8. Protein Synthesis, Modification and Trafficking
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Protein Synthesis, Modification and Trafficking – How do They Know Where to Go?
through a process of signal sequences, which are specific amino acid addresses that are recognized by cellular machinery
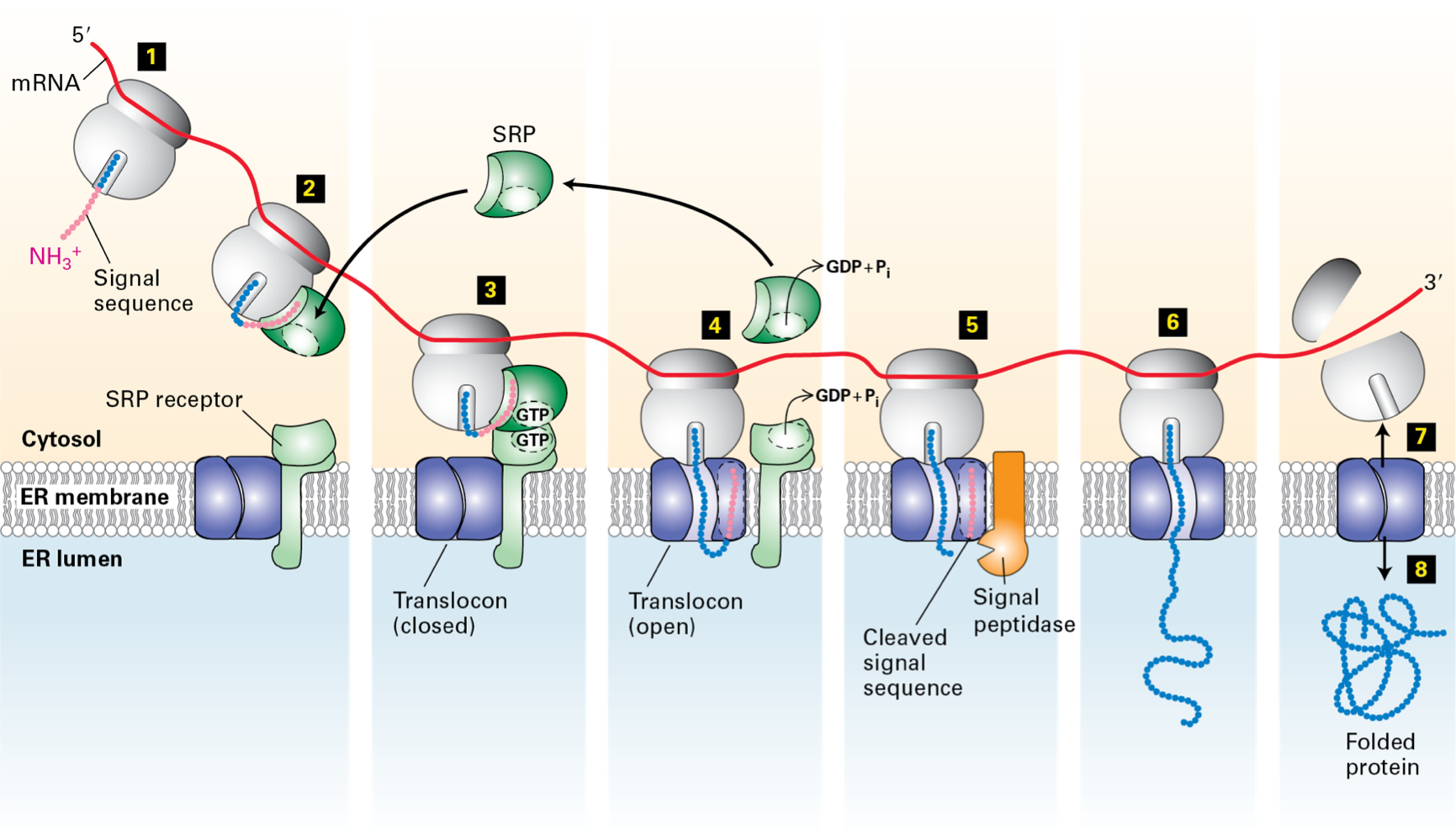
Protein Cotranslational Translocation
box 1: proteins are synthesised on poly ribosomes
16 - 30 NH end Amino Acids - Hydrophobic
signal sequence
box 2: SRP - signal receptor particle
6 proteins + 300 nucleotide RNA
binds to the signal sequence
protein synthesis stops
box 3: SRP/Ribosome/Nascent protein complex
docks to the RER
SRP receptor
box 4: Nascent protein is transferred to the translocon and protein synthesis re- commences
SRP - recycles
box 5: signal peptide cleaves the signal sequence
box 6-8: Nascent protein is extruded into the RER lumen
how to know the signal sequences is a RER specific targeting sequence?
A signal sequence is identified as an RER-specific targeting sequence because its presence on a nascent polypeptide chain causes the Signal Recognition Particle (SRP) to bind, temporarily halting translation and directing the ribosome to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum membrane for the protein's eventual translocation
Is there SRP?
protease - yes
Is GTP hydrolysis required for SRP recycling?
GMP - PNP - non hydrolyzable of GTP, GTP hydrolysis is required
is there a signal peptidase?
yes
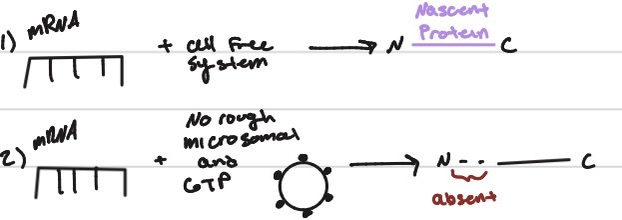
is the secretory protein totally inside the RER?
proteases - yes
how do we discover the translocon?
ohms law (V=IR)
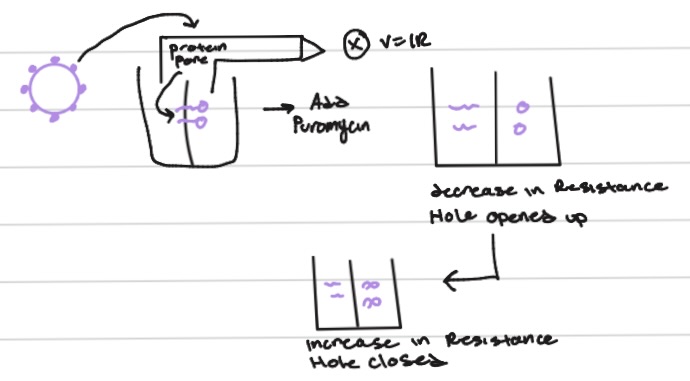
identify translocaon?
photaffinity label
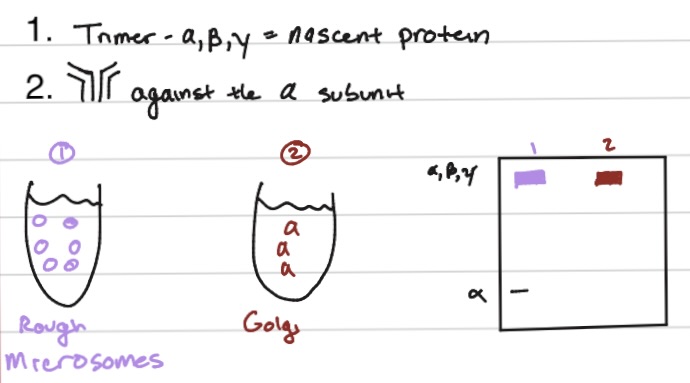
are multimeric proteins assembly in the rough ER?
in the RER - as this compartment is where protein folding, modification, and quality control take place before trafficking to other organelles like the Golgi apparatus.
what if something goes wrong in the RER? (proteins are abearent)
activation of the UPR pathway
attempt to resolve the stress by increasing folding capacity or, if unsuccessful, initiating Apoptosis (programmed cell death) and degrading the aberrant proteins via the proteasome.

Chaperones
the proteins, which assist the covalent folding or unfolding and assembly and disassembly of other macromolecular structures
monomers with a colecular weight of 70-100kDa
most of them are heat shock proteins (HSPs)
responsible for the folding, unfolding, assembly, and disassembly of proteins
ex: Dnak, DnaJ, GrpE, HtpG, and Hsp33
Chaperonins
the proteins, which provide favorable conditions for the correct folding of denatured proteins, preventing aggregation
oligomers with a molecular weight of 800kDa
have a shape of two donuts stacked on top of one another to create a barrel
responsible for the correct folding of denatured proteins, which prevent aggregation
ex: GroEL/GroES, TRiC
UPR (Unfolded Protein Response) pathway
Recognizes mis-folded Proteins and Degrades Them
Can Lead to Cell Death (Apoptosis) too under Severe Stress Conditions
Tunicamycin – stimulates UPR by blocking N-linked glycosylation of nascent proteins (later)
Salubrinal - Suppresses the UPR response
But how do RER Synthesized Proteins Become Integral Membrane (e.g. not secretory) Proteins with Different Topologies?
through a co-translational process involving a signal recognition particle (SRP), the Sec61 translocon channel, and the protein's own amino acid sequence
targets the ribosome to the RER membrane, where the nascent polypeptide chain begins to enter the Sec61 translocon channel
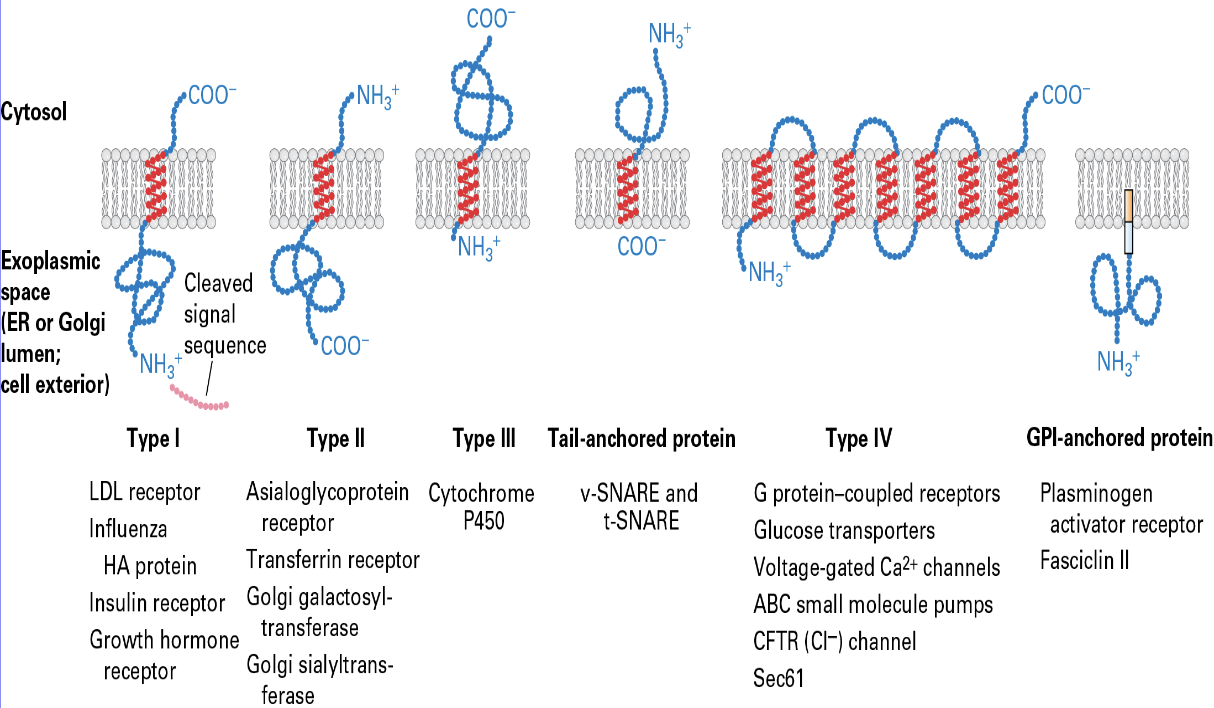
Type 1 single pass proteins
SRP + SRP receptor
signal sequences/peptidase
stop and transfer anchor
sequence - hydrophilic amino acids
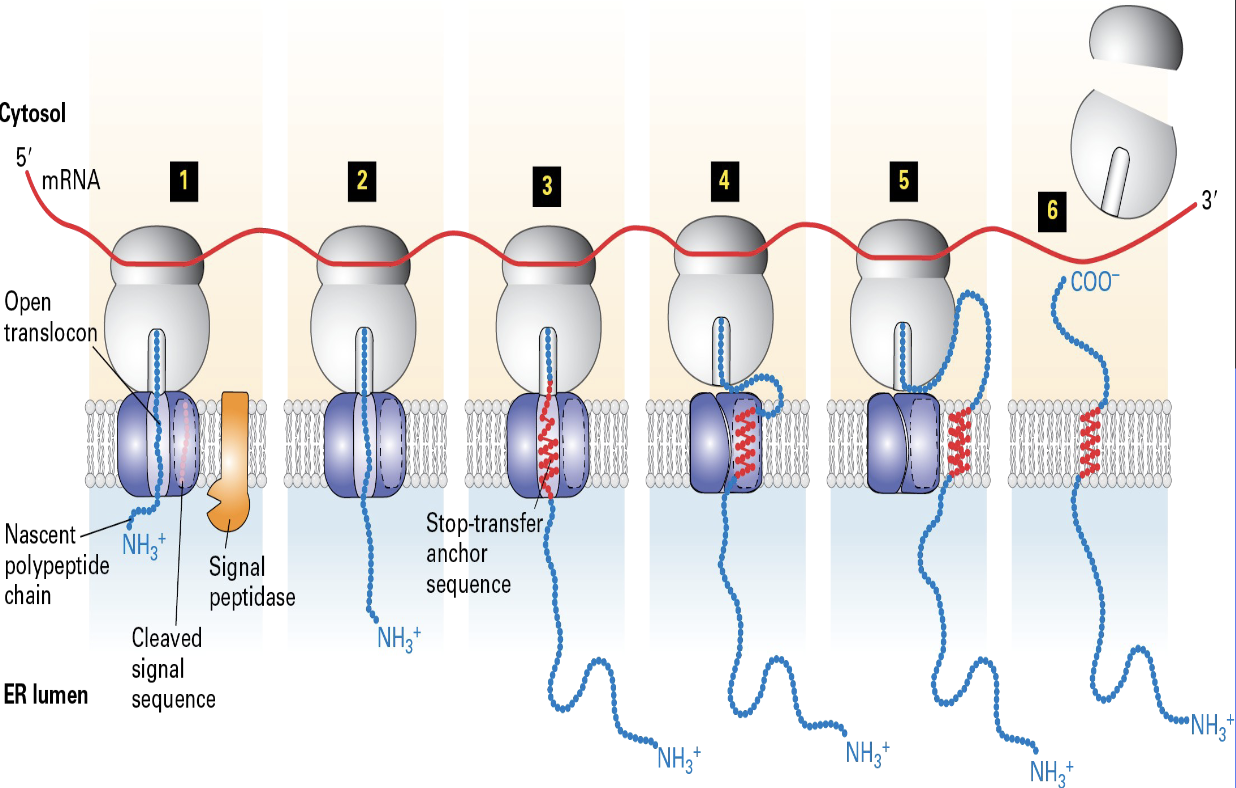
Type 2 single pass proteins
SRP + SRP receptor
internal signal sequnces
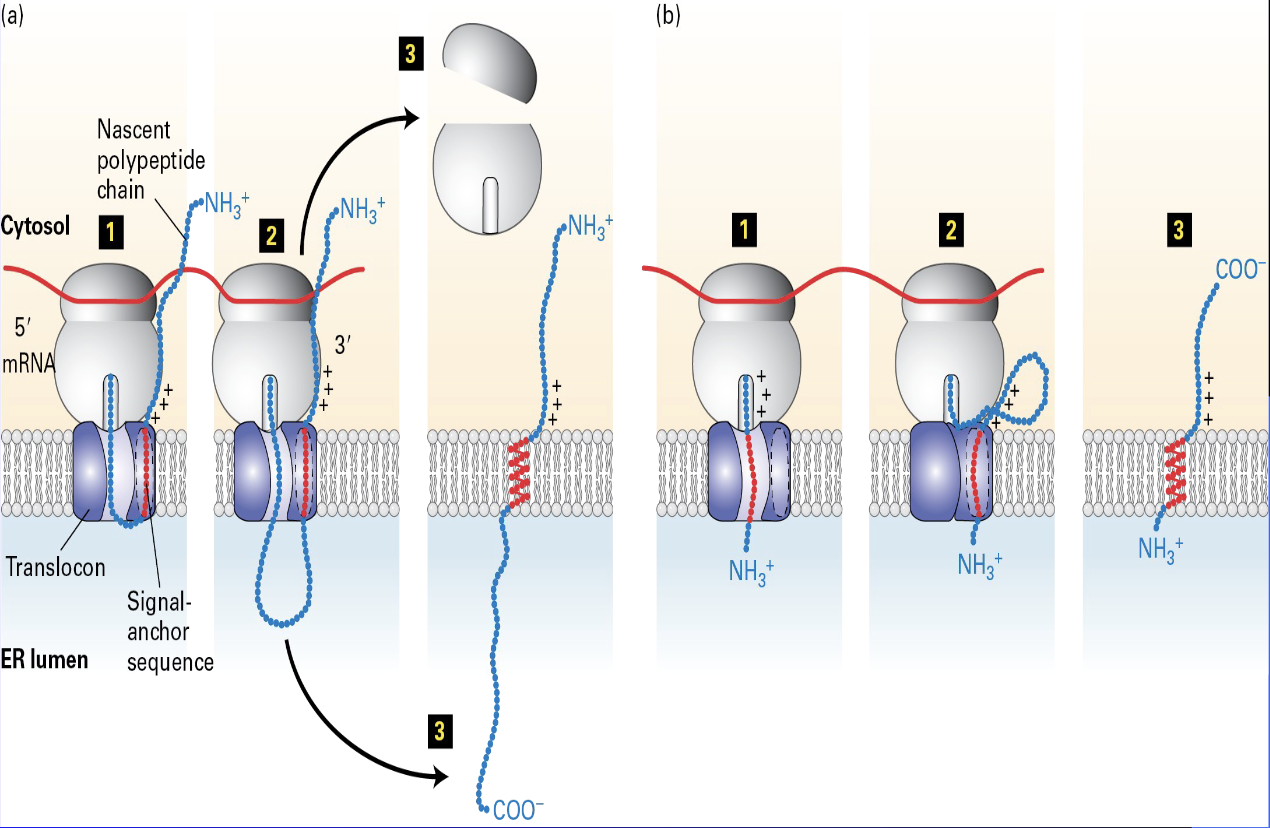
Tail advanced proteins
aka tail (carboxy end) - anchored proteins
RER
No SRP + SRP receptor
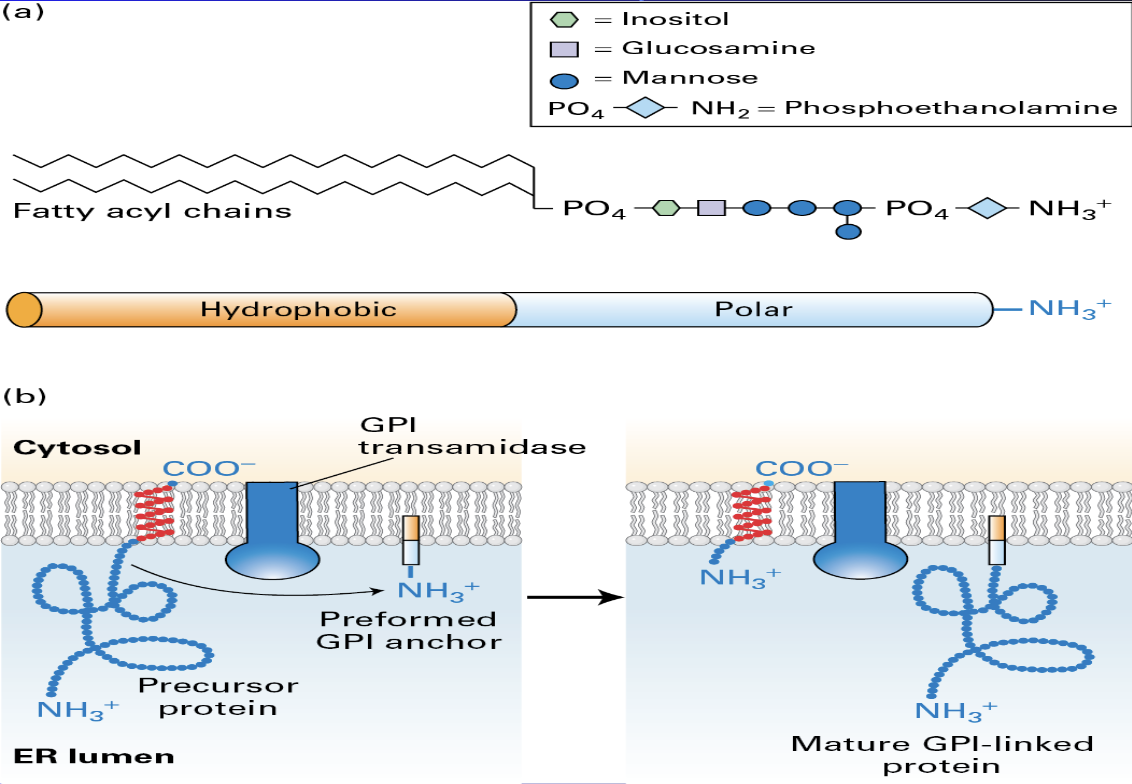
GPI (Glycosylphosphatidylinositol)
a complex glycolipid that anchors proteins to the outer surface of the cell membrane
n eukaryotes for roles like cell-surface receptors, enzymes, and adhesion molecules
Vesicular Traffic
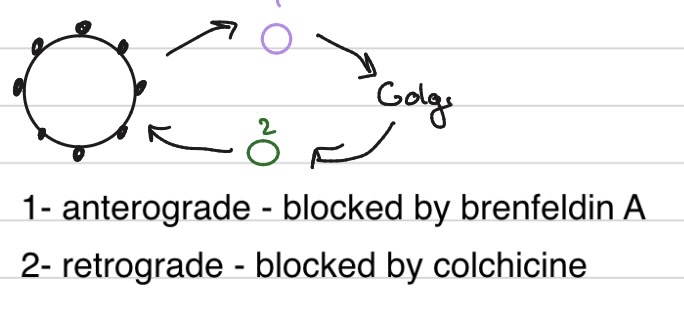
V-snare and T-snare - cofeis the specifity
COP II vesicles --> antergrade
COP I vesicles --> retrgrade
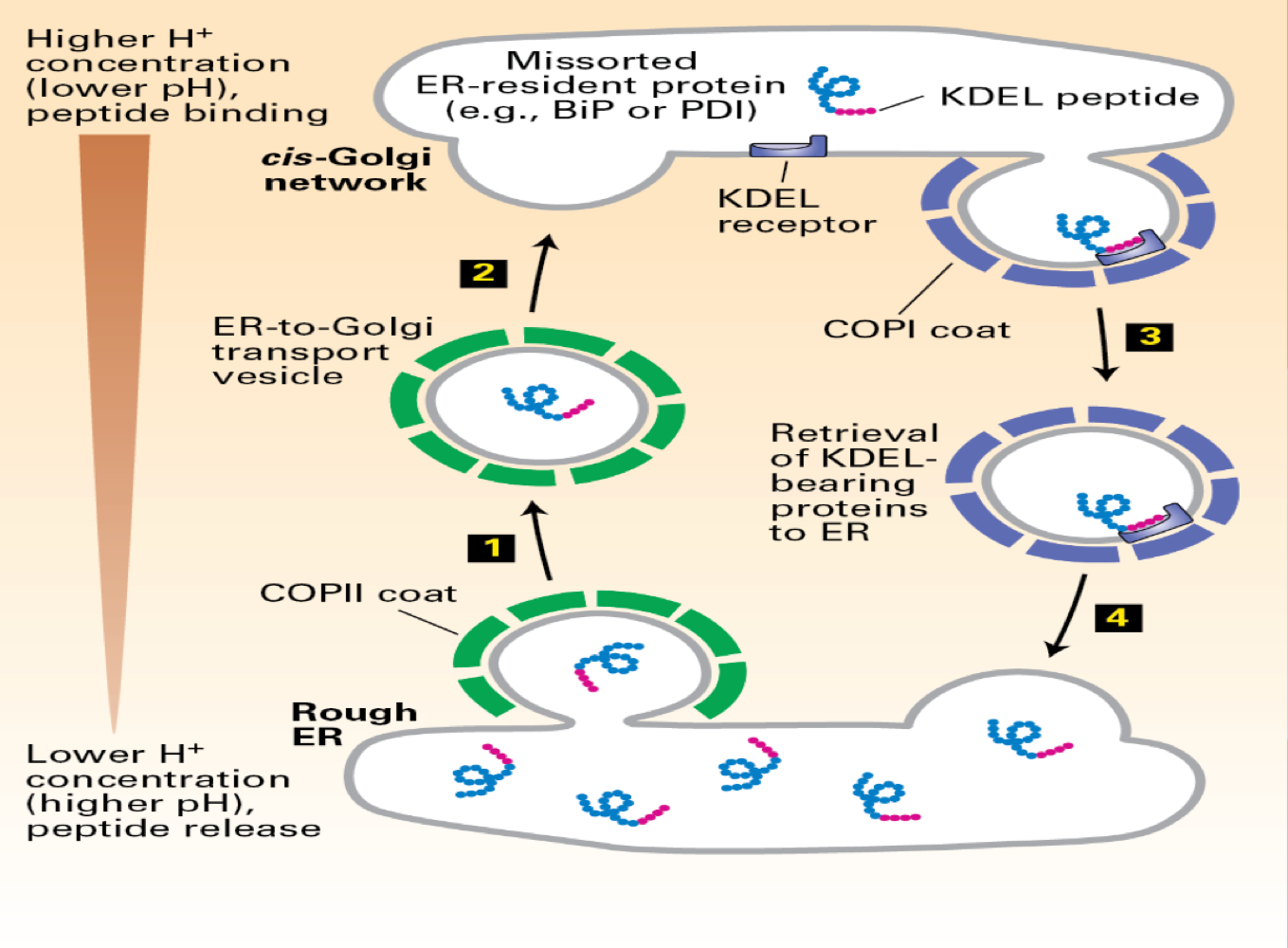
How about RER resident proteins? - POI, BiP - chaperone
KDEL - 4 amino acids - present on resident protein
decrease in pH - is critical --> KDEL binds to the KDEL receptor --> returns home
Dolichol Phosphate
an RER Intermediate that can add N-linked Oligosaccharides in the RER
sugars are removed
How important?
N-linked oligosaccharide chains are processed en route
involves initial trimming steps that serve as a quality control checkpoint for proper protein folding,
followed by elaborate modifications that create the diverse structures necessary for protein trafficking, stability, and recognition in cell-to-cell communication.
CDG - Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation
Mutations in the Dolichol-linked
Oligosaccharide Biosynthetic Pathway
How about Glycosylation
initatel in the RER
continuous --> Golgi
initial glycosylation is often due dolichol phosphate
O-Linked - linked to serine --> shorter
H-Linked - linked to serine --> asynergie long + branched
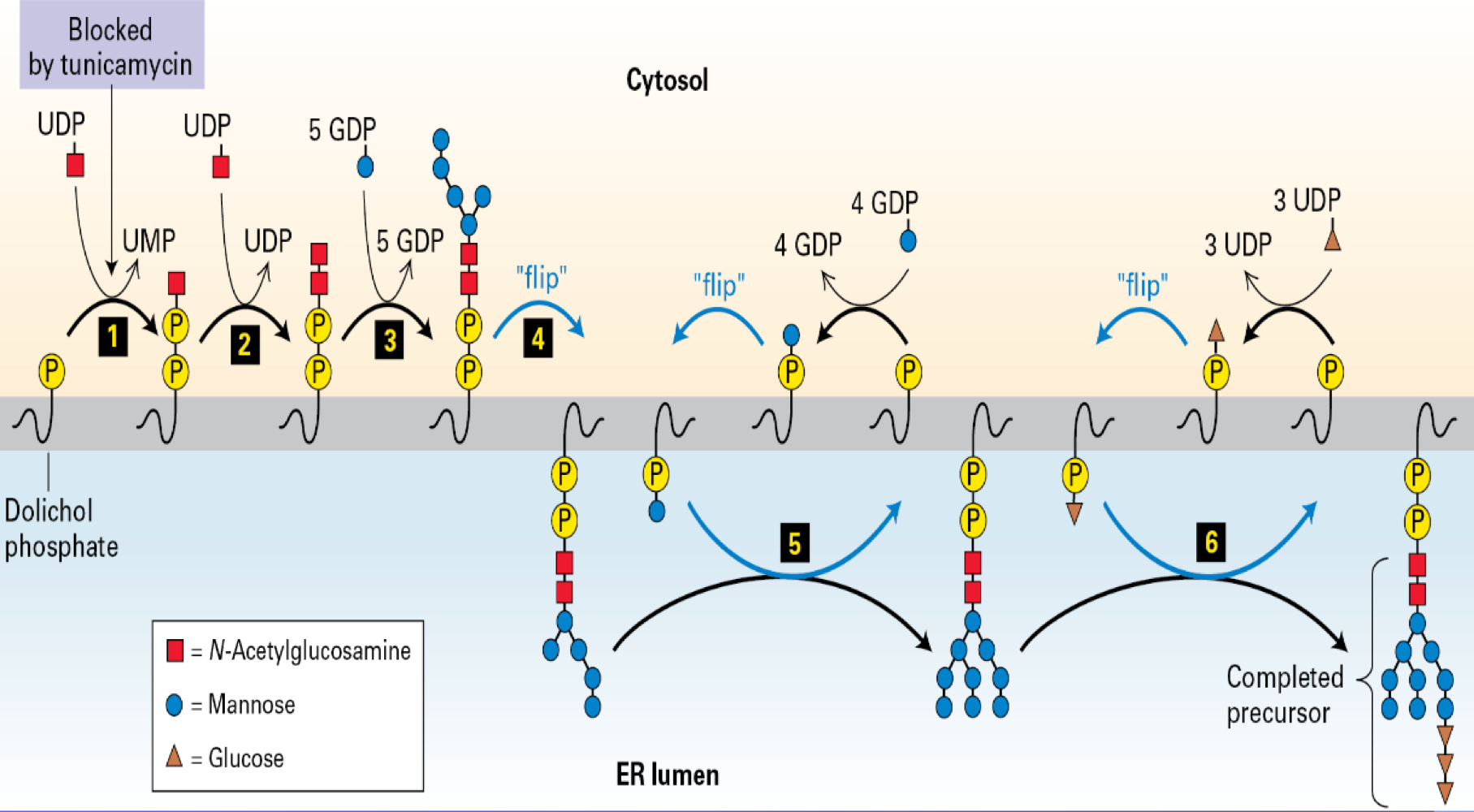
why glycosylation
increase protien varitey
critical for folding --> function
protects proteins from extracellular environment
How about mitochondria - how to study
in test tube

Are cytoplasmic factors involved (in the mito)?
yes - translocation
a. hsp70 - found in cytoplasm
b. hsp70 - also in mt matrix

are receptors required (in the mito)?
yes
how important is the mito targeting sequence (in the mito)?
:)

can folign proteins be translocated (in the mito)?
no
experiment with DHFR (dihydrofolate reductase) and usually found in the liver
where does translocation occur (in the mito)?
at contact points
how about cholorplasts
two pathways:
SRP pathay hdp70
pH dependent hsp70
Blood-Type-Altering Enzyme
developed at the University of British Columbia, successfully converted a Type A kidney to the universal Type O
offering hope to address the long wait times for Type O transplant candidates and potentially enabling universal donor blood for transfusions.
Peroxisomes
targets sequence is the COO- end
proteins enter through nuclear pores, 30 proteins
make < 40,000v + nations - differs
others need to be imported
imported as as FC + De
NLS = nuclear location signal impotrin
Secretory Pathways
a cellular process that synthesizes, folds, and transports proteins for secretion outside the cell or delivery to specific organelles
involves the movement of proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi apparatus, and to other locations
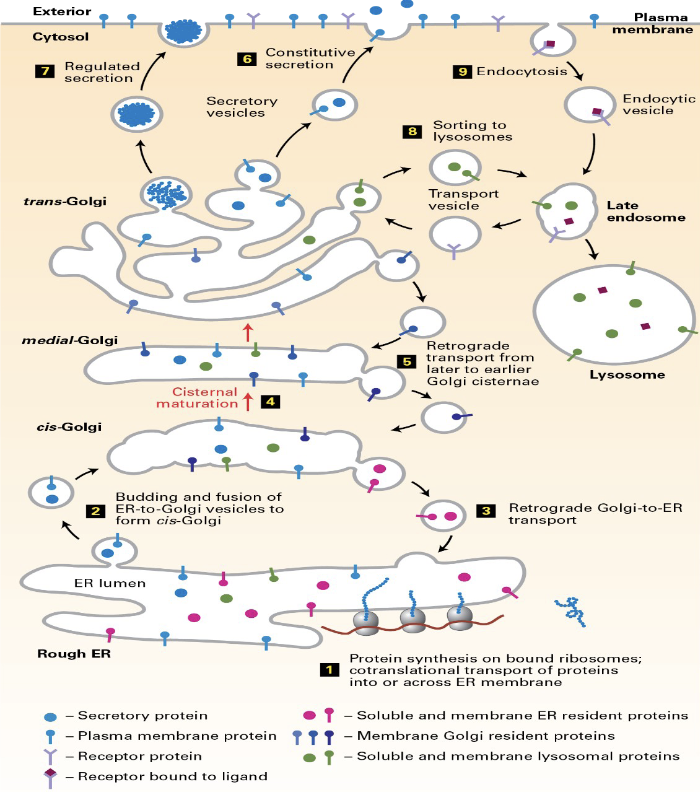
Golgi Apparatus
many compartments:
condeasation of proteins
gycosylation
ADD sulfate + phiphots
proeolytic processing
cis-golgi (addres tag is added for lysosmal proteins)
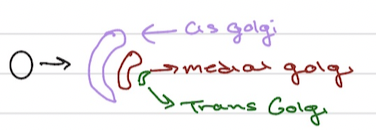
Trans Golgi Netwrok (TGN)
sorts proteins but not at first in the TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy)
last idenified in the RER pathway
MDCK cells on cell culture inserts --> typical phenotype
VSV (viscular ) G protein --> basal region
HA glycoprotein --> apical region
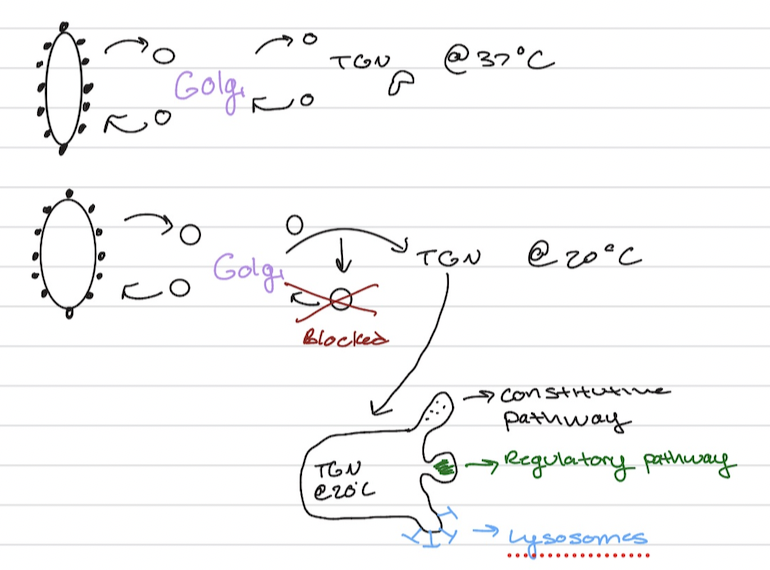
Constitutive Pathway
they are secreted as FAST as they are synthesized (ex: collagen)
immediatley sensitive to puromycin
no electron vesicles (small-"lucient")
Regulated pathway
proteins are stored in large vesicles - electron dense
point of secretion can be important
increase in Ca+2 is required for release
less senstive to puromycin"burst" of protein w/ outside signal
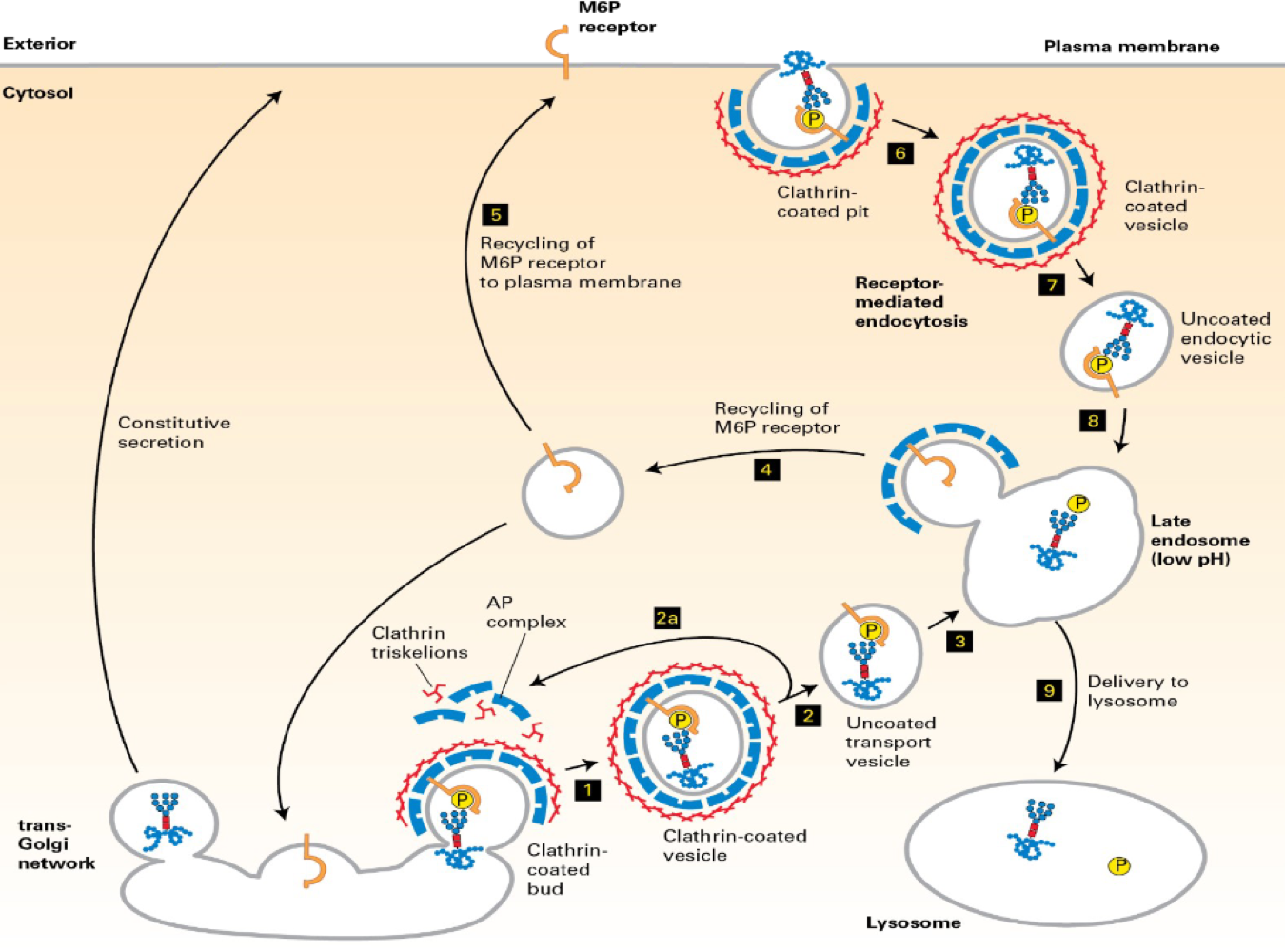
How about lyosomes?
"zip code" - manwose -6-phosphete --> lyosomes
m6P is added cis-golgi
but, some lysosome/enzymes use the constitutive pathway
but - m6P receptor in the otuter plasma membrane