Corso - acetylcholine
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what receptors does acetylcholine activate?
nicotinic receptors (N1 and N2)
muscarinic receptors (m1-5)
acetylcholine is a ________
biogenic amine
list the names of the biogenic amine neurotransmitters
acetylcholine
dopamine
norepinephrine
epinephrine
5-HT
melatonin
histamine
what NT is this?
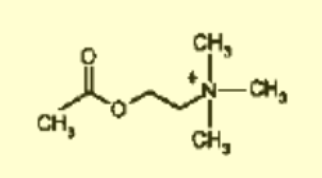
acetylcholine
what enzyme is used for the single step of acetylcholine synthesis?
choline acetyltransferase
what enzyme is used to degrade acetylcholine?
acetylcholinesterase
what acetylcholine receptor classes are FAST?
a. N1 and N2
b. m1, m3, m5
c. m2 and m4
a.
what acetylcholine receptor classes are SLOWER?
a. N1 and N2
b. m1, m3, m5
c. m2 and m4
b. c.
what acetylcholine receptor classes are excitatory - ligand gated sodium channels?
a. N1 and N2
b. m1, m3, m5
c. m2 and m4
a.
what acetylcholine receptor classes are excitatory via G-alpha-q, increasing IP3 and DAG?
a. N1 and N2
b. m1, m3, m5
c. m2 and m4
b.
what acetylcholine receptor classes are inhibitory via G-alpha-i, decreasing cAMP?
a. N1 and N2
b. m1, m3, m5
c. m2 and m4
c.
where is major ACh input?
hippocampus
ACh depletion in hippocampus causes ______
Alzheimer’s —> short term memory loss
which is the excitatory G-protein?
a. G-alpha-s
b. G-alpha-i
a.
which is the inhibitory G protein?
a. G-alpha-s
b. G-alpha-i
b.
which G protein results in increased cAMP?
a. G-alpha-s
b. G-alpha-i
a.
which G protein results in decreased cAMP?
a. G-alpha-s
b. G-alpha-i
b.
how do you obtain choline?
diet
acetyl coA is produced by _______
metabolism
choline acetyl transferase synthesizes ACh in the __________
cytoplasm
_____ is an immune disorder against the voltage gated calcium channels
LEMS
describe LEMS
disorder against voltage gated calcium channels
decreases the amount of ACh released at neuromuscular junction
__________ is an autoimmune disorder that blocks neuromuscular signaling
myasthenia gravis
what is TYPICAL myasthenia gravis (MG)?
autoantibodies to the alpha1 subunit of the N1 acetylcholine receptor
what is acquired slow channel syndrome?
autoantibodies to the epsilon subunit of the N1 acetylcholine receptor
what is neonatal myasthenia gravis (transient) or recurrent arthrogryposis
autoantibodies to the gamma subunit of the N1 acetylcholine receptor
what is the most common treatment for LEMS and MG?
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
what does botox do?
inhibits ACh release
what does atropine do?
m receptor antagonist
what does nicotine do?
N receptor agonist
what does muscarine do?
M receptor agoonist
a patient is suffering from myasthenia gravis, which class of drugs is most commonly prescribed?
a. acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
b. amphetamines
c. antibiotics
d. MAOIs
e. N1 receptor antagonists
a.
atropine is a:
a. N receptor agonist
b. M receptor agonist
c. N receptor antagonist
d. M receptor antagonist
d.
which of the following areas receives the heaviest projections from the nucleus basalis?
a. cerebellum
b. hippocampus
c. pons
d. substantia nigra
b.