Early Life and Diversification of Prokaryotes
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Unique Characteristics of Bacteria
No membranous nucleus - only a nucleoid region
Circular DNA which obeys classic pairing rules
No membrane bound organelles
Contain ribosomes that differ in size from eukaryotes
Some have endospores
resistant cells that develop when water or nutrients are lacking
dormant and can remain viable and survive for centuries in extreme conditions
Often form biofilms
Some have endospores
Some have capsules
Some have flagella - different from eukaryotes
Most Common Shapes
Cocci (spherical)
Bacilli (rods)
Spirals
History
Van Leeuwenhoek may have seen first prokaryotes with the microscope
Koch’s postulates
Microbe must be present in all cases of the disease
Microbe can be isolated and grown in pure culture
Microbe must cause the disease when inoculated into a healthy host
Microbe must be re-isolated from the newly infected host
Gram Positive (+)
Violet dye, darker color
Simpler cell walls
Thick layer of peptidoglycan
network of modified sugars and polypeptides
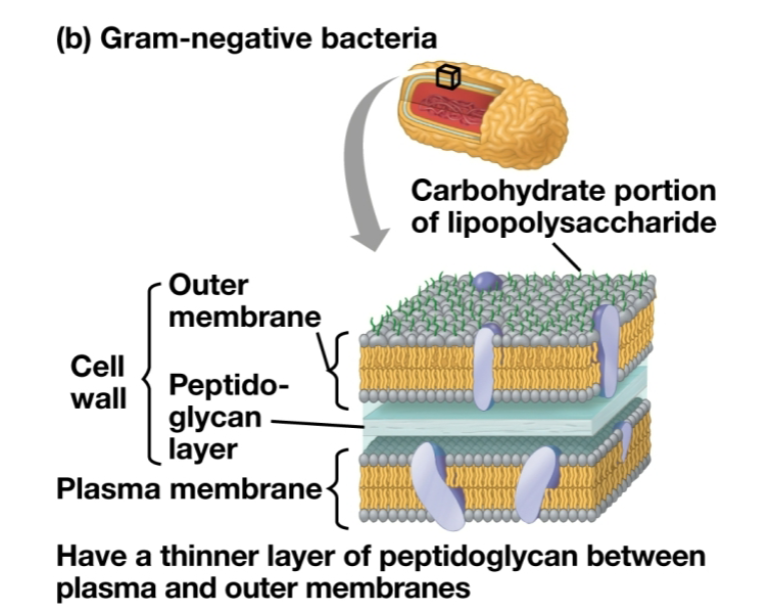
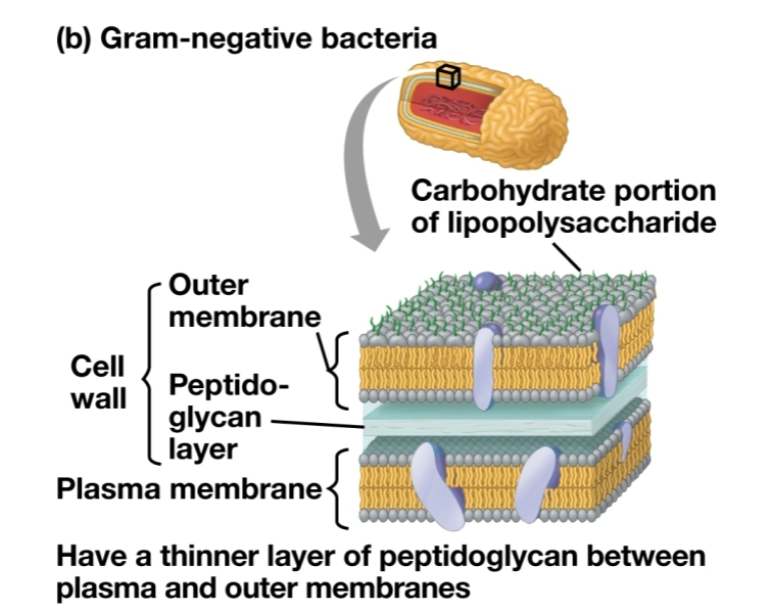
Gram Negative (-)
Red dye, lighter color
Less peptidoglycan
Outer membrane with lipopolysaccharides
Lipid portions of polysaccharides can be toxic
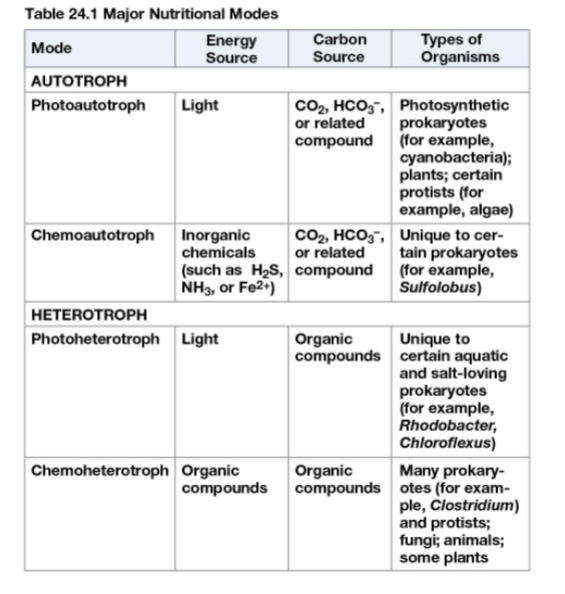
Major Nutritional Modes
Photoautotroph
Chemoautotroph
Photoheterotroph
Chemoheterotroph
Transformation
Prokaryotic cells alter their genotype with DNA taken up from the external environment
Transduction
Phages move prokaryotic genes from one host cell to another
Plasmids
Obligate Aerobes
Requires oxygen to grow
Aerobic respiration
Obligate Anaerobes
Can’t tolerate oxygen
anaerobic respiration
Nitrogen Fixation
Some prokaryotes use nitrogen fixation to convert atmospheric N2 to ammonia (NH3) that can be used by prokaryotes
Metabolic Cooperation
Cooperation between different prokaryotic species can create surface-coating colonies (biofilms)
Can cause infections, tooth decay, contamination of medical devices
F factor
F factor is a piece of DNA consisting of 25 genes required for the production of pili
May be present in the chromosome of an F plasmid
In conjugation, F+ plasmid donate DNA, F- plasmid receive DNA
Transfer of F plasmid converts an F- cell to a recombinant F+ cell.
Conjugation
Process where genetic material is transferred directly between prokaryotic cells
DNA transfer is one way in bacteria
ex. E. Coli, donor cell attaches to a recipient by a pilus, pulls it closer, and transfers DNA
Lineages: Protobacteria (All Gram Negative)
Subgroup alpha protobacteria
a. Rhizobium - lives in root nodules of legumes and fixes atmospheric N2
Subgroup beta protobacteria
a. Nitrosomas - converts NH4 to NO2
Subgroup gamma protobacteria
a. Legionella, Salmonella, Vibrio, Eschericia Coli (in the gut of mammals)
Subgroup delta protobacteria
a. Myxobacteria - produces a fruiting body
Subgroup epsilon
a. Campylobacter, Helicobacter
Lineages: Chlamydia (Gram Negative)
Chlamydia trachomatis blindness and urethritis
a. most common STD in the US
Lineages: Spirochetes (Gram Negative)
Treponema pallidum - syphilis
Borrelia burgdorferi - Lyme disease
Lineages: Cyanobacteria (Gram Negative)
Photosynthetic
May be solitary or filamentous
Lineages: Gram Positive Bacteria
Actinomycetes - important in soils
Clostridium Botulinum
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus pneumonia
Lineages: Archaea
Extreme Halophiles - live in high salt concentrations
Extreme Thermophiles - live in high temperature