Basic Clinical Skills Final
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Principles of Assessment
scene size-up
primary assessment
secondary assessment
working diagnosis
scene size up
done while approaching patient
body substance isolation
number of patients
primary assessment
identify immediate life-threats to your patient
general impression
mechanism of injury/nature of illness
responsiveness
ABC’s
ABC’s
airway
breathing
circulation
skin
secondary assessment
related to specific problems with your patient
patient history
physical examination
vital signs
diagnostic tests
working diagnosis
what your assessment leads you to believe is wrong with the patient
chief complain
what is bothering the patient the most
OPQRST
Onset
“how did your symptoms begin?”
“did it start rapidly or were the symptoms gradual?”
Provocation/Palliation
“does anything make the symptoms better or worse?”
Quality
“can you describe the type of pain you are feeling, for example is it sharp, dull…?”
Region/radiation
“where do you feel your pain, does it radiate anywhere else?”
Severity
“on a scale of 1 -10, 1 being no pain at all and 10 being the worst pain of your life, where would you rate your pain”
Time
“when did the pain first begin and how long did it last?”
SAMPLE
Signs and Symptoms
Allergies
“do you have any allergies”
Medications
“what medications are you currently taking?”
Past Medical History
“what medical problems have you been diagnosed with?”
Last Oral Intake
“what was the last thing you ate or drank?”
Events leading up to injury/illness
“what were you doing before or during the injury?”
Physical examination techniques
observe
auscultate
palpate
Physical Exam
Body systems approach
focus questioning and exam on the particular body system that is most likely involved
observe for discoloration, swelling, deformities
auscultate for abnormal body sounds
palpate for rigidity, masses, crepitus
Reassessment
subsequent sets of vital signs
unstable patient: every 5 min
stable patient: every 15 min
Diagnosis
label for condition based on your assessment, patient history, physical exam, and vital signs
differential diagnosis
working diagnosis
small list of potential diagnoses
traditional approach to diagnosis
assess patient
list of conditions or diagnoses
further evaluation
final diagnosis
secondary assessment - unresponsive medical patient
scene size up and primary assessment
begin with physical exam and baseline vital signs
obtain patient history from bystanders
look for thins like medical alert bracelets and medication bottles to help guide assessments
trauma patient assessment
c spine precautions
rapid trauma assessment
trauma assessment
D- Deformities
C- Contusions
A- Abrasions
P- Punctures
B- Burns
T- Tenderness
L- Lacerations
S- Swelling/Symmetry
Myocardial Infarction
caused by fatty deposits in the artery that limit blood flow
complete loss of blood flow to area of cardiac muscle that causes pain and eventually cell death
Left sided heart failure
left ventricle is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood to the body
when L ventricle has trouble pumping, blood backs up into lungs causing pulmonary edema
Right sided heart failure
right ventricle is responsible for pumping deoxygenated blood to the lungs
when R ventricle has trouble pumping, blood backs up into the tissues of the body, causing peripheral edema
gravity dependent, legs are most common site
diabetes type 1
pancreatic cells do not produce or secrete insulin appropriately
glucose cannot enter blood cells
requires lifelong management and cannot be reversed
diabetes type 2
cells become less receptive to insulin
often seen with sedentary lifestyle and high sugar diets
often reversible in early stages
can require oral diabetic medications or even insulin administration for treatment
CVA
death of injury of brain tissue from oxygen deprivation
causes
ischemic
blockage of artery supplying blood to part of the brain
hemorrhagic
bleeding from a ruptured blood vessel in the brain
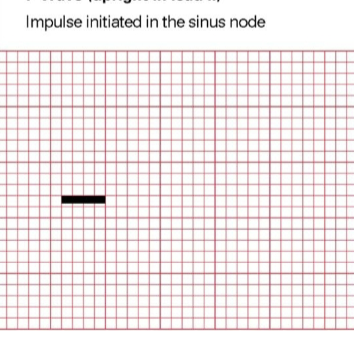
P wave - impulse initiated in the sinus node
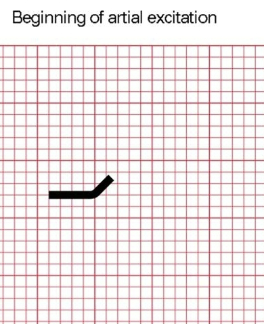
P wave - beginning of atrial excitation
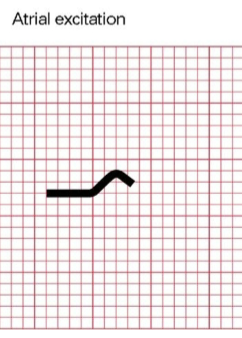
P wave - atrial excitation
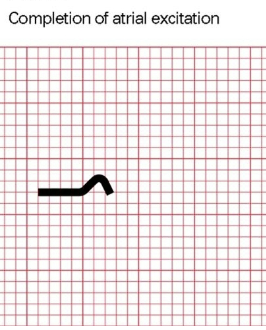
P wave - completion atrial excitation
P-R interval
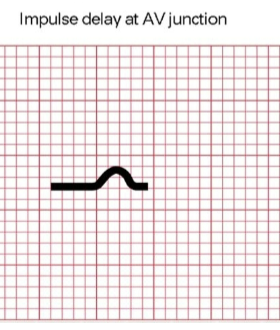
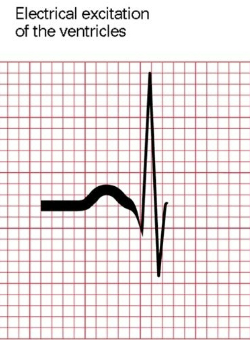
QRS complex
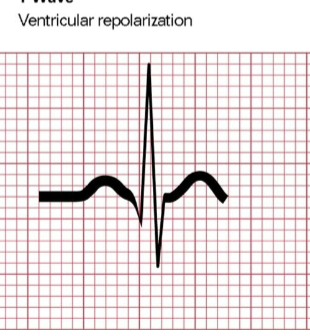
T wave
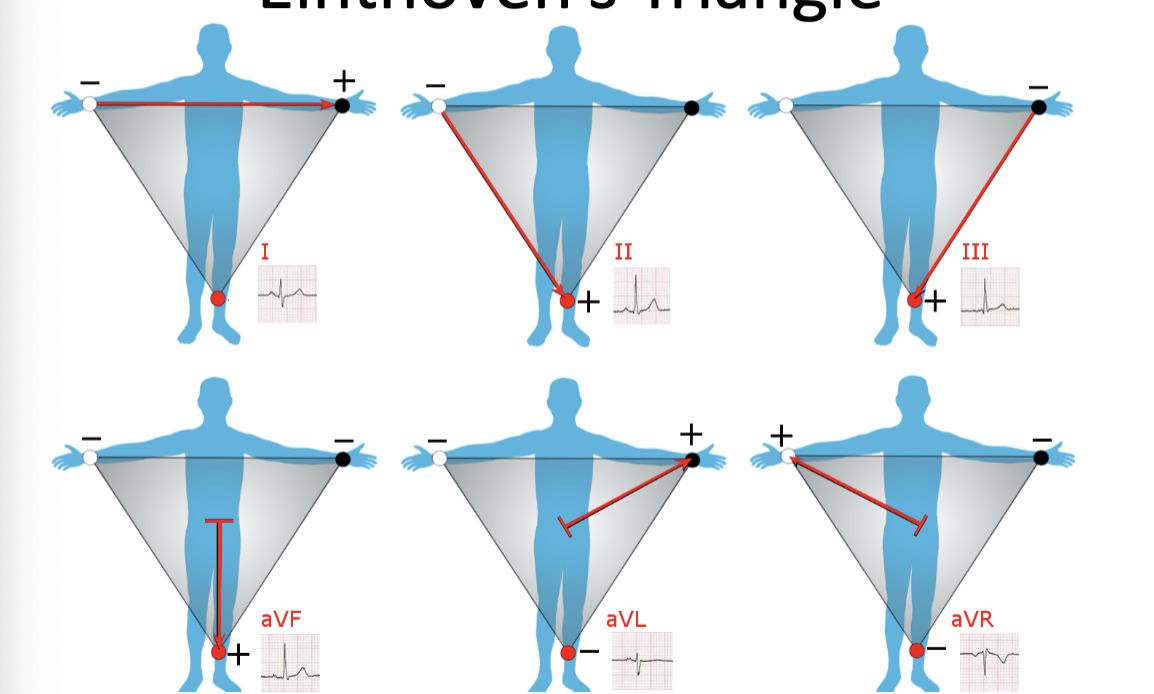
Einthoven’s Triangle
12 Lead ECG
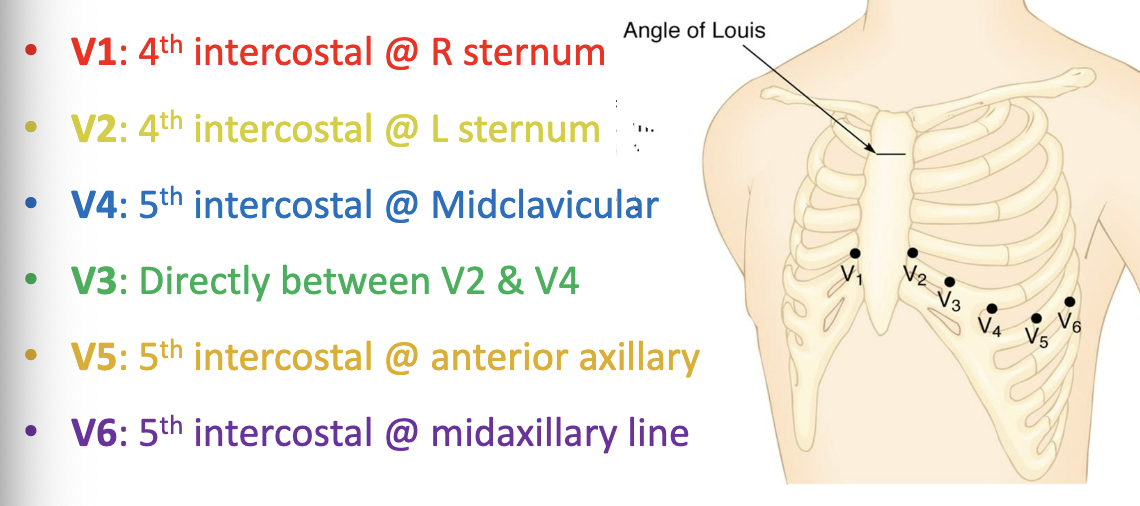
ECG Elements
Normal ranges
PR interval
0.12 - 0.20 s
QRS interval
<0.12 s
QT interval
0.33-0.42 s
Five Step Rhythm Analysis
Analyze rate
atrial
ventricular
Analyze rhythm
Analyze P wave morphology
Analyze PR interval
Analyze QRS morphology
Six second method
count 30 large boxes
count # of QRS in 6s
multiply by 10
time consuming and least accurate
R-R interval #1
count # of small boxes between R waves
divide 1500 by #
only works on regular rhythms
triplicate method
count # of large boxes between R waves
reference table
fast and reliable
only works on regular rhythms
Point of Care Testing
Purpose: Perform laboratory testing at the patient’s bedside
saves time to obtain important information
not as accurate and often does not replace obtaining actual lab results
Urine Dipstick Test
urine dip analysis
leukocytes - white blood cells? infection?
nitrites - uti?
protein - kidney disfunction?
pH - problems with kidney?
Blood - problems with kidney or urinary tract?
Specific gravity - more “stuff” in urine?
Ketones - body burning fat instead of sugar for energy?
Bilirubin - liver problems"?
glucose - diabetes?
bleeding
follow blood-borne pathogen precautions
protect wound from contamination
seek medical attention if bleeding is excessive and/or stitches are required
bleeding procedures
apply direct pressure with a sterile dressing or clean pad over the site to stop the bleeding
apply more pressure if bleeding does not stop
if dressing becomes saturated, apply a 2nd dressing over the first
apply pressure
if bleeding still does not stop and multiple dressings have been applied, apply tourniquet
types of dressings
gauze pads
adhesive strips
trauma dressings
improvised dressing
purpose of dressing
cover an open wound
control bleeding
prevent infection and contamination
absorb blood and wound drainage
protect wound from further injury
RICES
R- Rest
prevents further injury and allows for initiation of bleeding
I - Ice
reduce swelling, bleeding, inflammation, and pain
C - Compression
reduces swelling and bleeding
E - Elevation
decrease blood flow and controls edema
S - Stabilization
reduces muscle spasm in the injured are by assisting in relaxation of associated muscles
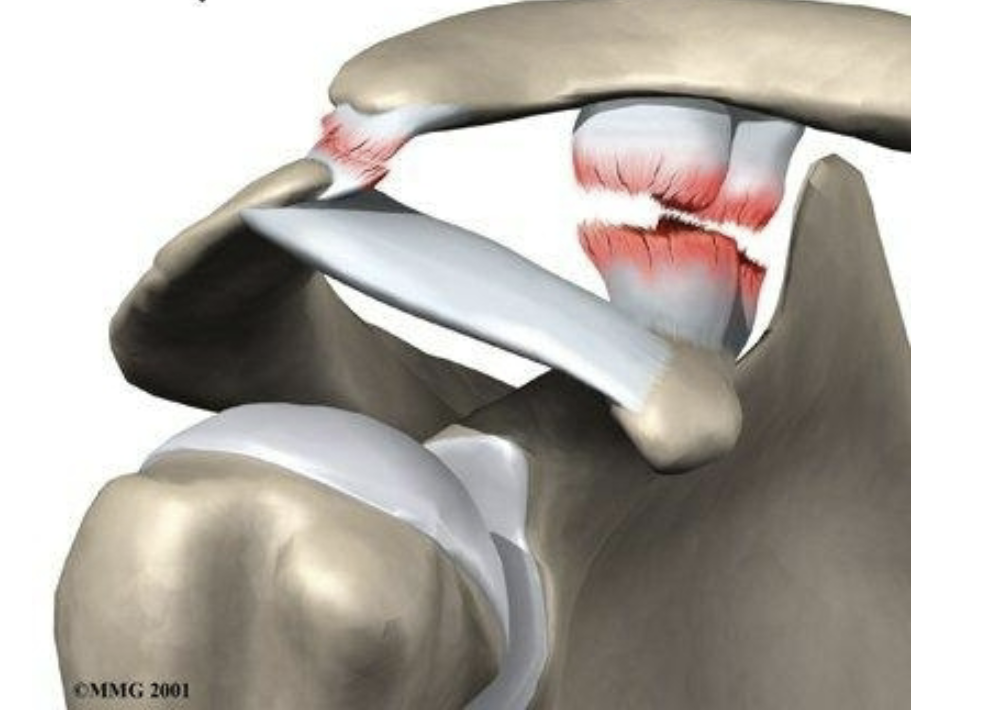
Acromioclavicular separation
clavicle is higher on one side
limited mobility
extreme pain in shoulder
loss of function
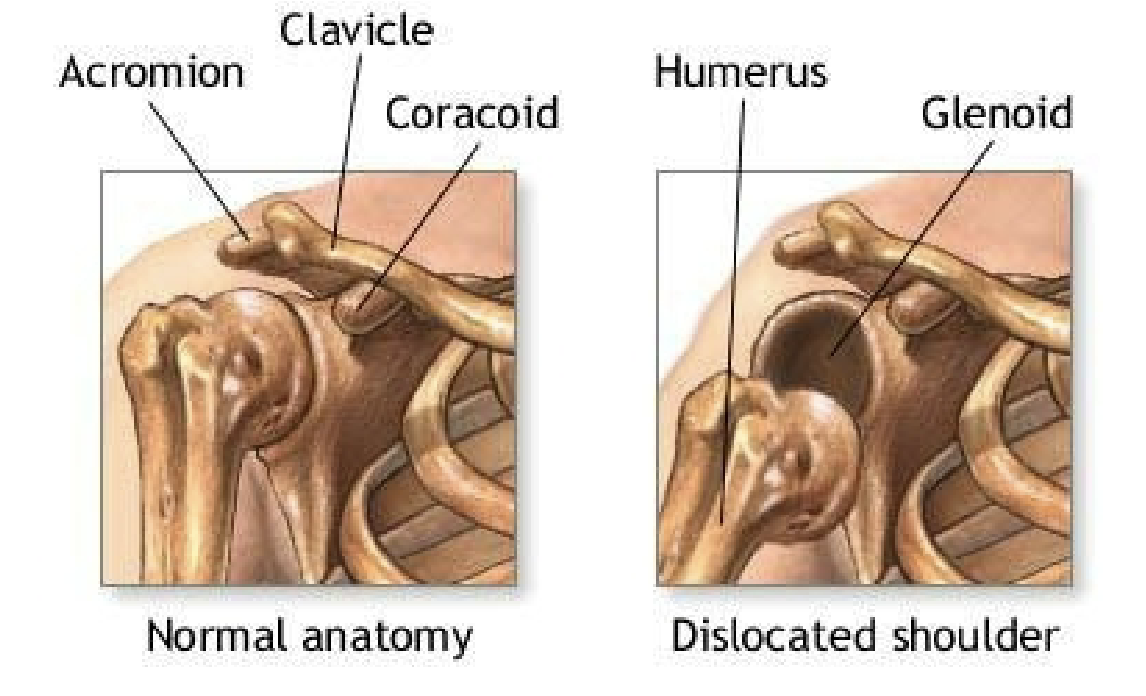
Shoulder dislocation
shoulder appears squared off
complete loss of function
previous history of dislocations
Sling and swathe
support and protect the upper extremities
used to support an injury to shoulder and arm
signs of extremity fracture
pain and tenderness
deformity
swelling
inability to move extremity
potential for broken skin surface
general care for fractures
reduces pain
prevents damage to muscle, nerves, and blood vessels
prevents a closed fracture from becoming an open fracture
reduces bleeding and swelling
hyperthermia
heat cramps
heat exhaustion
heat stroke
Hypothermia
shivering
loss of muscle function, LOC, vitals
slurred speech
disoriented
dehydrated
hypoglycemia
low blood glucose
hyperglycemia
high blood glucose
HbA1c test
measures a patient’s average blood glucose level over a 3 moth period
measures percentage of RBC that have glucose attached to hemoglobin
assists in the diagnosis of prediabetes and diabetes
also assists with diabetic patient management
allergic reactions
may cause anaphylactic shock causing respiratory arrest
seek immediate medical attention
consider assisting patient with epi-pen
S&S of shock
increased HR
rapid, weak pulse
hypotension
irritability
difficulty maintaining body temp
skin becomes pale and cyanotic
seizure
do not restrain the person during convulsions
attempt to assure safety by ensuring that the person does not injure themselves
seek medical attention
when seizure is over, complete physical exam
place in recovery position
low flow oxygen devices
nasal cannula
simple mask
high flow oxygen devices
partial-rebreathing mask
nonrebreathing mask
bag-valve-mask
air-entrainment masks
CPAP
Nasal cannula
nasal prongs
various sizes
use pressure-compensated Thorpe tube flow meter
adults: 1-6 L/min
infants: 0-2 L/min
Simple mask
flow rate 5-10 L/min
nonrebreathing mask
PRM with one-way valves
bag and mask
side ports
exhaled gasses cannot enter reservoir
flow rate: 10-15 L/min
Bag-Valve Mask
Inhalation
squeeze the BVM
created positive pressure
airway structures and lungs get distended
increases size of chest
pushes air into lungs
exhalation
release the BV<
releases positive pressure
allow structures and lungs to return to resting position
decreases size of chest
pushes air out
CPAP
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
uses continuous positive pressure to open alveoli for gas exchange
bronchospasm
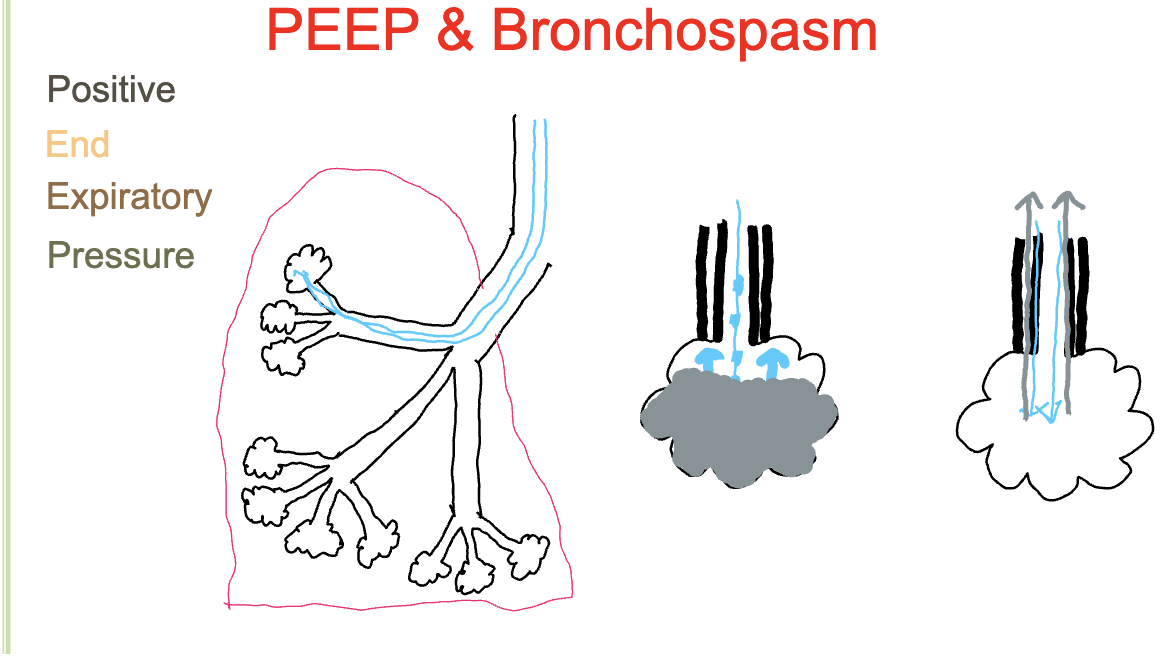
oxygen enclosures
hoods (over head)
tents (over bed)
isolettes (enclose infant)
Different gases
oxygen
air
nitrogen
carbon dioxide
helium
hazards of oxygen therapy
if the tank is punctured or a valve breaks off, the supply tank can become a missile
oxygen supports combustion
oxygen and oil do not mix under pressure
Safety Indexed connection systems
american standard compresses gas cylinder outlet
inlet connections (American Safety System) (ASSS)
Pin-indexed safety system (PISS)
Diameter-indexed safety system (DISS)
challenges of telehealth
less stable and sanitary environment
no access to immediate help
requires active patient involvement in their own care
privacy
insurance coverage
more difficult to do a proper exam
advantages of telehealth
increased access of healthcare providers/easier access of healthcare
reduces ED/Hospital/EMS overcrowding
patient comfort
tech used in telehealth
EKG monitoring patch
blood glucose monitoring patch
portable ultrasound
in hospital telehealth robot
point-of-care blood analyzer