TEAS - Cardiovascular
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
What are the main functions of the cardiovascular system?
Gas exchange, delivery of nutrients and hormones, and waste removal.
What are the three main components of the cardiovascular system?
Heart, blood, and blood vessels
What is the function of the heart?:
To pump blood through the arteries
What do arteries do
blood vessels carry blood away from the heart
What do veins do?
blood vessels carry blood back to the heart
Where does the exchange of materials between blood and cells occur?:
In the capillaries
What does the circulatory system transport?
Oxygen, nutrients, hormones, ions, and fluids
What does the circulatory system remove?
Metabolic wastes like carbon dioxide and urea.
What is the equation for cellular respiration?
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O
How does oxygen enter the blood?
It moves down its partial pressure gradient into alveolar capillaries and binds with hemoglobin
What does oxygen bind to in red blood cells?
Hemoglobin
Why is oxygen important for cells?:
It enables cells to convert glucose into ATP during cellular respiration
How is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
Dissolved in blood, bound to hemoglobin, or as bicarbonate ions.
Where is carbon dioxide removed from the blood?
It diffuses out of the alveolar capillaries and mostly travels as bicarbonate ions
Where is urea transported for removal?
To the kidneys for filtration
What else do the kidneys regulate besides waste?
Blood levels of fluids and ions.
How are digested nutrients like glucose, amino acids, and fats delivered to cells?
Via the circulatory system
How do hormones reach their target cells?
Through the bloodstream
How are lipid-soluble molecules transported in the blood?
With the help of carrier proteins
What is the average human body temperature?
About 98.6 °F or 37 °C
Where does heat exchange mainly occur in the body?
At the surface of the skin
What blood vessels help regulate body temperature?
Cutaneous arterioles
What detects changes in body temperature?
Thermoreceptors (sensory neurons
What part of the brain receives signals from thermoreceptors?
The hypothalamus
What does vasodilation do?
body temp too warm, the smooth muscle relaxes, and the arterioles dilate. Vasodilation allows more blood to flow through the capillary beds near the surface of the skin, and more heat is lost to the surroundings.
What does vasoconstriction do?
If temp too cool, the smooth muscle contracts, and the arterioles constrict. Vasoconstriction reduces the volume of blood that flows near the body’s surface, which minimizes heat loss to the surroundings.
What two other processes help regulate body temperature?
Sweating and shivering
Epicardium
outer layer; protects the heart and secretes lubricating fluid.
Myocardium
middle muscular layer; contracts to pump blood.
Endocardium
innermost layer; lines heart chambers and valves.
Atria (Right and Left)
The right atrium receives blood from the vena cava
left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary veins
Ventricles (Right and Left)
The right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary trunk,
left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta.
What is the function of the tricuspid valve?
Prevents backflow into the right atrium during ventricular contraction.
What is the function of the pulmonary semilunar valve?
Prevents return of blood into the right ventricle.
What is the function of the bicuspid (mitral) valve?
Prevents backflow into the left atrium during ventricular contraction.
What is the function of the aortic semilunar valve?
Prevents backflow into the left ventricle as blood exits to the aorta.
What is the endothelium and where is it found?
A thin inner lining of blood and lymphatic vessels, composed of squamous endothelial cells; lines the entire circulatory system including the heart's interior.
What functions does the endothelium serve?
Acts as a selectively permeable barrier.
Reduces friction in vessels.
Releases endothelins for vasoconstriction.
Secretes chemicals to prevent or promote blood clotting
What is systolic pressure?
maximum pressure that is exerted during systole. the ventricles contract, forcing blood into the aorta and pulmonary trunk. As the blood enters the arteries, the elastic walls stretch to accommodate the increased volume,
What is diastolic pressure?
Diastole is the period in which the ventricles relax and blood pressure is at its lowest point.
What units are used to measure blood pressure and what do the numbers represent?
Blood pressure is measured in mmHg.
First number: Systolic pressure
Second number: Diastolic pressure
What is the function of the systemic circuit?
It carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle through the aorta to the body’s tissues, and returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium via the vena cava.
Why is blood pressure higher in the systemic circuit compared to the pulmonary circuit?
Because the systemic circuit is longer and must pump blood throughout the entire body, requiring more pressure.
In the systemic circuit, which blood vessels carry oxygen-rich blood?
Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood in the systemic circuit.
What happens to vessels in the systemic circuit when oxygen levels are low?
They dilate to promote blood flow to oxygen-deprived tissues.
What is the path of deoxygenated blood in the pulmonary circuit?
Right ventricle → pulmonary trunk → pulmonary arteries → lungs → pulmonary veins → left atrium.
What is unique about the oxygen levels in pulmonary circuit vessels?
Pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood, and pulmonary veins carry oxygenated blood (opposite of systemic circuit)
How does the pulmonary circuit respond to low oxygen levels?
It causes vasoconstriction to redirect blood to better-ventilated lung regions.

What is the role of the SA node in heart conduction?
It initiates the electrical impulse that triggers atrial contraction, seen as the P wave on an ECG.

What does the AV node do in cardiac conduction?
It slows the electrical impulse, creating the PR segment on the ECG.

What is the function of the Bundle of His and Purkinje fibers?
They transmit impulses to the ventricles, causing ventricular contraction seen as the QRS complex.
P wave:
atrial depolarization
QRS complex:
ventricular depolarization
T wave:
ventricular repolarization
What is the U wave on an ECG?
A small wave that may follow the T wave, representing further ventricular repolarization.
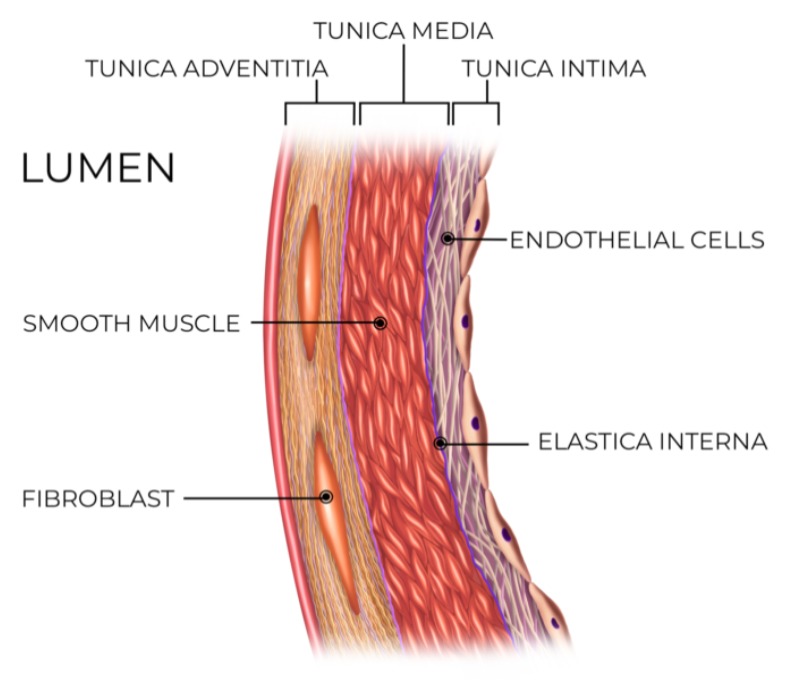
Tunica intima
innermost wall of blood vessels
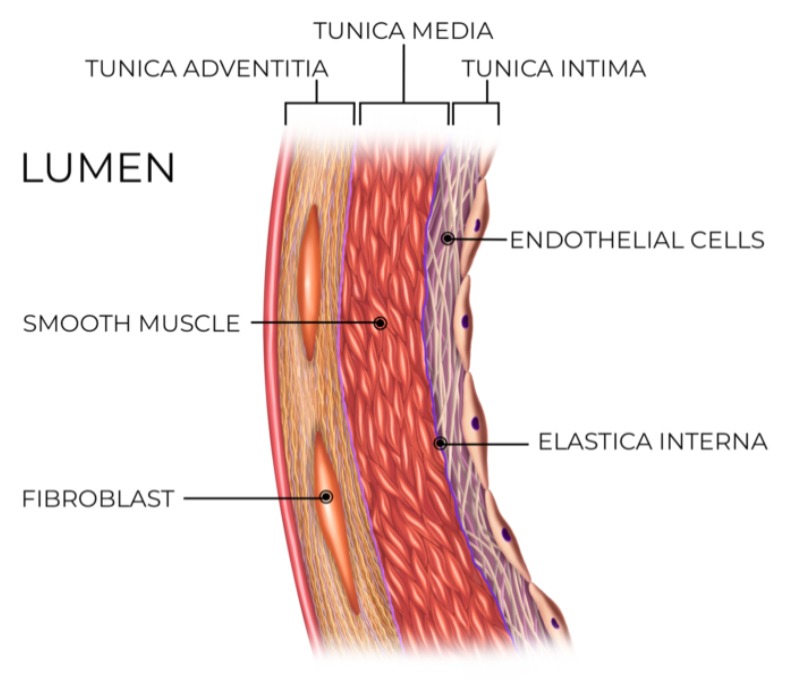
Tunica media
middle layer of blood vessels containing smooth muscle and elastic fibers
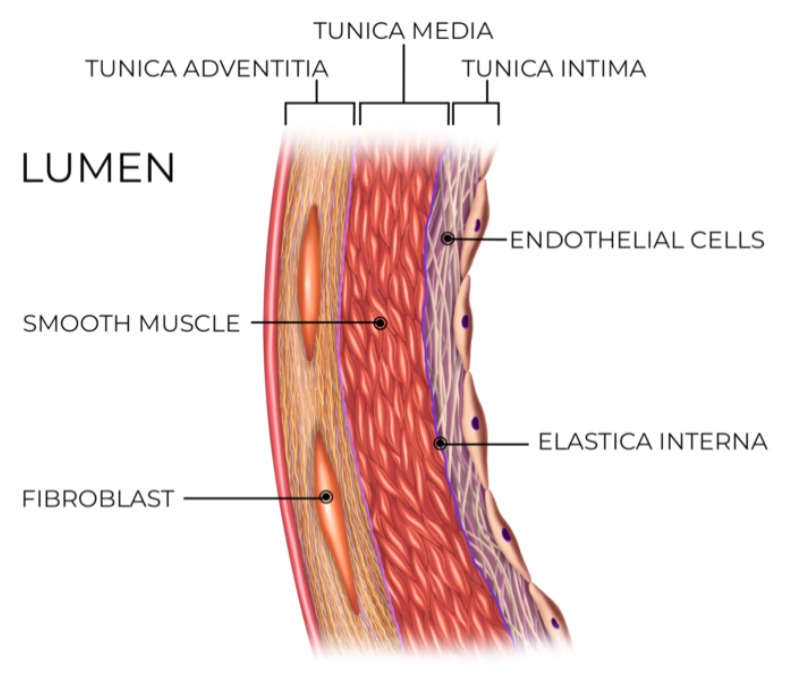
Tunica adventitia
outermost layer of blood vessels
Where is blood pressure highest in the circulatory system?
In the aorta and major arteries of the systemic circuit.
Where is the steepest drop in blood pressure found?
At the arterioles, due to increased resistance and reduced vessel diameter.
Where is blood pressure lowest?
In the vena cava.
What is laminar blood flow?
Smooth, streamlined, and silent blood flow common in most of the circulatory system
What is turbulent blood flow and when does it occur?
Swirling, noisy flow that occurs at high velocities, obstructions, sharp turns, or narrow vessels.
What is the full sequence of vessels in both circuits from arteries to veins?
Arteries → Arterioles → Capillaries → Venules → Veins
What is the function of capillaries in both the systemic and pulmonary circuits?
They allow for gas and nutrient exchange with tissues through thin walls via diffusion.
What is the role of Purkinje fibers in heart conduction?
They carry electrical impulses from the bundle branches to the ventricles, causing them to contract.