All Lectures: NRTIs
1/100
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
name the nucleoside RT inhibitors
zidovudine
lamivudine
emtricitabine
stavudine
didanosine
abacavir
tenofovir
zidovudine acronyms
ZDV and AZT
zidovudine brand names
retrovir
retrovis
zidovudine is an analog of ____ with an ___ subbed at the C3’ position
thymidine; azido
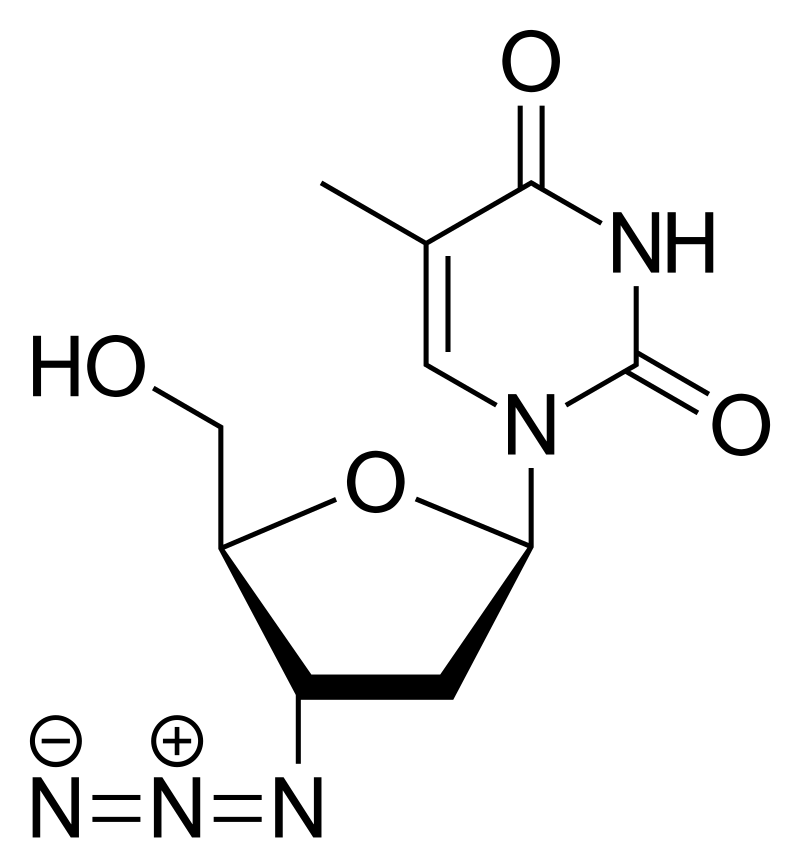
what drug is this
zidovudine
zidovudine is converted into ___
5’ mono, di, or tri phosphates
Zidovudine is converted into 5’-mono-, di-, and tri- phosphates by which enzyme?
thymidine kinase
phosphorylated zidovudine incorporates into DNA of the virus to…
stop the synthesis of DNA and replication of virus
zidovudine is also called
azidothymidine (AZT, ZDV)
ADE of zidovudine
myelosuppression
what is the only HIV drug that shows reduction in perinatal HIV transmission?
zidovudine
you cannot use zidovudine with which other NRTI due to pharmacodynamic interactions?
stavudine
zidovudine + stavudine leads to…
pharmacodynamic interactions
avoid use of zidovudine with ______ due to decreased levels of zidovudine
tipranavir
zidovudine + tipranavir leads to…
decreased levels of ZDV
what was the first approved treatment for HIV
zidovudine
didanosine is also called
Dideoxynucleotides or ddNTPs
Didanosine are nucleotides that lack…
C-3’ hydroxyl group on the deoxyribose sugar
brand name of Didanosine
videx
Didanosine is a ____ dideoxynucleotide
purine
Didanosine is an analog of ____
inosine/purines
why is Didanosine is typically given orally
to avoid acid instability
didanosine causes less ____ than AZT
myelosuppression
Didanosine causes less myelosuppression than ____
AZT
toxic effects of Didanosine
hyperuricemia
pancreatitis
myelosupression
t or f: Didanosine is a prodrug
T
Didanosine is bioactivated by metabolism to ____ by cellular enzymes, inhibiting RT
2’,3’-dideoxyadenosine 5’-triphosphate
the ____ form of Didanosine is the competitive inhibitor of viral RT
triphosphate
Didanosine is incorporated into the developing viral DNA which leads to
chain termination and viral replication inhibition
if ddI is used with tenofovir it can lead to…
increased conc of ddI
ddI + tenofovir will lead to a(n) ________ conc of ddI and higher rates of virologic failure
increased
dosage change for tenofovir + ddI
decrease ddI dose to 250 mg qd
didanosine + stavudine have ____ interactions
pharmacodynamic
didanosine + ______ have pharmacodynamic interactions and additive toxicities
stavudine
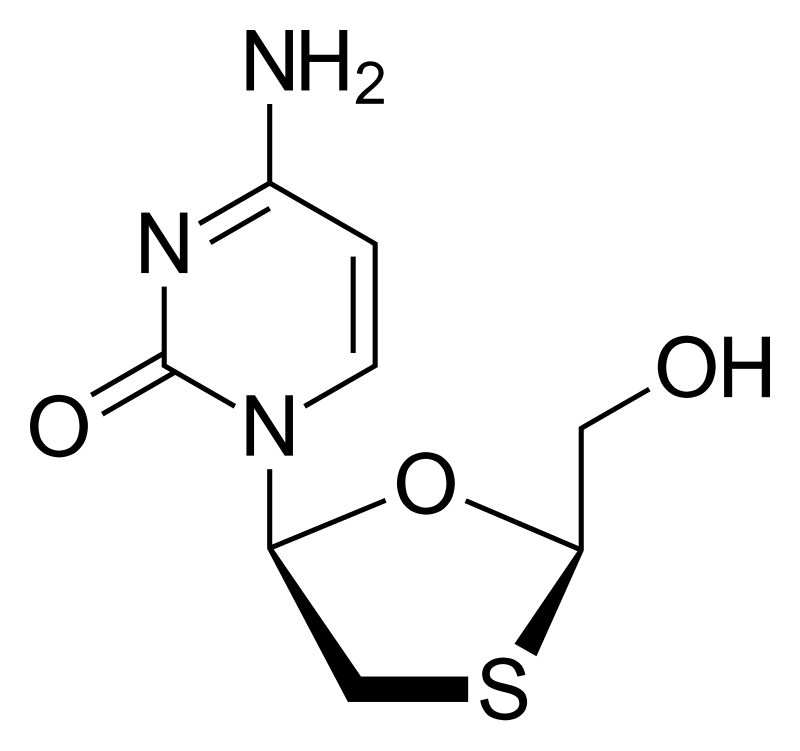
what drug is this
lamivudine
lamivudine has pharmacodynamic interactions with…
ETC (emtrictabine)

what drug is this
zalcitabine
lamivudine is also called
3TC, (-) 2’3’ didexy-3’thiacytidine
lamivudine is a nucleoside analog that is related to ____ with the replacement of ____
zalcitabine;
one CH2 with S
lamivudine is synergistic with ___ against HIV1 and HBV
AZT (zidovudine)
which enantiomer of lamivudine is more active and less toxic
negative
Cellular 3’,5’-exonuclease cleave terminal ____-lamivudine monophosphate (MP) incorporation into viral DNA 6-fold faster than ____-lamivudine MP from the viral terminus.
+; -
Mutation that causes resistance to lamivudine will make the virus more susceptible to which drug?
AZT
combo of lamivudine and AZT in HIV pts causes an increase in ____
CD4 cells
addition of sulfur to zalcitabine to make lamivudine is dope asf bc it leads to…
slower metabolism, better bioavail, and less toxic
dosing options for lamivudine
150 mg BID or 300 mg QD
lamivudine ADE
Headache, fatigue, peripheral neuropathy, neutropenia
emtricitabine is a ___ nucleoside analogue
pyrimidine
ETC is also active against
HBV (hepatitis B)
why is addition of the F on emtricitabine dope asf
less likely to be metabolized and it increases bioavail and activity
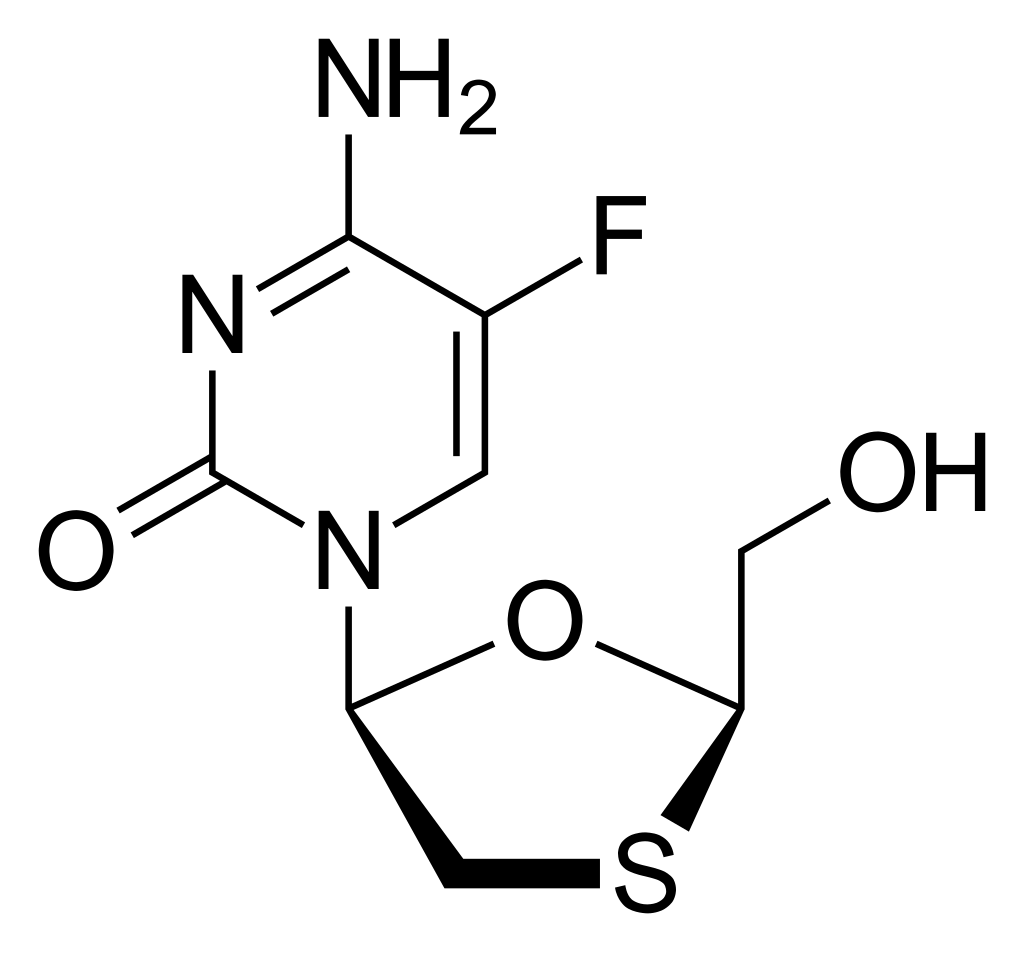
what drug is this
emtricitabine
all NRTIs are…
prodrugs
ETC has pharmacodynamic interactions with…
3TC (lamivudine)
ETC + 3TC leads to ________ interactions
pharmacodynamic
ETC does not inhibit…
CYP450 enzymes
dose of ETC
200 mg qd
emtricitabine ADE
rash, HA, dizzy, insomnia, diarrhea, nausea, weakness, cough abnormal dreams, hyperpigmentation of palms and soles of feet
what two reactions lead to ETC’s metabolism?
oxidation and cojugation
ETC oxidation metabolism
oxidation of thiol (S) to form C-3’ sulfoxide
ETC conjugation metabolism
conjugation with glucuronic acid to form 5’-O-glucuronide
stavudine is also called
D4T
what is the important characteristic of stavudine’s structure
double bond ∆2’,3’ position on the deoxyribose ring
which form of Stavudine is active? and whats its % bioavail?
Triphosphate form
85%
which form of stavudine is active?
triphosphate
MOA of stavudine
phosphorylated triphosphate form is active and competes with deoxythymidine triphosphate for incorporation into viral DNA to stop replication
ADE of stavudine
neuropathic effects
stavudine + ____ or _____ leads to pharmacodynamic interactions
ddI or AZT
stavudine + ddI + AZT leads to…
pharmacodynamic interactions
abacavir is also called
ABC
abacavir is extensively metabolized to ___
5’ triphosphates
what is dope about abacavir structure?
has a cyclopropane which makes it less likely to be metabolized
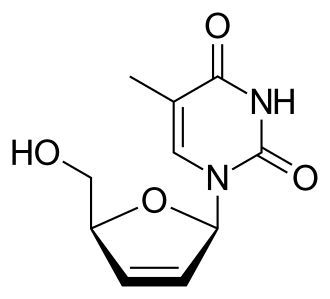
which drug is this
stavudine
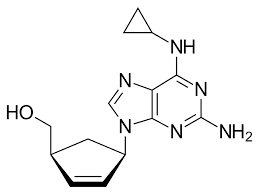
which drug is this
abacavir
dosing options of ABC
300 mg BID or 600 mg qd
abacavir leads to which ADE
depression, dizzy, anxiety, thrombocytopenia, increased transamidases, allergic reactions (anaphylaxis, rash, fever, etc)
ABC is a ____ analog
purine
ABC has an oxygen that is replaced with a carbon which leads to…
more stability and increases duration of effects
avoid use of ABC with ____ due to decreases in ABC conc
tipranavir
avoid use of ABC + tipranavir due to…
decreases in ABC conc
does ABC require renal adjustments?
no
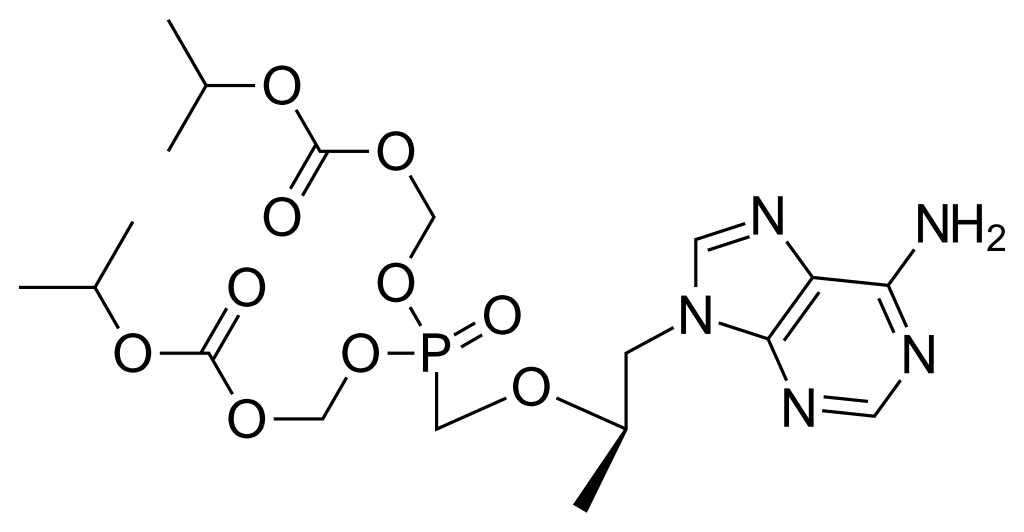
which drug is this
tenofovir diphosphate
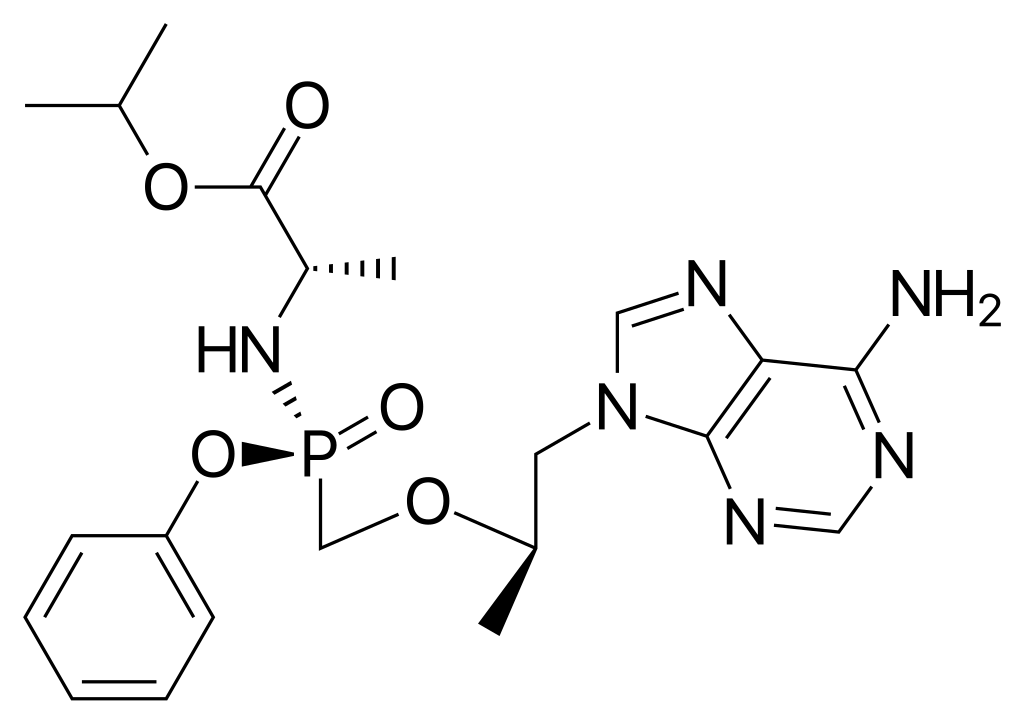
what drug is this
tenofovir alafenamide
what is the active form of tenofovir
tenofovir diphosphate
why is tenofovir diphosphate the active form of tenofovir
higher bioavail due to added phosphates, also higher water solubility
tenofovir disoproxil ADE
nephrotoxicity, bone toxicity, rash, diarrhea, HA, depression, nausea, fanconi syndrome
indication of tenofovir
HIV and HBV
HIV prophylaxisis
renal adjustments of tenofovir disoproxil are needed if CrCl is…
< 50
TDF is converted to the active form in the ____
blood
TAF is converted to active form in the ___
lymphocytes and macrophages
TAF cannot be used in pts with CrCl of ____
< 30
TAF can be used if CrCl is < 15 if…
pt is on dialysis
what is the only metabolite of lamivudine
trans-sulfoxide
which enzyme metabolizes lamivudine into trans-sulfoxide?
sulfotransferases
what are the metabolites of emtricitabine
C-3’ sulfoxide and 5’-O-glucuronide
how is emtricitabine metabolized into C-3′-sulfoxide epimers
oxidation of the thiol moiety
how is emtricitabine metabolized into 5′-O-glucuronide
conjugation with glucuronic acid
to make Emtricitabine’s Sulfur a chiral center it would have to have…
an oxygen, a lone pair e-, two C’s
which two enzymes are responsible for metabolizing abacavir
alcohol dehydrogenase and glucuronosyltransferase
alcohol dehydrogenase metabolizes abacavir into
5′ carboxylic acid metabolite
glucuronosyltransferase metabolizes abacavir into
5′-glucuronide metabolite