Rate of reaction
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is rate of reaction determines as
Determined as rate of change in concentration
How is rate expressed
Per unit of time
1/ time
S^-1
Rate of reaction general idea
Increase in product concentration // TIme
Decrease in reactant concentration // Time
Mol dm^-3 s^-1
Instantaneous rate of reaction
take a tangent on the part of the curve
fastest at the start, slows down
How to measure rate
change in volume of gas
change in mass
change in transmission of life
change in concentration, measure with titrations
change in concentration using conductivity
non-continuous method: ‘clock reaction‘
change in volume of gas
volume against time
gas syringe
Change in mass
If the reaction gives off gas, doesn’t work with hydrogen, too light
Change in light transmission
can be done if reactants of products are coloured
Works by: passing light of a selected wavelength through solution
As concentration of colour increases, absorbs more light, less light transmitted
Change in concentration using titration
cannot be done continuously, as reaction continues
Method of quenching used, otherwise the reaction keeps proceeding
stops reaction at a moment in time
Change in concentration
Depends on ions and on their charges
Non-continuous method: ‘clock reaction‘
time taken to reach a fixed point
time is a dependent variable
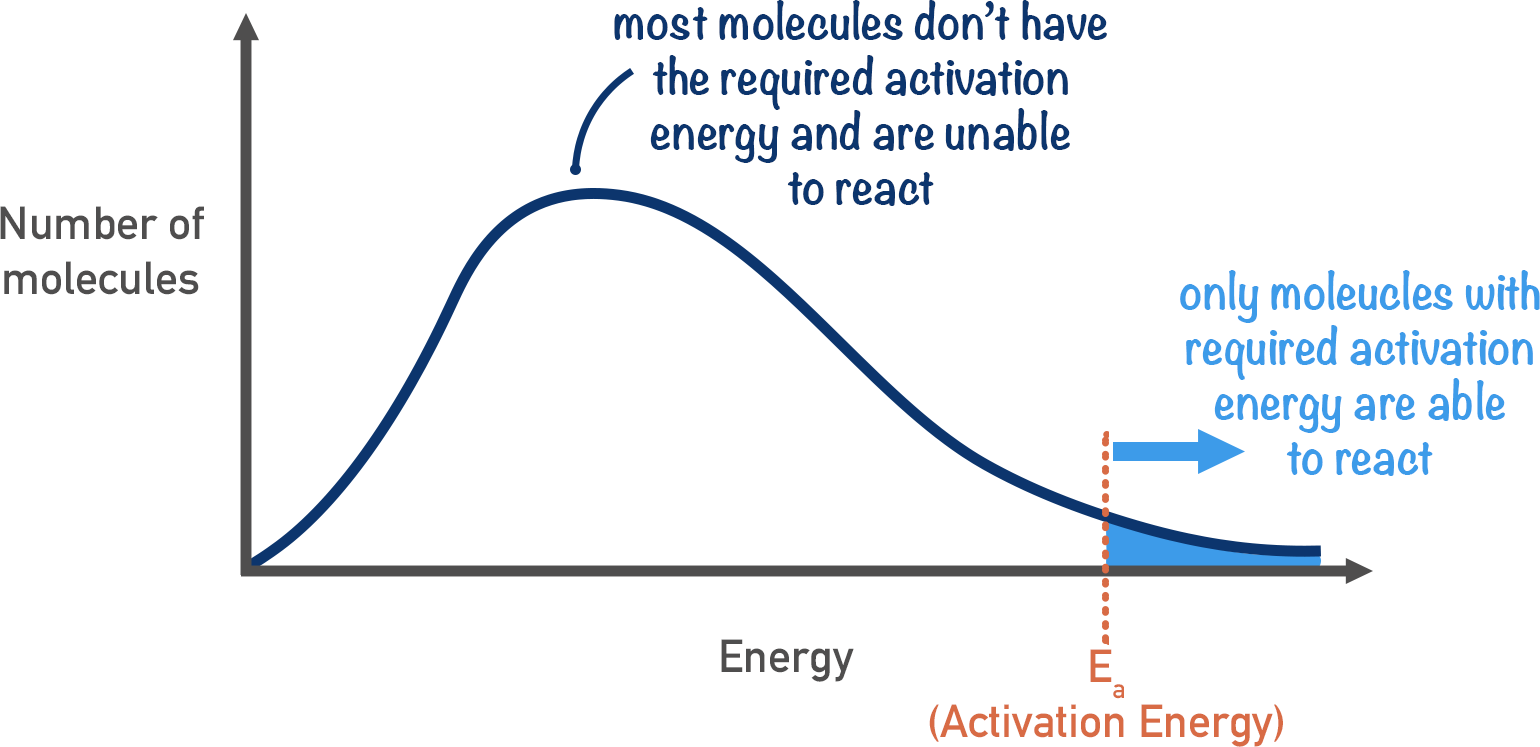
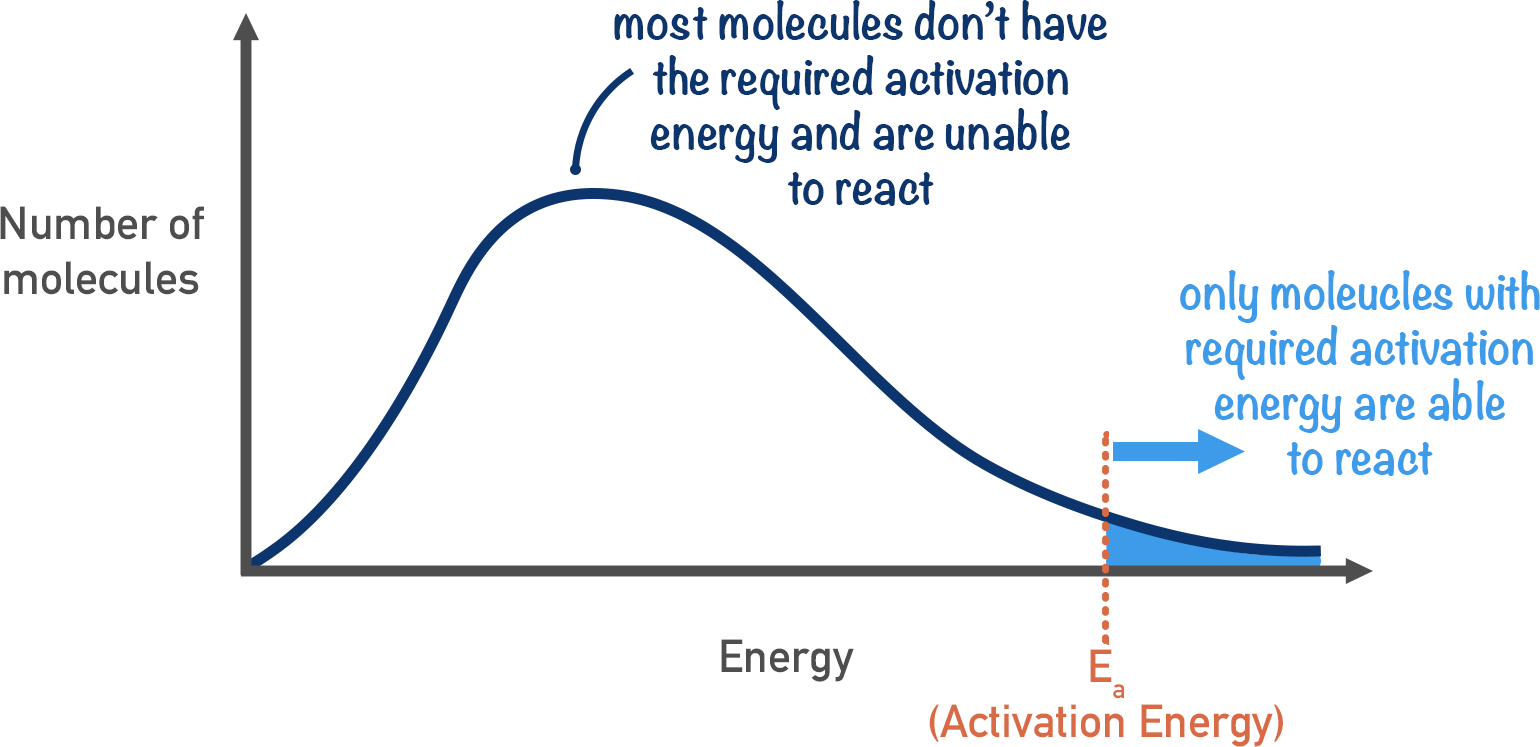
Maxwell-Boltzmann energy distribution curve
Nature of collisions and the influencing factors
Kinetic energy causes for particles to collide, breaking and forming new bonds
influencing factors
energy of collision
geometry of collision
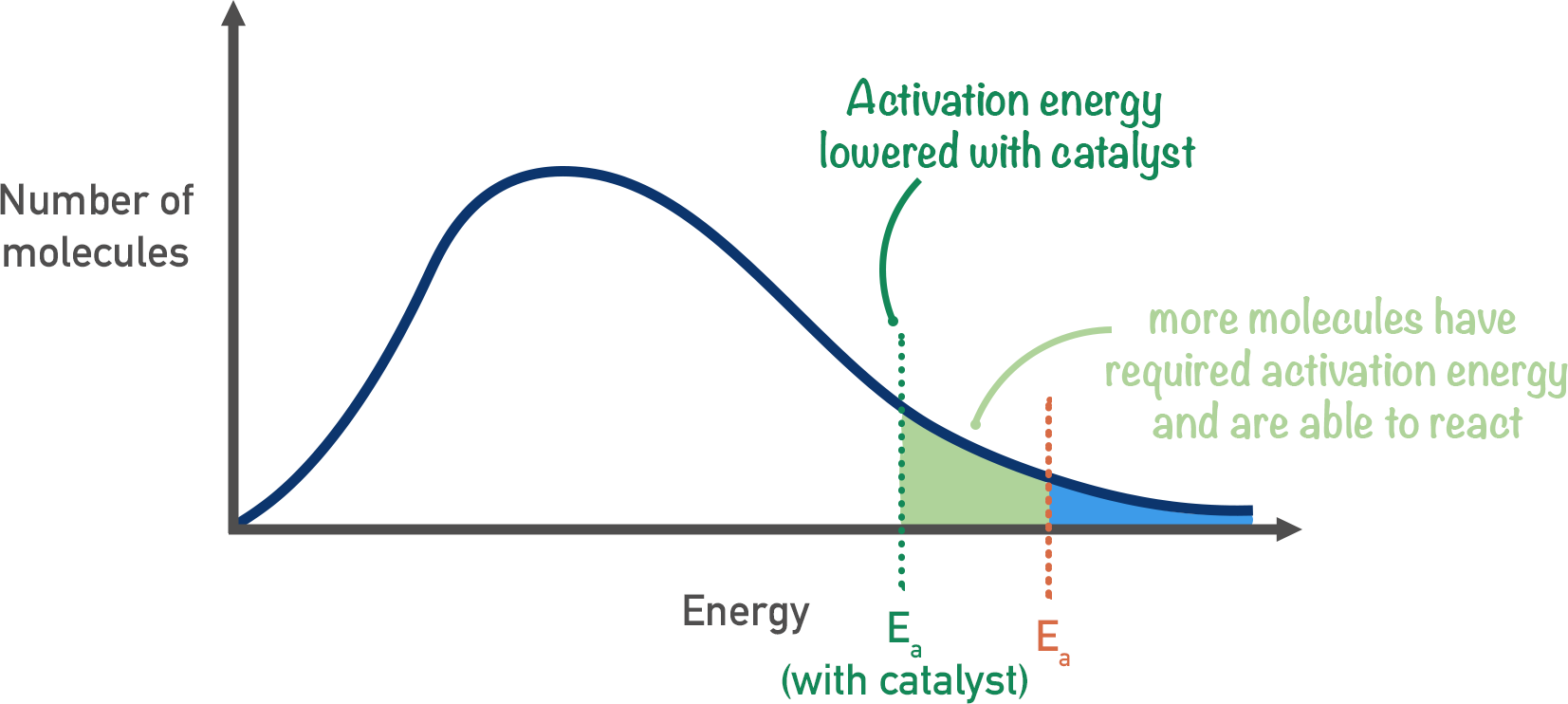
What is activation energy
the energy required for overcoming the repulsion and breaking bonds to allow reactions
what is transition state
when energy supplied, reactants achieve transition state
Endothermic vs Exothermic
endothermic - require heat, cool surroundings
exothermic - release heat, warm surroundings
Maxwell boltzman curve with Ea
What is the geometry of collisions
the orientation of particles
Temp influencing rate of reaction
As temp increase, so does kinetic energy.
more particles collide succesfully
Concentration
as concentration increase, so does rate
as concentration increase, frequency increases
pressure
increasing pressure, increase rate of reaction
higher pressure, compresses gases, increasing concentration, increasing frequency
Surface area
Increasing SA, Increases rate
allows for more reactions
Catalyst
Provide alternative route, Ea lower
equal for forwards and backwards reaction