Fundamental Concepts in Applied Biochemistry
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
What is biochemistry?
Chemistry of the organs and tissues of the body and of the various physiological processes related to life
What are the most common chemical processes related to life?
The synthesis and metabolism of amino acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and fatty acids
What are the two types of cells?
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic
What are prokaryotic cells?
Cells that consist of a single closed compartment surrounded by a plasma membrane, which lacks a defined nucleus and has a relatively simple internal organization
What are eukaryotic cells?
Cells that contain a defined, membrane-bound nucleus and extensive internal membranes that enclose organelles
Are bacteria prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes
Are archaea prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes
Are animals, plants, fungi, and protists prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes
What do pro- and -kary- mean in the word “prokaryote”?
Before nucleus
What does eu- mean in the word “eukaryote”?
True
What is the plasma membrane?
An outer covering that separates the cell’s interior from its surrounding environment
What is cytoplasm?
Made up of cytosol and the cellular structures suspended in cytosol
What is DNA?
Genetic material of the cell
What are ribosomes?
Molecular machines that synthesize proteins
What is the prokaryotic cell wall made out of?
Peptidoglycan
What does the capsule of prokaryotes do?
Helps the cell attach to surfaces in its environment
What are fimbriae?
Hair-like structures that are used for attachment to host cells and other surfaces
What are flagella?
Whip-like structures that act as rotary motors to help bacteria move
What are lysosomes?
Recycling centers of the cell
What are peroxisomes?
Organelles that carry out oxidation reactions and produce hydrogen peroxide
What is a nucleus?
An organelle that houses the cell’s genetic material
What are mitochondria?
Organelles that product adenosine triphosphate/ATP
What are the two types of metabolism?
Anabolism and Catabolism
What is catabolism?
Breaking down of organic molecules
What is anabolism?
Building organic molecules
What is the body’s main energy source?
Glucose
What is coenzyme derived from Vitamin B3?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, NAD+/NADH
What is a coenzyme derived from Vitamin B2?
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD/FADH2)
What are the bulk elements that the body needs daily?
H, C, N, O, Na, P, S, Cl, K, Ca
What are the trace elements that the body needs a few milligrams of per day?
Fe, Cu, Zn, Mg, V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Se, I, Mo
What is the net dipole of CO2?
Zero
What is the degree of the O-C-O bond in CO2?
180
What is the degree of the H-O-H bond in water?
104.5
What is the dipole of water?
Electric
What is a hydrogen bond?
A bond between hydrogen and a highly electronegative atom
Is O2 polar or nonpolar?
Nonpolar
When is oxygen generated by plants?
During photosynthesis
What are electrolytes?
Substances that dissociate into anions and cations
What are non-electrolytes?
Substances that do not dissociate into anions and cations
What are weak electrolytes?
Substances that dissociate partly
What is an acid?
A substance that produces H3O+ in an aqueous solution
What is a base?
A substance that produces OH- in an aqueous solution
What are the six most common strong acids?
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4
What are the four most common strong bases?
LiOH, NaOH, KOH, Ba(OH)2
Is an acid or a base a proton donor?
Acid
Is an acid or base a proton acceptor?
Base
What is a conjugate acid-base pair?
Any pair of molecules or ions that can be interconverted by transfer of a proton
What molecule do Bronsted-Lowry definitions not require to be a reactant?
Water
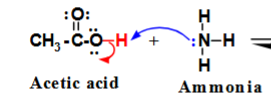
Which is the proton acceptor?
Ammonia
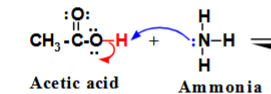
Which is the proton donor?
Acetic acid

Is the acid or the base unionized?
Acid

Is the acid or the base unionized?
Base
T/F: An acid can be positively, neutral, or negatively charged.
True
T/F: A base can only be negatively charged or neutral.
True
Is HCl monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic?
Monoprotic
Is H2CO3 monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic?
Diprotic
Is H3PO4 monoprotic, diprotic, or triprotic?
Triprotic
T/F: The stronger, the acid, the stronger its conjugate base.
False
What is a strong acid?
One that reacts completely or almost completely with water to form H3O+ ions
What is a strong base?
One that reacts completely or almost completely with water to form OH- ions
HCl is
A strong acid
HBr is
A strong acid
HI is
A strong acid
HNO3 is
A strong acid
H2SO4 is
A strong acid
HClO4 is
A strong acid
LiOH is
A strong base
NaOH is
A strong base
KOH is
A strong base
Ba(OH)2 is
A strong base
Lithium hydroxide is
A strong base
Sodium hydroxide is
A strong base
Potassium hydroxide is
A strong base
Barium hydroxide is
A strong base
Hydrochloric acid is
A strong acid
Hydrobromic acid is
A strong acid
Hydroiodic acid is
A strong acid
Sulfuric acid is
A strong acid
Perchloric acid is
A strong acid
What is the name of HCl?
Hydrochloric acid
What is the name of HBr?
Hydrobromic acid
What is the name of HI?
Hydroiodic acid
What is the name of HNO3?
Nitric acid
What is the name of H2SO4?
Sulfuric acid
What is the name of HClO4?
Perchloric acid
What is the name of LiOH?
Lithium hydroxide
What is the name of NaOH?
Sodium hydroxide
What is the name of Ba(OH)2?
Barium hydroxide
What is the name of KOH?
Potassium hydroxide
What is an acid-base reaction?
A proton transfer reaction
What is the name of a substance that can act as either an acid or a base?
Amphiprotic
What is the most important amphiprotic substance?
H2O
What would prevent a substance from being a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
Lacking a hydrogen atom
What is Ka?
An acid ionization constant
What is Keq?
The equilibrium constant
How is Keq found?
[A-][H3O+]/[HA][H2O]
How is Ka found?
Keq[H2O] = [A-][H3O+]/[HA]
How are pKa and Ka related?
pKa = -logKa
What happens when pH < pKa?
The protonated forms HA and BH+ predominate
What happens when pH = pKa ?
HA = A- and BH+ = B