SBI4U chapters 8&9 - NS and endocrine system
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Homeostasis
Tendency for body to maintain a constant internal environment
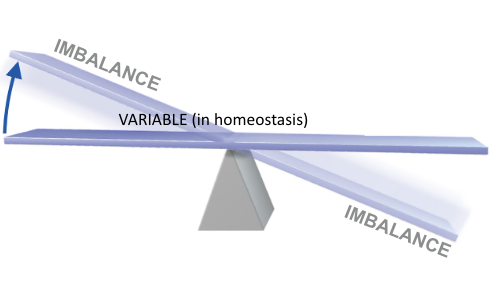
What disturbs homeostasis
External and internal stimuli
Components of a feedback system
Sensor (affector), control centre, effector
Sensor/affector
Detects changes in condition and sends message to control centre
Control centre
Acts as a regulator, receives info from sensors, determines appropriate response and sends signals to effectors
Effector
Responds to signal from control centre and changes environment to restore balance
Negative feedback loop
Homeostasis is returned to normal
Positive feedback loop
Strengthens change in variable (ex. contractions)
Nervous system
Senses and responds to change within body and external environment and regulates body structures/processes to maintain homeostasis
Central nervous system
Brain and spinal cord - processes info sent by nerves
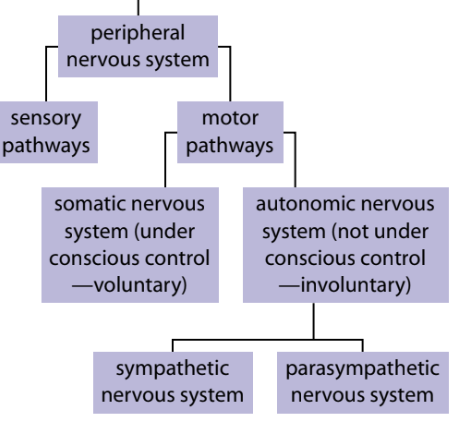
Peripheral nervous system
Nerves that carry sensory messages to CNS and sends messages from the CNS to muscles and glands
Neurons
Structural units of the nervous system
Glial cells
Nourish neurons, remove waste from them, and prevent infection (ex. schwann cells)
Types of neurons
Sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons
Sensory neuron
Transmit impulses from the sensory receptors to the CNS
Interneuron
Act as a link between sensory and motor neurons
Motor neuron
Transmits information from the CNS to effectors
Membrane potential
Charge separation across membrane of a neuron (-70mV)
Na+/K+ pump
Uses ATP to transport 3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ into the cell
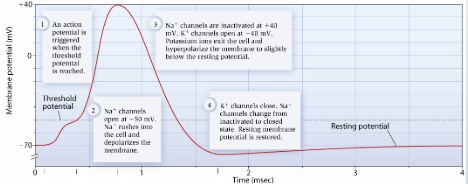
Action potential
Change in the electrical membrane potential of a neuron that allows it to transmit signals
Synapse
Space between 2 neurons
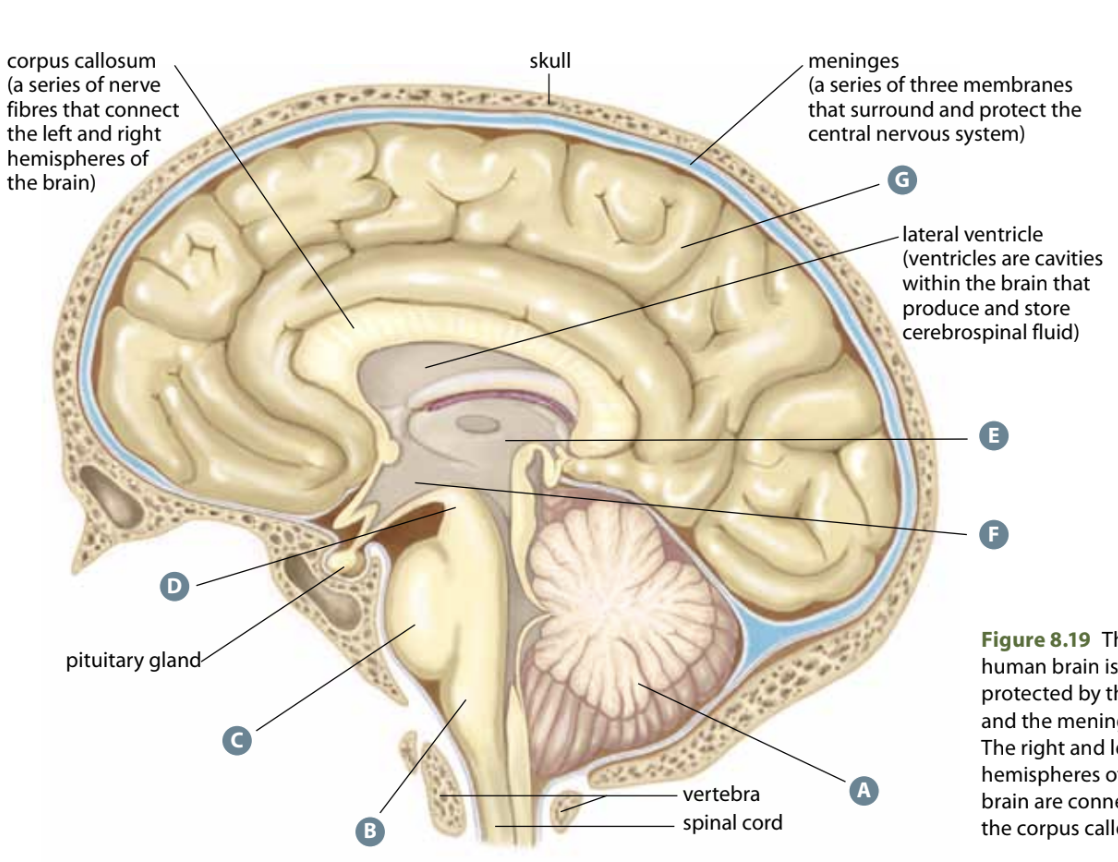
Structure A
Cerebellum - involved in posture, reflexes, motor skills
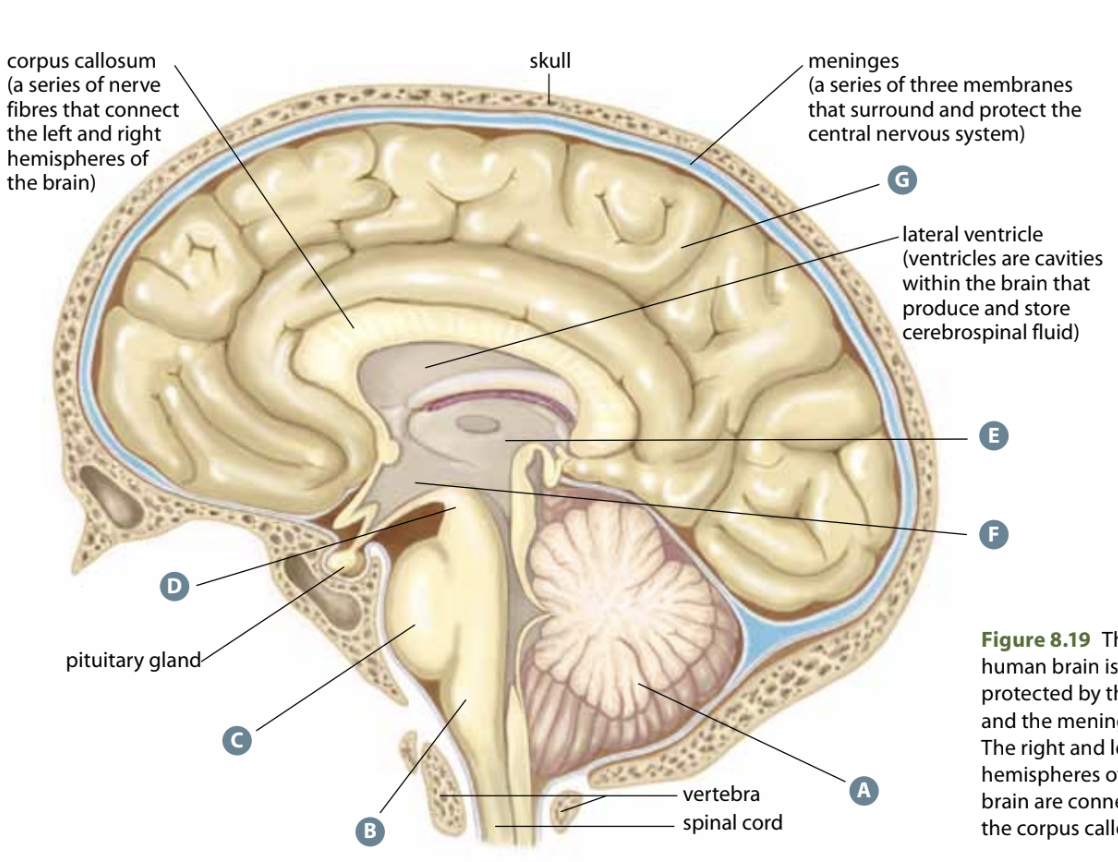
Structure B
Medulla oblongata - Coordinates bodily functions for homeostasis like HR
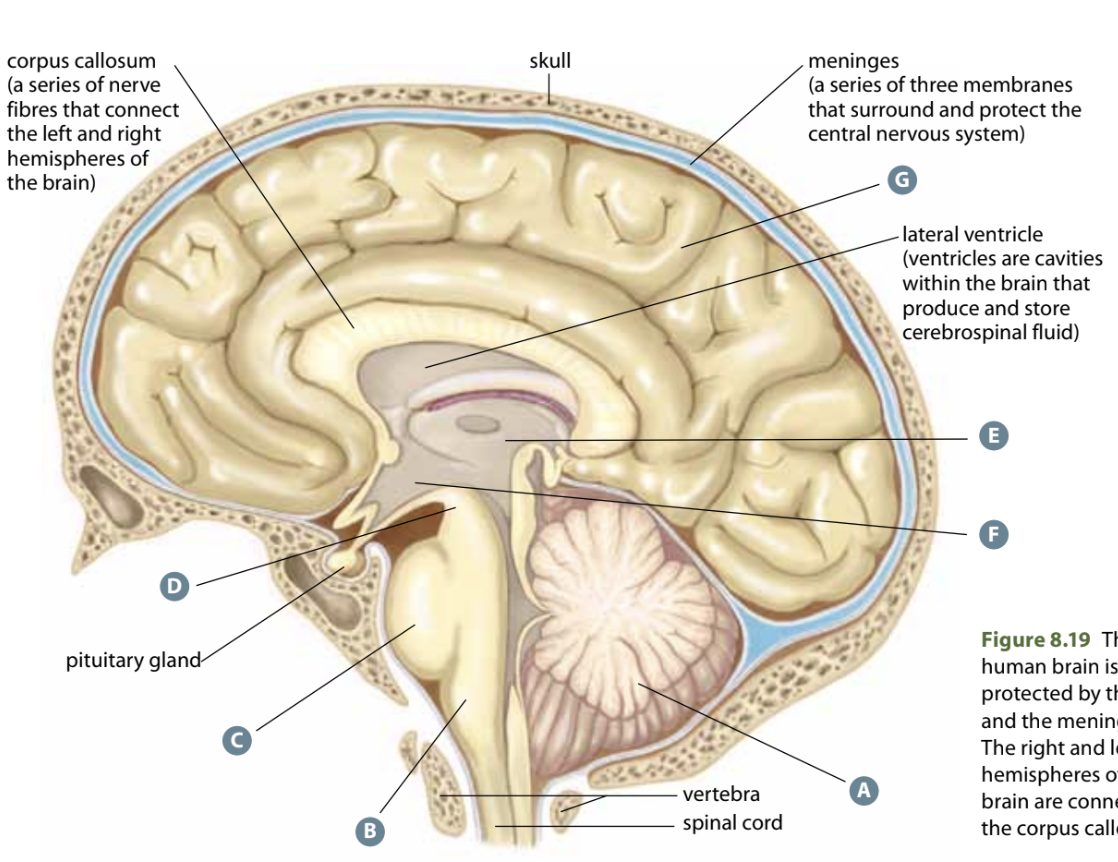
Structure C
Pons - Relay centre between neurons of right/left halves of the cerebrum
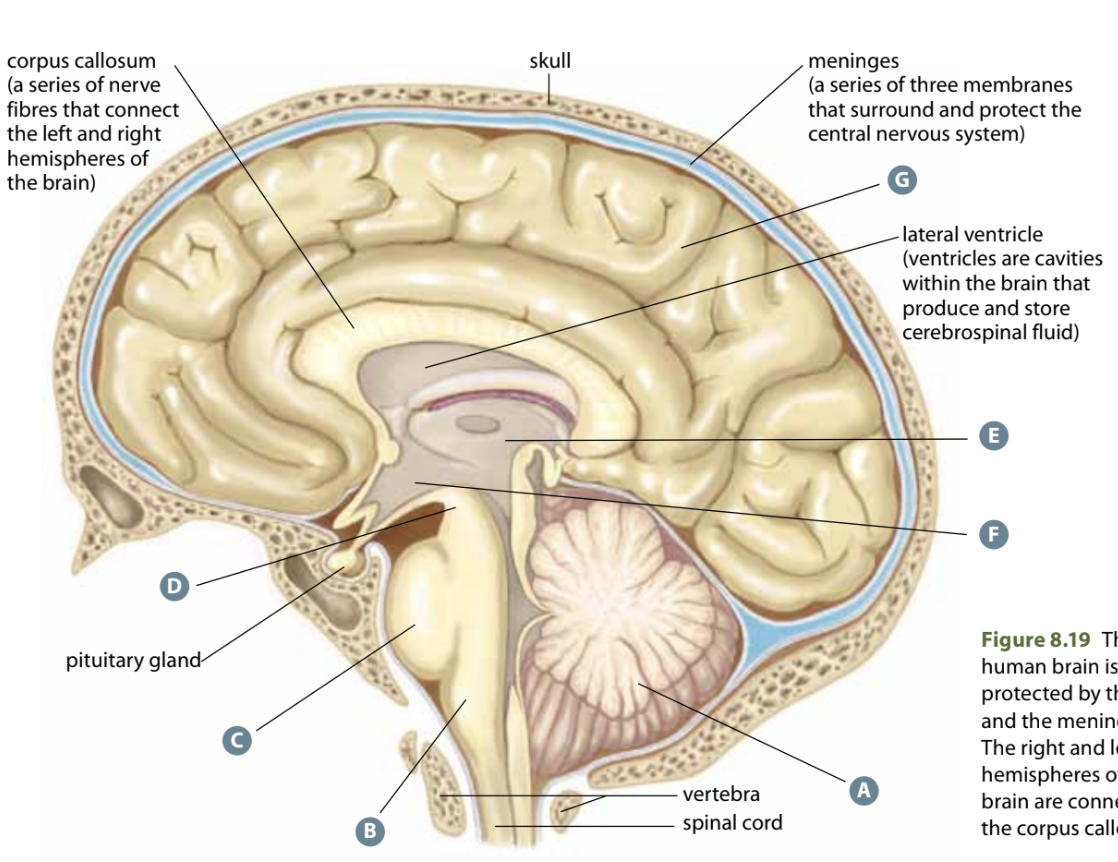
Structure D
Midbrain - Processes info from neurons in eyes, ears, and nose
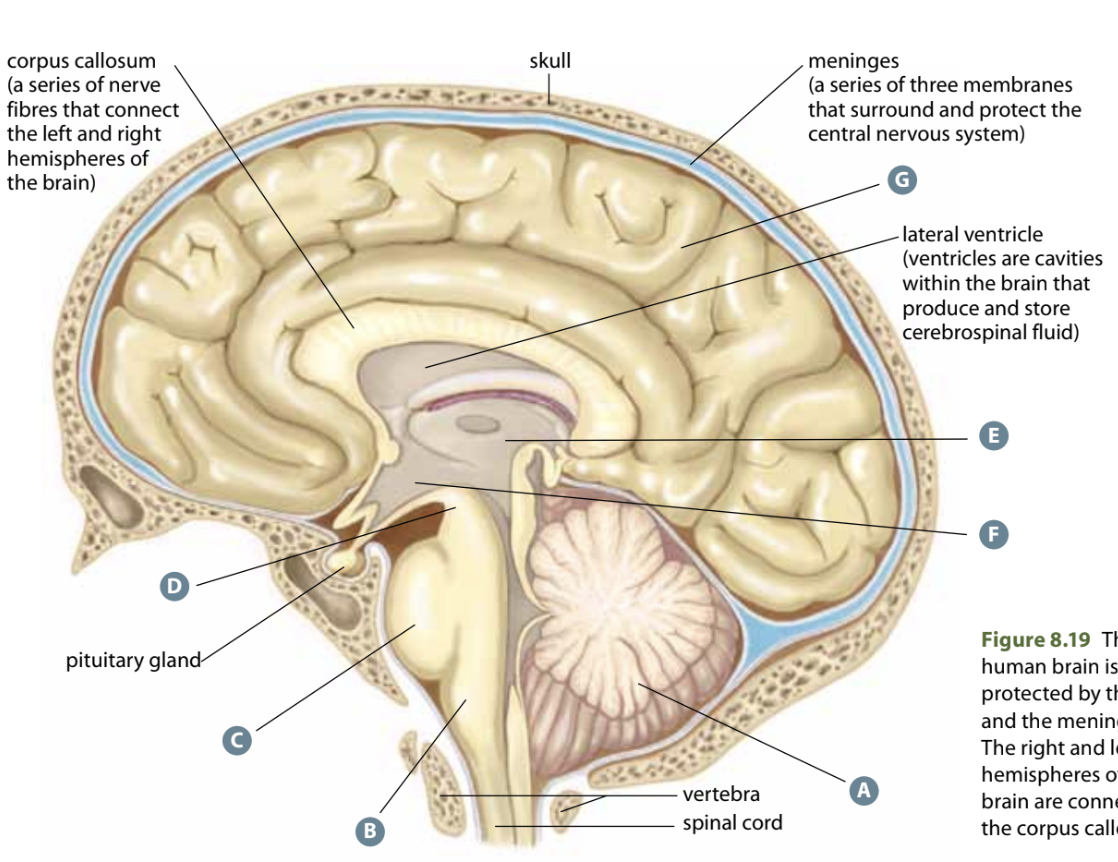
Structure E
Thalamus - connects various parts of the brain together
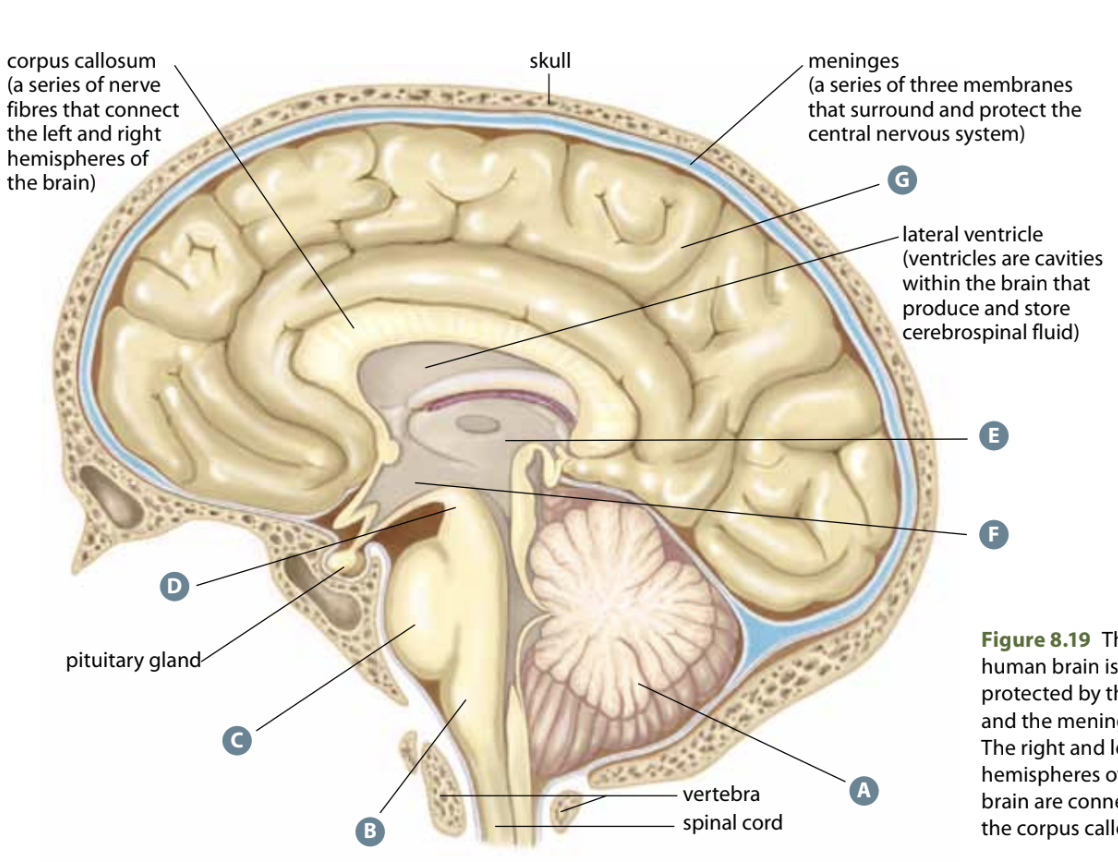
Structure F
Hypothalamus - regulates BP, HR, temp, emotions, controls pituitary gland
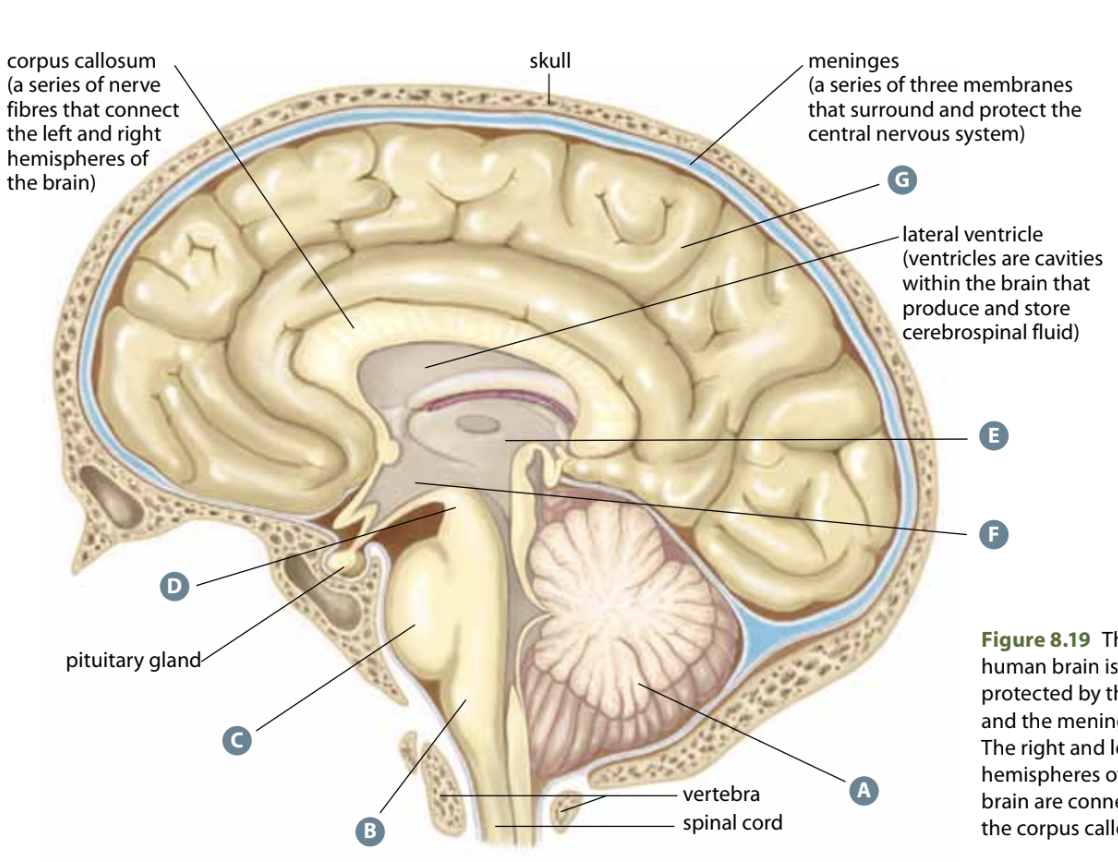
Structure G
Cerebrum - largest part of the brain, memory, consciousness, language
Hormone
Chemical messenger
Endocrine gland function
Secretes hormones into the bloodstream
Glands/organs of endocrine system
Pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, testes, ovaries
Target cells
Contains receptor cells for hormones
Water soluble hormones
Hormone binds to receptor, activates ATP→ cAMP
Lipid soluble hormones
Hormone diffuses through membrane, binds to receptor inside nucleus, activates mRNA synthesis → protein synthesis
Pituitary gland lobes
Posterior and anterior
Posterior pituitary gland
Stores and secretes ADH and Oxytocin (produced in the hypothalamus)
Anterior pituitary gland
Produces and secretes FSH, LH, TSH, ACTH, PRL, hGH
Pathway of hGH
Pituitary gland → hGH production → Liver → growth factors from liver → bone, muscle, fat cells
Hypersecretion of hGH
Gigantism (childhood) acromegaly (adulthood)
Hyposecretion of hGH
Dwarfism
Thyroid gland
Regulates metabolism, secretes thyroxine (T4)
Thyroxine
Targets cells in the heart, skeletal muscles, liver, kidneys
Low production of T4
Hypothyroidism or cretinism
Overproduction of T4
Hyperthyroidism, Grave’s disease
Pathway of thyroid feedback loop
Hypothalamus → TRH → pituitary gland → TSH → thyroid gland → T4 Production → inhibits release of TSH and TRH
Calcium homeostasis
Calcium levels are regulated by calcitonin and PTH
Adrenal glands
Regulates stress response and blood sugar
Components of adrenal glands
Adrenal medulla
Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
Secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine - regulates short term stress
Adrenal cortex
Produce glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids - trigger long term stress
Most abundant glucocorticoid
Cortisol - ACTH targets adrenal cortex, which secretes cortisol
Hormones of the pancreas
Insulin and Glucagon
Islets of langerhans
Clusters of endocrine cells that secrete hormones of the pancreas
Insulin
Secreted by beta endocrine cells, lowers blood glucose
Glucagon
Secreted by alpha endocrine cells, increases blood glucose
Functions of the endocrine system
metabolism
Growth and development
sexual function
sleep
mood
stress
response to injury
Gonads
Pair of organs that produce reproductive cells and sex hormones
Sex hormones
Controls the development and function of the reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics
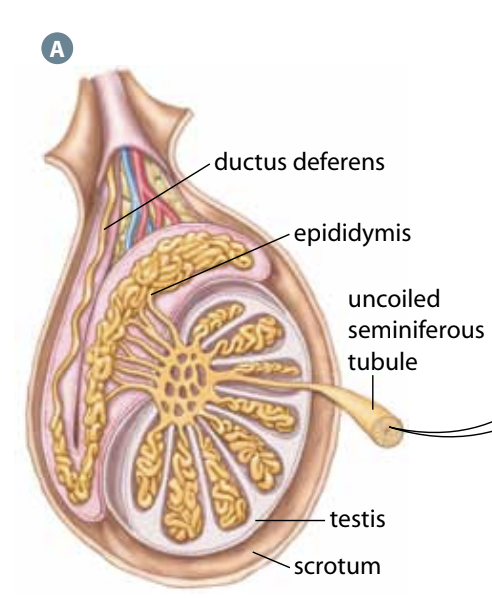
Seminiferous tubules
Where sperm are produced
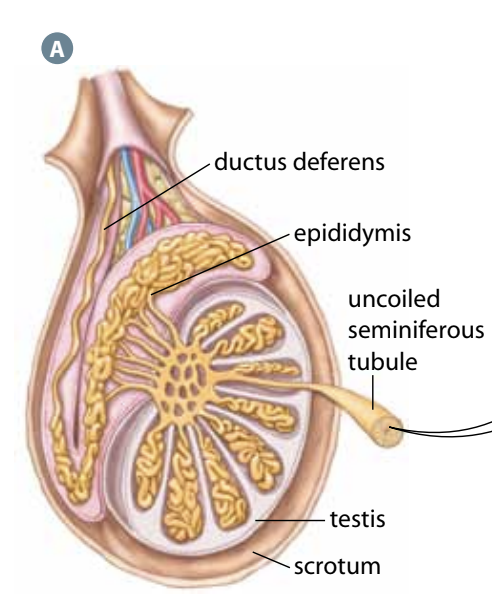
Pathway of sperm
Made in seminiferous tubules → Transported to epididymis → Matured sperm go to ductus deferens to be stored
Semen
Sperm mixed with fluids from seminal vesicles, cowper’s gland, and the prostate gland
Puberty pathway (male)
Hypothalamus produces GnRH → acts on ant. pit. gland → releases FSH and LH → testes produce sperm and release testosterone
Male hormone regulation
FSH causes the seminiferous tubules to release inhibin
Inhibin
Produced by seminiferous tubules to inhibit the production of FSH to regulate male hormones
Endometrium
Uterine lining
Pathway of an egg
Stored in ovaries → once fertilized, moves to oviduct → goes to uterus
Estrogen
Female sex hormone produces in ovaries - maintains sexual organs and secondary sex characteristics
Progesterone
Female sex hormone produced by corpus luteum to prep the uterus for a fertilized egg
Ovarian cycle pathway
increase in FSH → follicle matures → follicle releases estrogen and progesterone → ant. pit. inhibits FSH → estrogen triggers GnRH release → LH also released → follicle bursts and ovum is released