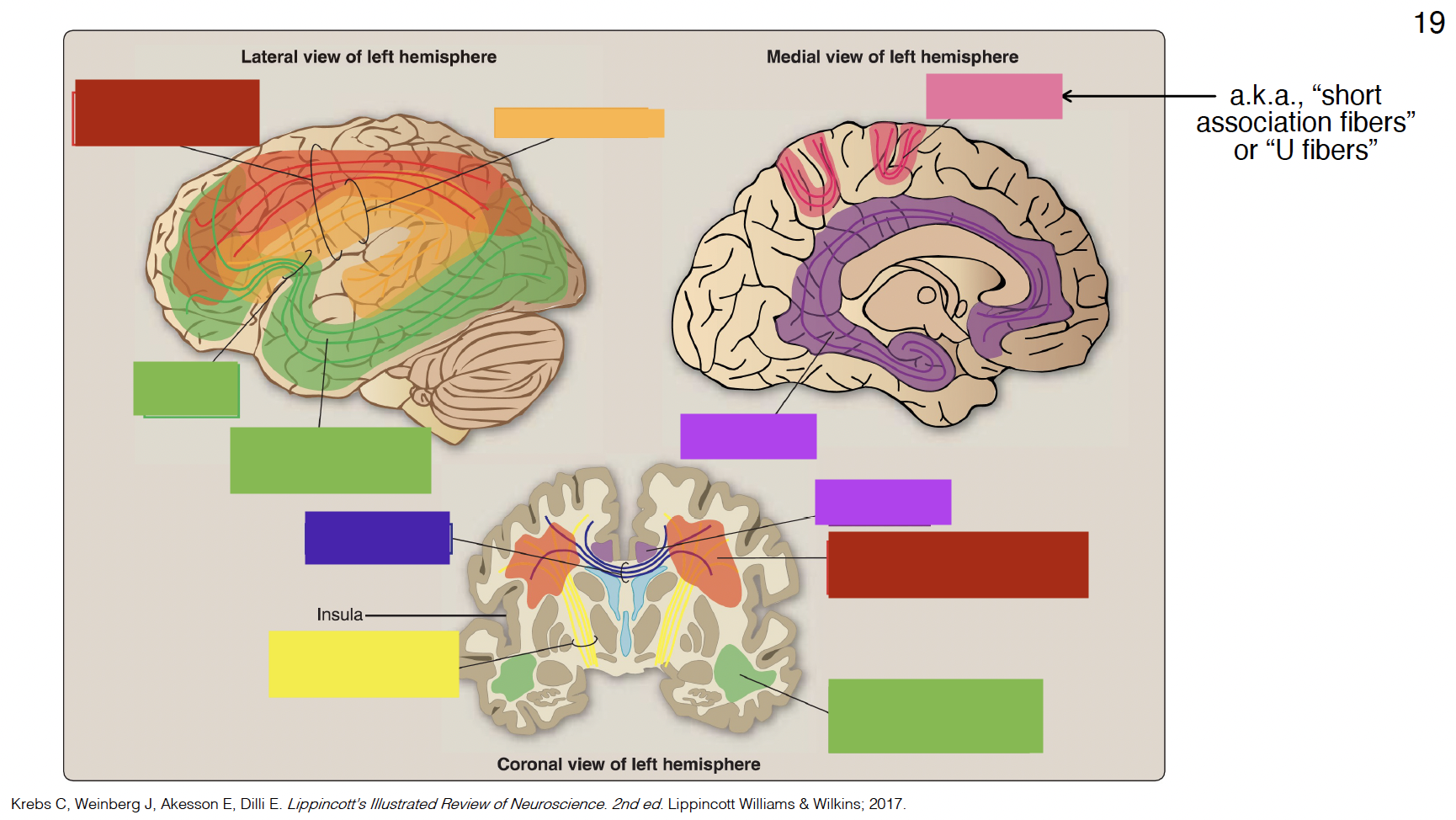
big green
inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus
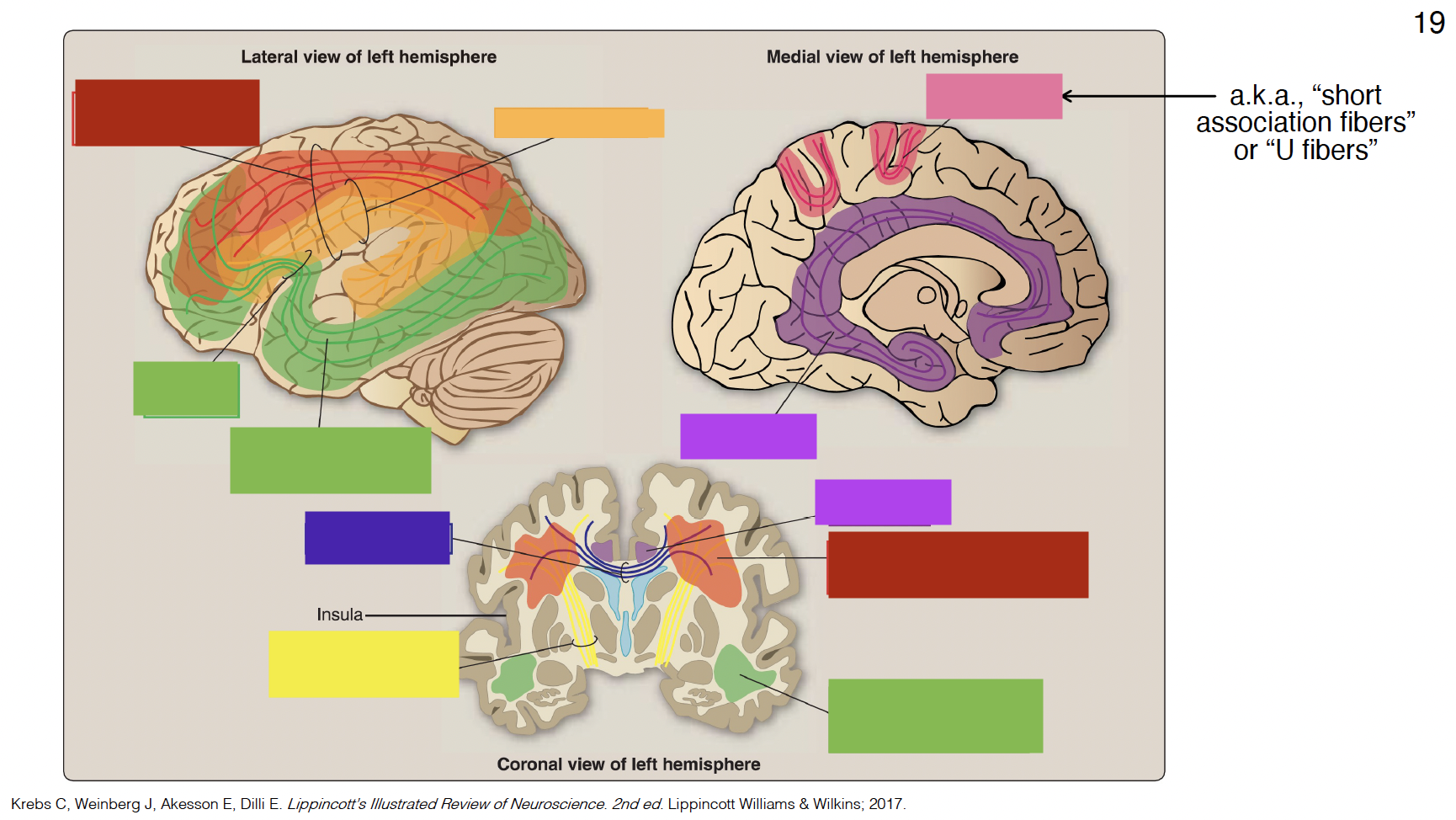
small green
uncinate fasciculus
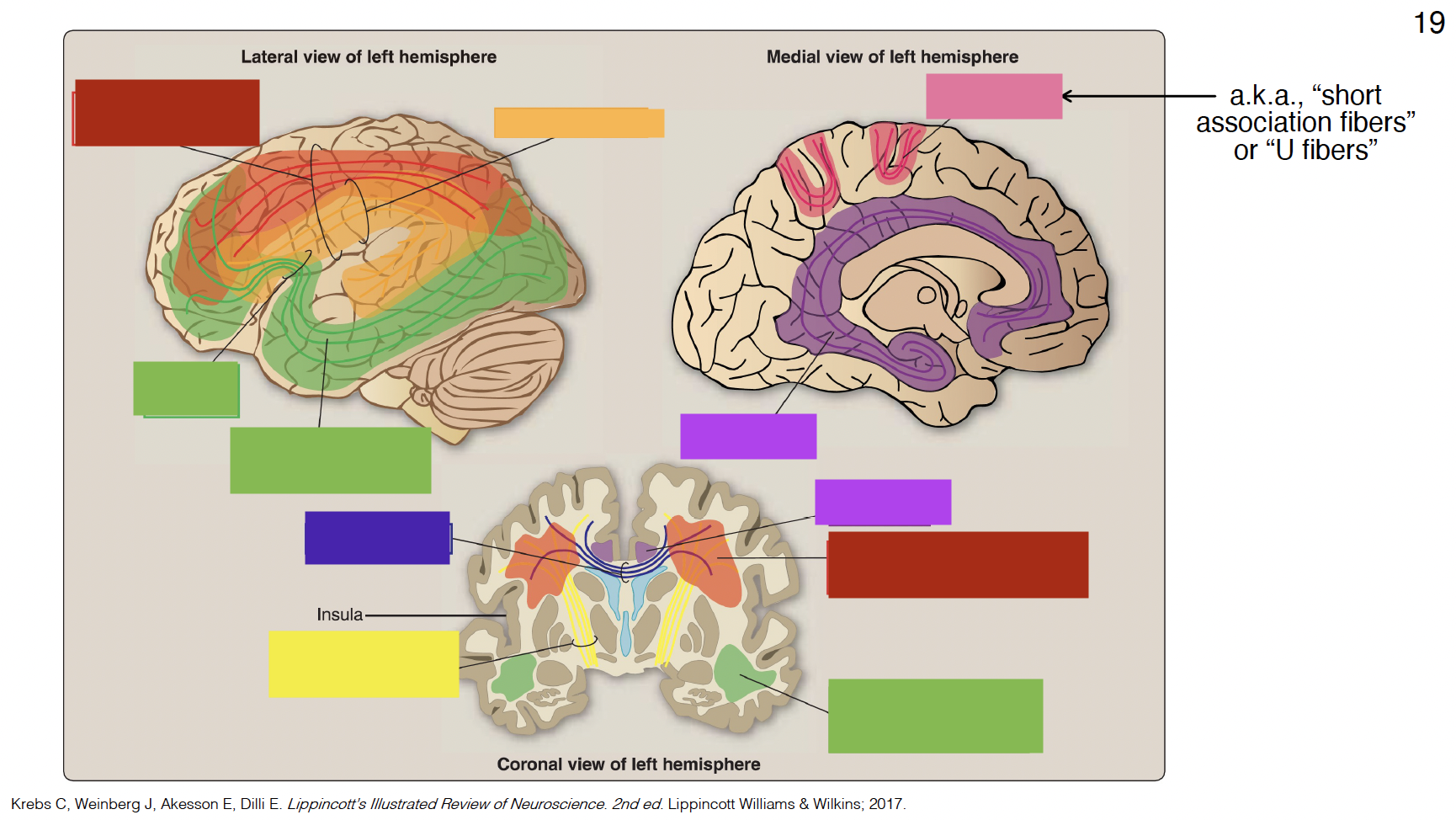
purple
cingulum
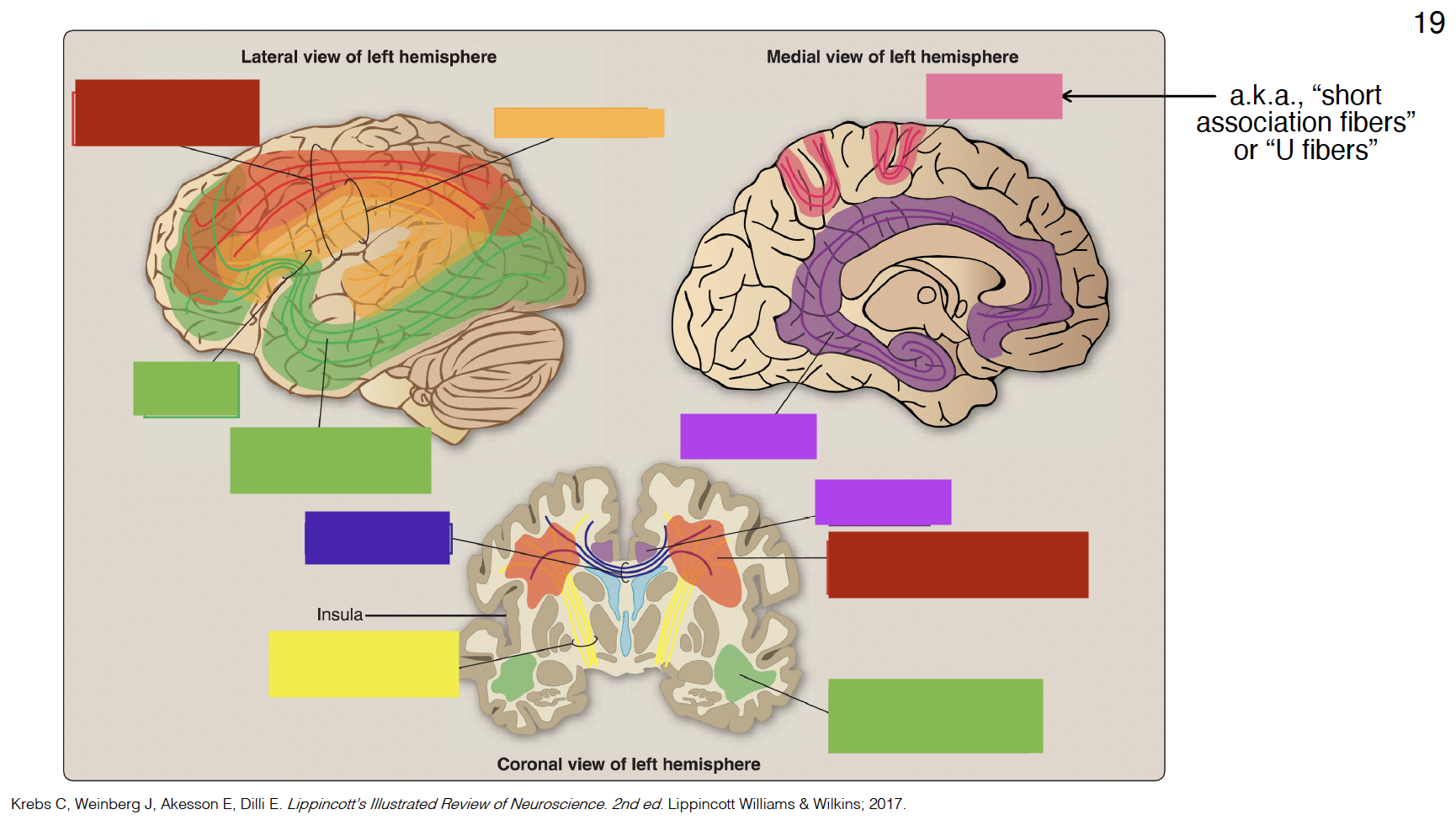
indigo
corpus callosum
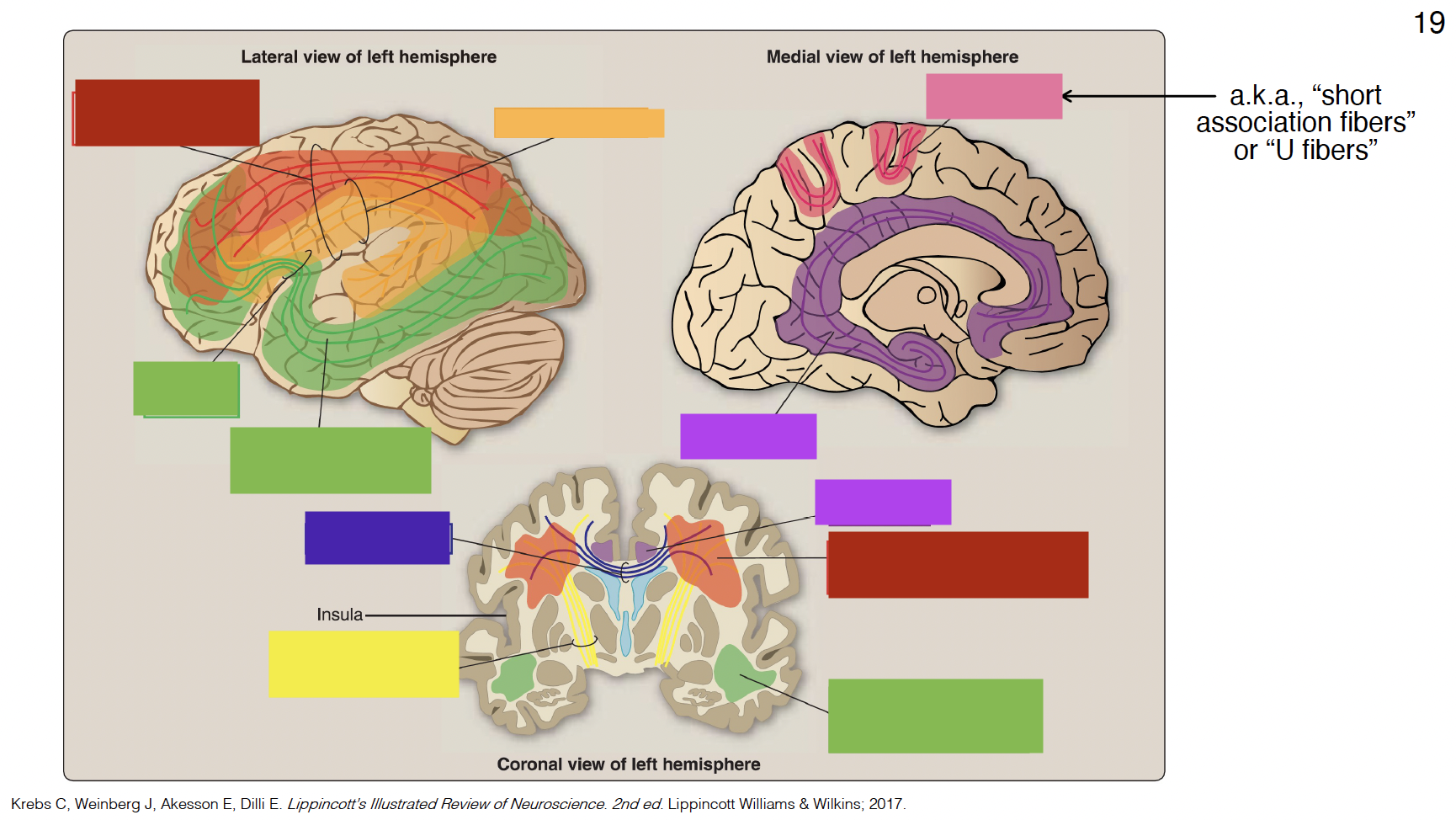
yellow
internal capsule
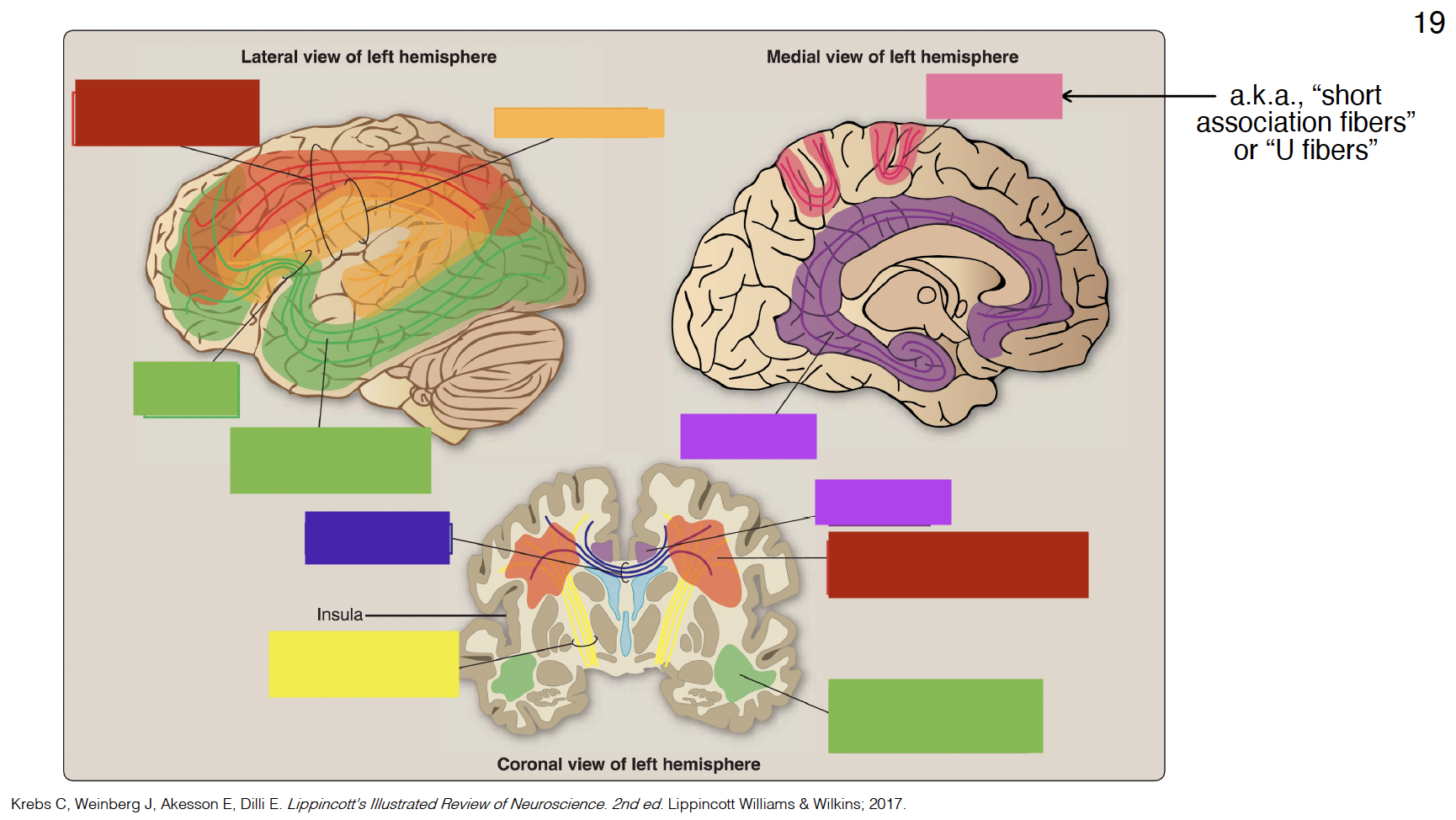
pink
arcuate fibers
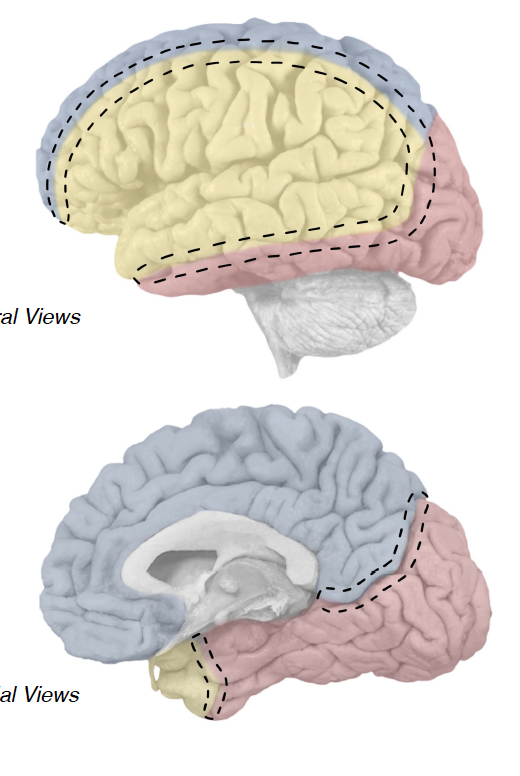
powdery blue
anterior cerbral artery (ACA)
medial aspect of frontal and parietal lobes
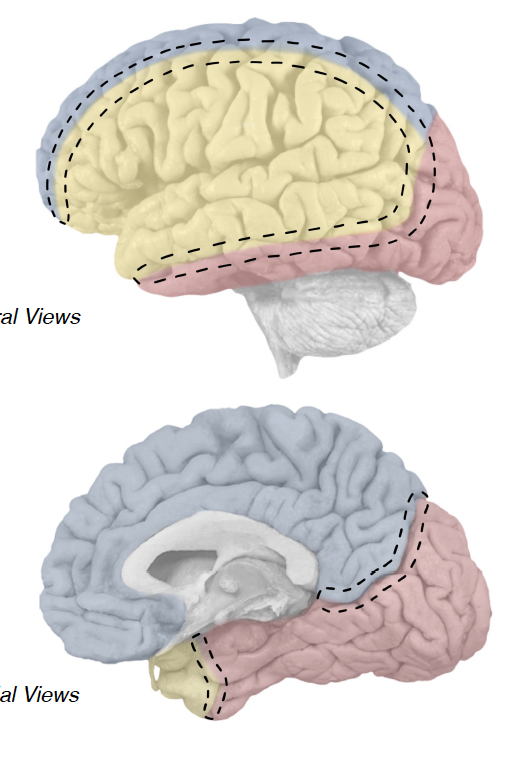
powdery yellow
middle cerebral artery (MCA)
vast majority of lateral cortex
frontal pole of temporal lobe
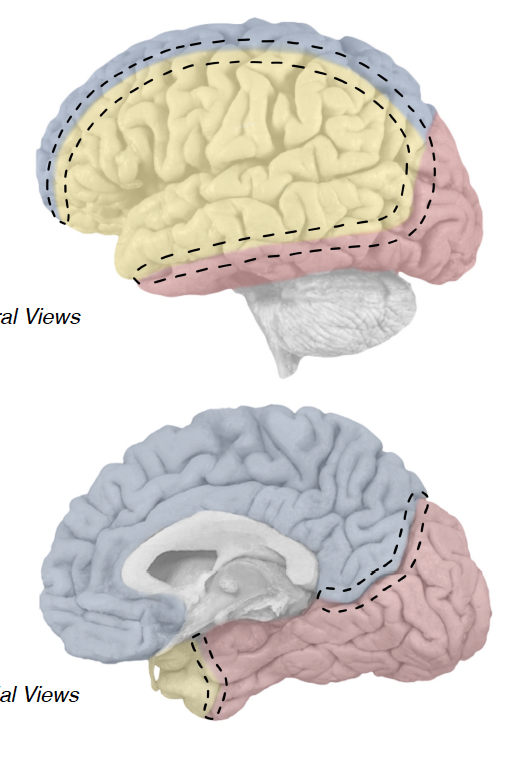
powdery red
posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
entire occipital lobe
medial and inferior aspects of temporal lobe
neon pink
short association fibers (arcuate)
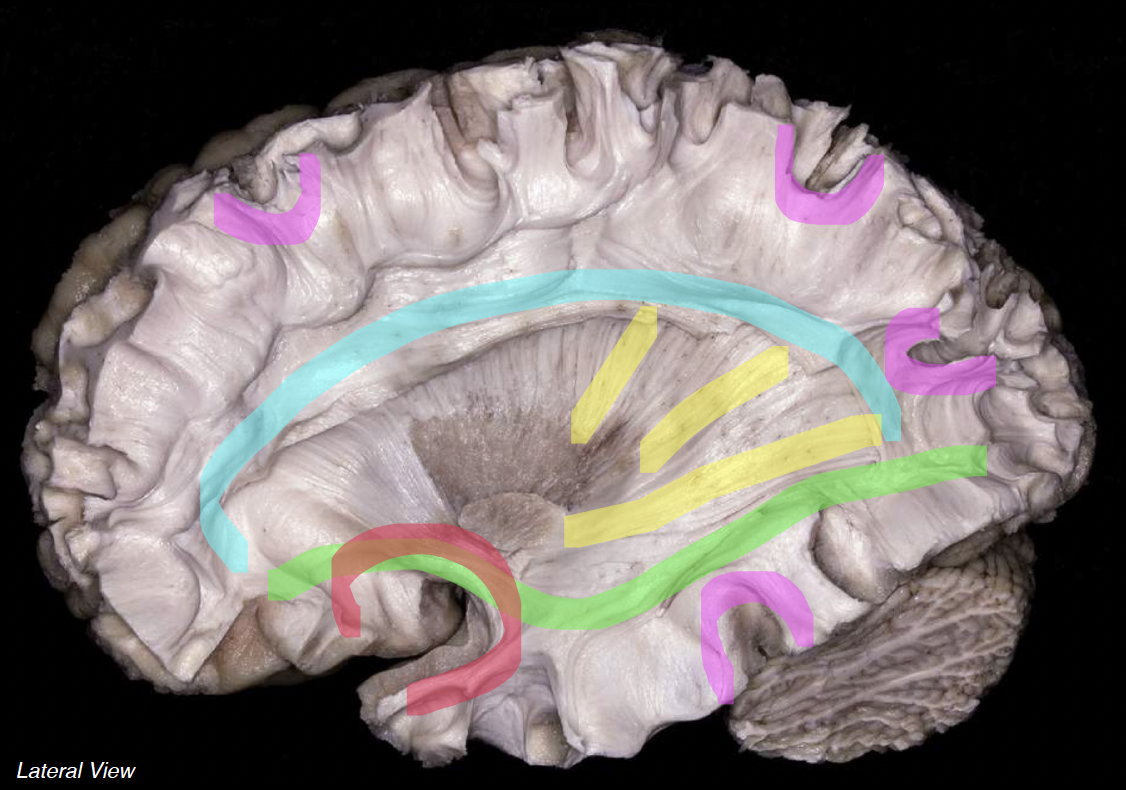
cyan
superior longitudinal fasciculus
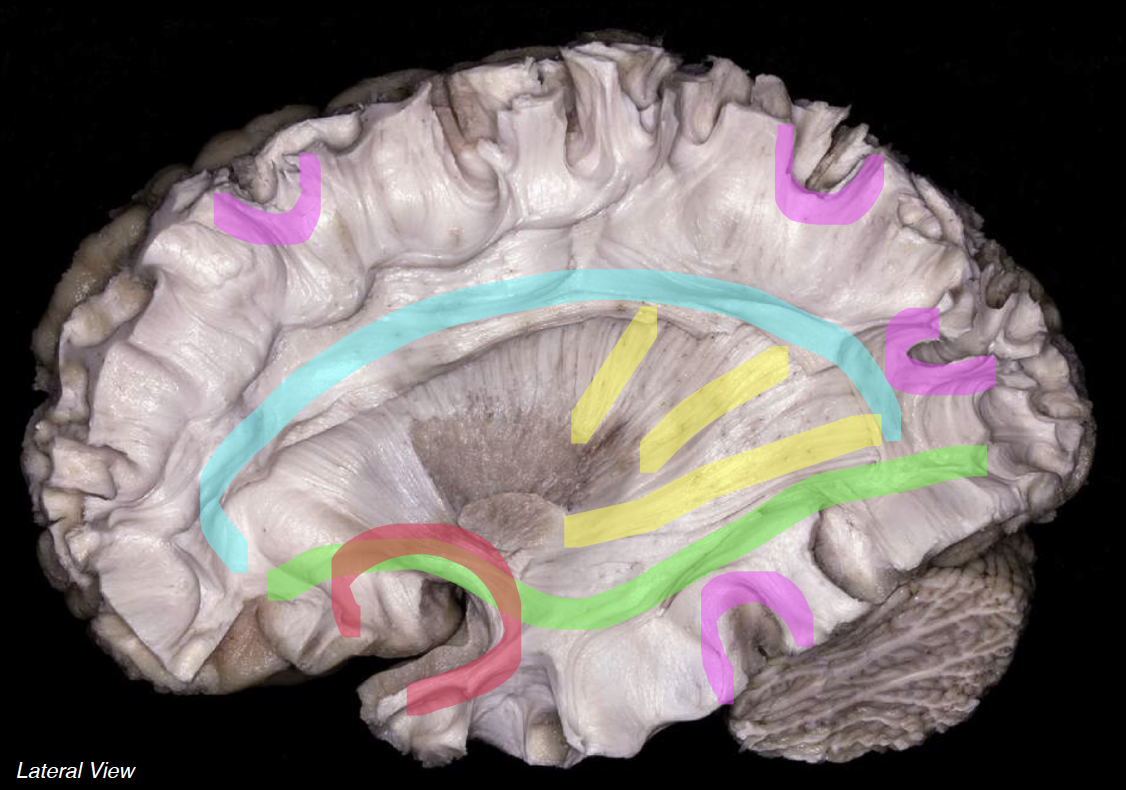
neon green
inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus
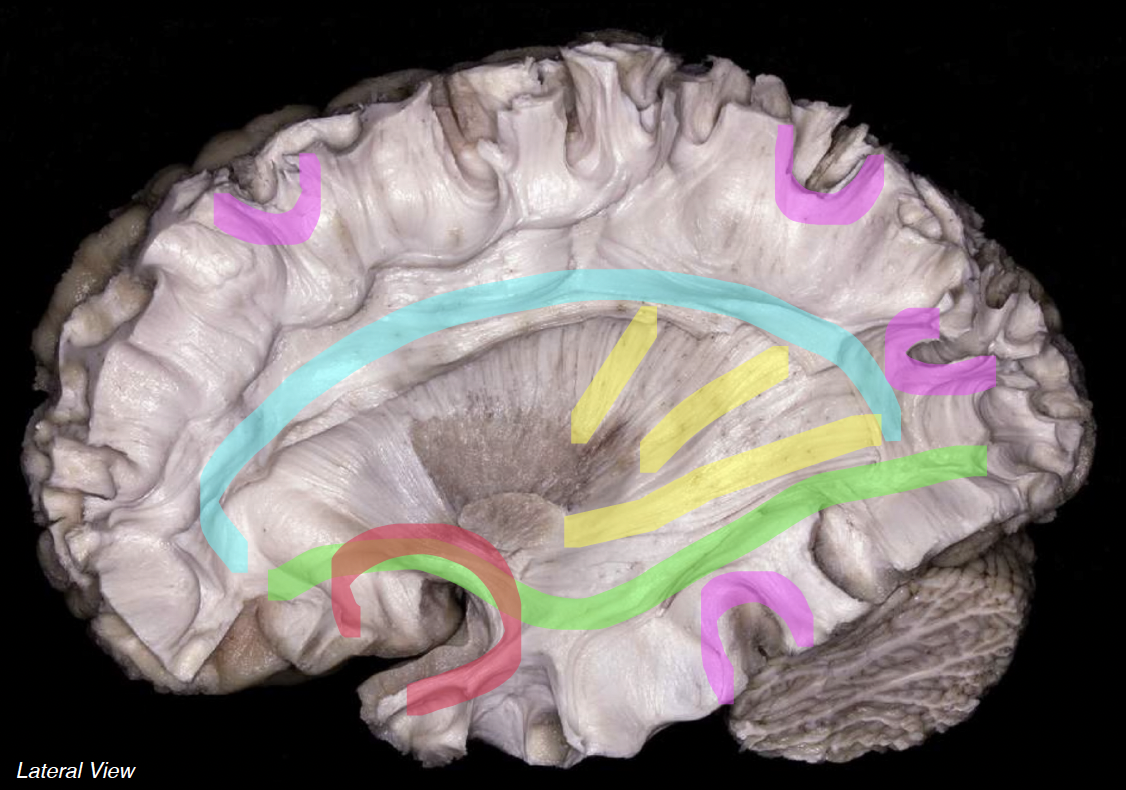
neon red
uncinate fasciculus
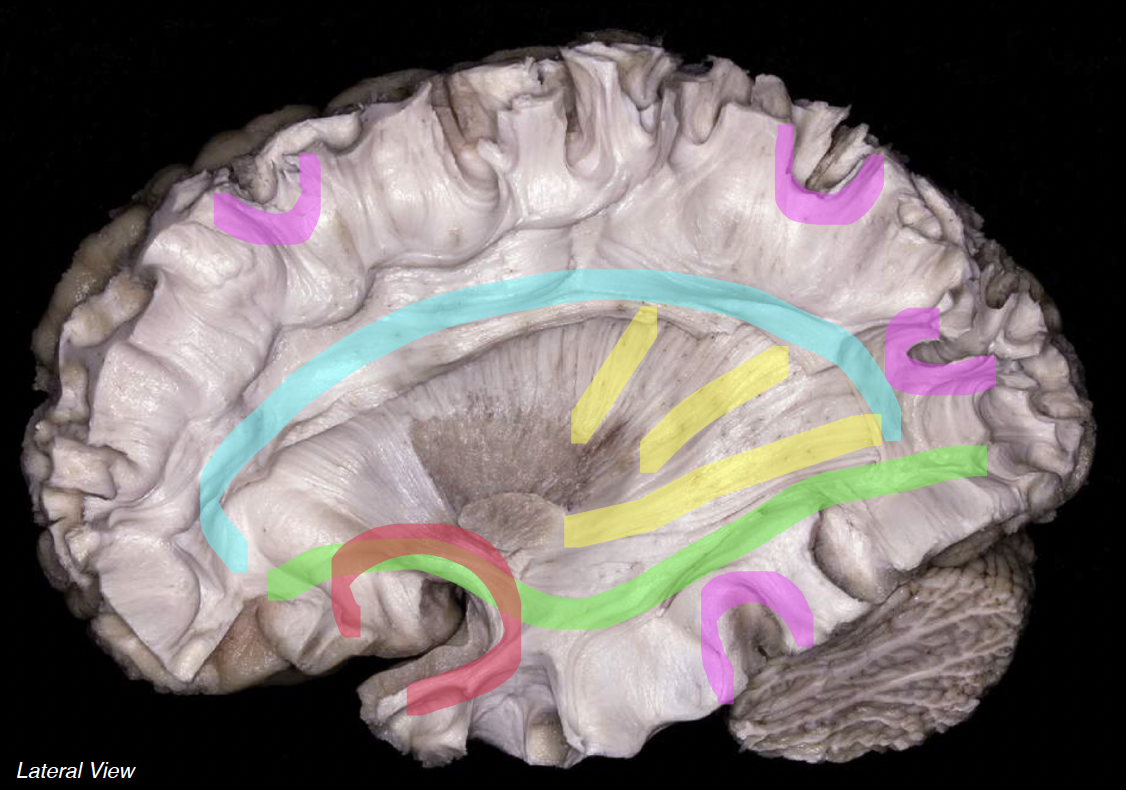
neon yellow
projection fibers
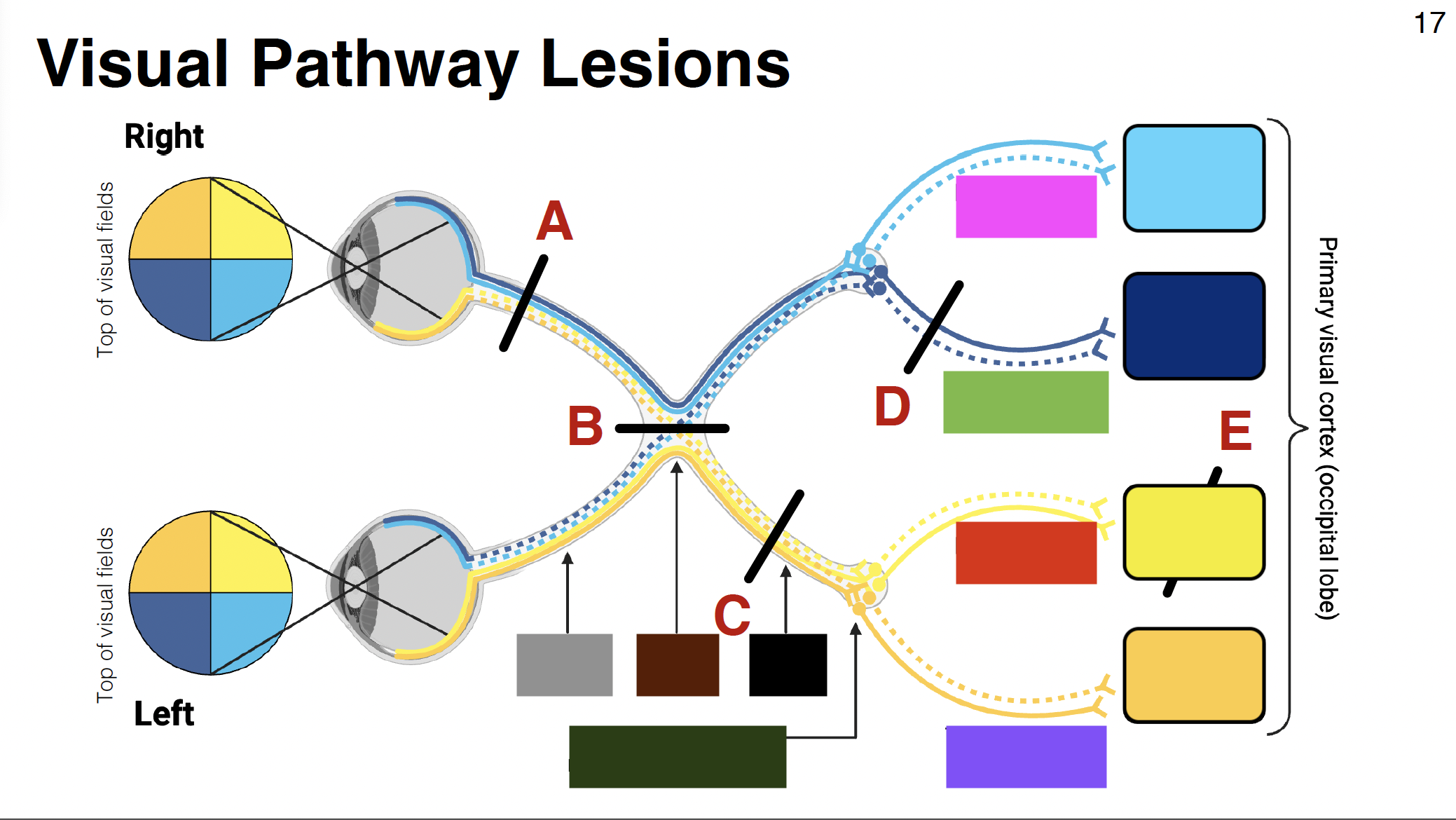
light blue
above calcarine sulcus
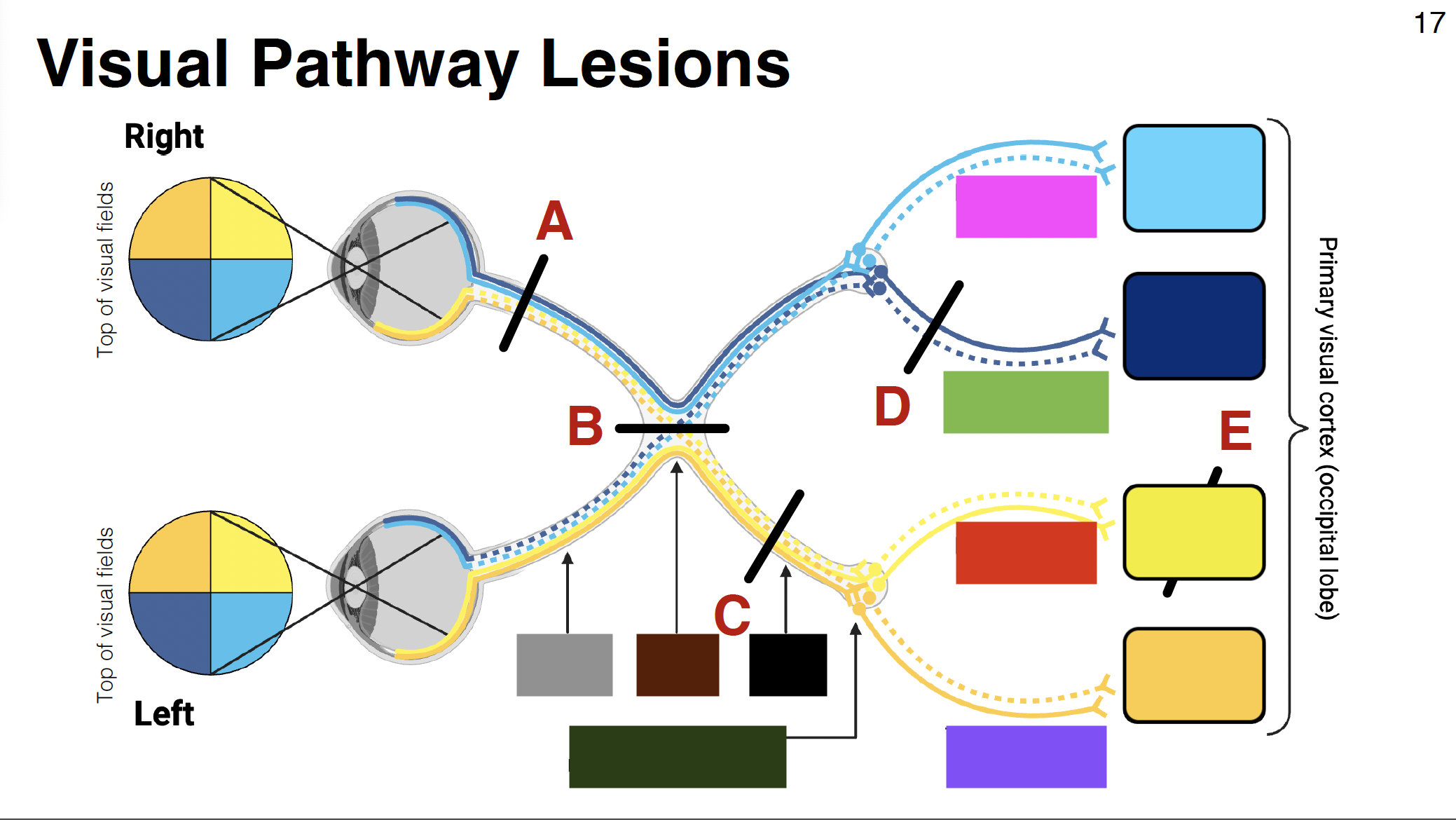
dark blue
below calcarine sulcus
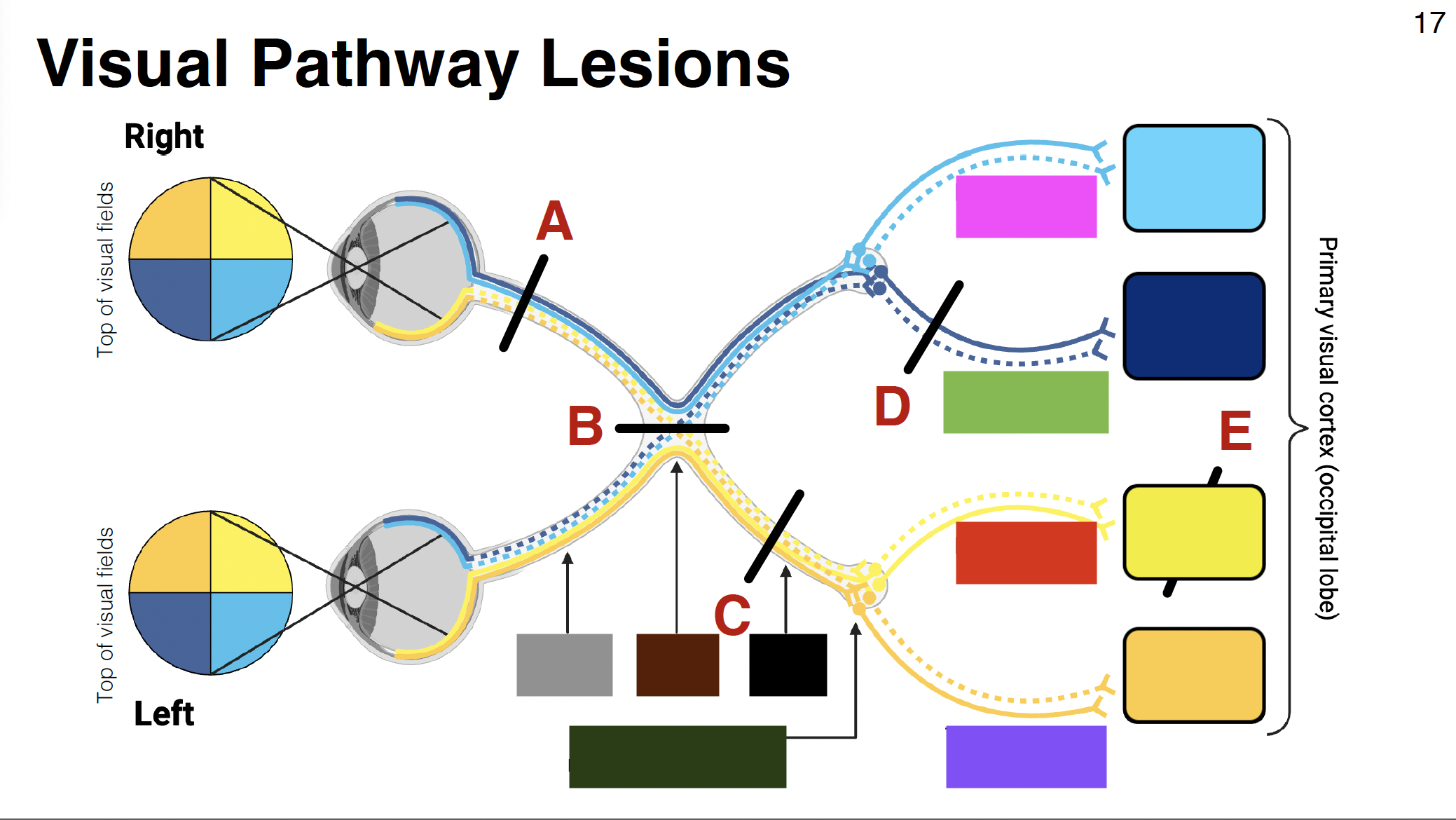
light yellow
above calcarine sulcus
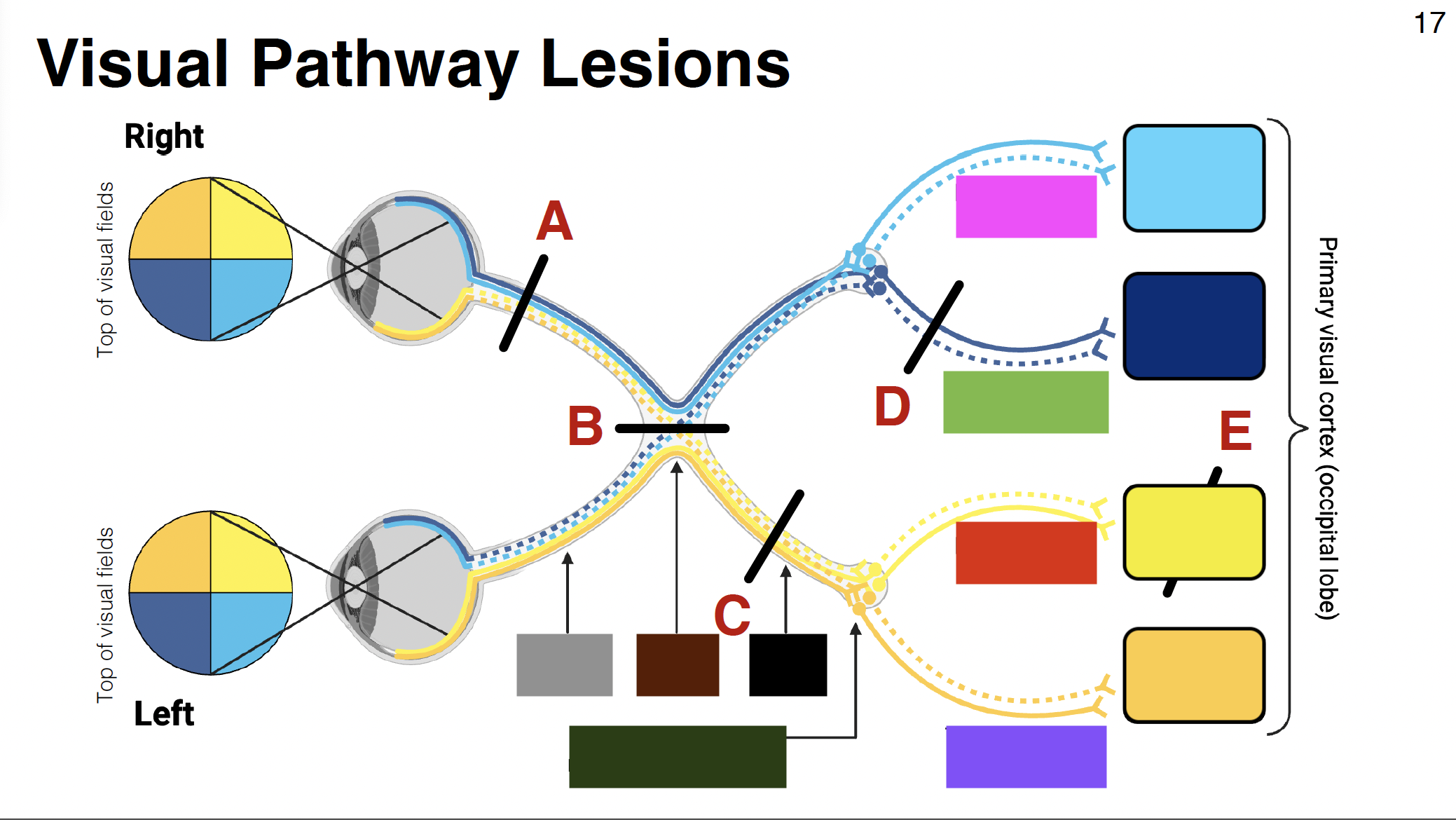
dark yellow
below calcarine sulcus
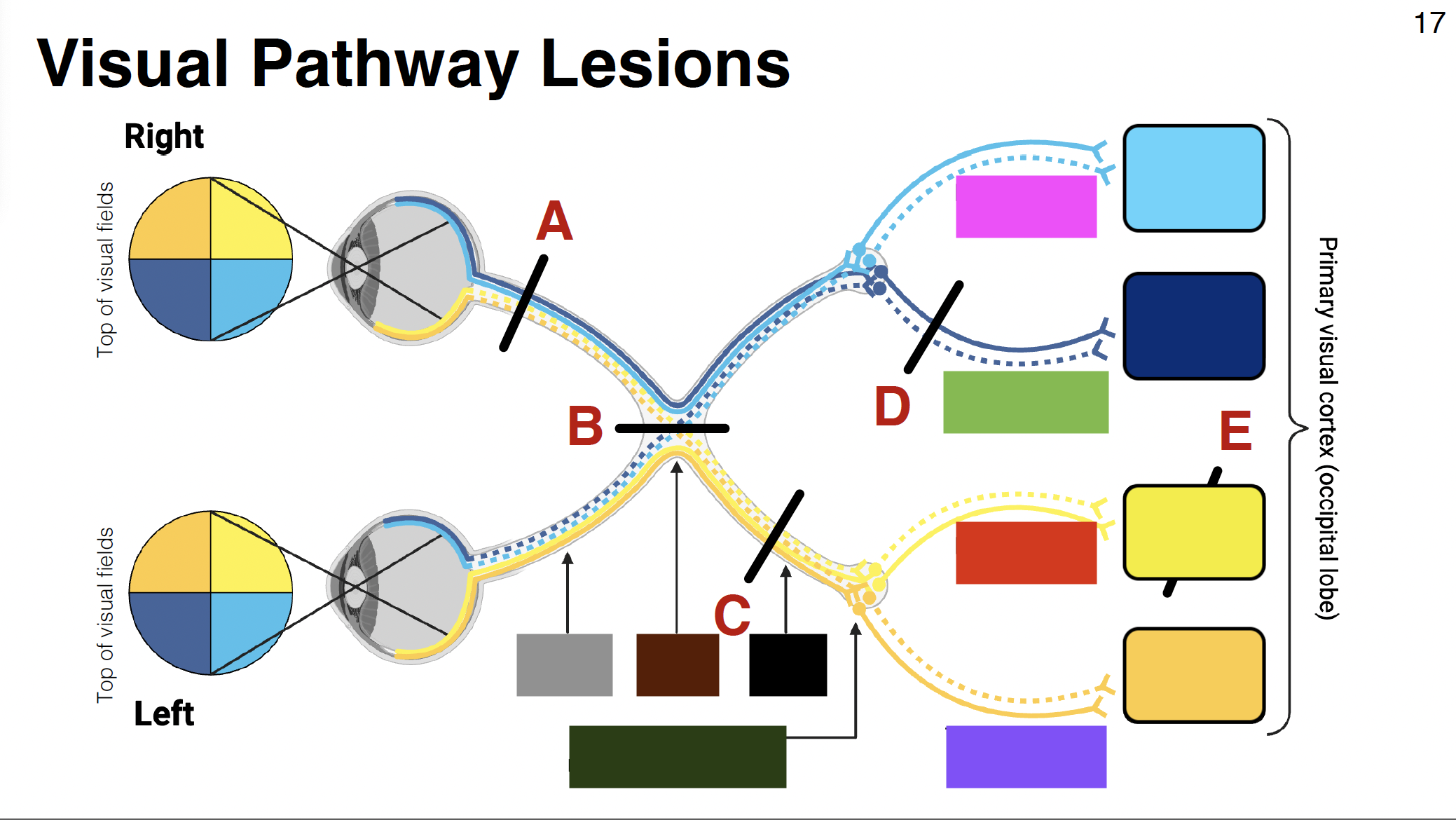
pink visual
parietal optic radiations
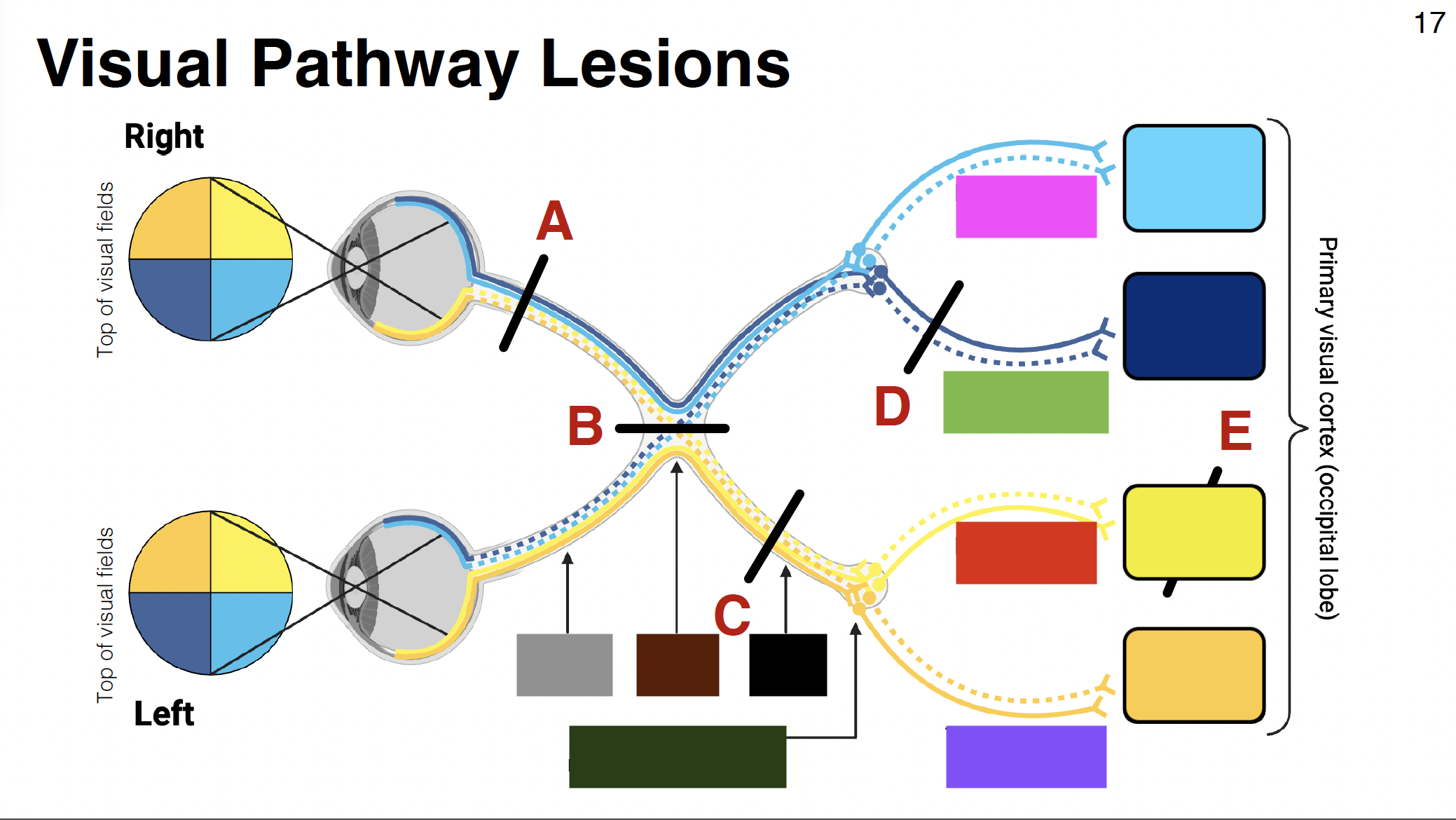
green visual
temporal optic radiations
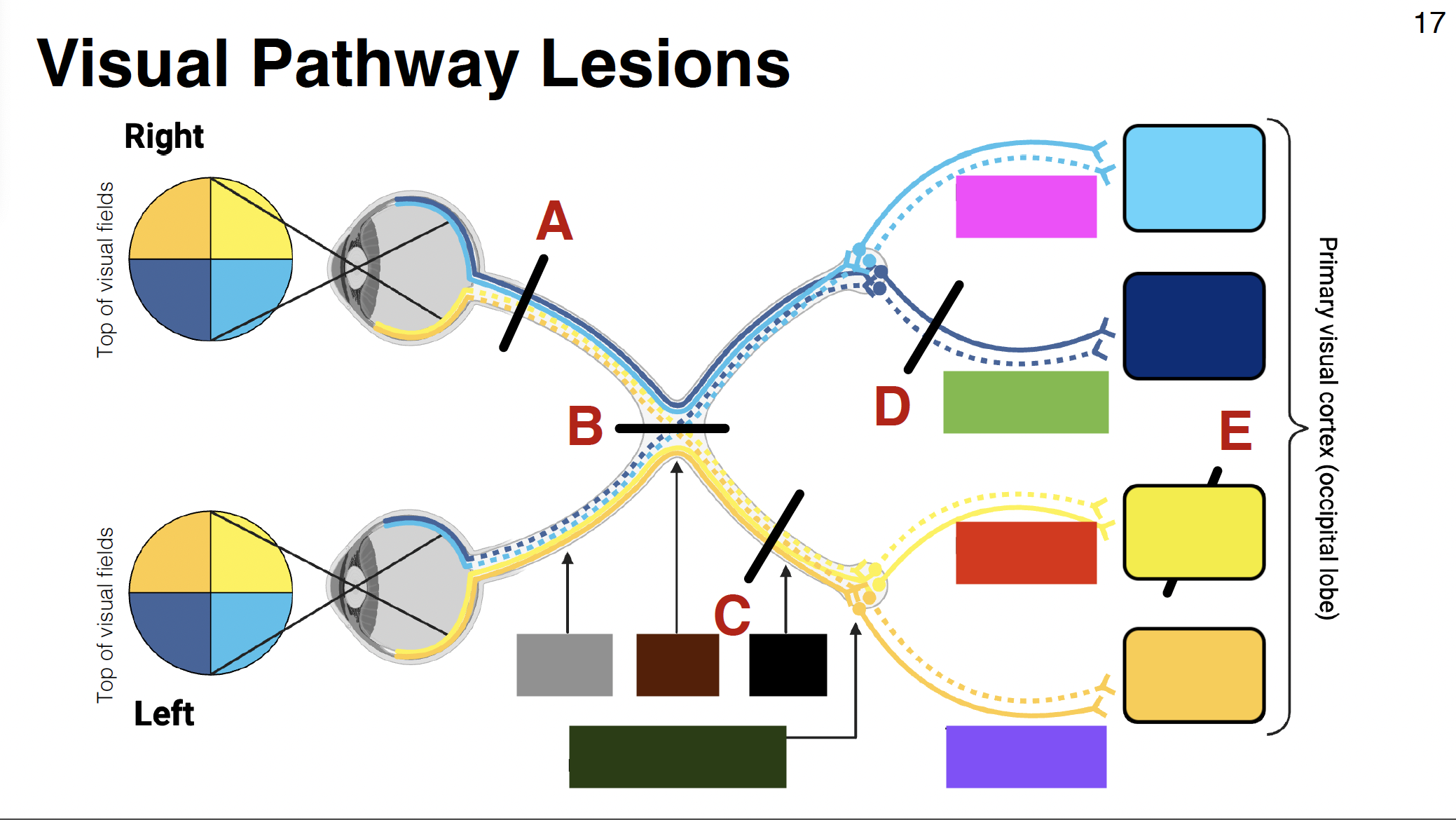
red visual
parietal optic radiations
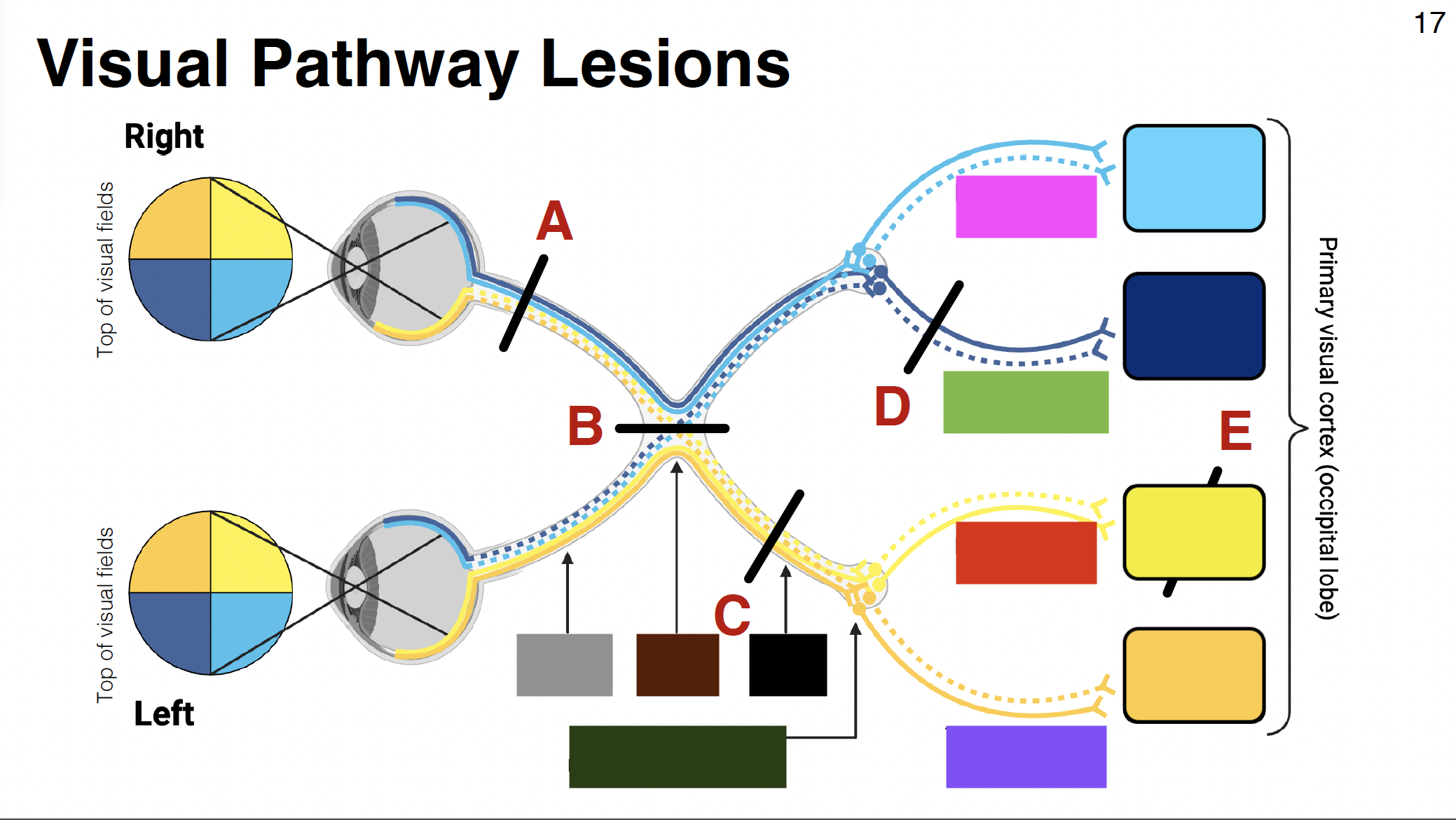
purple visual
temporal optic radiations
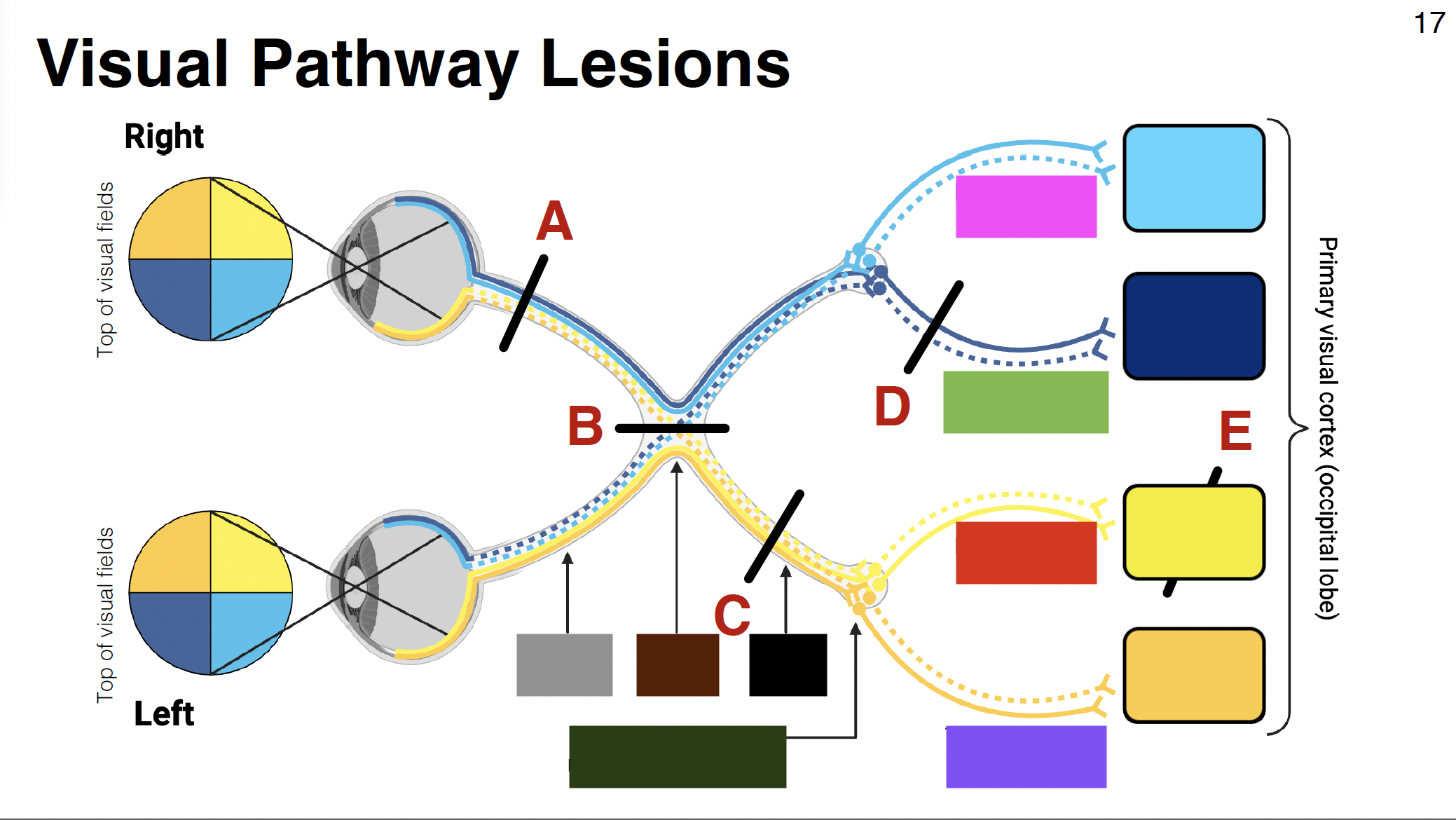
grey
optic nerve
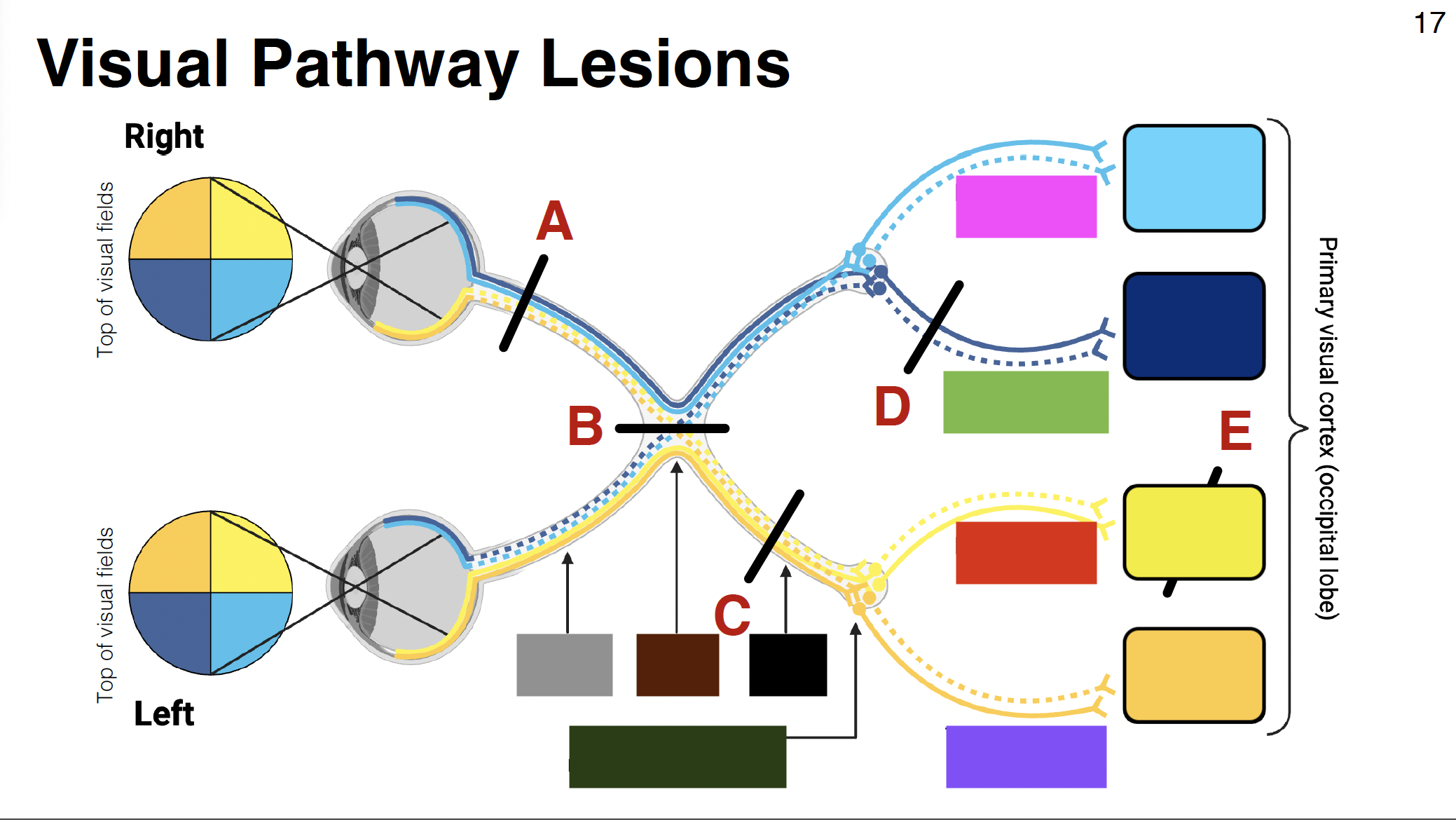
brown
optic chiasm
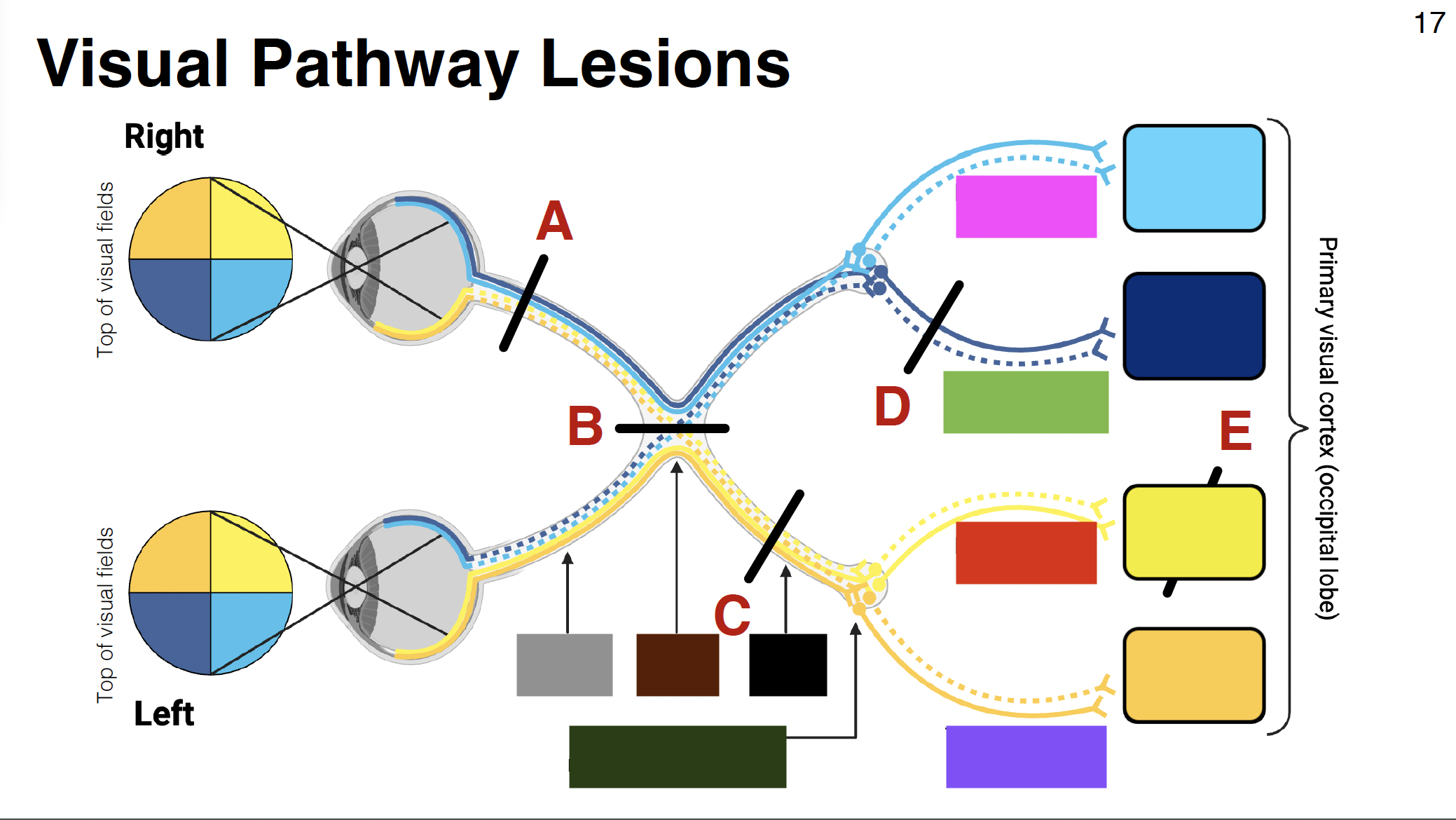
black
optic tract
without it: depth perception is impaired
misalignment between what each eye sees
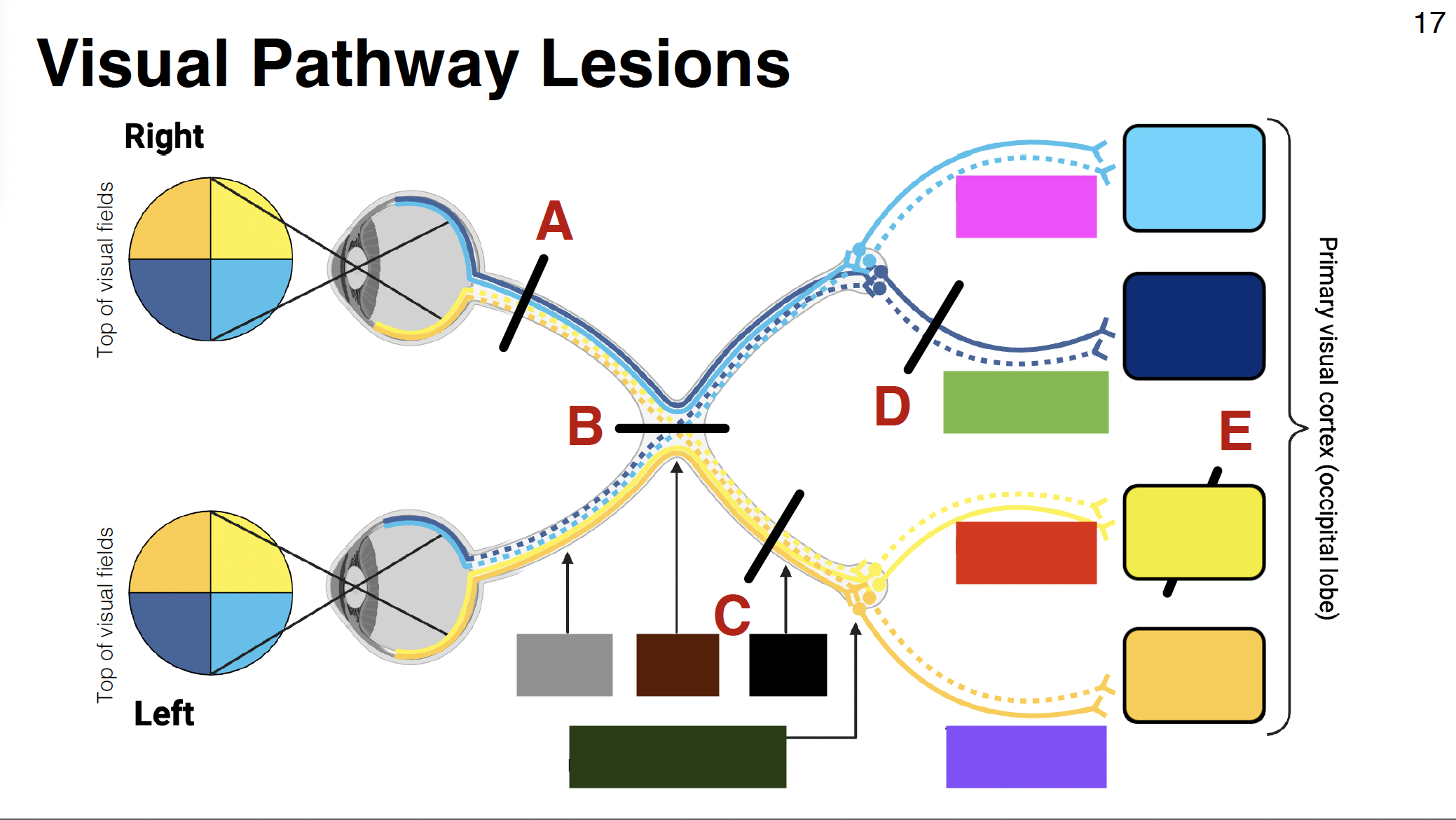
dark green
LGN of thalamus