Cardiovascular System: Blood
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
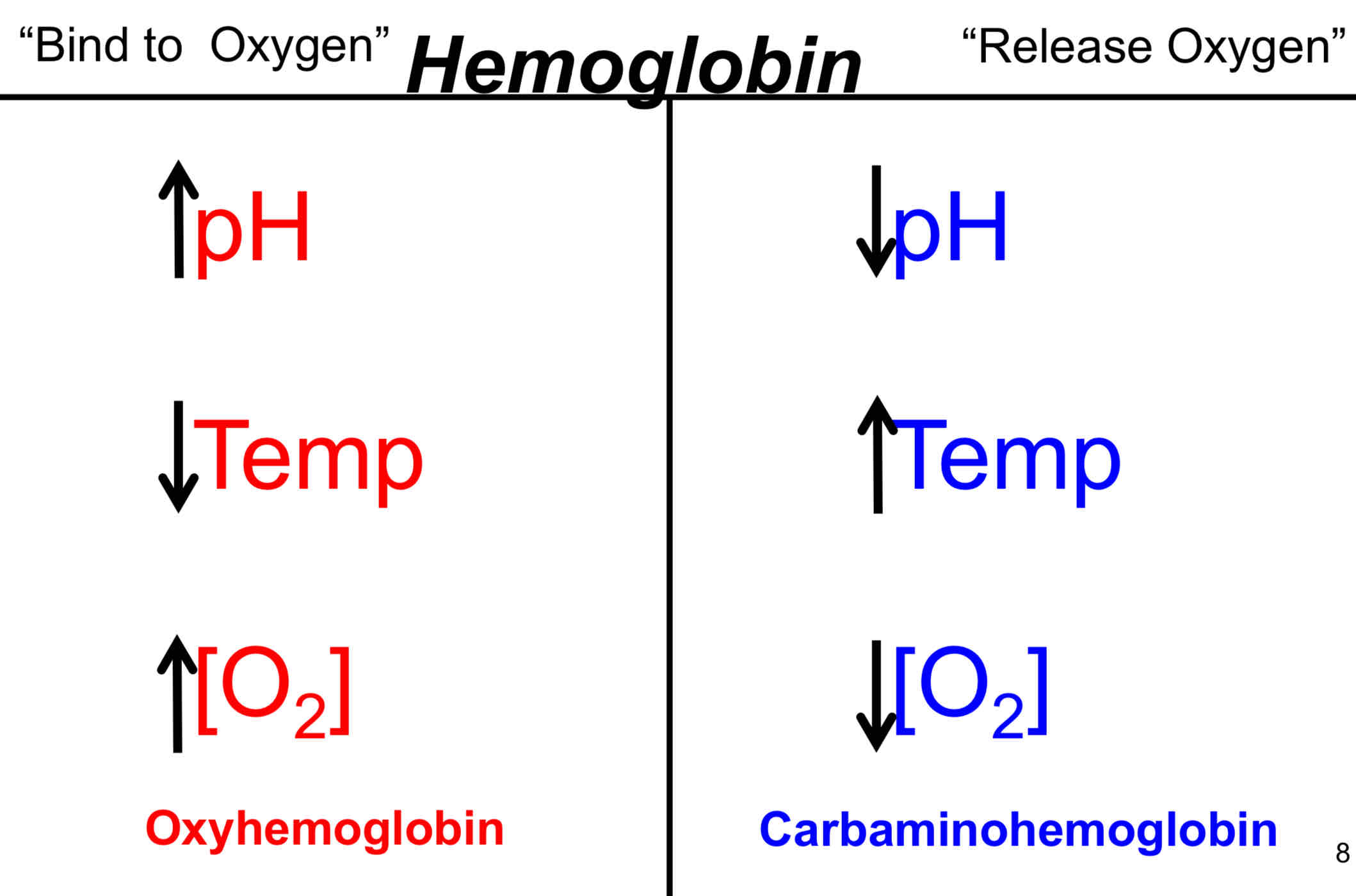
Bohr Effect
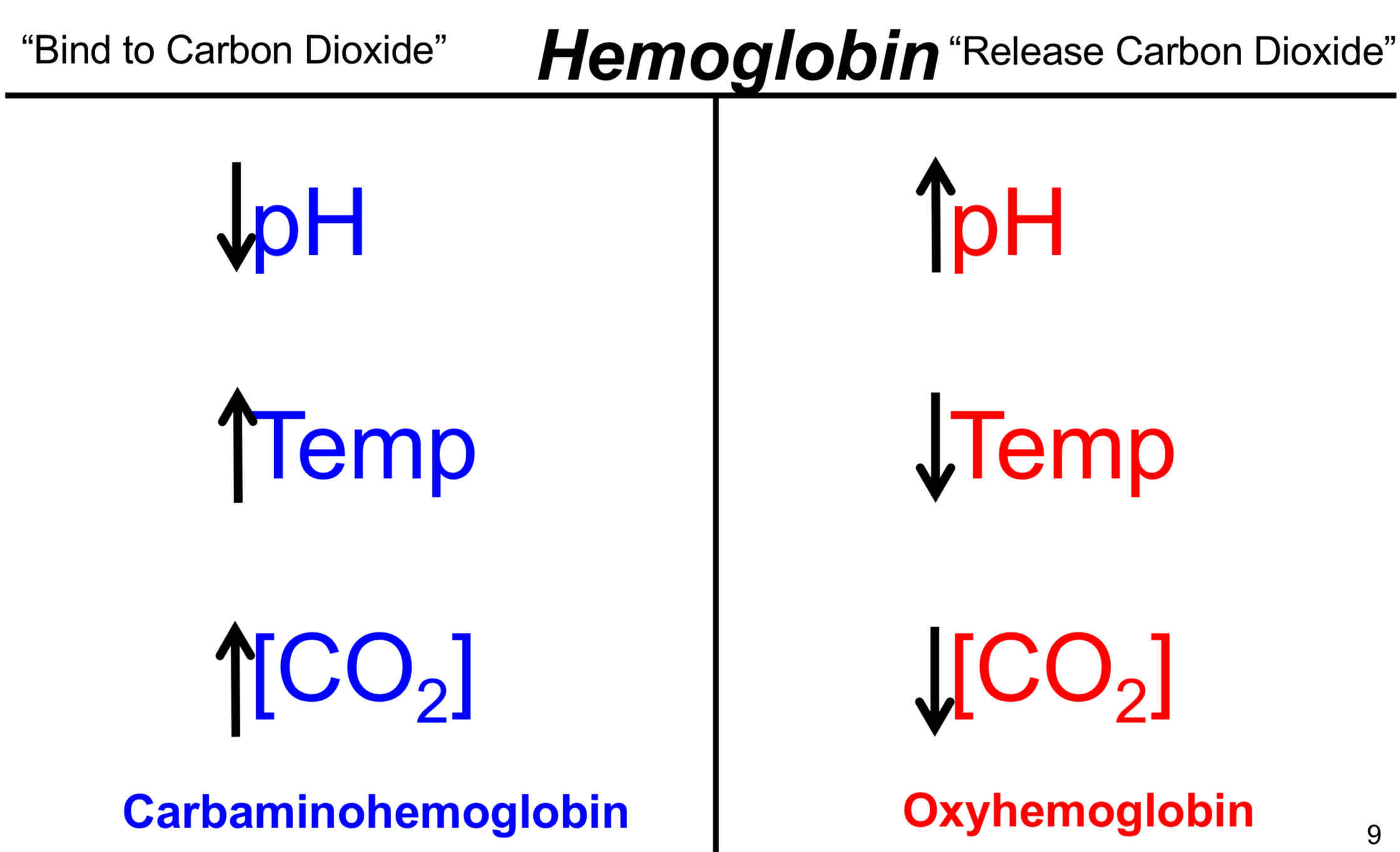
Haldane Effect
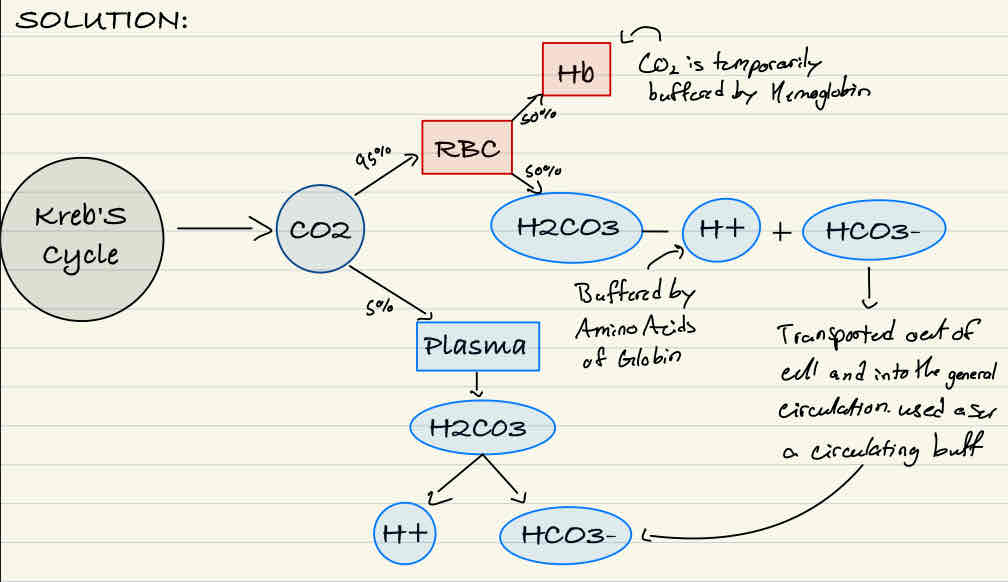
The solution to the CO2 problem…
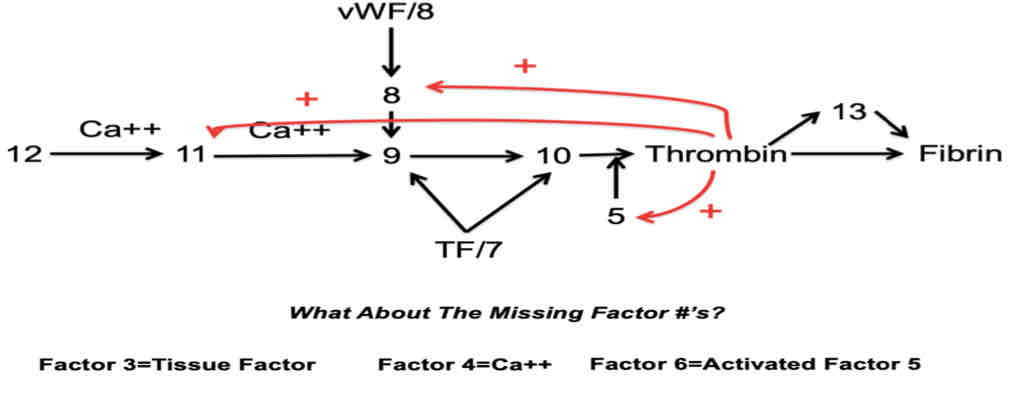
Thrombin
Primary role is conversion of Fibrinogen to Fibrin.
It activates platelets
Activates FV, FVII, FXI, and FXIII
What is the major pathway for secondary hemostasis?
Tissue Factor Pathway
Why would a vitamin K deficiency create a clotting disorder?
It is an essential factor for making 2, 7, 9, and 10 in the liver.
Heparin
A protein the triggers anti-thrombin, stops progression of a clot.
Triggers for clotting
Collagen, vWF, Tissue Factor, and Thrombin
Virchow’s Triad
The three causes of intravascular clotting,
Stasis
Hypercoagubility
Endothelial Injury
Cascade of proteins Secondary Hemostasis
Important events (in order) to occur in humoral activation.
Macrophage which has encountered antigen processes it, display it with MHC II protein on surface.
Via T cell receptor and CD4, T helper cell binds to this. APC secretes II-1 which activates the T helper cell.
T helper cells bind to B cells and release II-4 which activates B cell. The B cell then becomes a plasma cell and releases antibodies.
What is meant by “cell-mediated immunity”?
CD8 T cells are activated by the release of II-2 from T helper cells. CD8 cells recognize antigens on the surface of infected cells, attach to these cells and secrete perforins, Perforins punch holes into the infected cells, killing them.
How vaccines can prevent illness.
Vaccine creates anitbody response by injecting a foreign antigen. This creates memory B & T cells (Eliminating antigens).
Cardinal signs of Inflammation.
Heat, redness, swelling, pains and loss of function.
Why is chronic inflammation bad?
Inflammation creates additional tissue damage, which leads to continues inflammation.
Different kinds of acquired immunity.
Active Artificial: Immunization
Active Natural: Disease followed by recovery
Passive Artificial: Intravenous Anitbodies (IgG)
Passive Natural: Breastfeeding
Antigen
A substance that confers identity.
Anitbody
Protein molecule produced by activated B cell (Plasma Cells).
What do antibodies do?
Attach to antigens
Agglutination: Antibodies link cells, viruses together to make clumps that attract macrophages.
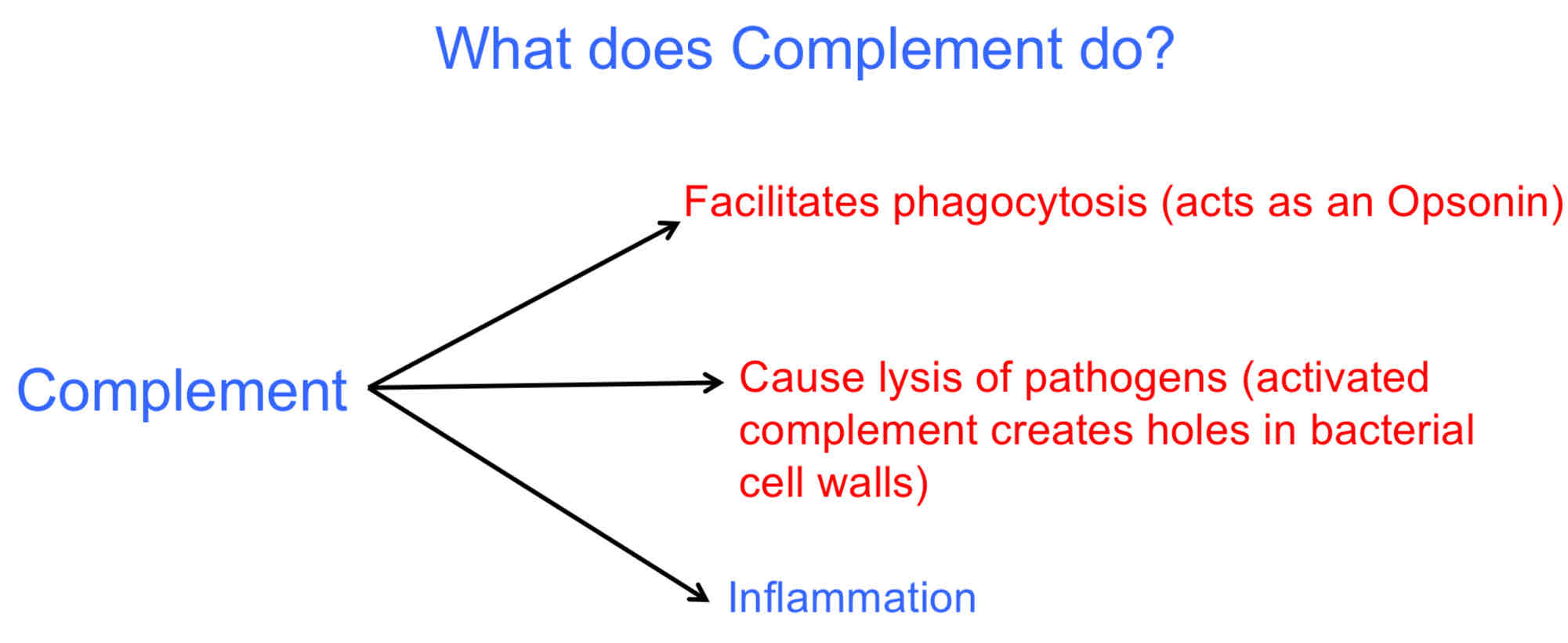
Opsonization: an opsonin is something that promotes phagocytosis.
Complement fixation.
Precipitation: toxin molecules come out of solution.
Neutralization: Toxins, viruses inactivated.
Interferon (IFN)
Signaling proteins produced by virus infected monocytes and lymphocytes.
Secreted proteins - Key anti-viral proteins because they inhibit protein synthesis.
“Interfere” with virus replication.
Warn the neighboring cells that a virus is around
Complement
Is a large number of distant plasma proteins that react with one another (C1-C9)
Complement can bind to microbes and coat the microbes.
It is essential part of innate immune response.
It enhances the adaptive immune response.
What does Complement do?
Tumor echos is Factor (TNF)
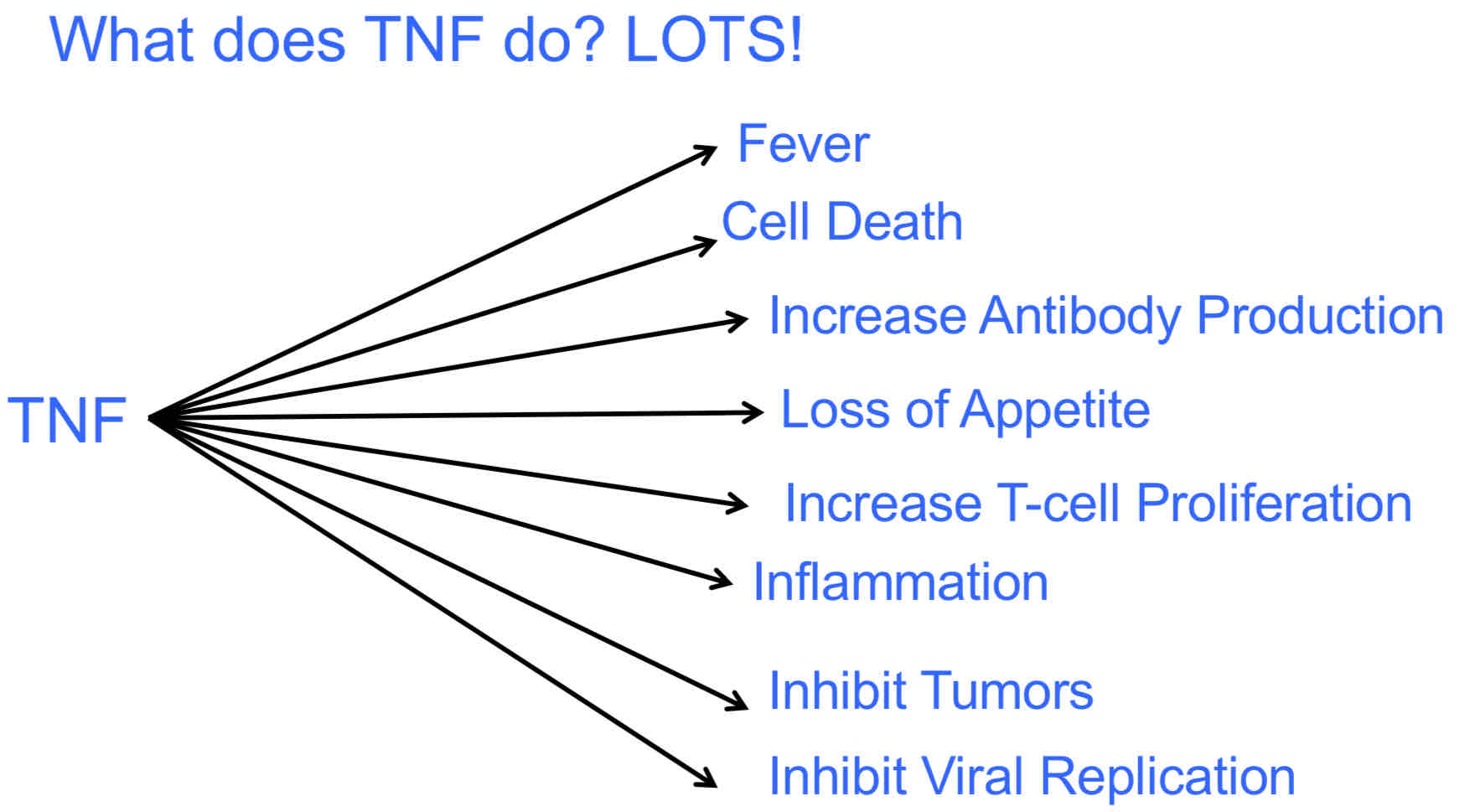
The main role of TNF is in the regulation of immune cells.
It is also an endogenous pyrogen (can induce fever).
Also can induce apoptosis cell death, cachexia, inflammation, and inhibit tumorigenesis and viral replication, etc…
What does TNF do?
Interleukins
Interleukins are numbered 1-37
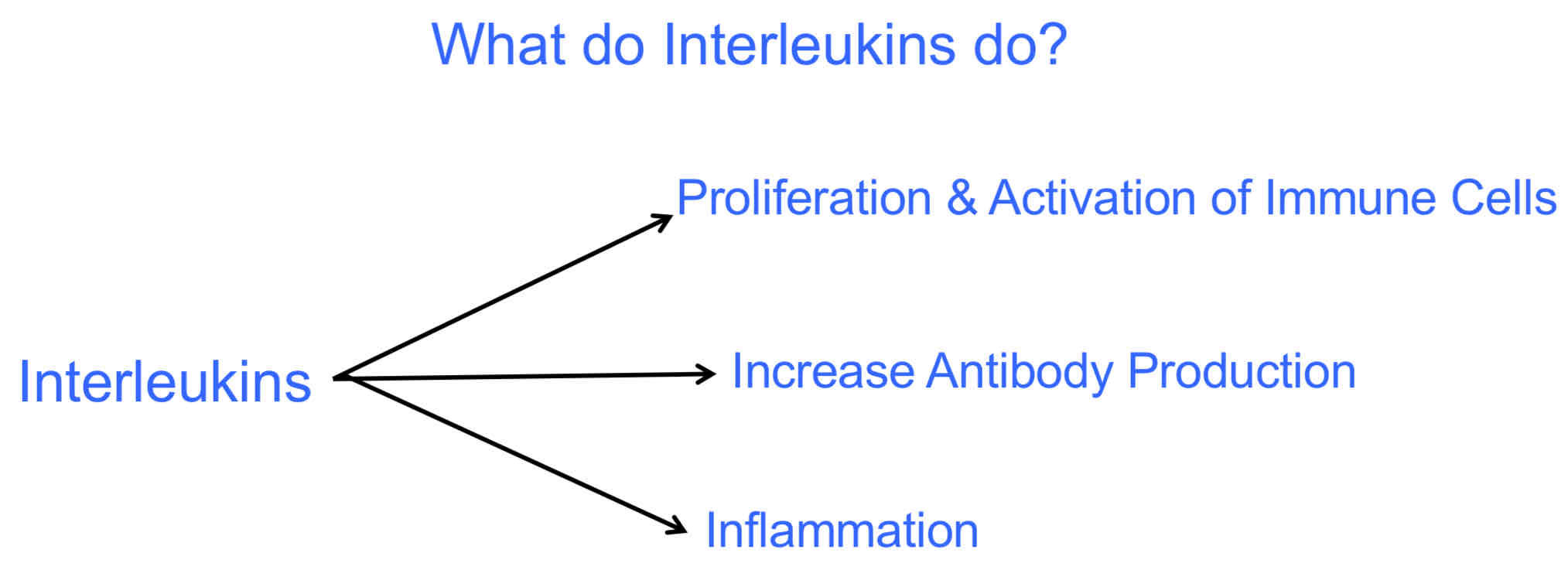
They are not stored inside cells.
They are quickly synthesized and secreted in response to infection.
They are key modulators of behavior of immune cells.
Mostly secreted by T-lymphocytes & Marcophages.
What do Interleukins do?
Most abundant White Blood Cells.
Neutrophils
Most abundant antibody in blood.
IgG