BSC 201: Exam 2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Eumetazoan
true animals with differentitiaed tissues
contains radiata and bilateria
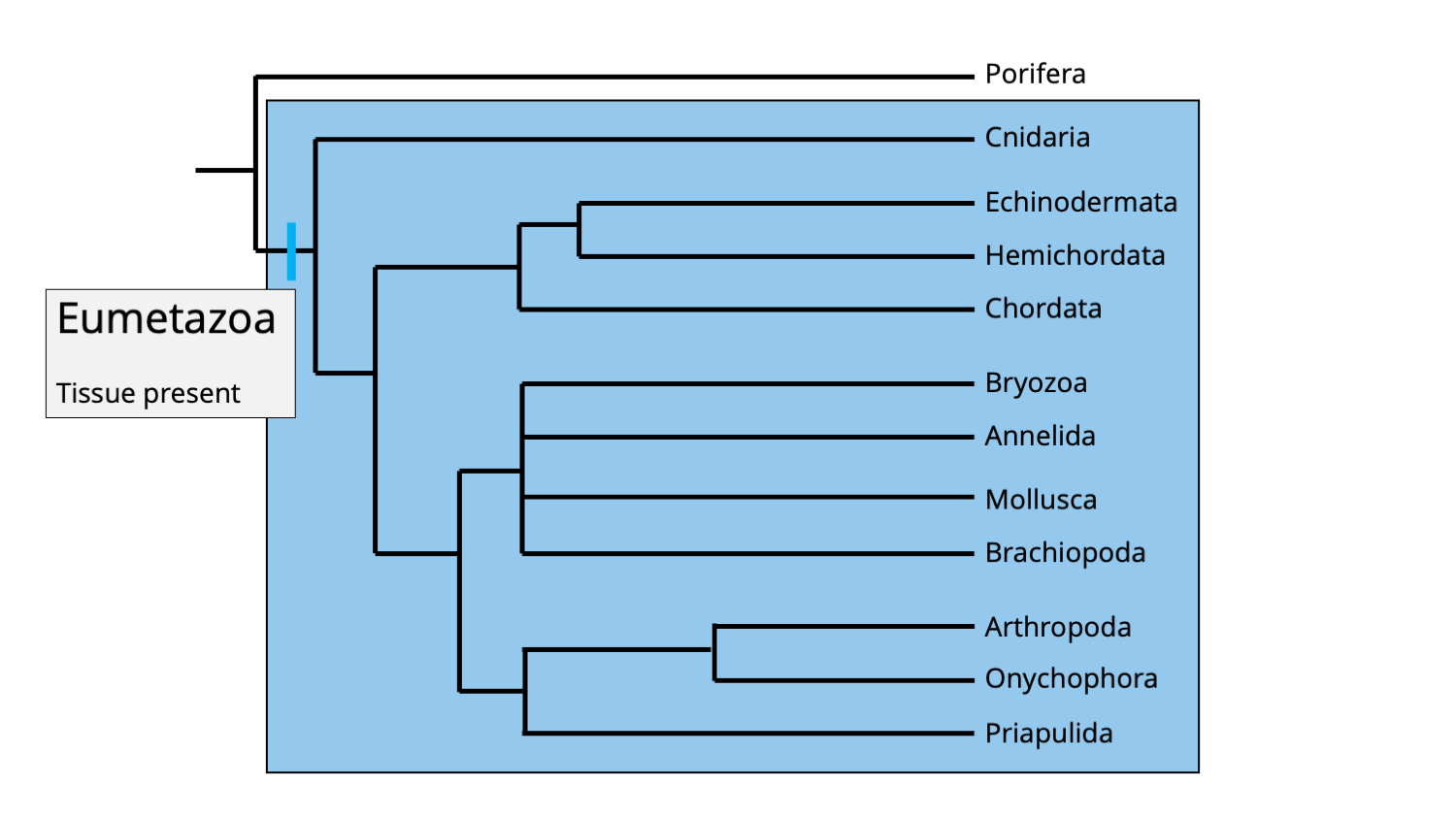
Metazoa
the most basal grouping og animals
CHoanoflagellates are NOT are common ancestor arguments
Choanocytes are not part of the developmental pathway of sponges; they appear only in adult sponges
collar cells appear in a few othr animal taxa; if trait is ancestral it has been lost in most taxa
Evidence of common ancestry between choanoflagellates and metazoa
proteins used by colonial choanoflagellates for cell communication and adhesion are homologous to those that metazoans use in cell-to-cell signaling
Lophotrotrohoza
bilterian protostomia
Ecdysozoa
bilterial protostomia that goes through ecydsis
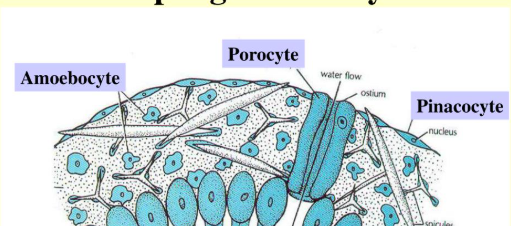
Phylum Porifera
basal animals that lack true tissues
no symmetry
no nerves, muscles, mouth or digestive system
sessile
reproduce sexually and asexualyl
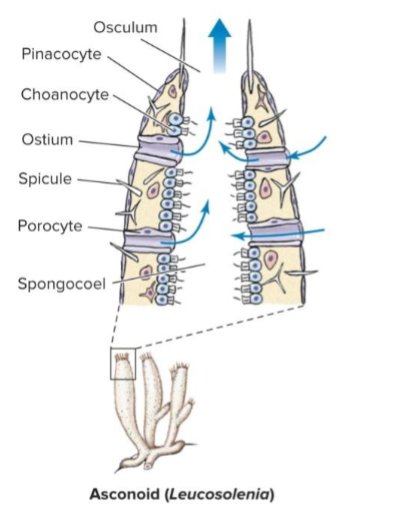
Asconoid
porifera body plan, where choanocytes line the inside of the spongocoel
water enters through the ostium, which are liend with proocytes
only occurs in class Calcarea
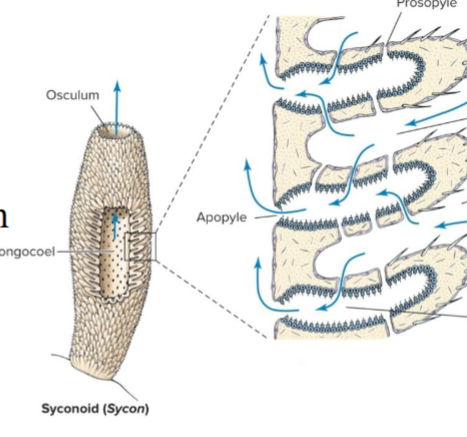
Syconoid
porifera body plan
tubular body wall with a single osculum
body wall forms radial canals that is lined with choanocytes
water enters through the ostia into the choanocytes, where it is pushes through the apopyle and into the spongocoel
may be found in class Calcarea or Hexactinellida
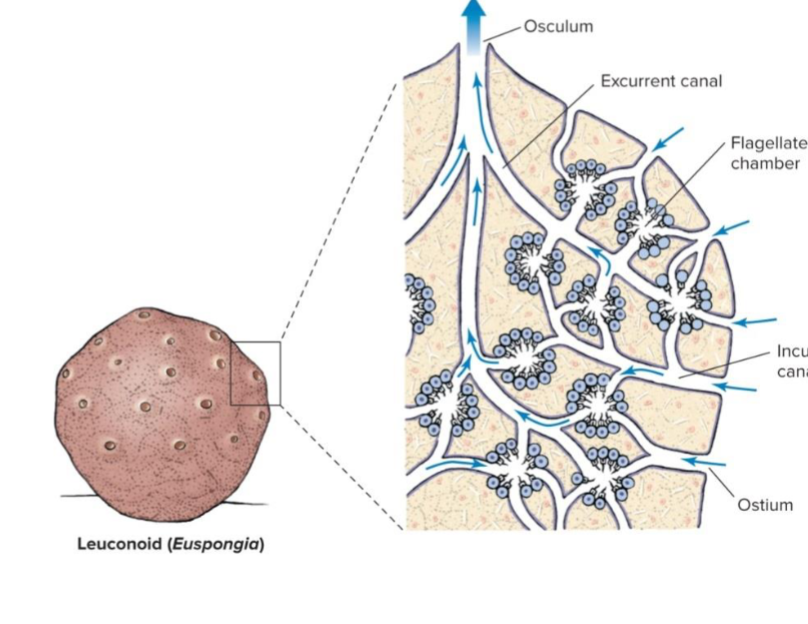
Leuconoid
Porifera body plan
most complex body plan w/ the highest surface area
contains chambers with choanocytes
water enters through the ostium and is pumped through an incurrent canal and into a flagellated chamber. Water is then pushed to the excurrent canal and out many osculum
most common between classes, exlusive in Demospongiae
Archaeocytes
amoeboid cells found in sponge that can transfrom into any of the animal;s more specalized cell types
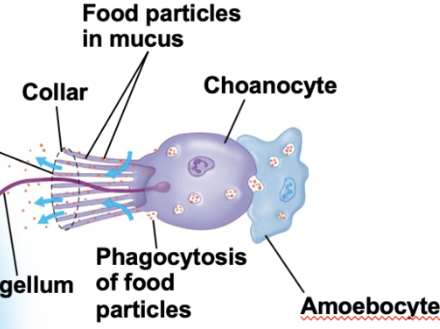
Pinacocytes
flat cells the line on the outside of a sponge, as well as the internal canals of a sponge