5: Adrenal Glands
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
How many Adrenal Glands are there in the body?
2
Where are the Adrenal Glands located?
Superior Pole on each Kidney
The adrenal gland is composed of the?
Adrenal Cortex & Adrenal Medulla
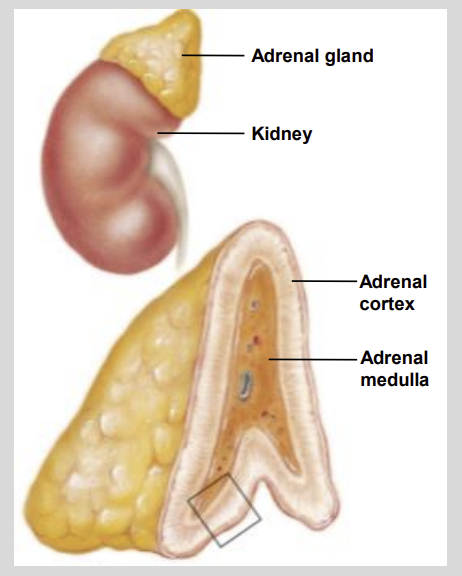
The Adrenal Cortex & Adrenal Medulla are structurally and functionally?
Different
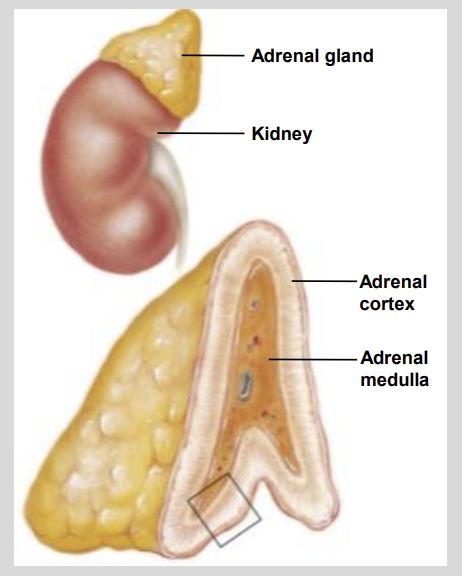
The adrenal cortex secretes?
corticosteroids which are
Steroid hormones that control Mineral & Energy Balance.
The adrenal medulla secretes the?
Catecholamine Hormones (Adrenaline & Noradrenaline).
which complement the SNS flight-orfight response
Steroids act via?
Nuclear receptors on target tissues.
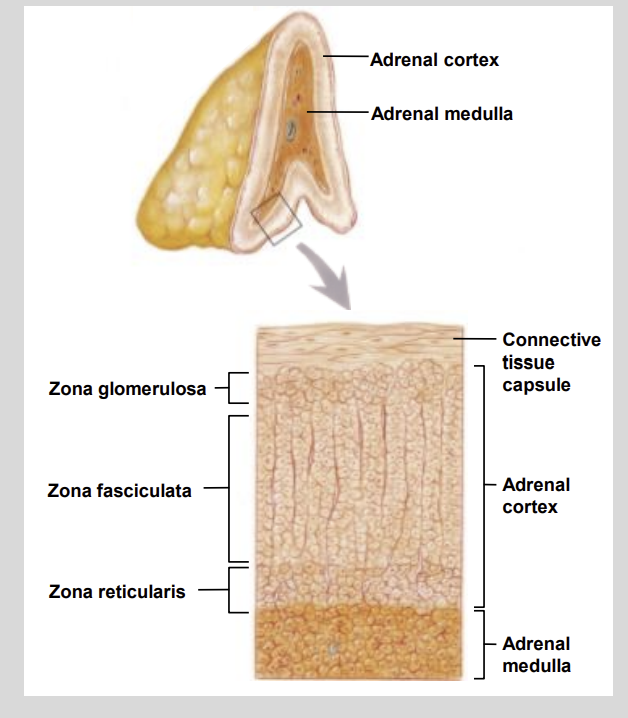
The Adrenal Cortex has 3 Zones called?
Zona glomerulosa
Zona fasciculata
Zona reticularis
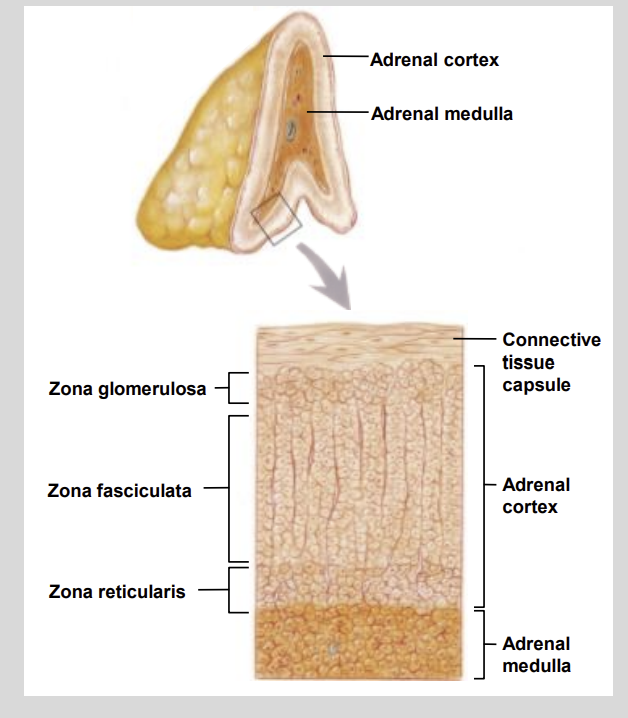
The 3 Adrenal Cortex zones are structurally and functionally…?
Different
Zona Glomerulosa produces?
Aldosterone
the most potent mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are the important regulators of?
Na + and K+ Balance.
Aldosterone acts to by stimulating the kidney to retain?
Na+ and secrete K+
The actions of Aldosterone function to?
promote increases in blood volume and maintain electrolyte balance.
Angiotensin II also stimulates the secretion of?
Aldosterone
The zona fasciculata produces?
Cortisol
the predominant glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids act to regulate?
Glucose & Other Organic Molecules
Cortisol production is stimulated by?
ACTH
Cortisol production effects on the body include…?
Degradation of Proteins
Stimulation of gluconeogenesis
Inhibition of glucose utilisation
- Raise BGLStimulates lipolysis
- Breakdown of Fat
The actions of cortisol result in an increase of?
Increased BGL
And Fatty Acids in the blood.
The zona reticularis can also produce?
Cortisol
However, the zona reticularis is better known for the production of?
Adrenal Androgens
Androgens supplement the major … Hormones?
Sex Hormones
Androgens are ana?
Anabolic Steroids
What is Cushing Syndrome?
Develops due to chronically elevated levels of Glucocorticoids.
Occurs mainly in patients prescribed high doses of glucocorticoid medication
or by a tumour of the pituitary / Adrenal Gland
What are the Common S&S of Cushing Syndrome?
Hyperglycaemia
Hypertension
Buffalo Hump / Fat pad at the back of the neck
Rounded Face
What is Addisons disease?
Also known as Adrenal Insufficiency.
caused by inadequate production of corticosteroids.
Insufficient levels of cortisol results in?
Hypoglycaemia
The cells of the adrenal medulla are modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons called?
Chromafin Cells.
The chromaffin cells are innervated by?
Preganglionic Sympathetic Axons
Chromaffin cells release adrenaline and noradrenaline into the blood at a ratio of about ?:?
4:1
The effects of systemic catecholamine release is similar effects to local SNS stimulation but the effects last?
10x Longer
The catecholamine hormones result in?
Increased Cardiac Output
Dilate Coronary Vessel
Increased Alertness
Increased Respirations
Increased BGL & Fatty Acids.
A tumour of the adrenal medulla is referred to as a?
Pheochromocytoma
The Tumor of the Adrenal Medulla causes hypersecretion of?
Epinephrine & Noradrenaline
which produces an effect similar to continuous sympathetic nerve stimulation
Symptoms of Phaeochromocytoma include?
The symptoms of this condition are
hypertension,
elevated metabolism,
hyperglycaemia