A&P 2 LAB PRACTICAL Sheet Info
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
What type of blood has neither A nor B antigen and both anti a and anti b antibodies
O
The liquid matrix of the blood is called
plasma
The percentage of blood volume mad up of red blood cells is called
hematocrit level
If a blood has both a and b antigens, no antibodies, what types of blood cause this person receive?
all blood
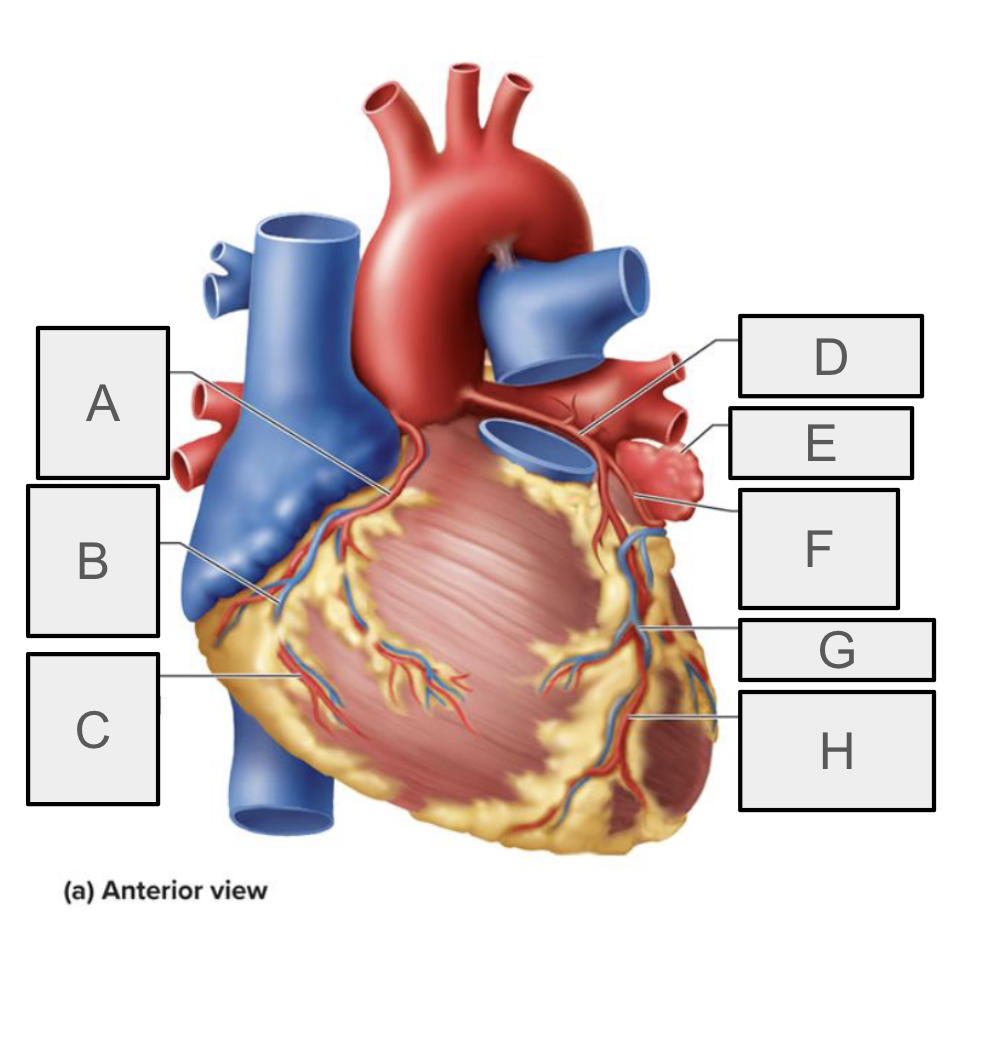
What is A
Right coronary artery
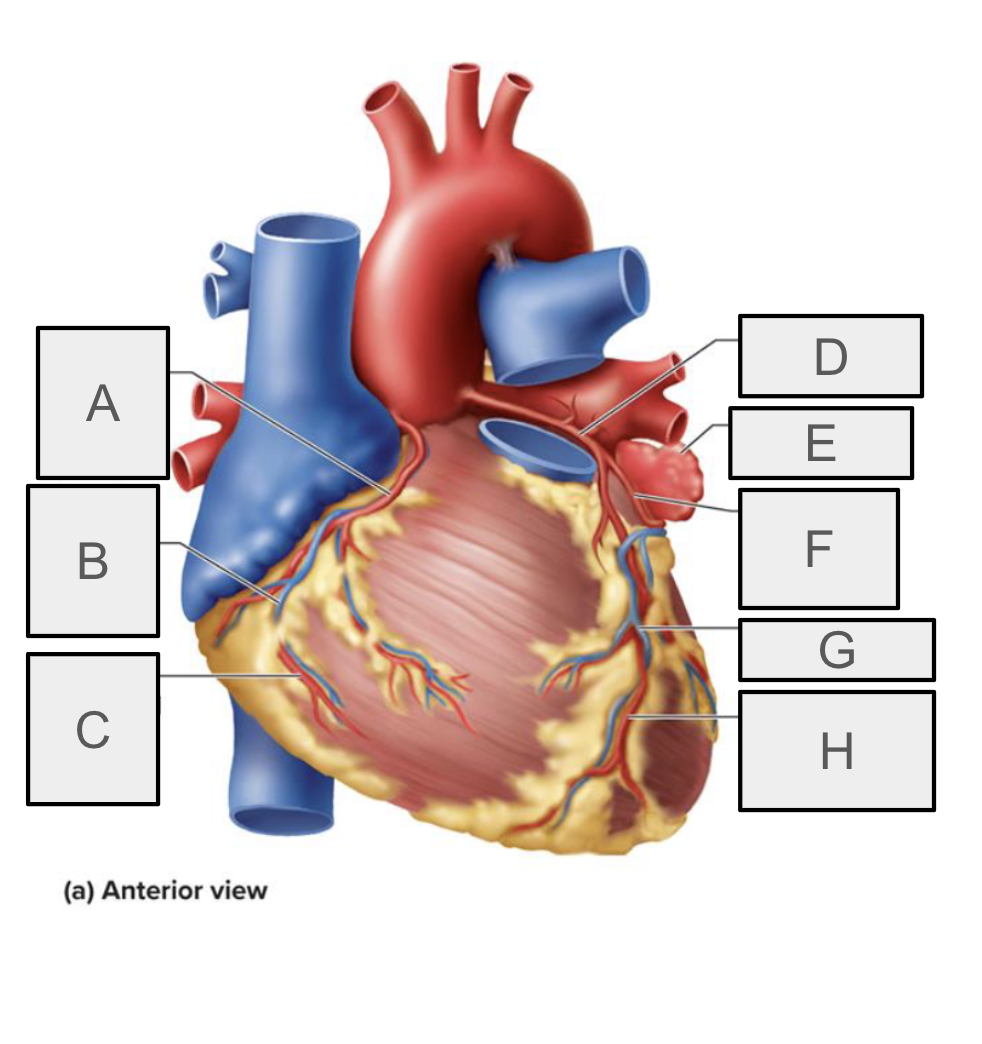
What is B
small cardiac vein
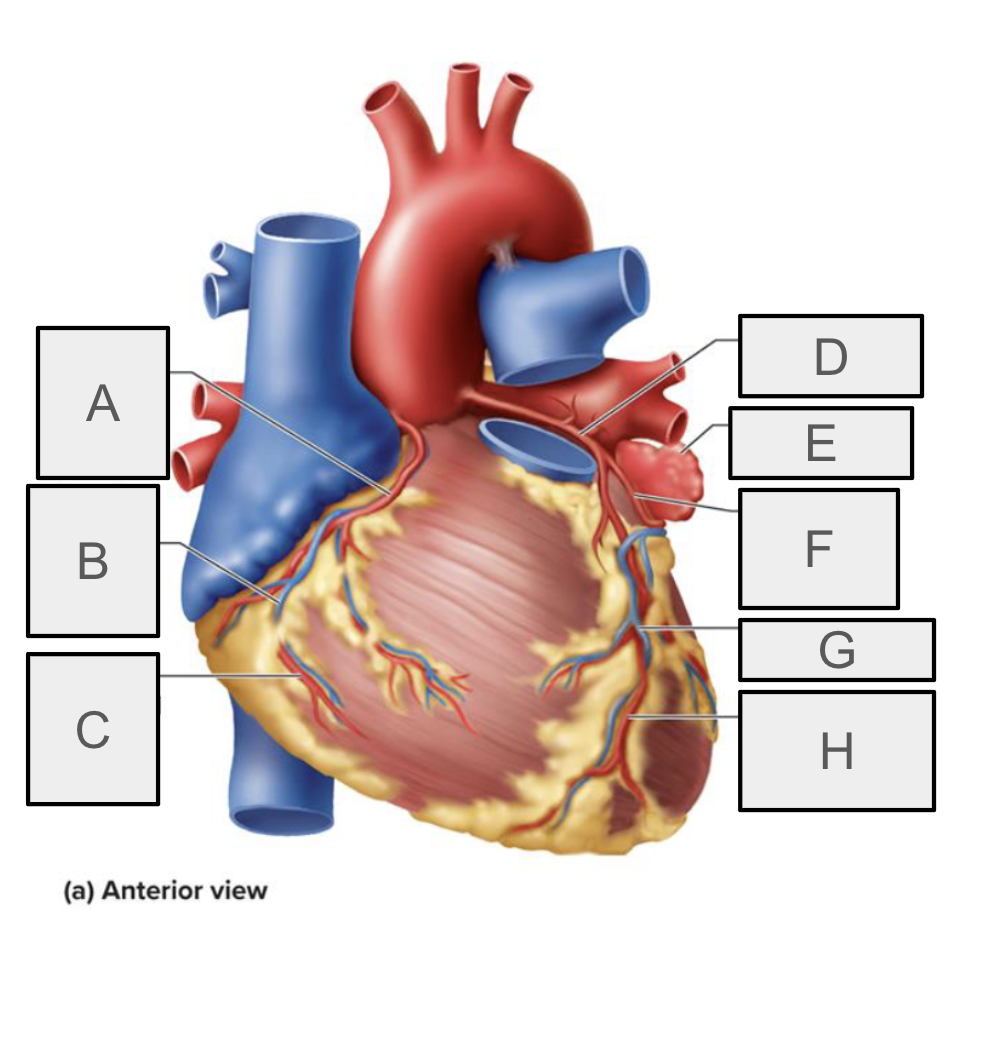
What is C
Right marchinal branch of RCA
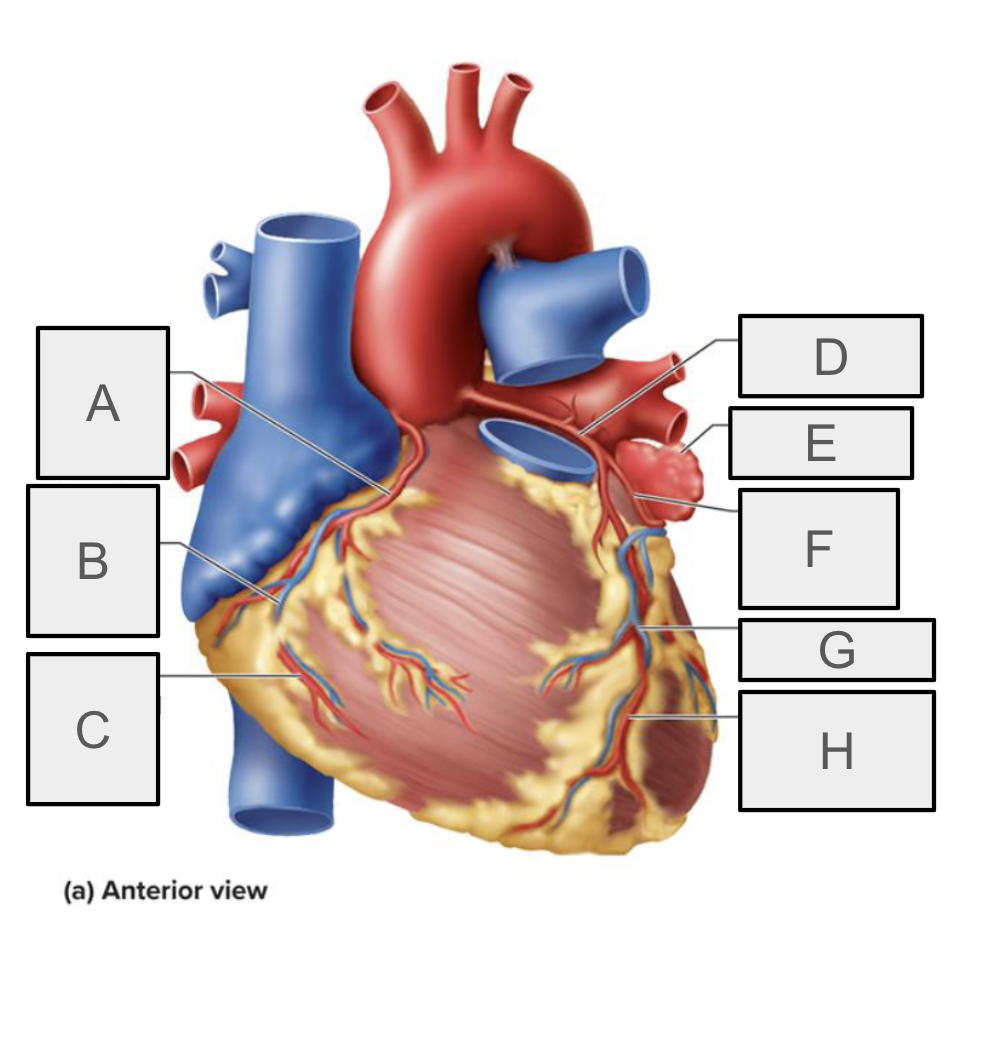
What is D
Left coronary artery
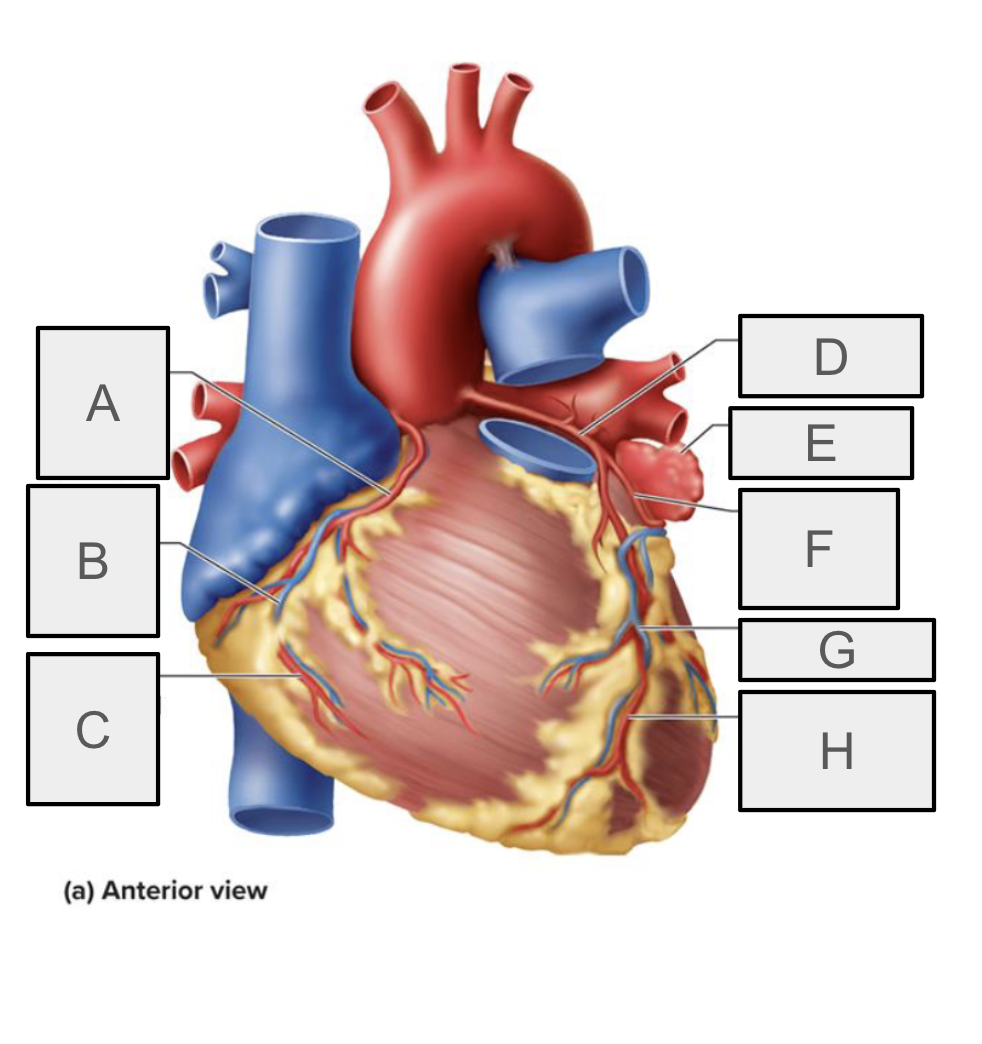
What is E
Left auricle
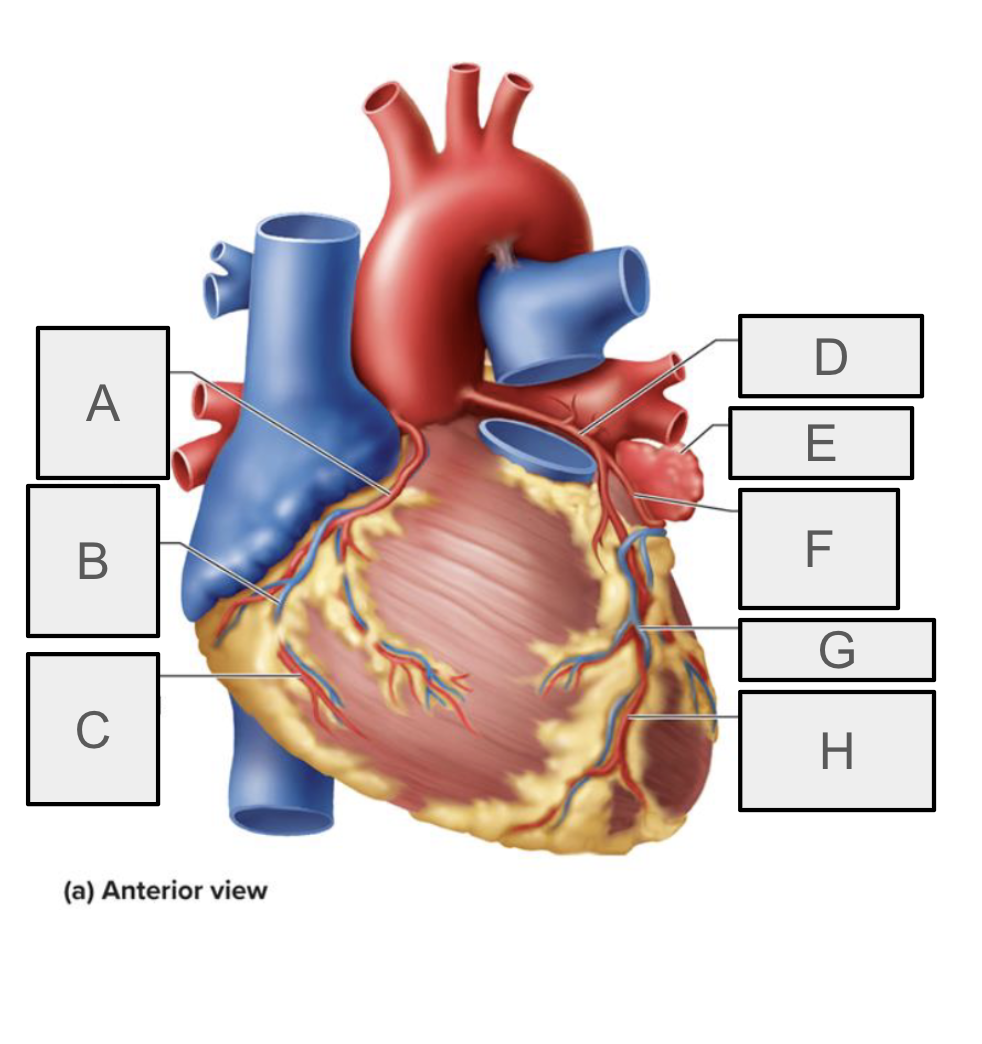
What is F
Circumflex branch of LCA
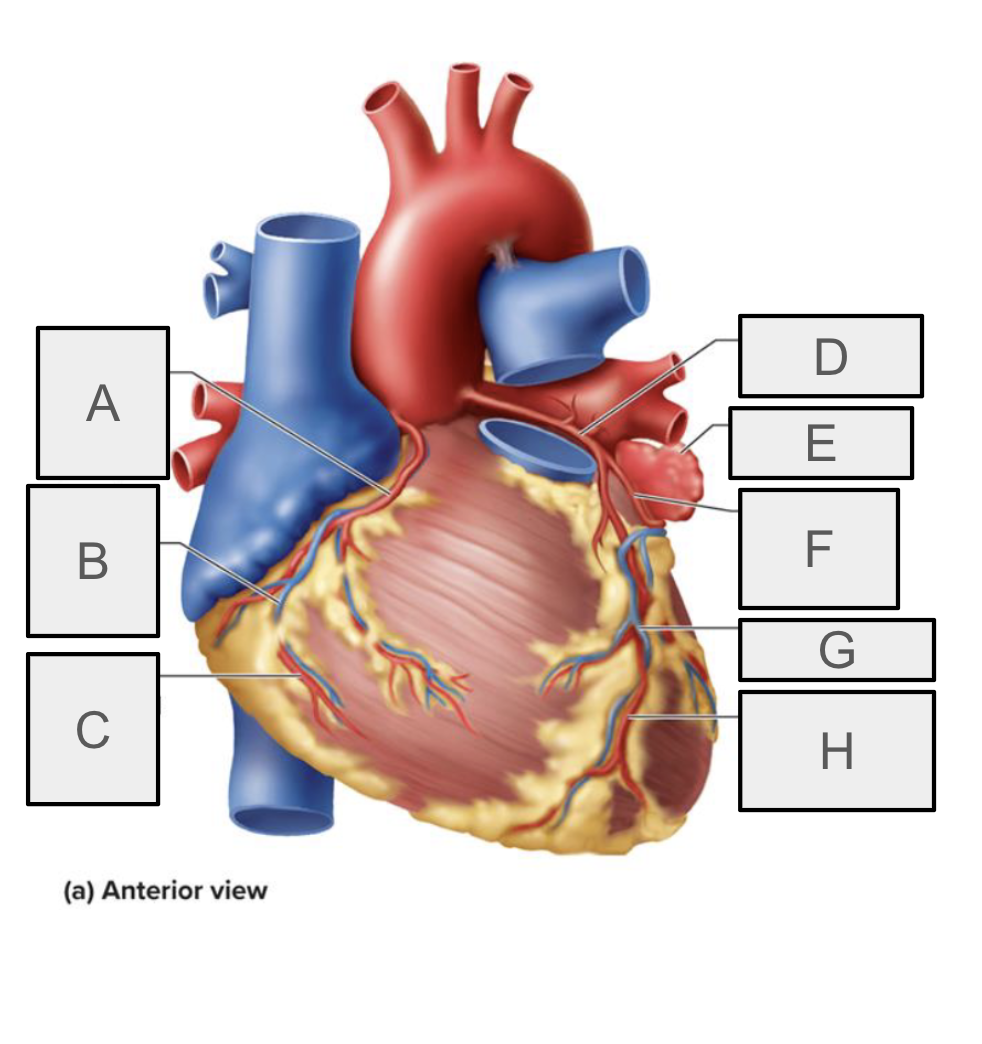
What is H
anterior interventricular branch of LCA (LAD)
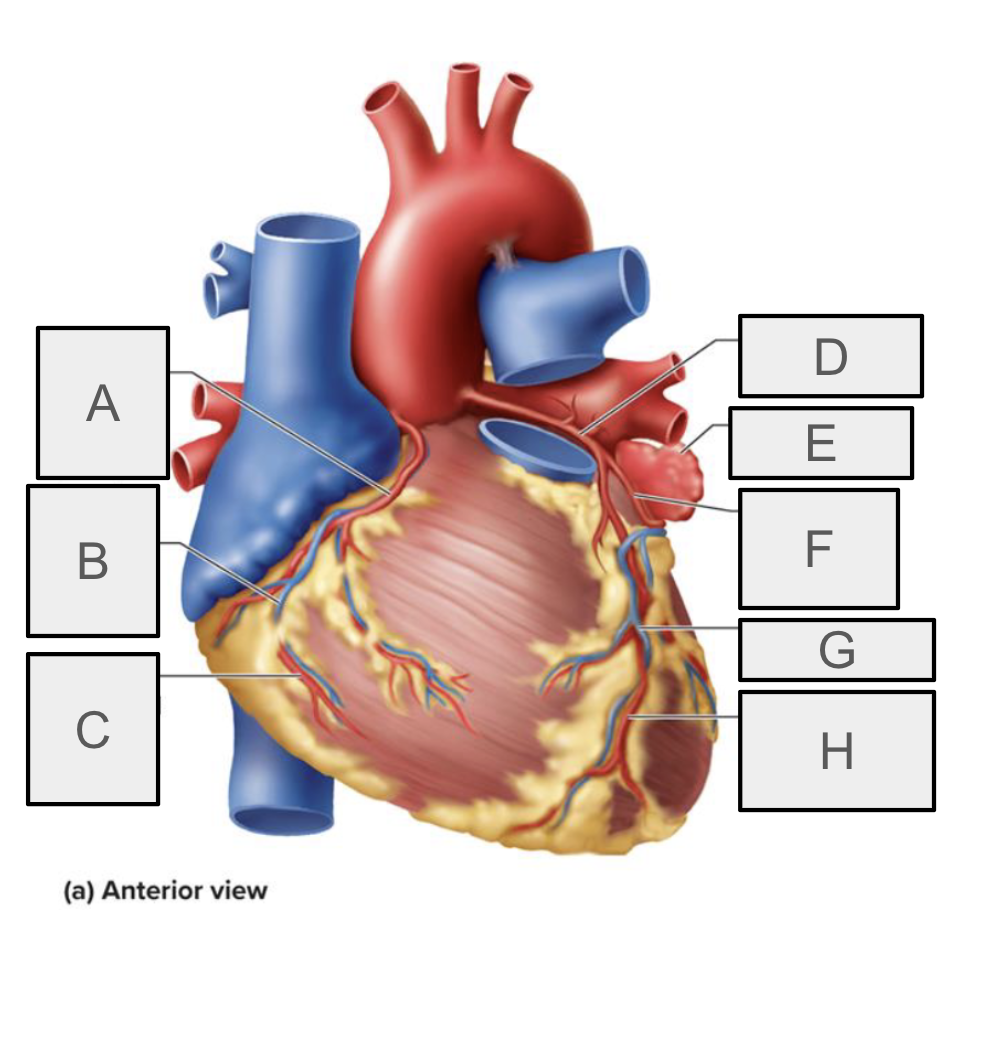
What is G
Great cardiac vein
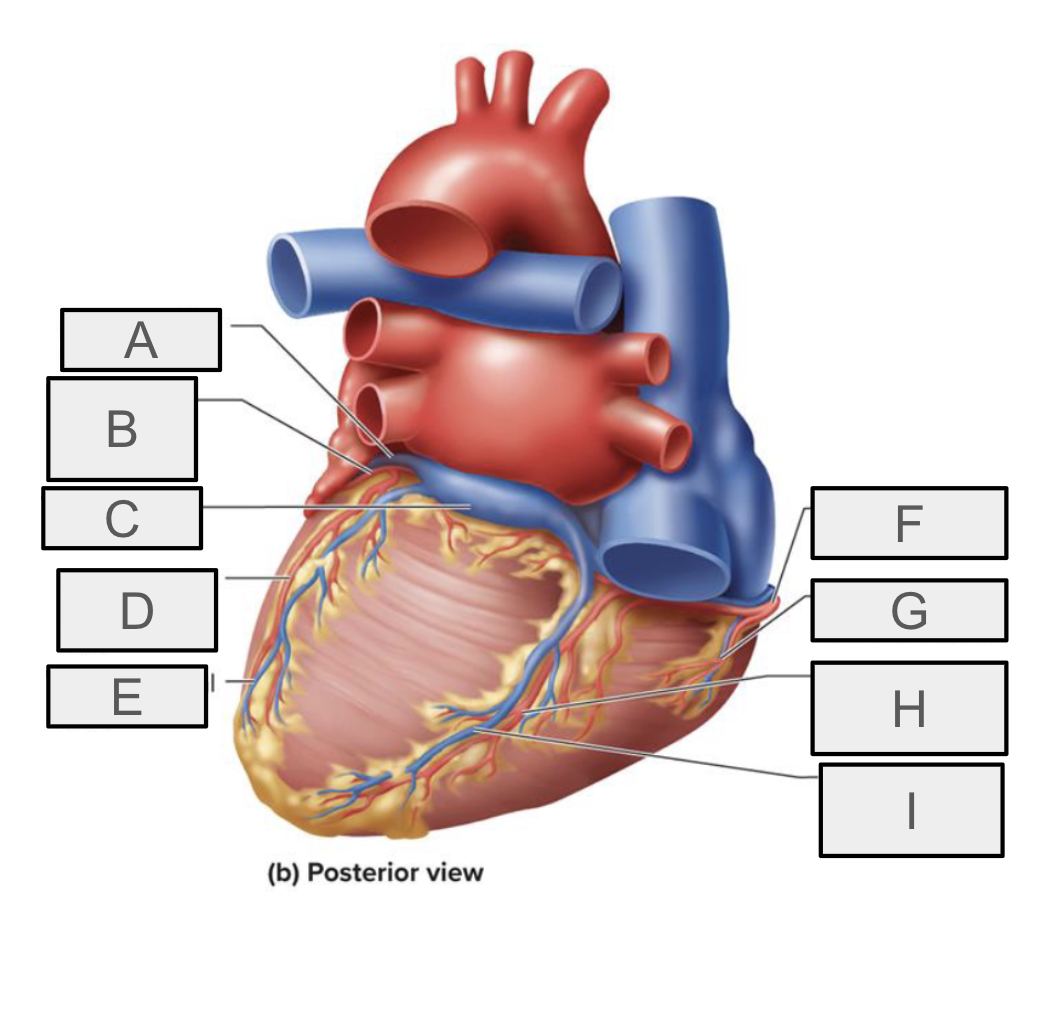
What is A
great cardiac vein
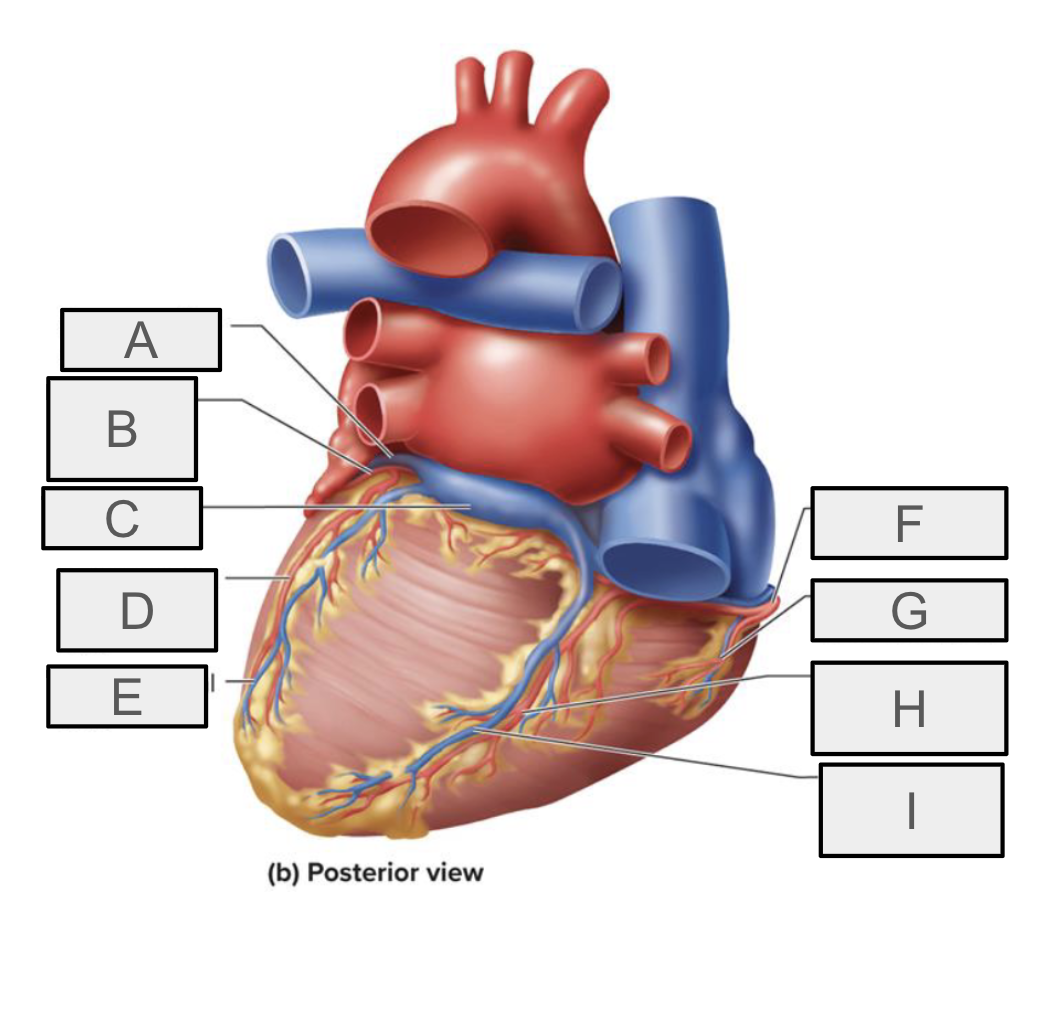
What is B
circumflex branch of LCA
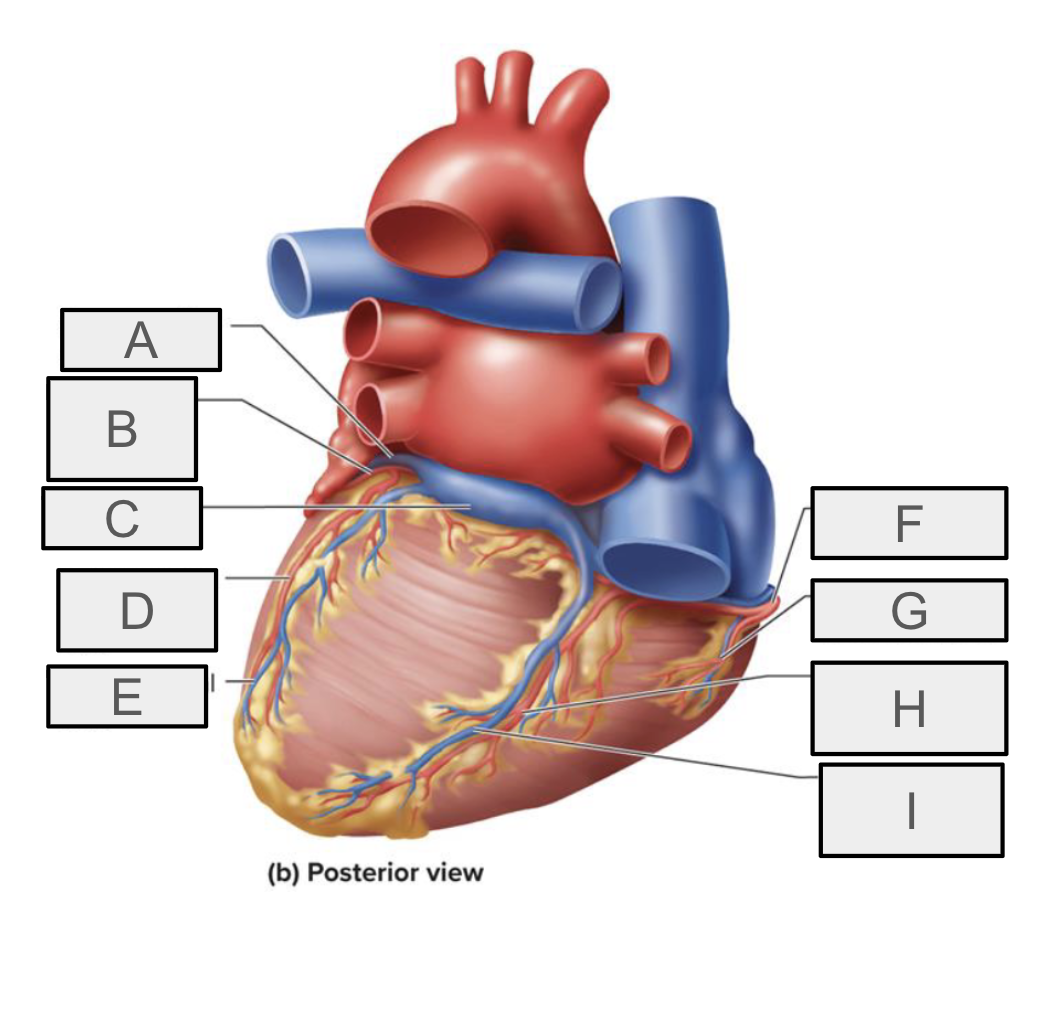
What is C
coronary sinus
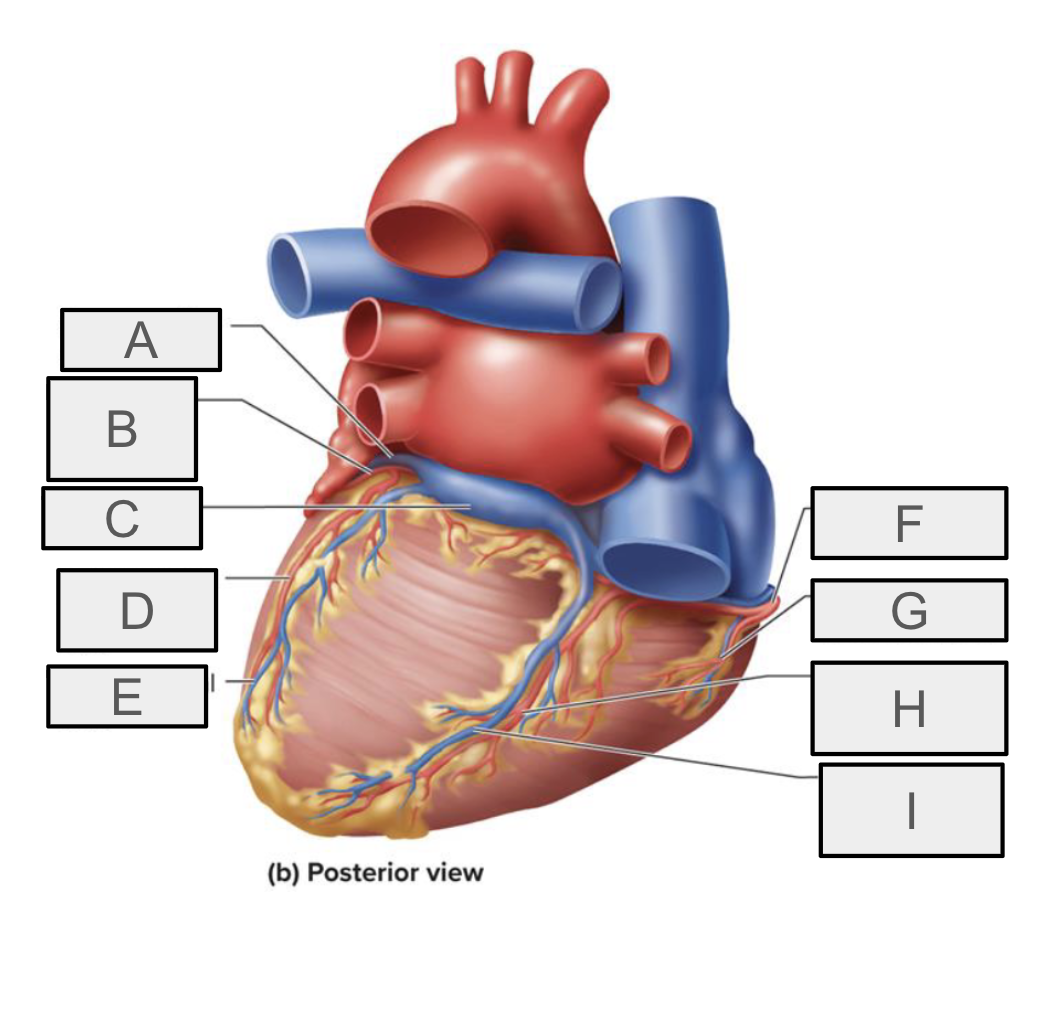
What is D
left marginal branch of LCA
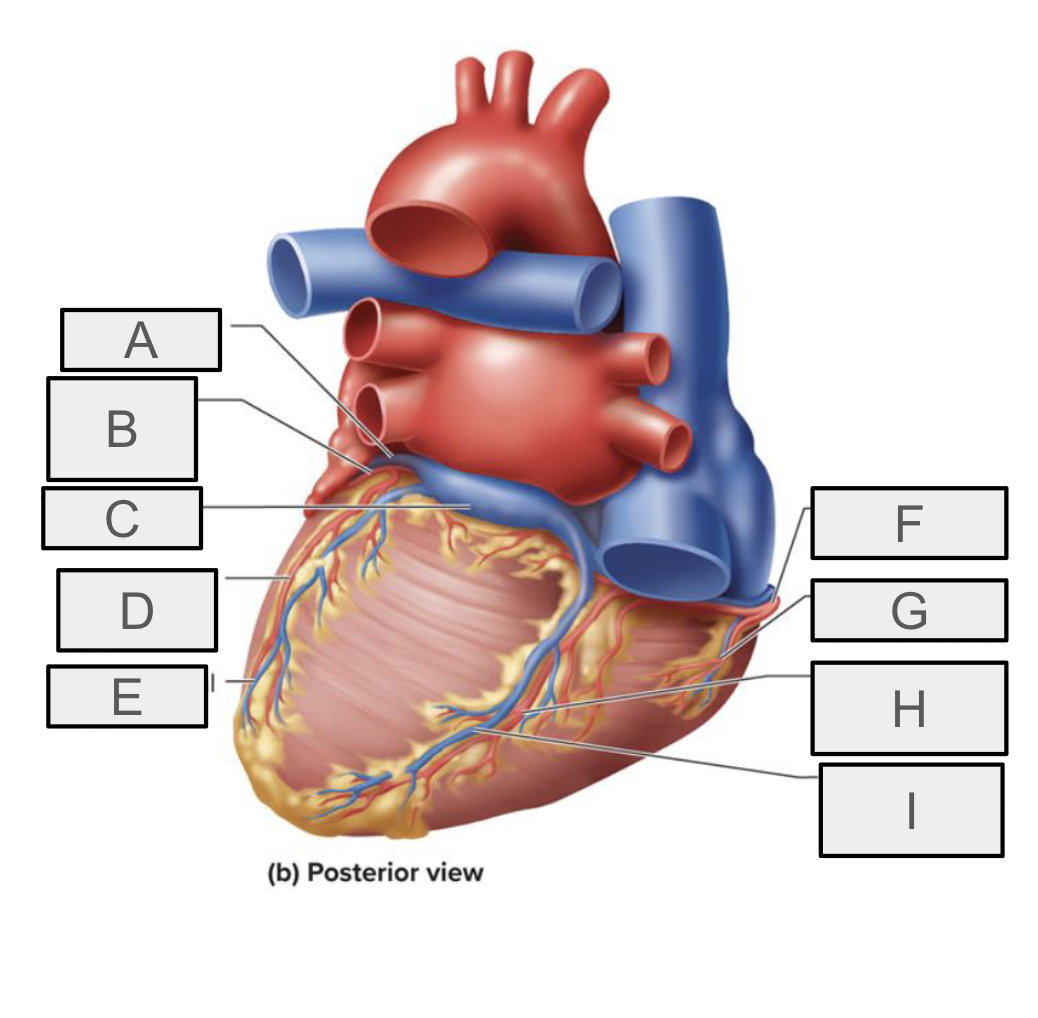
What is E
left marginal vein
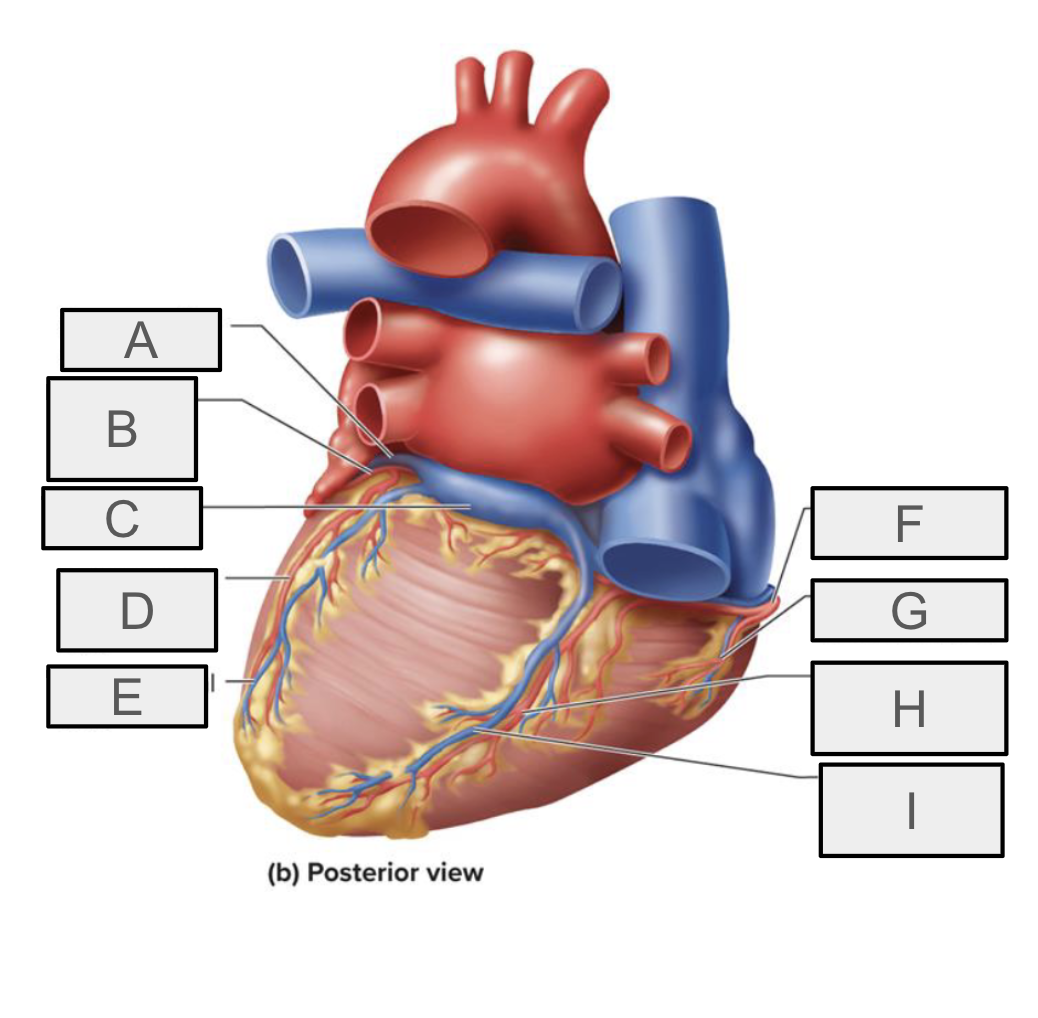
What is F
right coronary artery
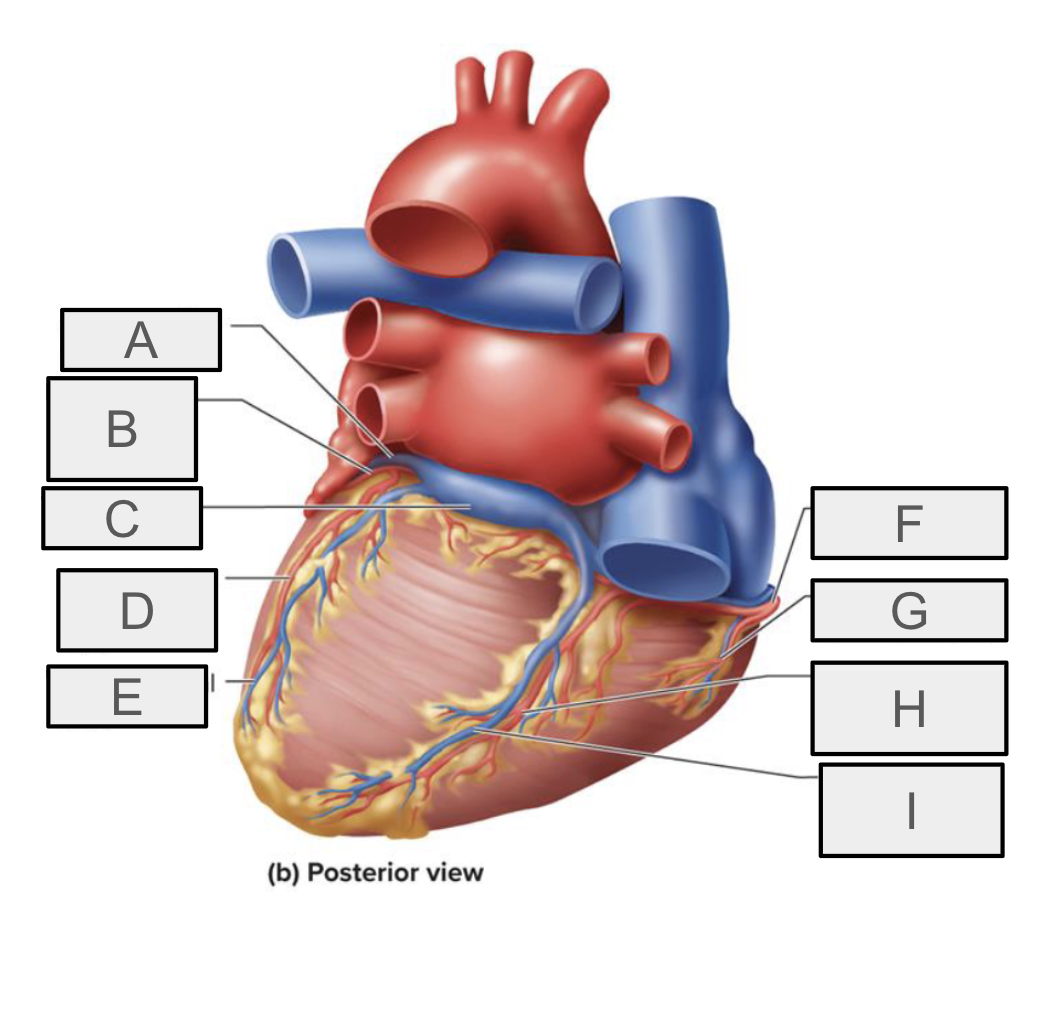
What is G
right marginal branch of RCA
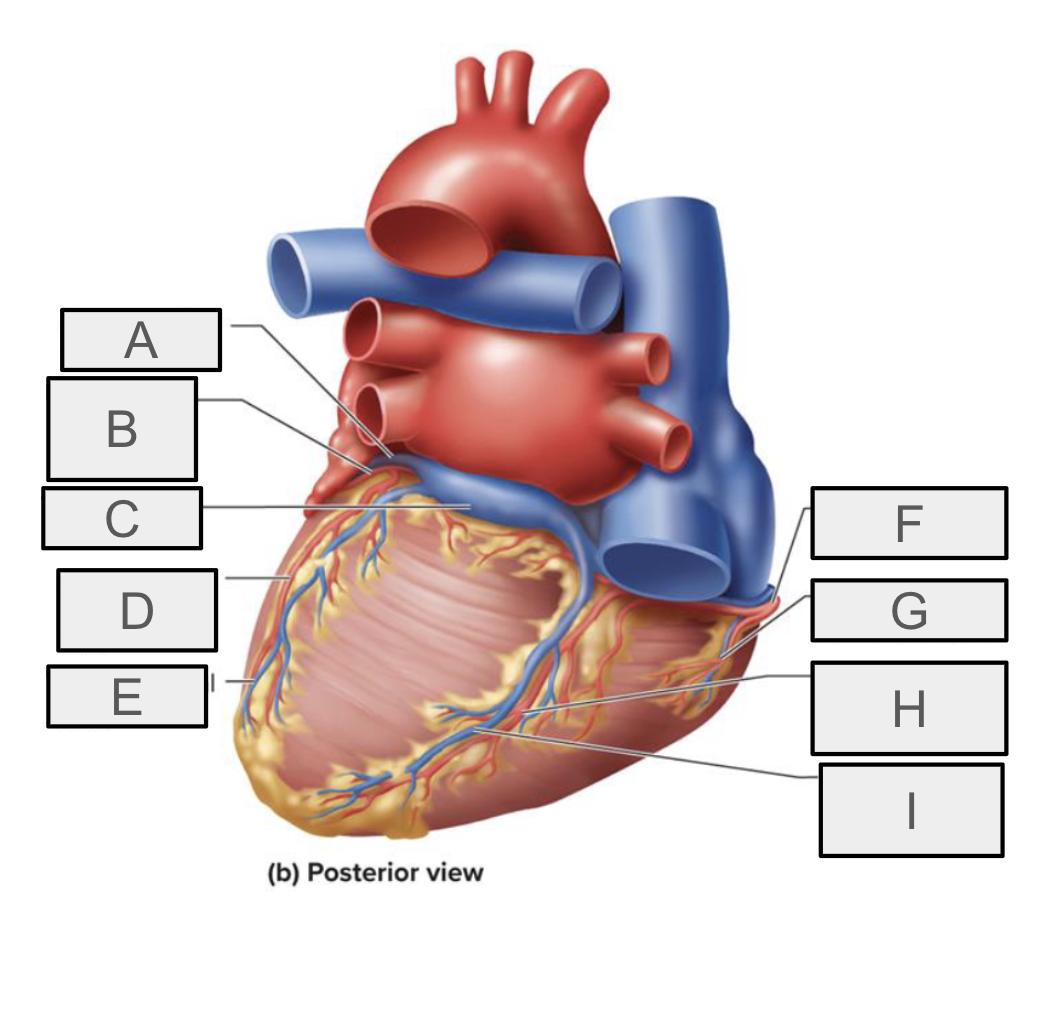
What is H
posterior interventricular branch of RCA
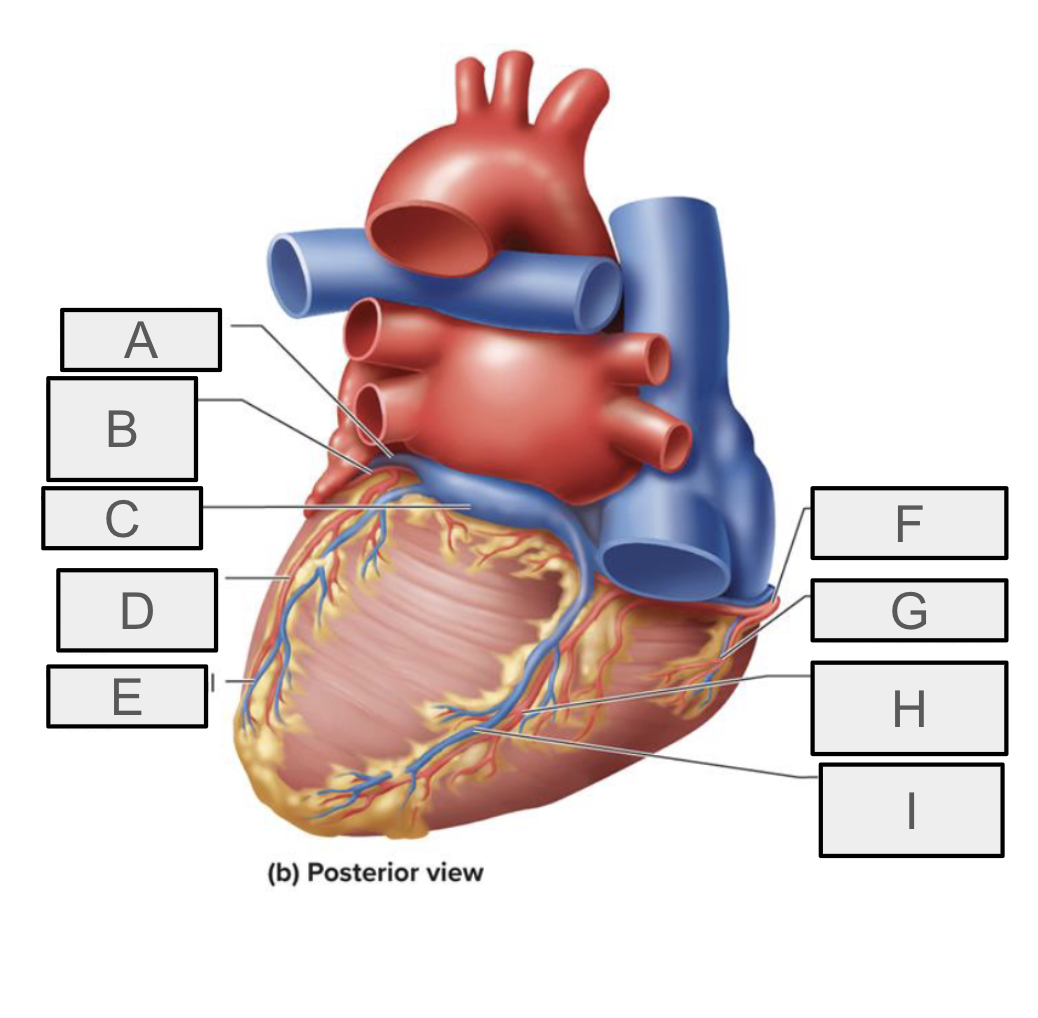
What is I
Posterior interventricular vein
The most muscular single chamber of the heart is the:
left ventricle
The arteries and veins serving the lungs are called the _ circuit.
pulmonary
Which of these has a nucleus with the most complex shape?
neutrophil
if blood contains too few red blood cells, the most urgent problem will be:
reduced ability to carry oxygen in the blood
Where are platelets made?
bone marrow
A person with type B-positive blood can safely get a blood transfusion from:
Someone with O or B type blood, either Rh positive or negative.
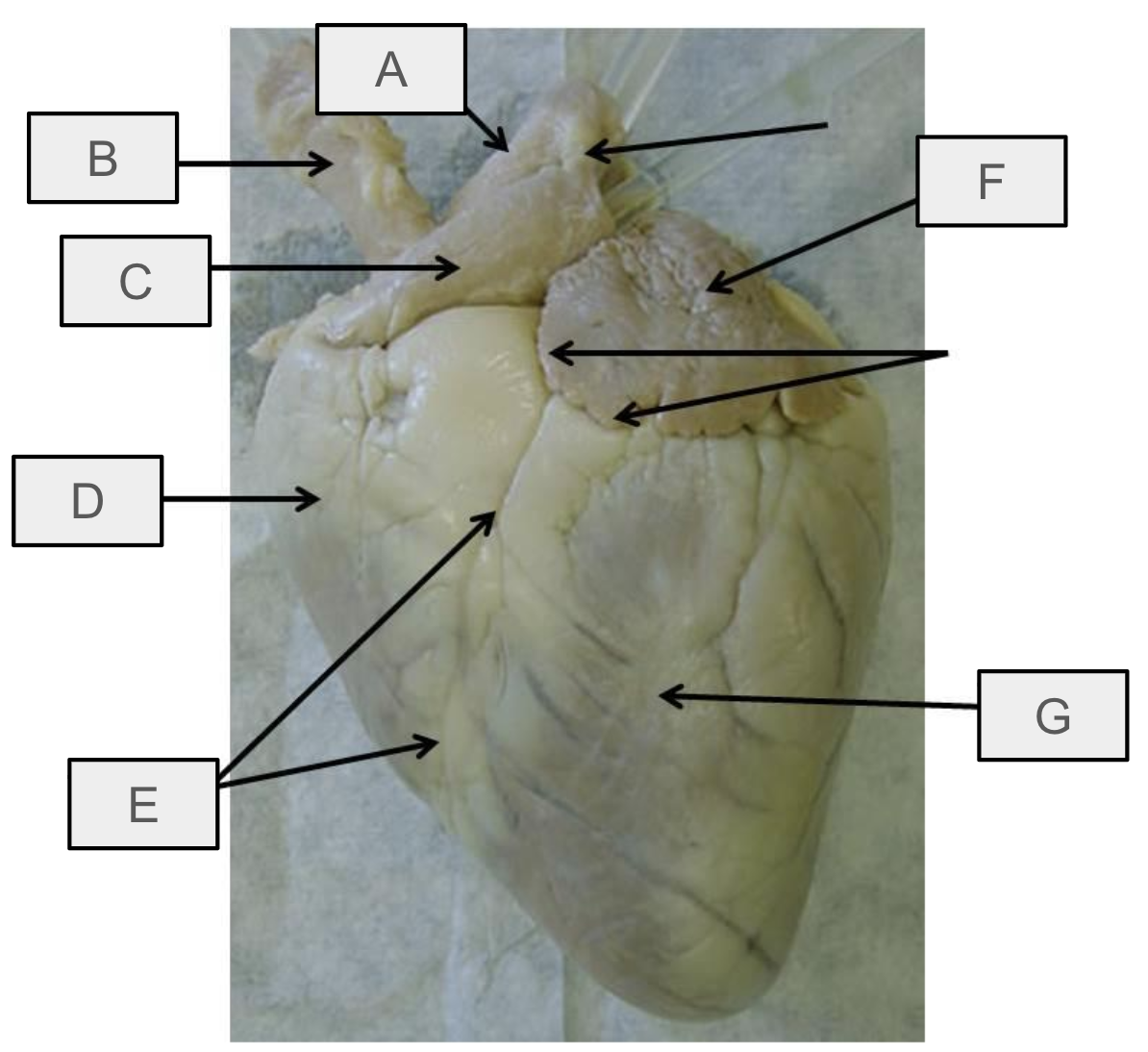
What is A
Aorta
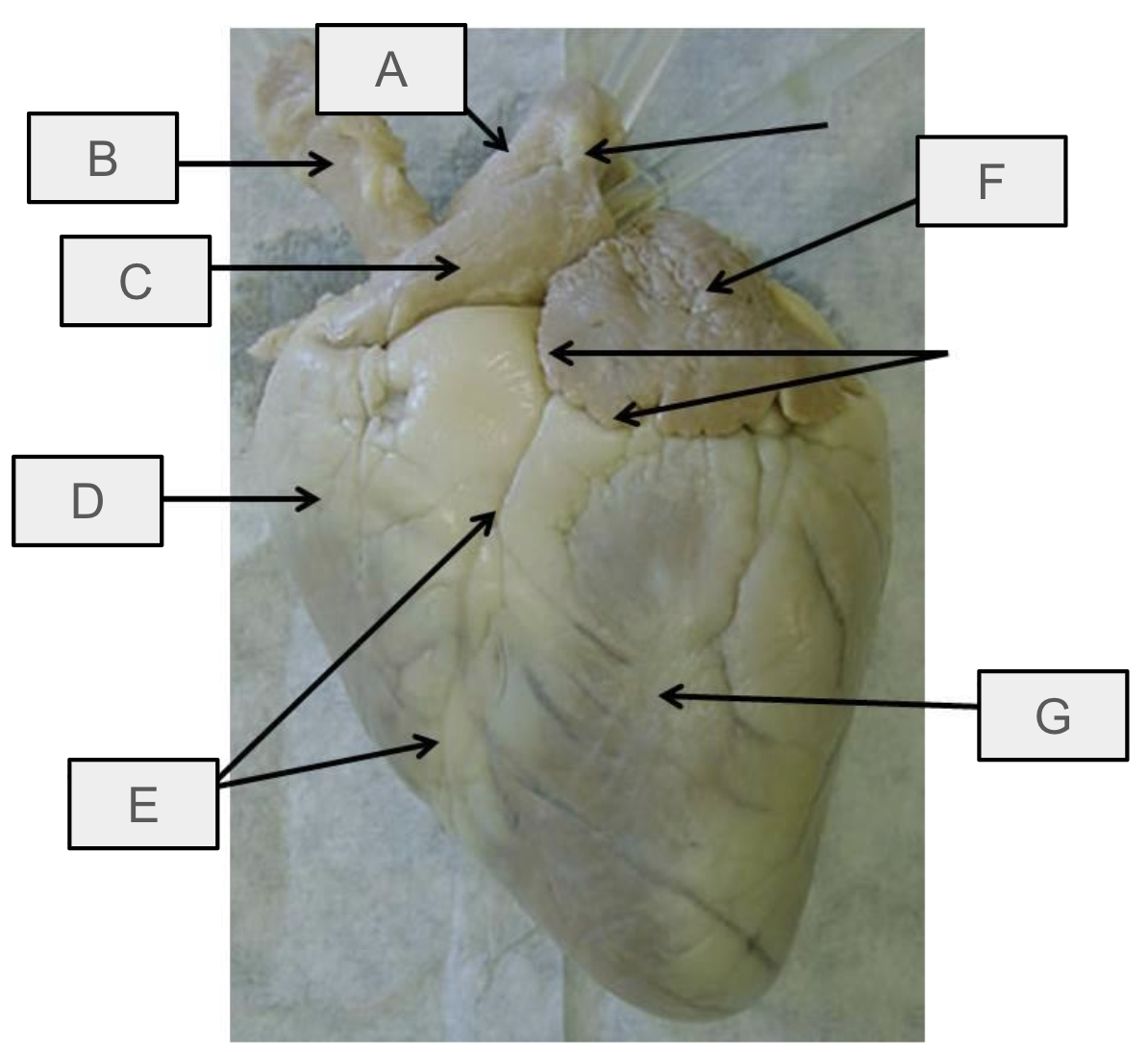
What is B
brachiocephalic trunk
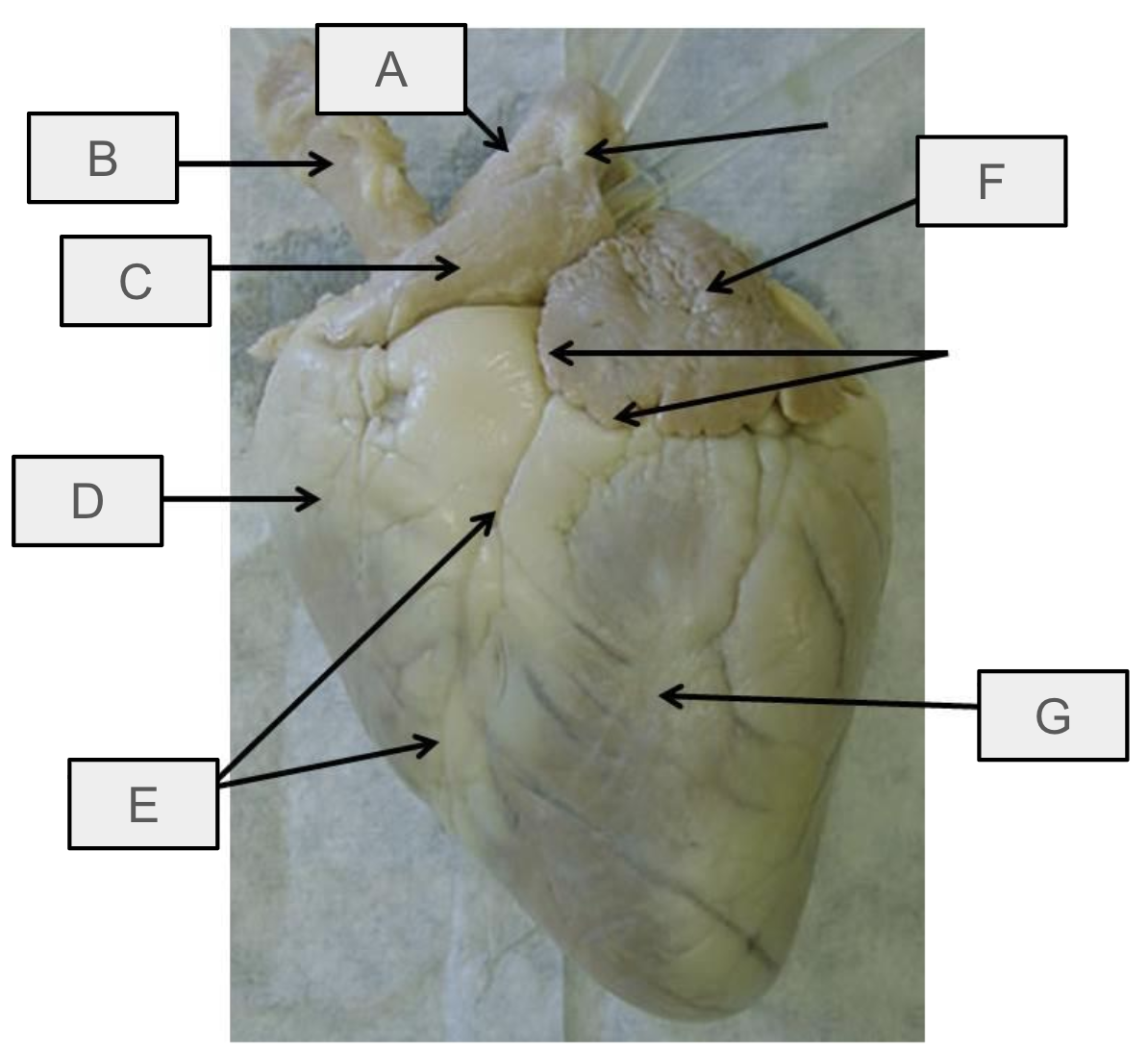
What is C
pulmonary trunk
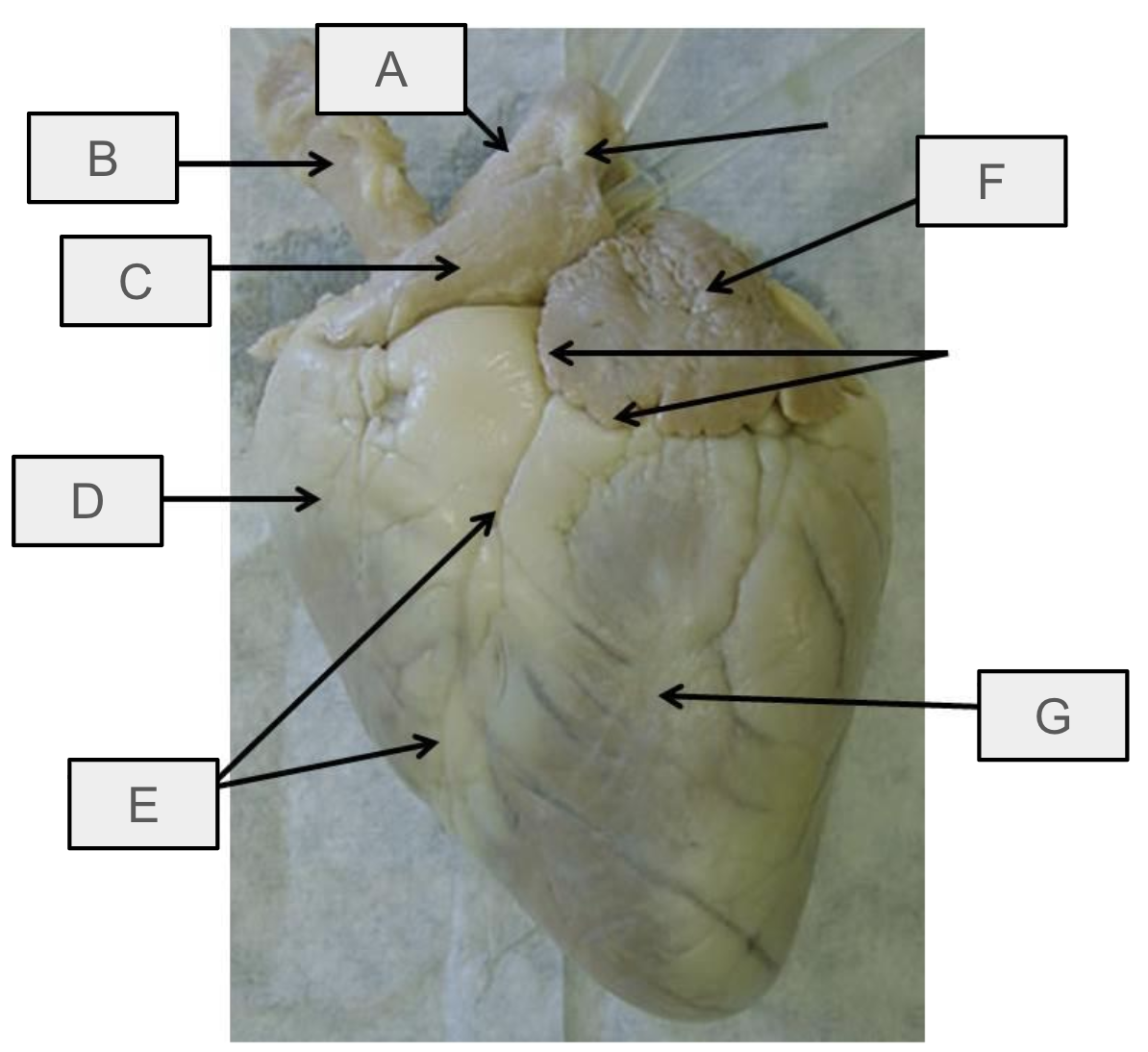
What is D
Right ventricle
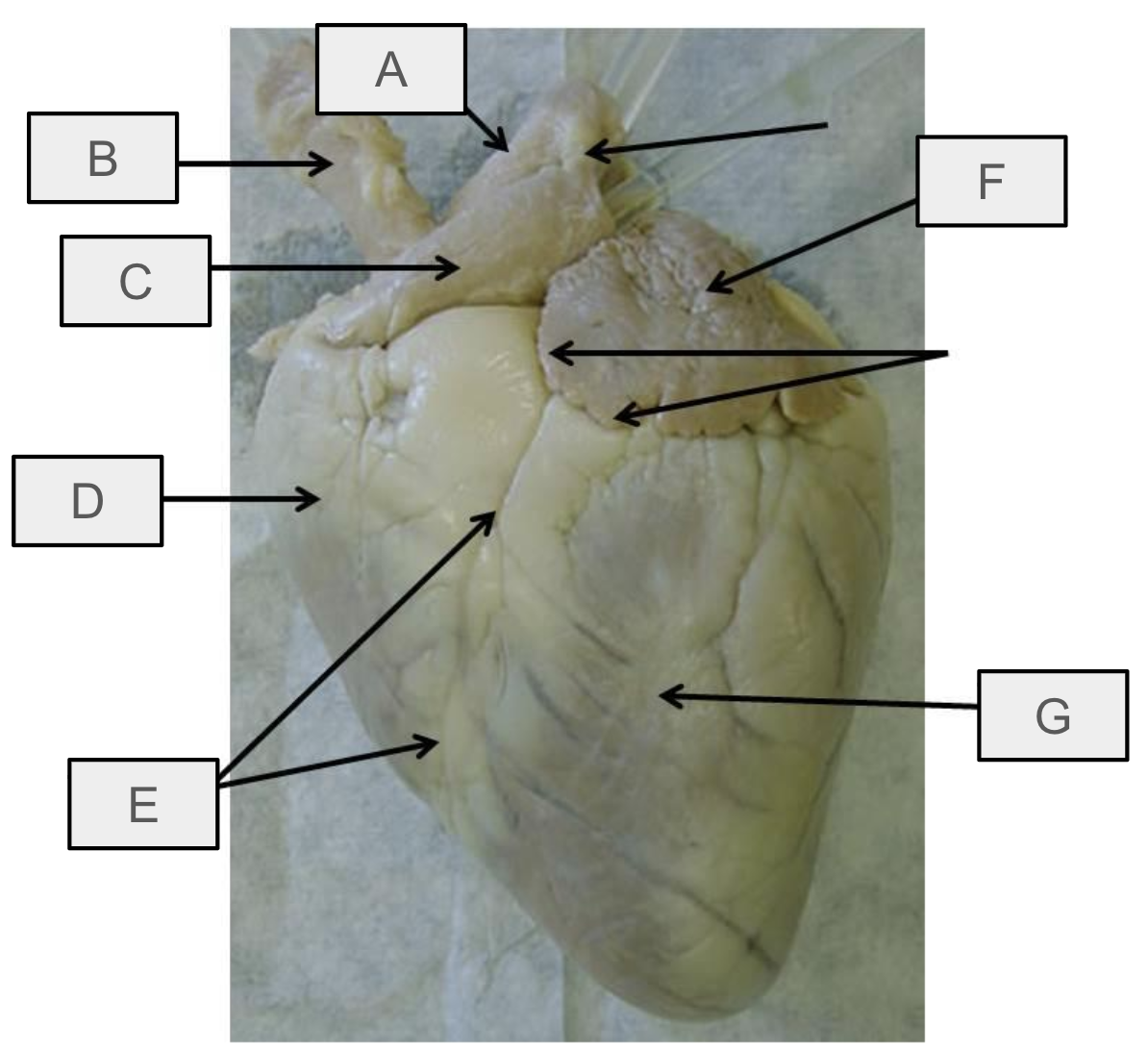
What is E
anterior interventricular sulcus
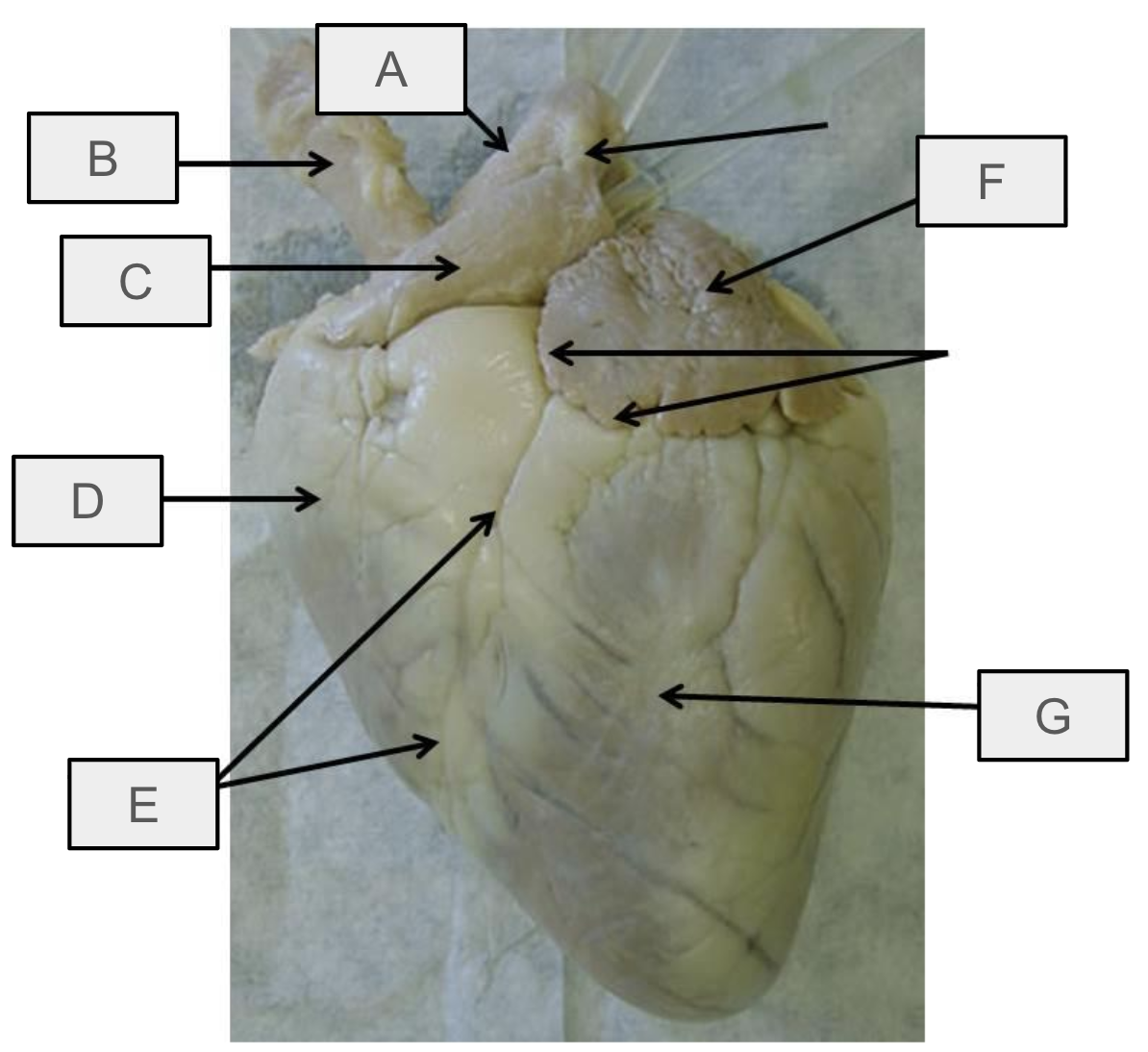
What is F
Left atrium
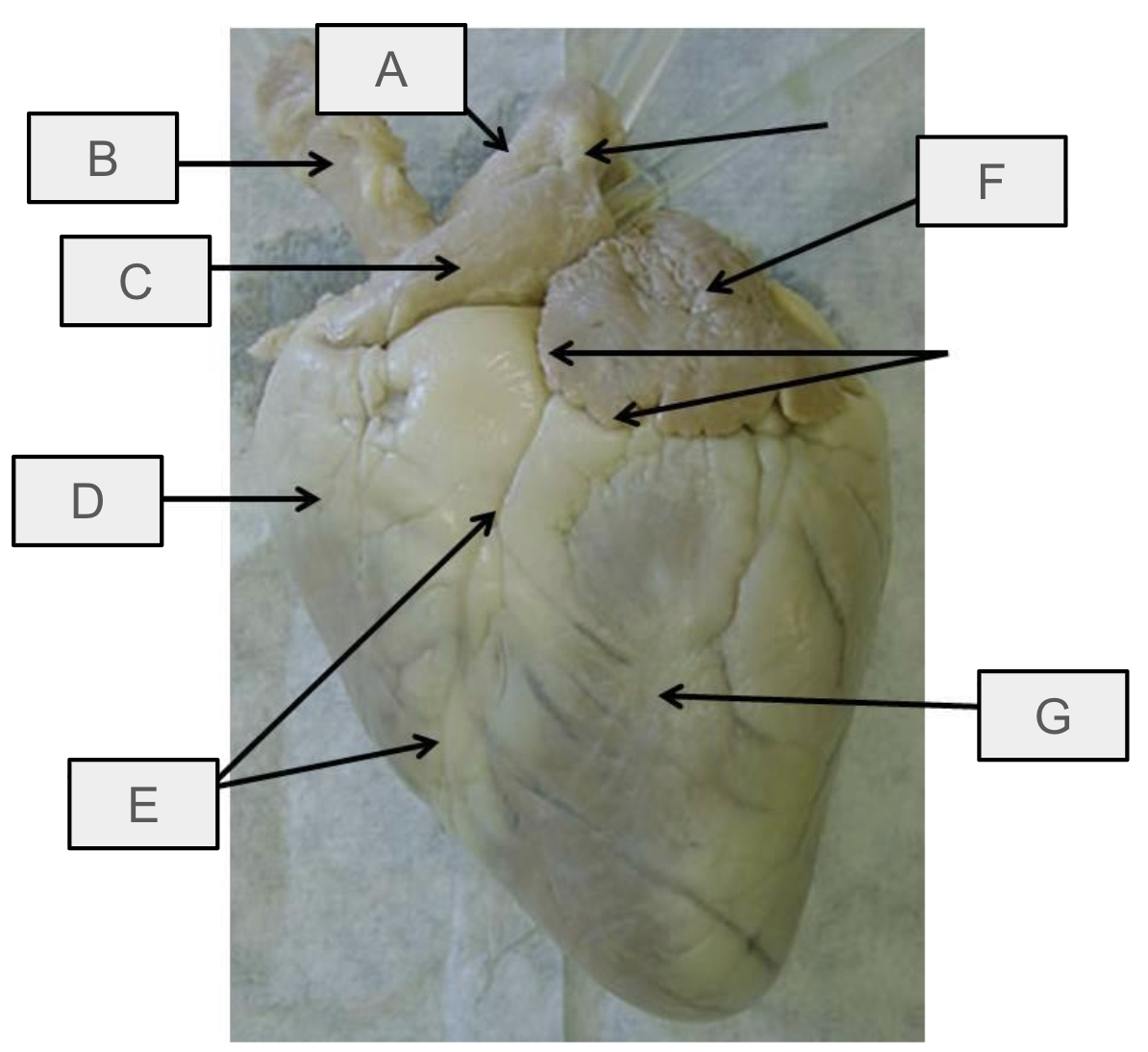
What is G
Left ventricle
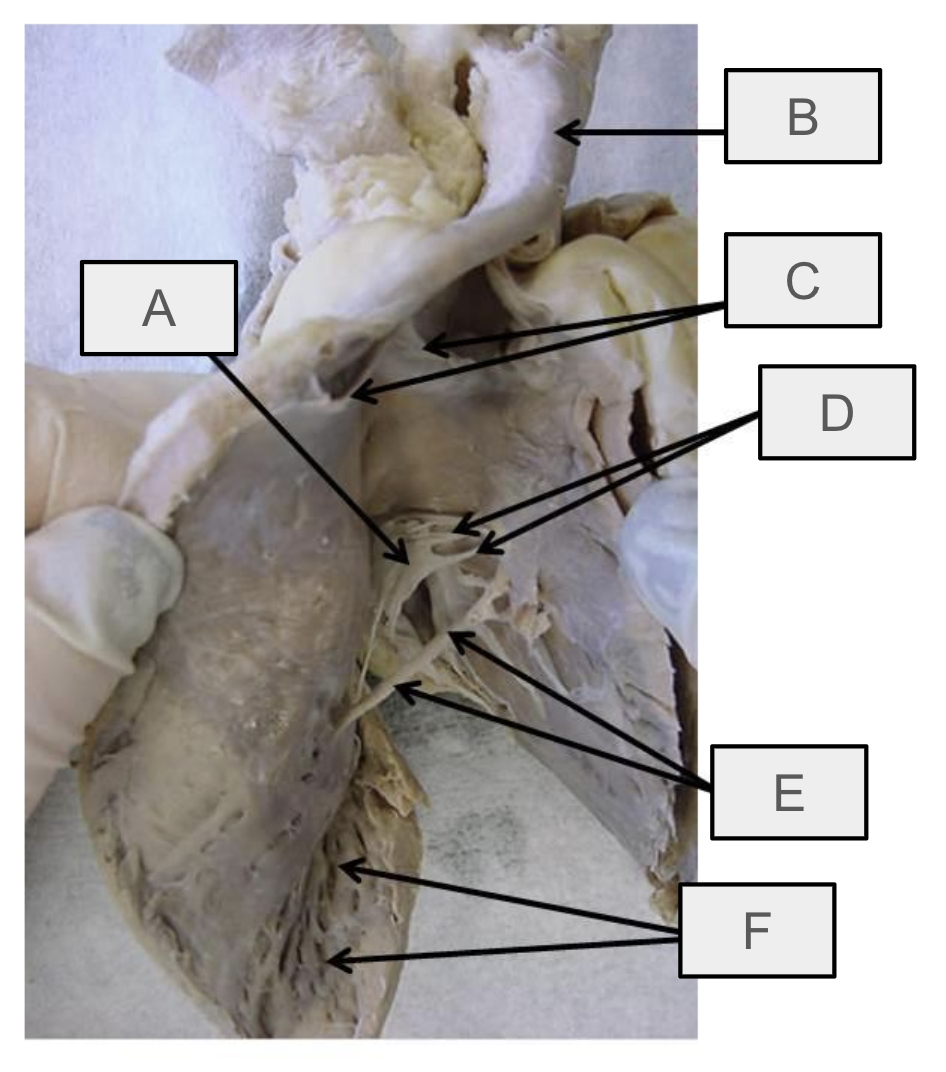
What is A
tricuspid valve
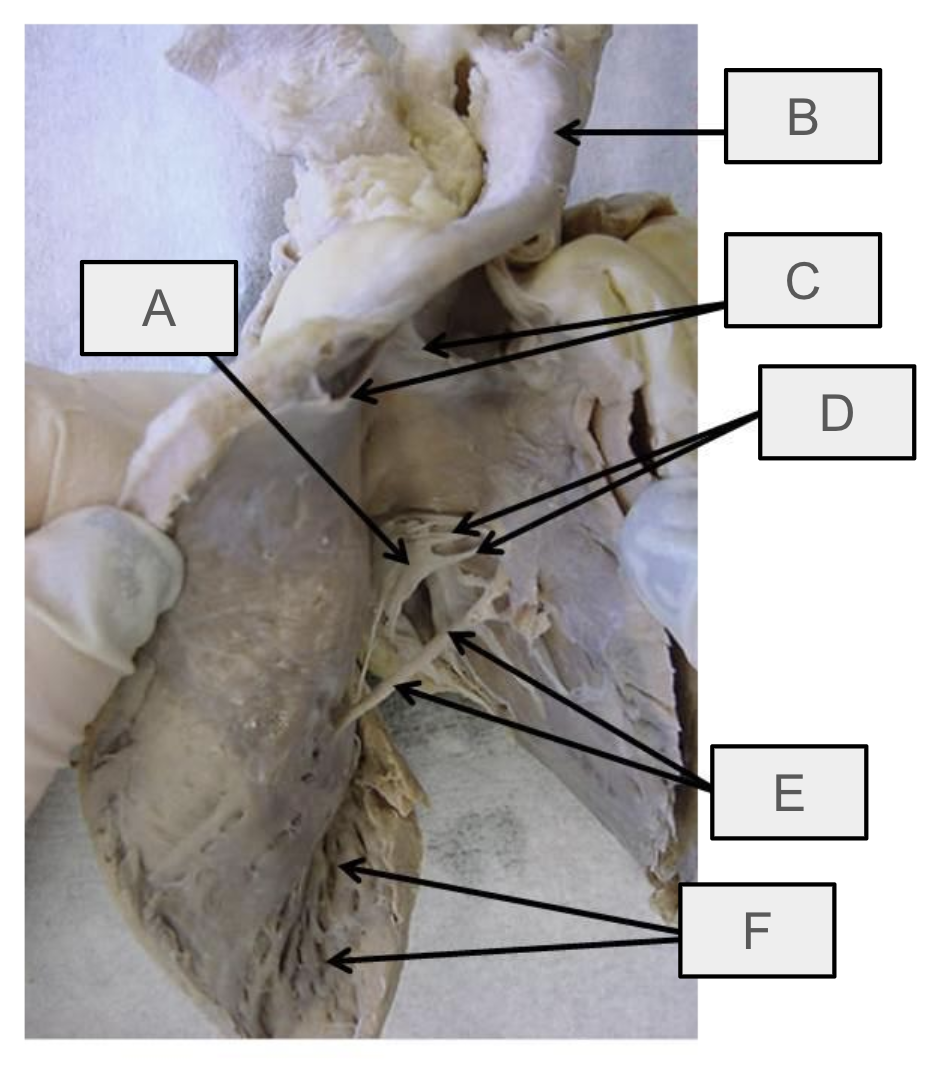
What is B
pulmonary trunk
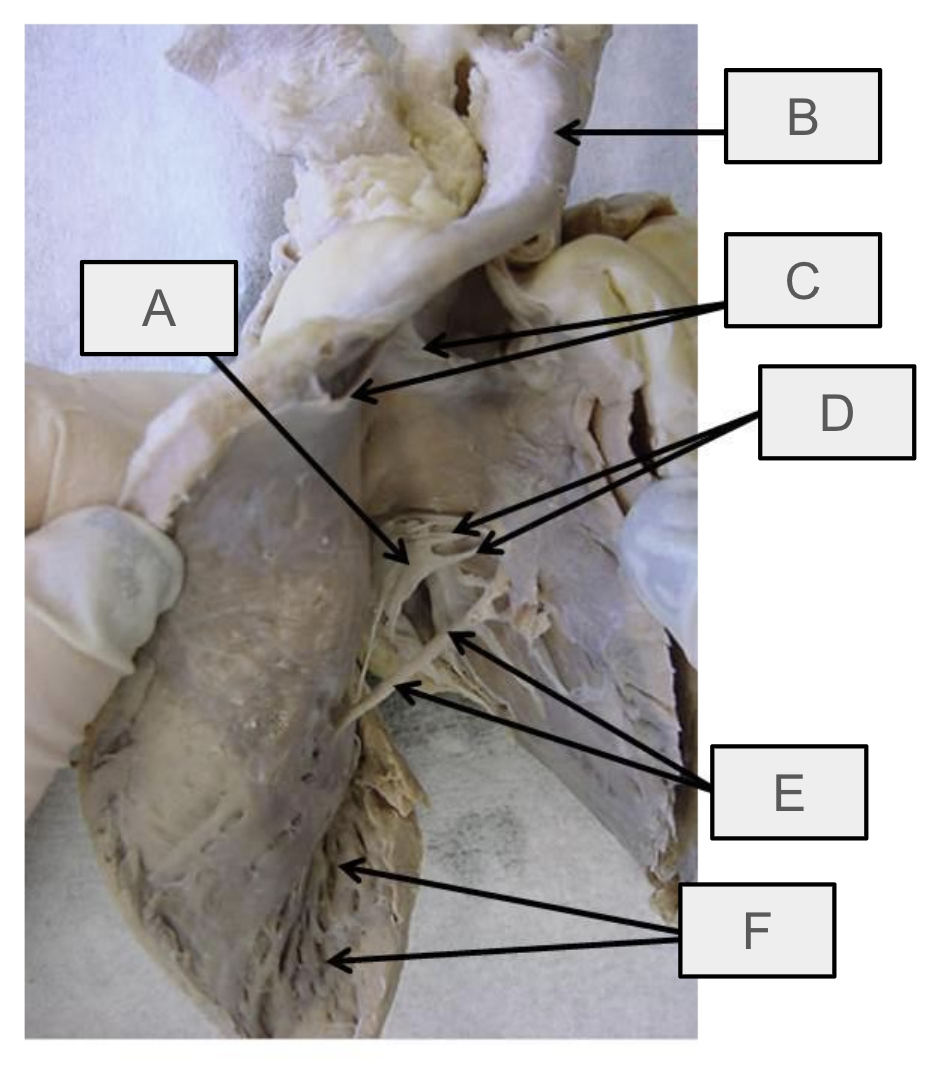
What is C
pulmonary semilunar valve
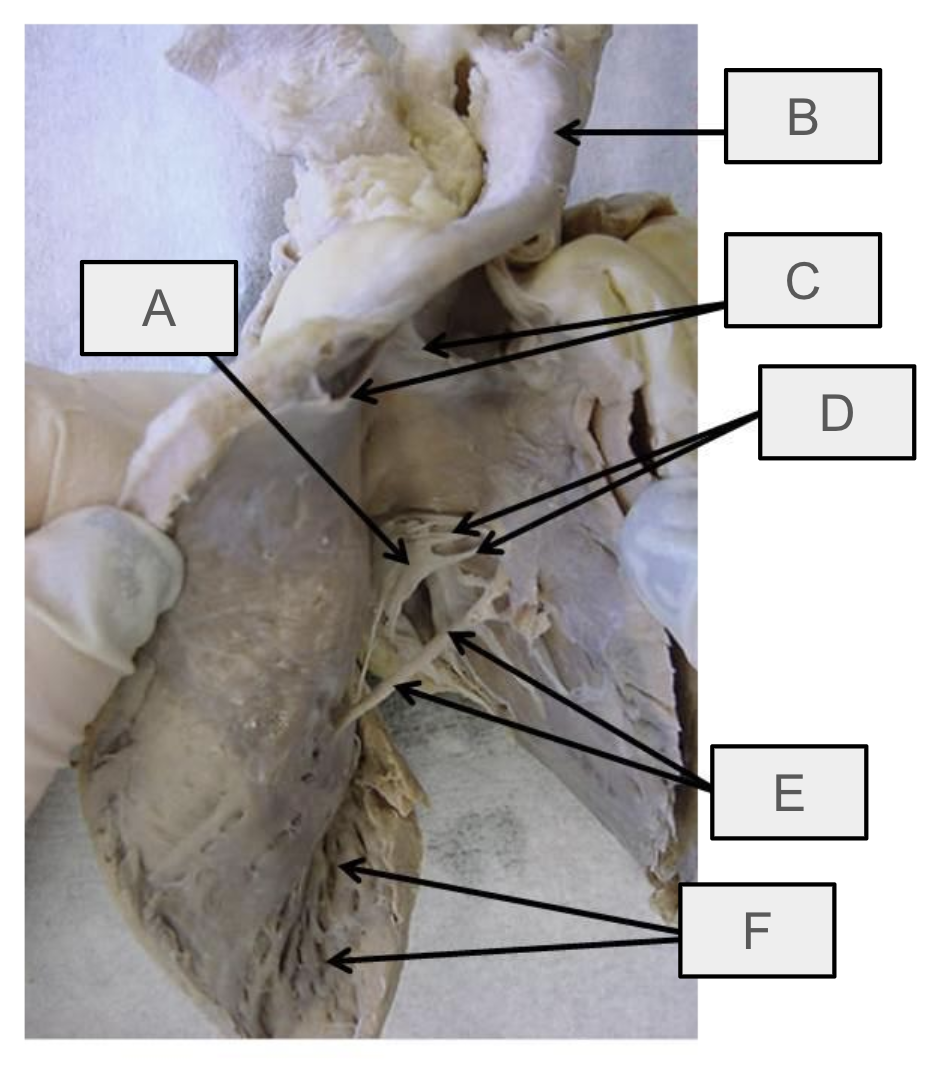
What is D
chordae tendineae
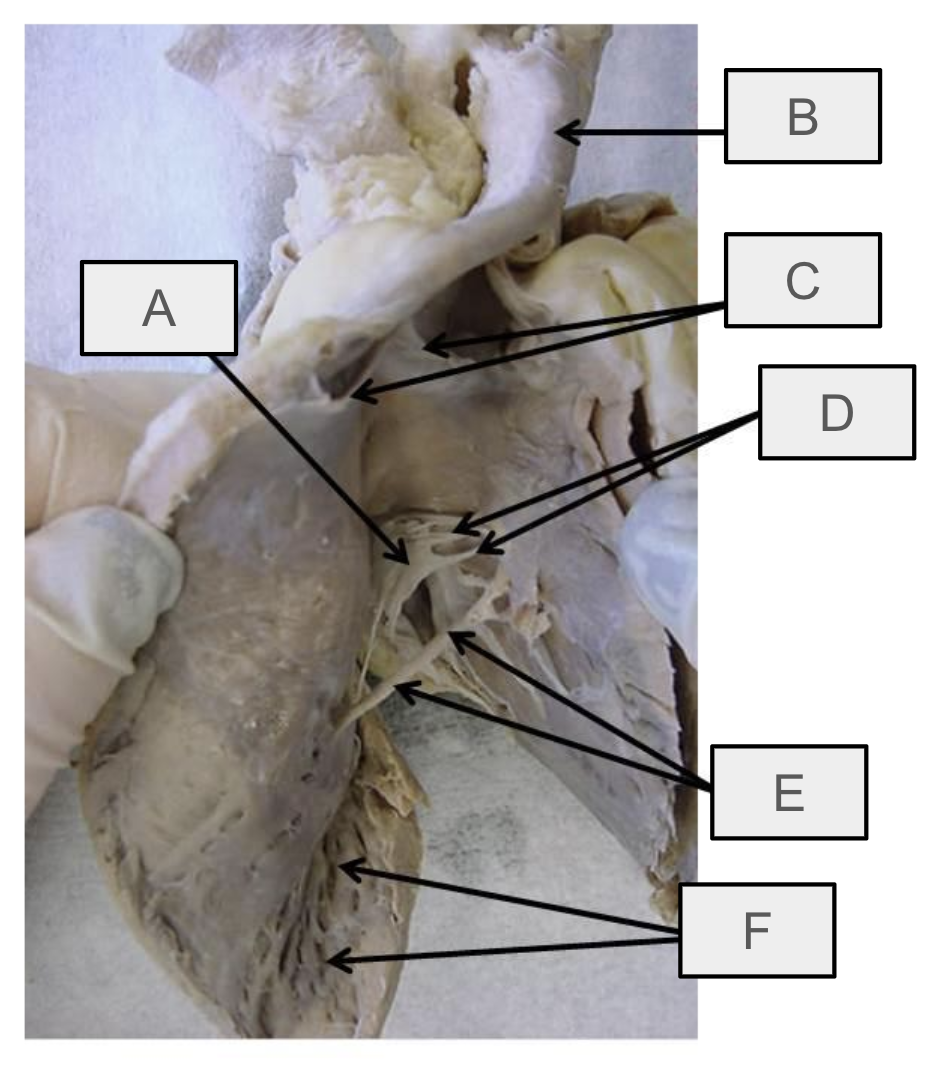
What is E
moderator band
What is F
trabeculae carneae
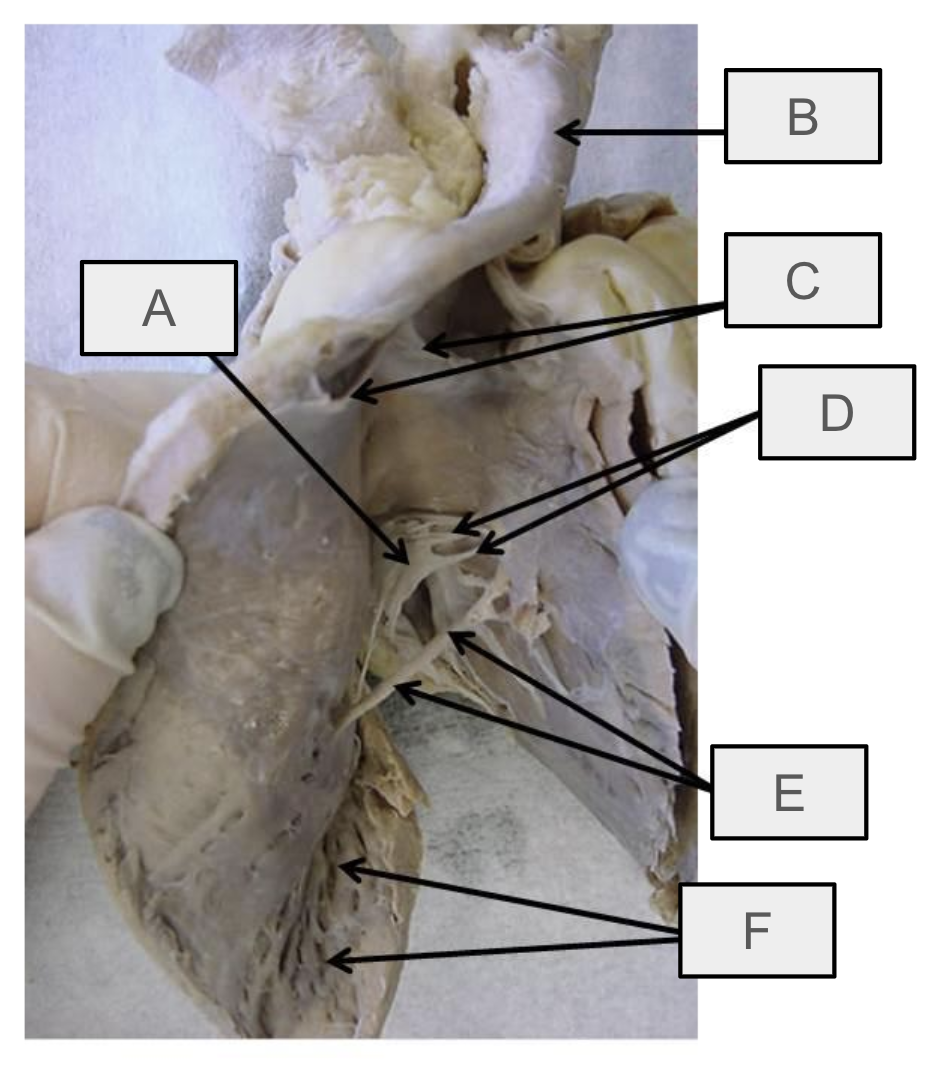
What is A
aortic semilunar valve
What is B
mitral valve
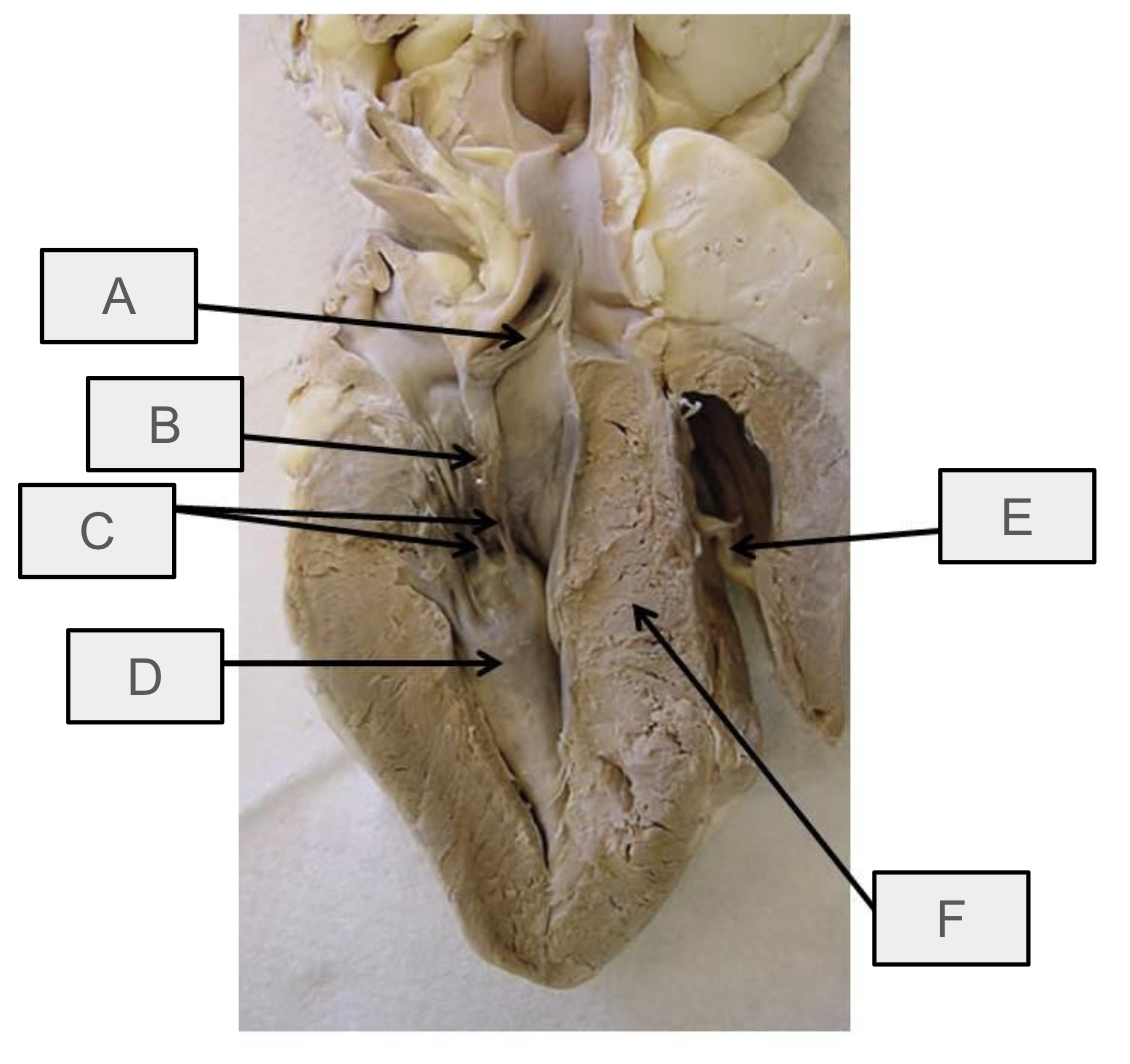
What is C
chordae tendineae
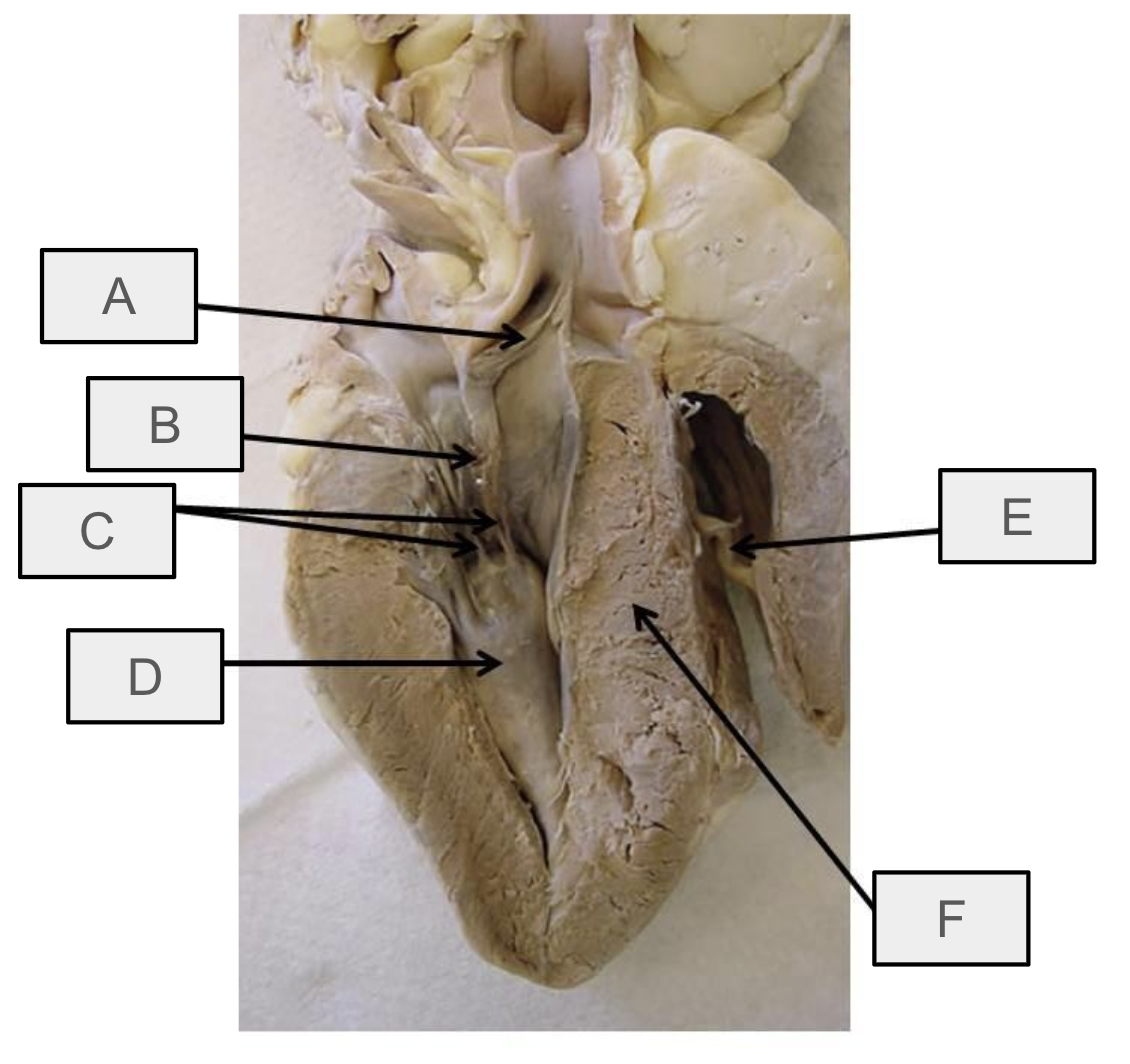
What is D
papillary muscle
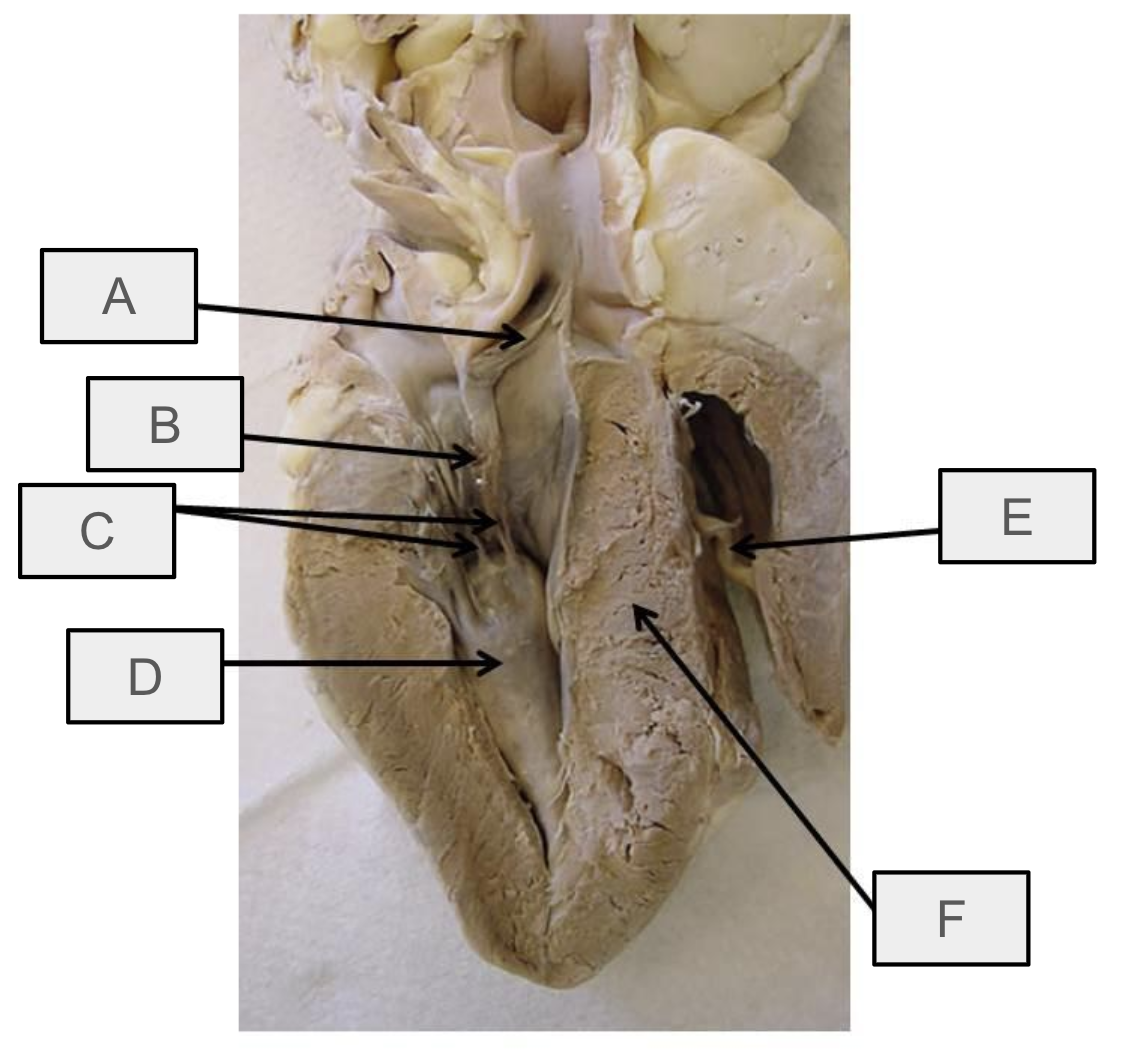
What is E
moderator band
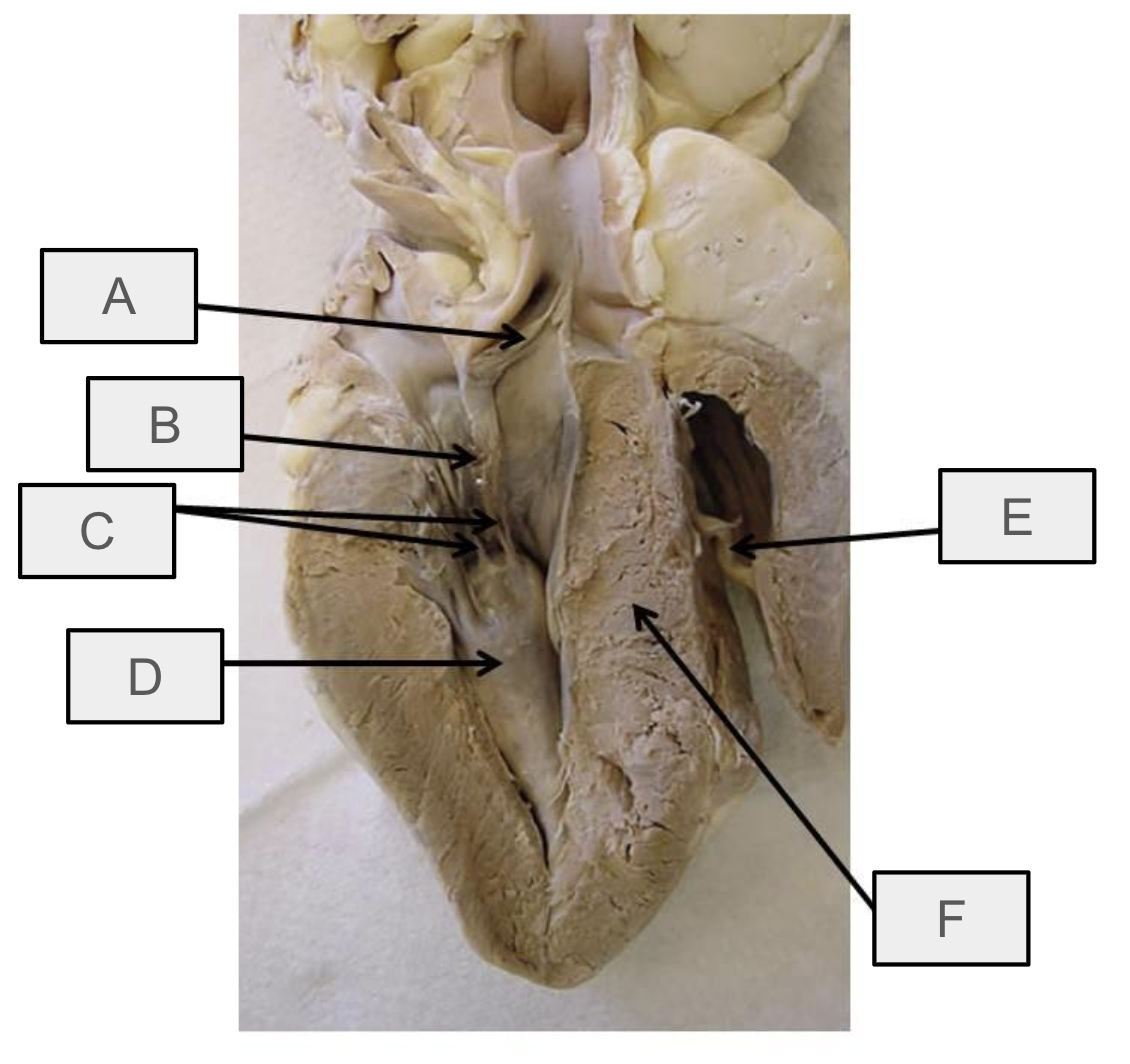
What is F
interventricular septum
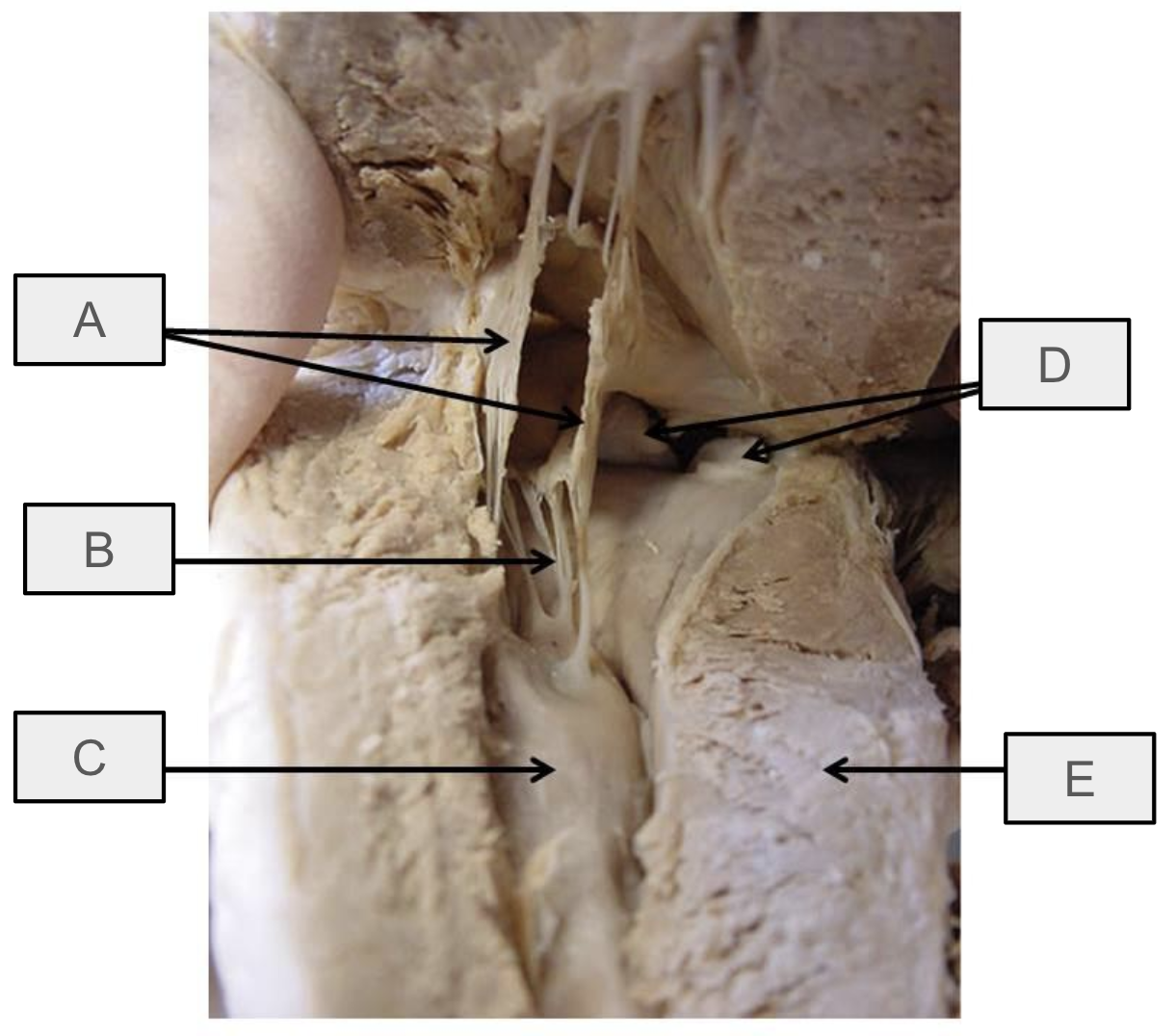
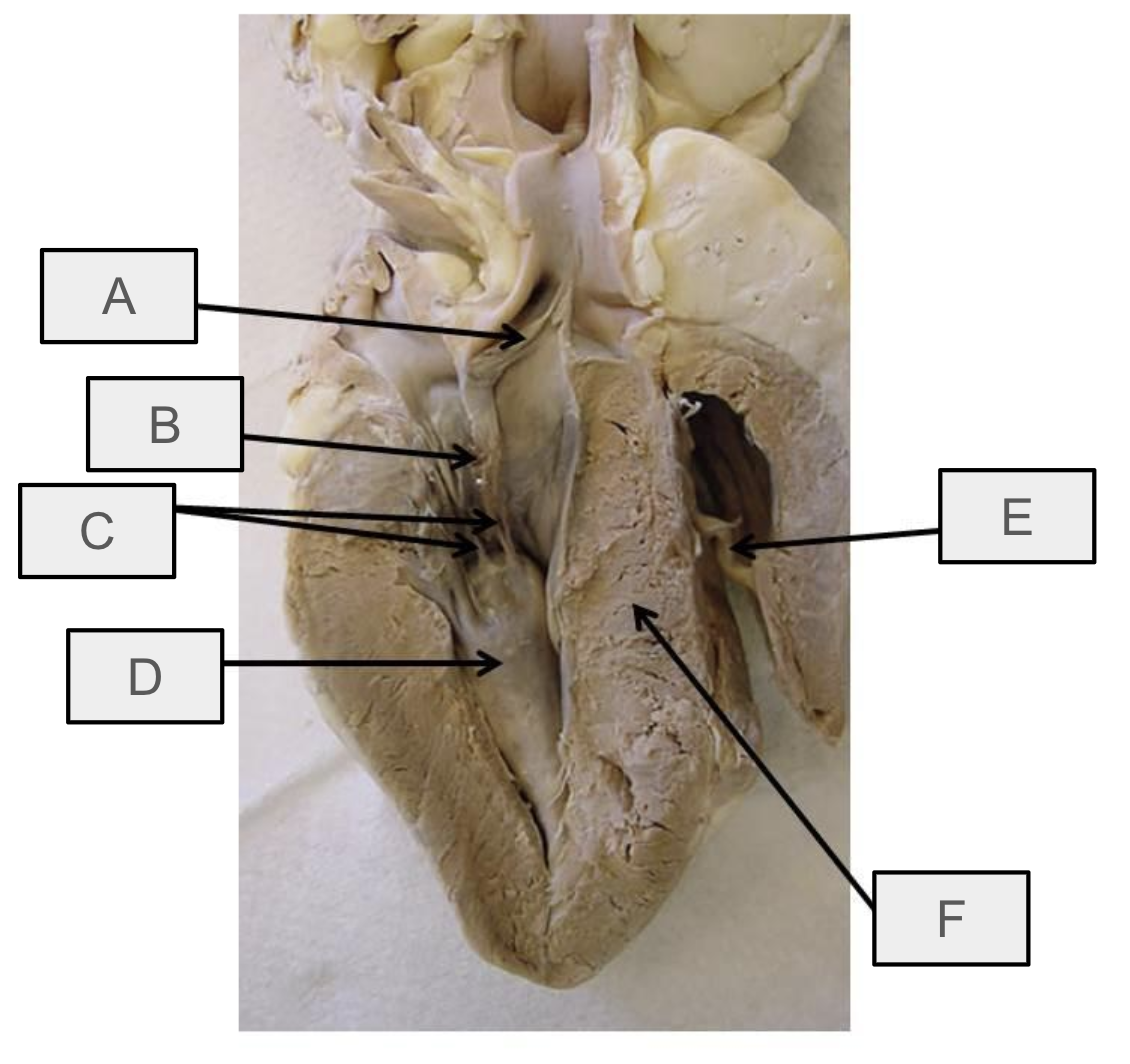
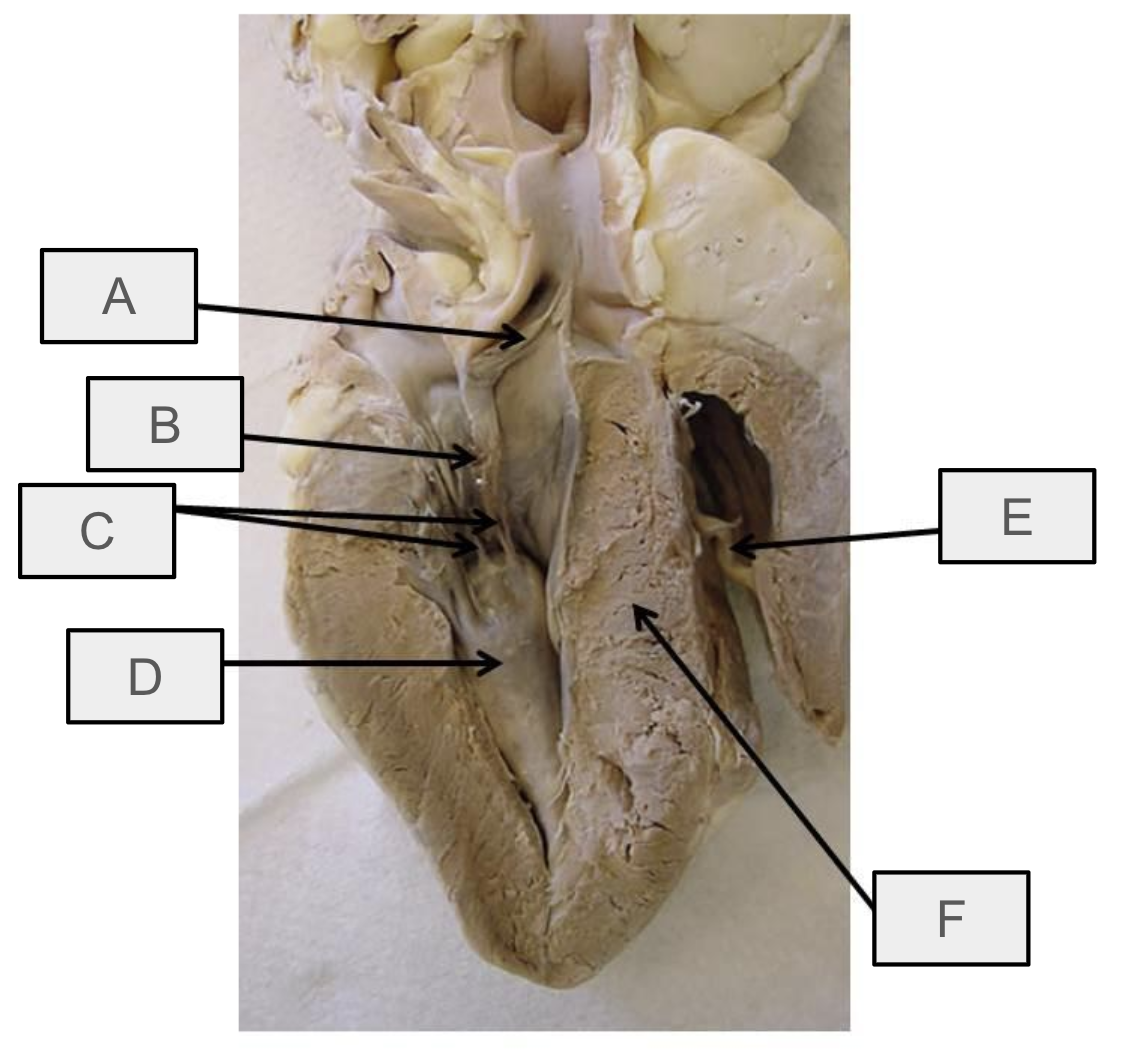
What is A
mitral valve
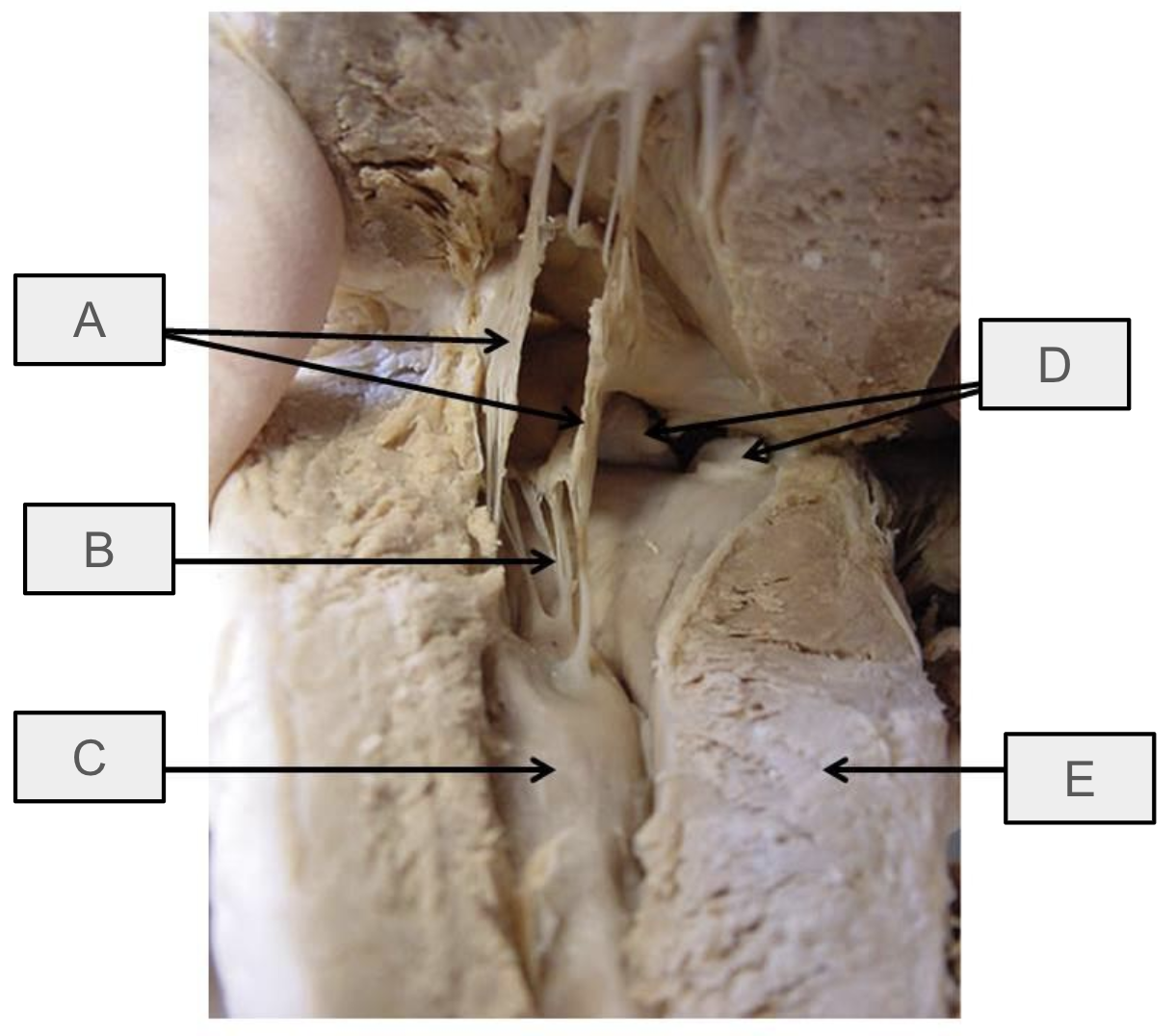
What is B
chorae tendineae
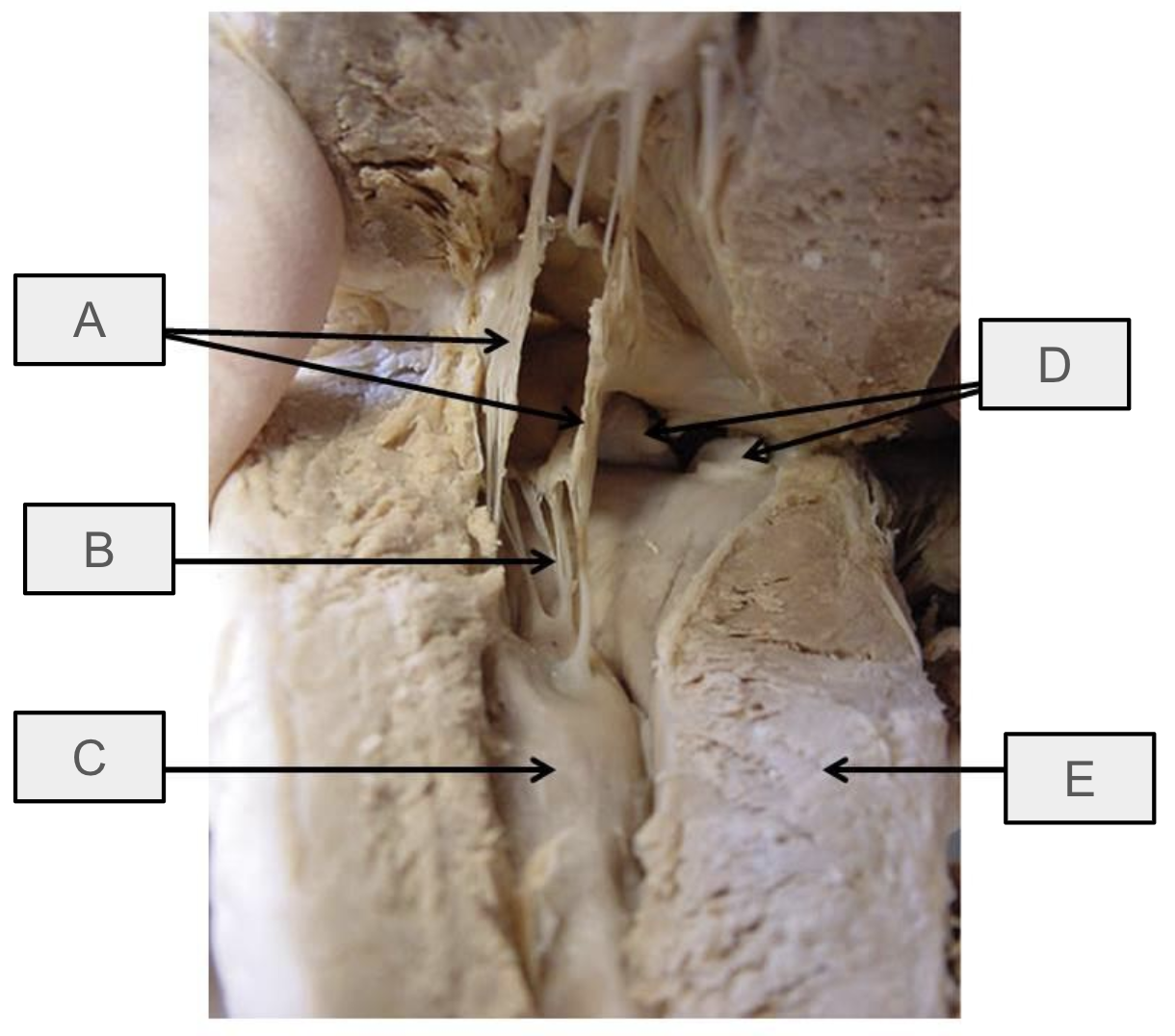
What is C
papillary muscle
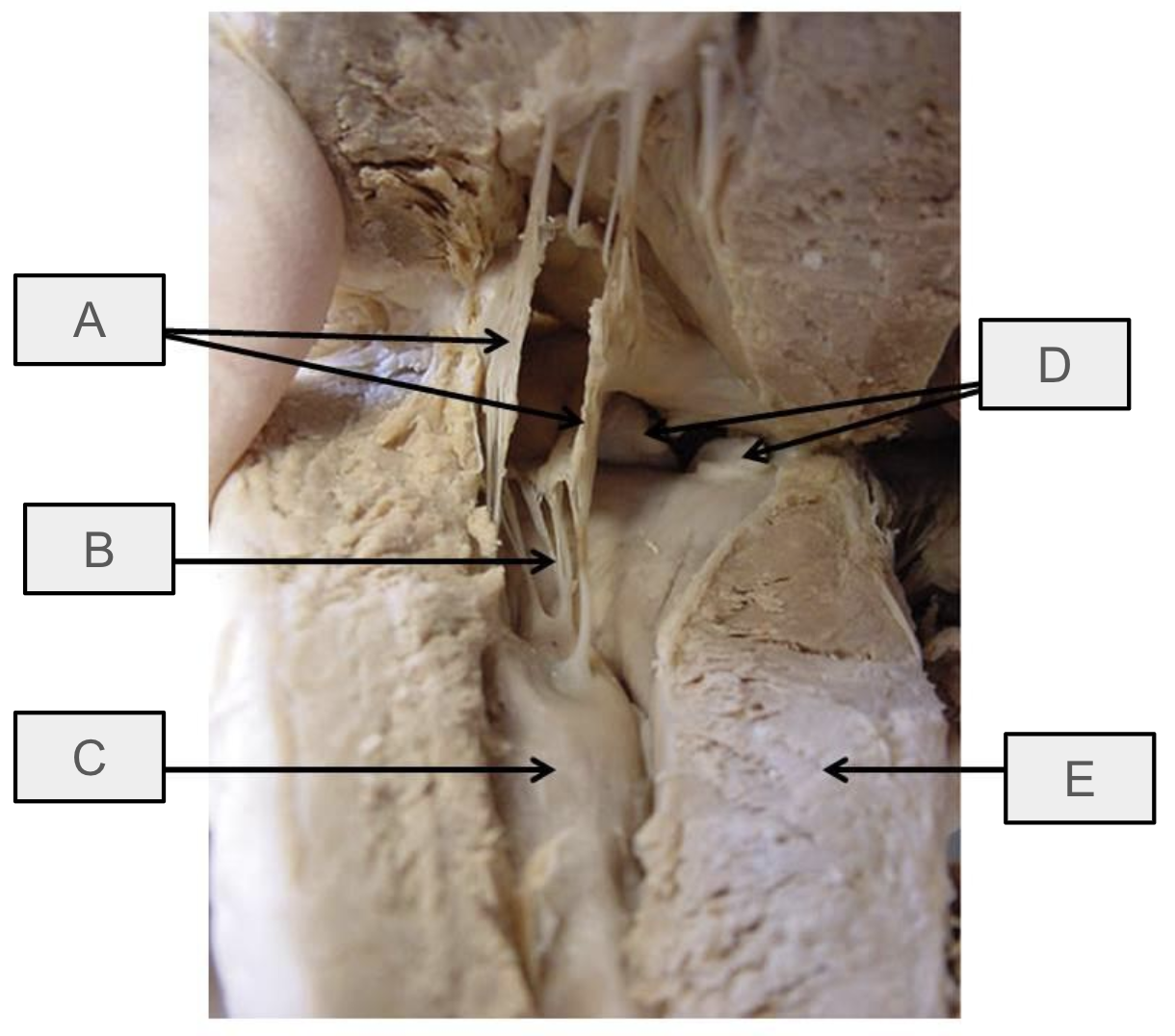
What is D
aortic semilunar valve
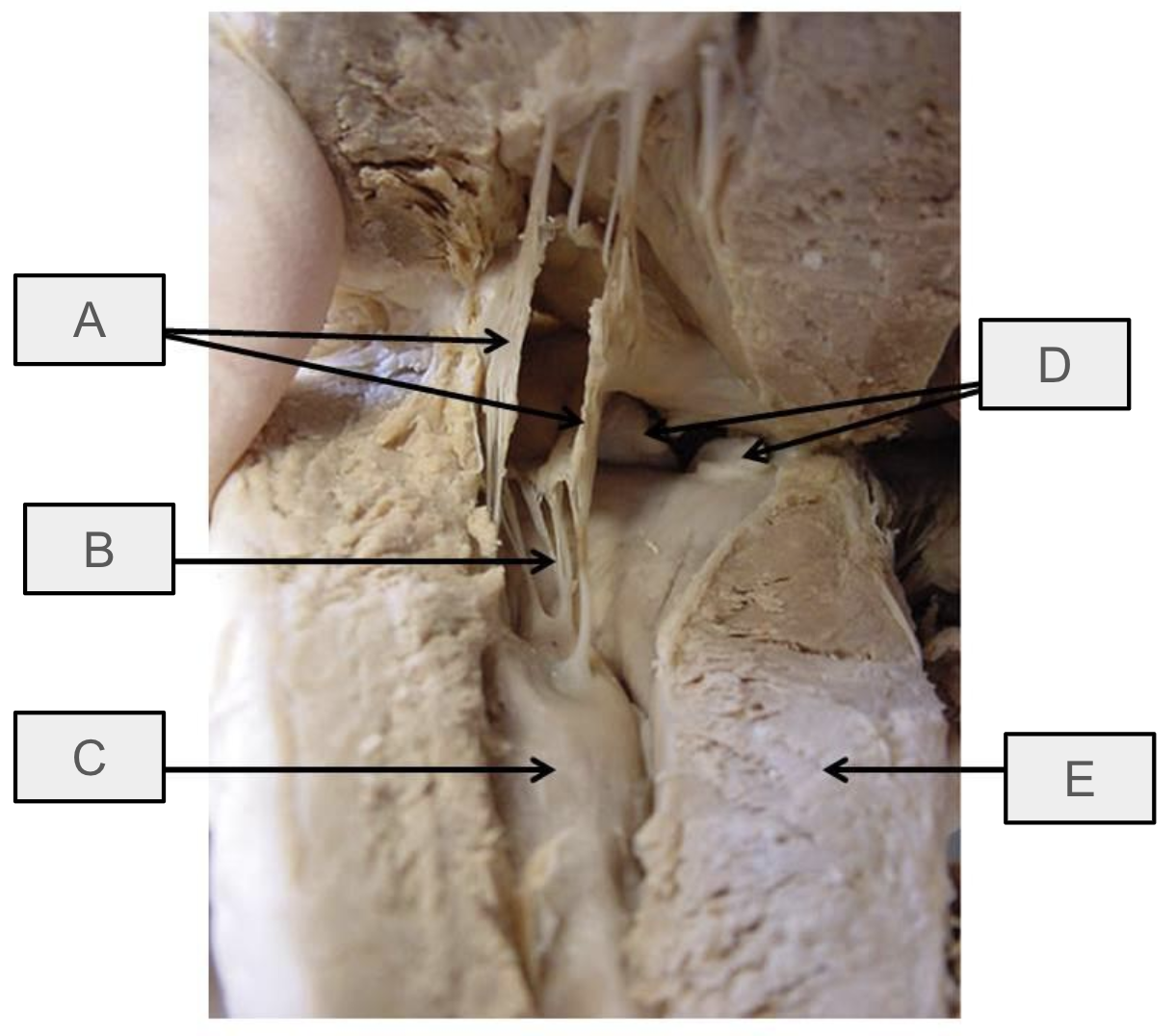
What is E
interventricular septum
A person with type B positive can safely get a blood transfusion from
someone with O or B type blood, either Rh positive or negative
A person with type A negative can safely receive blood from
A negative or O negative
A person with type O negative can safely receive blood from
O negative only
A person with type B negative can safely receive blood from
B negative or O negative
If there is agglutination in anti a and anti d, what would be the blood type?
A positive
If there is agglutination in anti a and anti b, what would the blood type be?
O negative
What is the difference between interval and segment in an EKG?
segment is the empty space between and interval is the actual wave

What is the condition shown?
second degree atrioventricular heart block
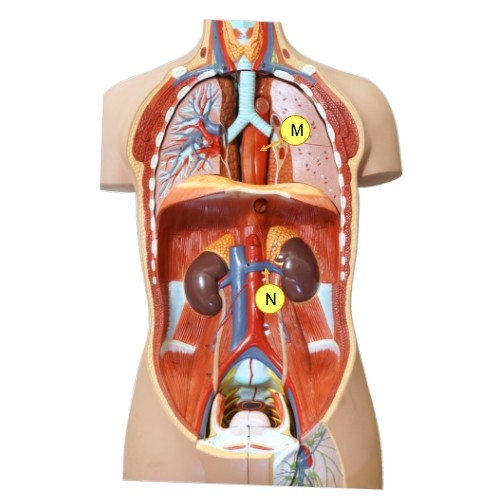
What is M?
Thoracic aorta
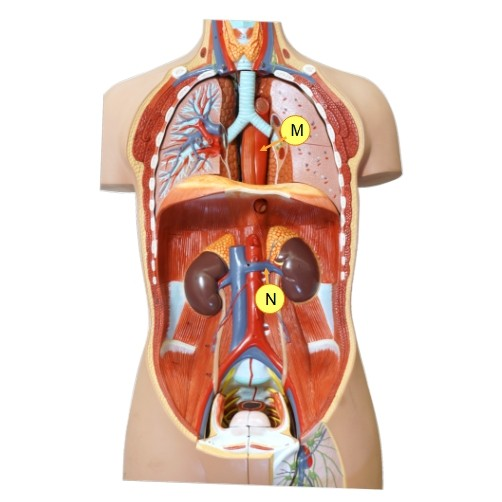
What is N?
renal vein
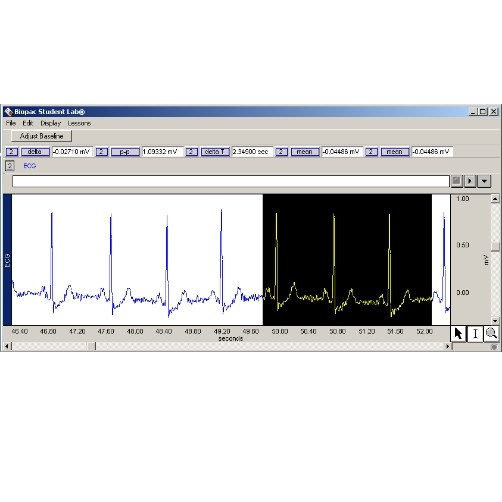
Select the correct setup of values for computing heart rate in BPM from the highlighted data.
(3 / 1.093 mV) x 60
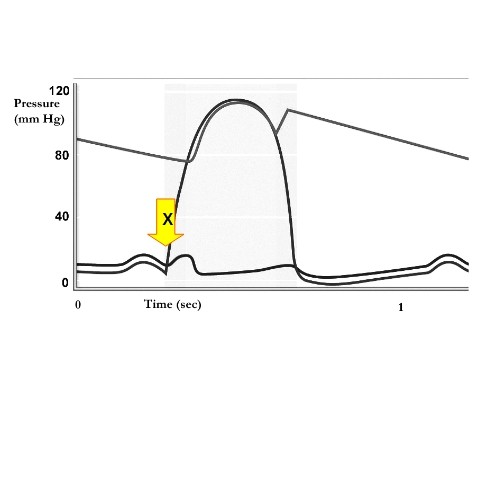
The curves represent aortic, left ventricular, and left atrial pressure levels over time. At time X, the valve condition change in progress is:
av valves closing
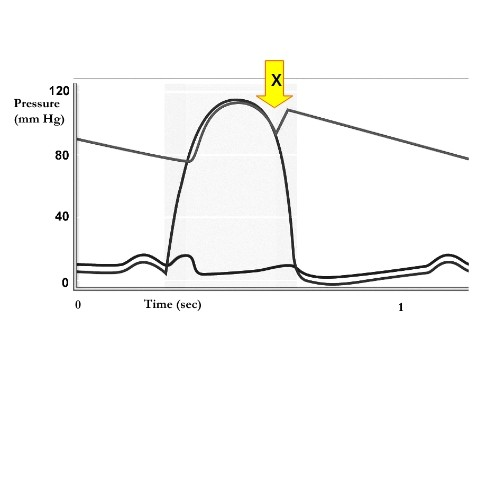
The curves represent aortic, left ventricular, and left atrial pressure levels over time. At time X, the valve condition change in progress is:
Pulmonary and aortic semilunar valves closing
A red blood cell is making one trip through the systemic circulation. Line up the named blood vessels with the order in which an RBC would pass through them. With these: external iliac, common iliac, and inferior vena cava
First: external iliac vein
Second: common iliac vein
Third: inferior vena cava
A red blood cell is making one trip through the systemic circulation. Line up the named blood vessels with the order in which an RBC would pass through them. With these: abdominal aorta, common iliac artery, external iliac artery, femoral artery
First: Abdominal aorta
Second: Common iliac artery
Third: External iliac artery
Fourth: Femoral artery
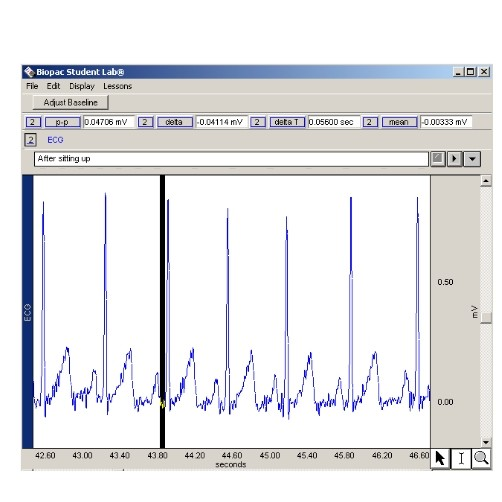
The highlighted period of time is a P-Q ______.
Its value is _____. Copy all digits of value, and follow with units.
segment; .05600 sec
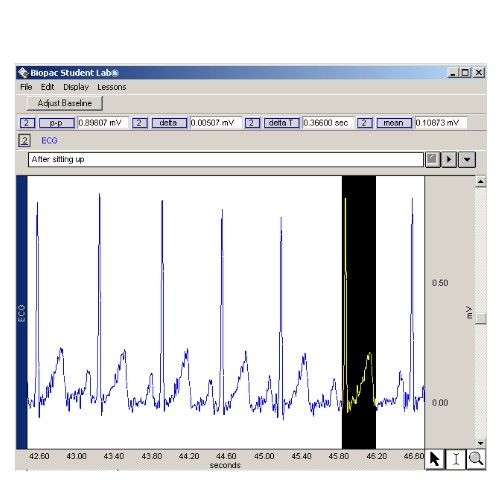
The highlighted period of time is an Q-T ____.
Its value is _____.
interval
0.36600 seconds
What is the funciton of a red blood cell?
to carry oxygen
What is the function of a platelet?
blood clotting
What is the function of a neutrol?
phagocytizes bacteria
What is the function of monocyte?
Differentiates into macrophages which phagocytizes pathogens
What is the function of a lymphocyte?
B and T cells of adaptive immune response
what is the function of eosinophils?
important in allergic reactions
What is the function of a basophil?
release histamine and heparin
What is antigen?
any large molecule capable of binding to an antibody or immune cells and trigger an immune response
What is an antibody?
a protein that reacts with an antigen and aids in protecting the body
Where is an antibody found?
in blood plasma
What will be the pacemaker of the heart if the SA node is damaged?
AV node
What does valve insufficiency mean?
a condition where a heart valve does not close properly, allowing blood to flow backward
When would mitral insufficiency produce a murmur?
systole
What problem would occur if the P-R interval got a lot shorter?
improper filling of the ventricles would occur
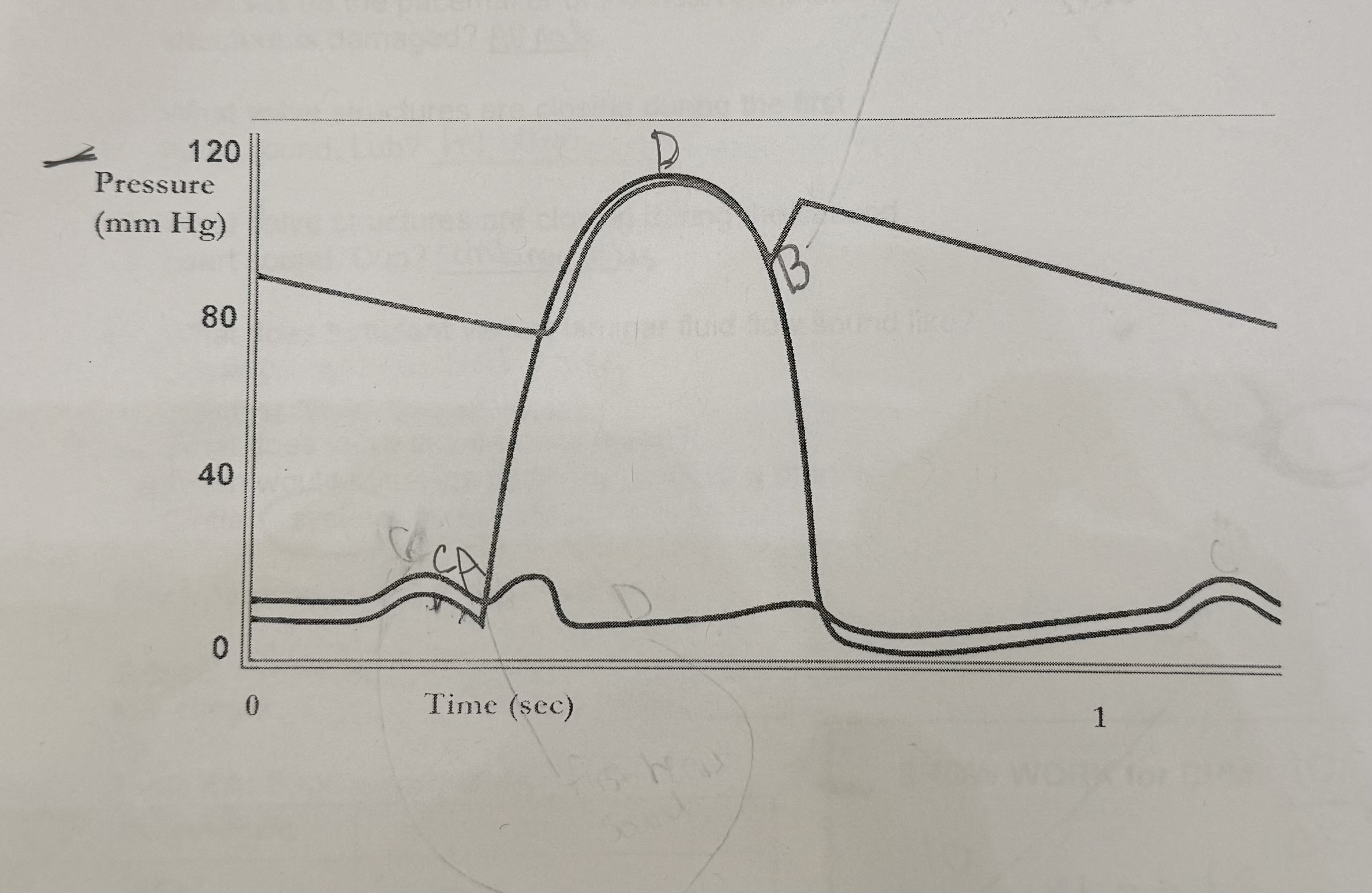
What happens at A?
mitral valves close, first heart sound
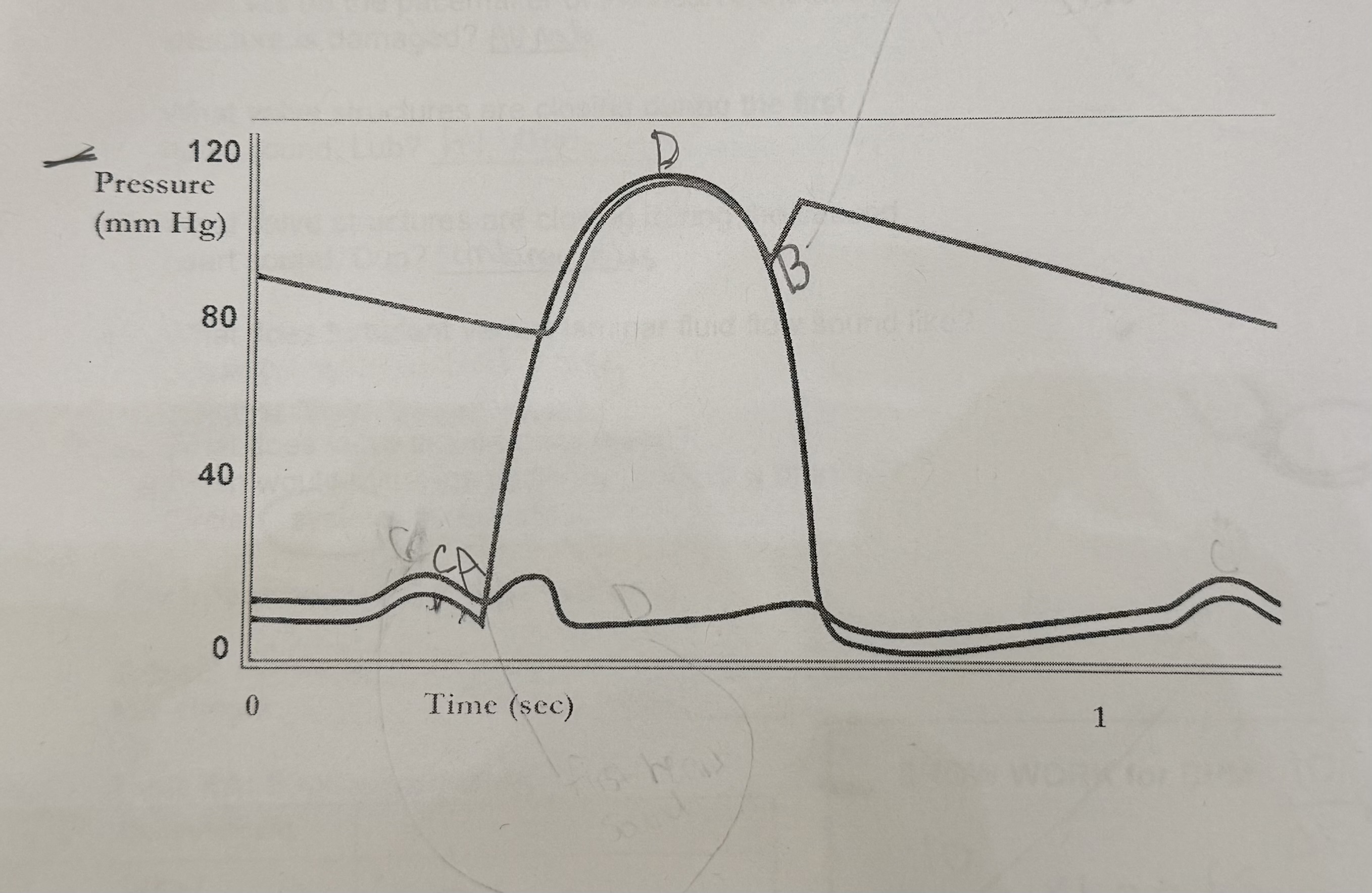
What happens at B?
semilunar valves close, second heart sound
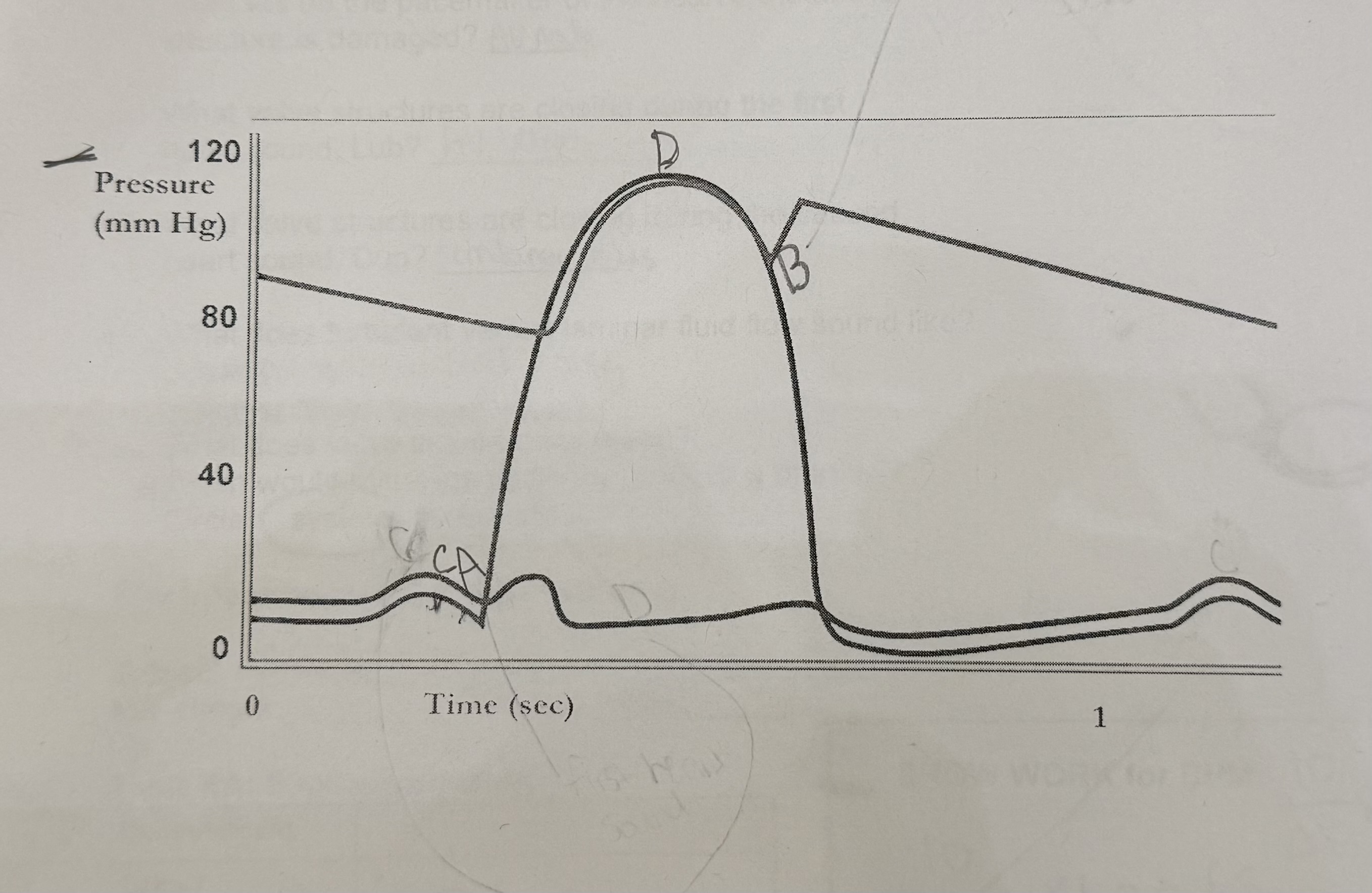
What should happen at C?
the QRS complex should start
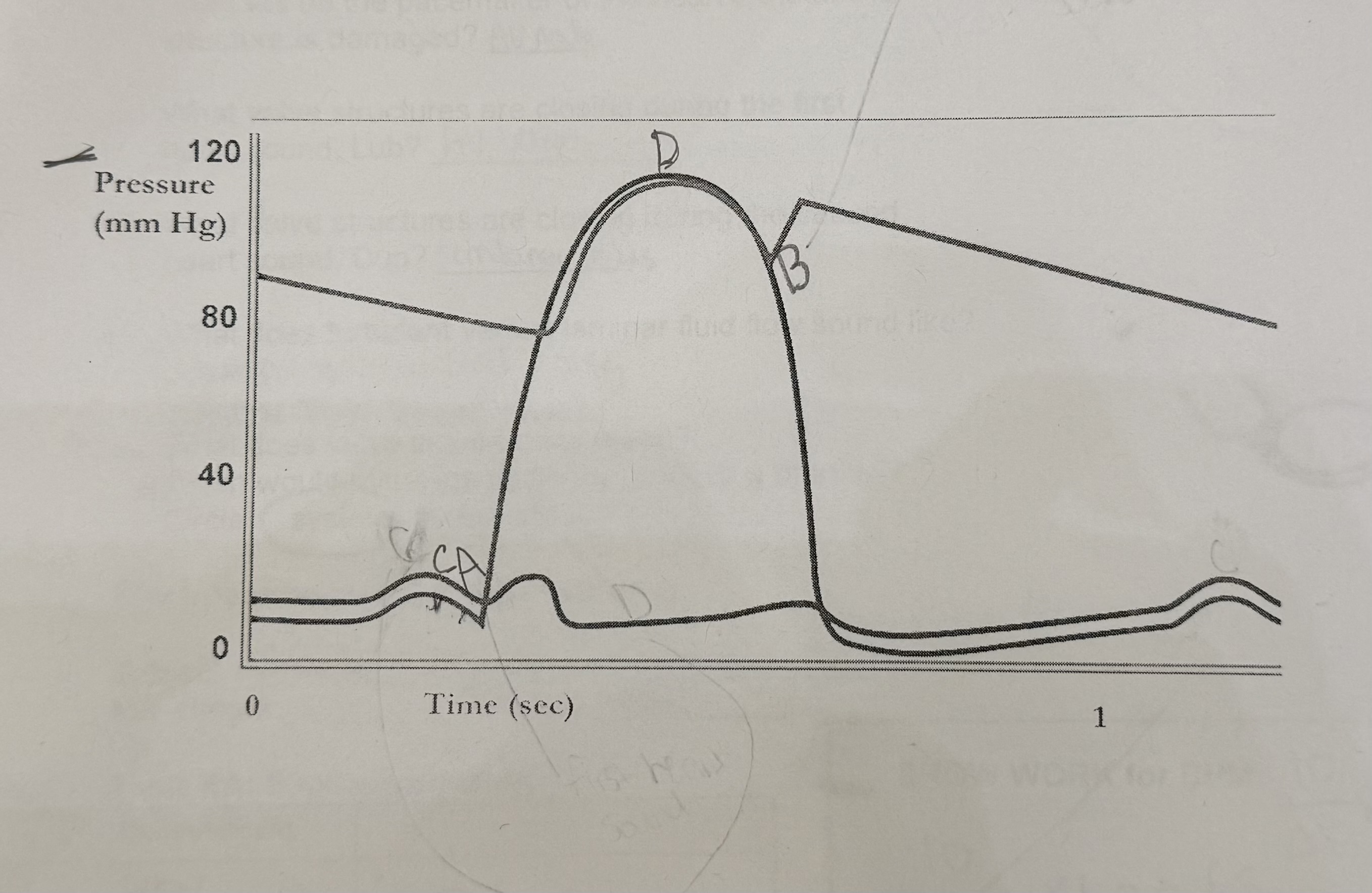
What should happen at D?
time the T wave should start
The artery will have a _____ tunica media than the vein
thicker
the artery will have a _____ visible lumen than the vein does
smaller
During exercise, blood vessel resistance in muscle tissue should ____
decrease
During exercise, blood vessel resistance in gut and skin should ____
increase
During exercise, Total peripheral resistance of the circulation should ____
decrease
During exercise, the MAP should _____
increase
What is Mean Arterial Pressure
the average pressure in the arteries during a cardiac cycle (heartbeat)
During exercise, pulse pressure should ___
increase
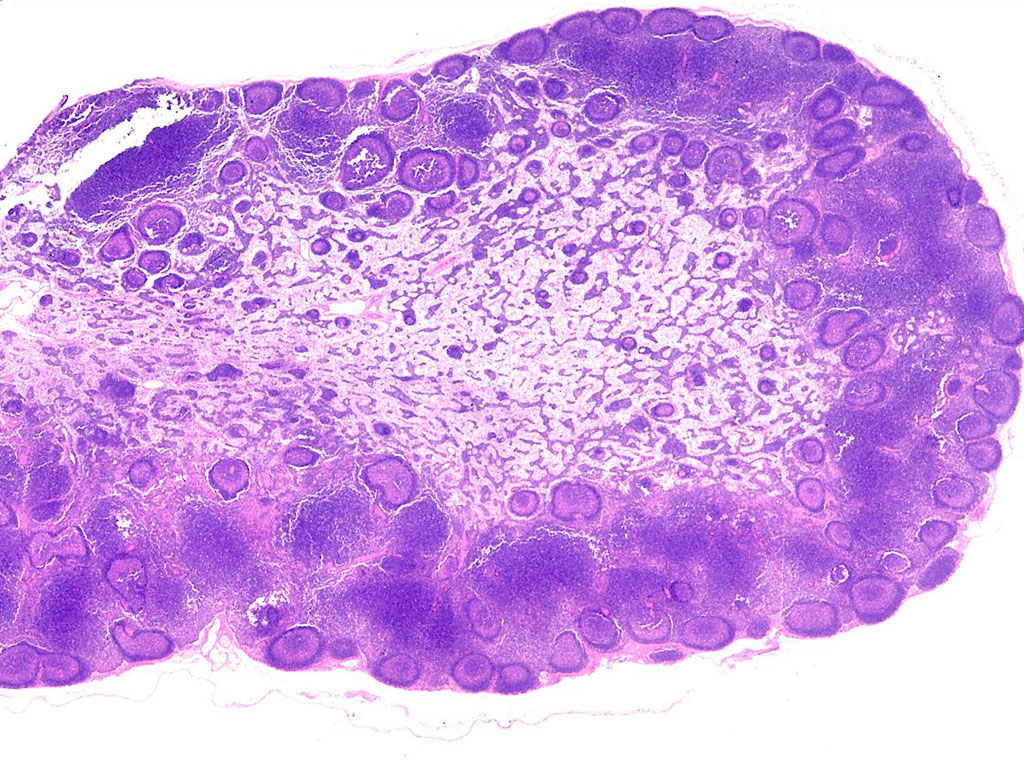
What is this a slide of?
lymph node
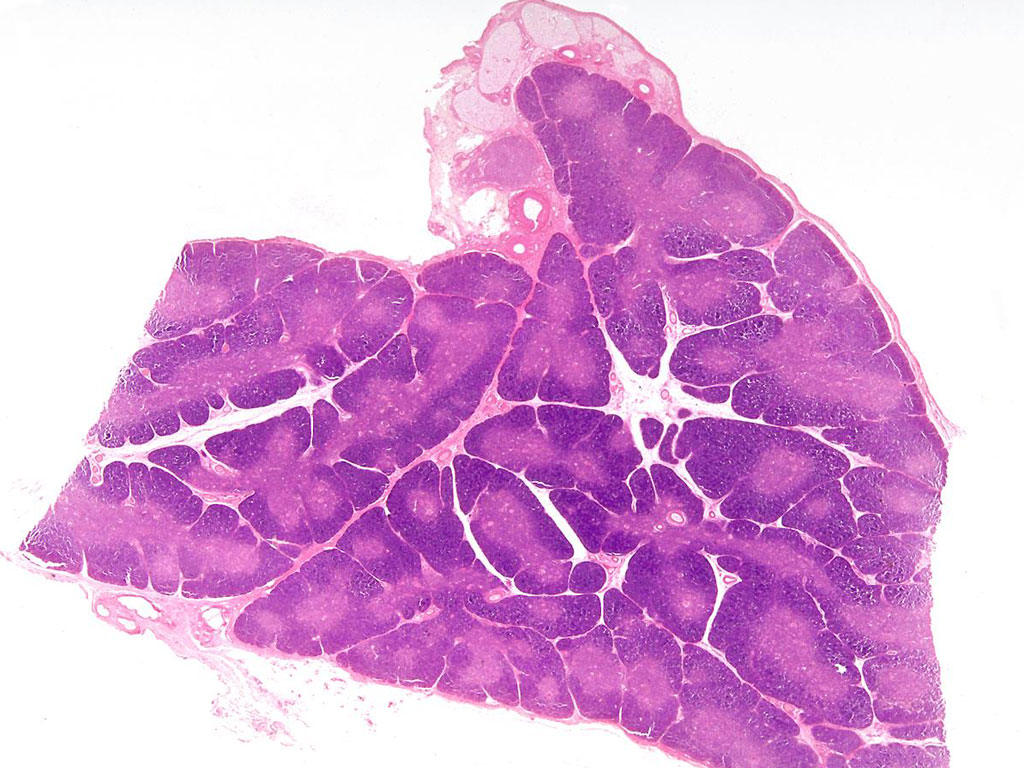
What is this a slide of?
thymus
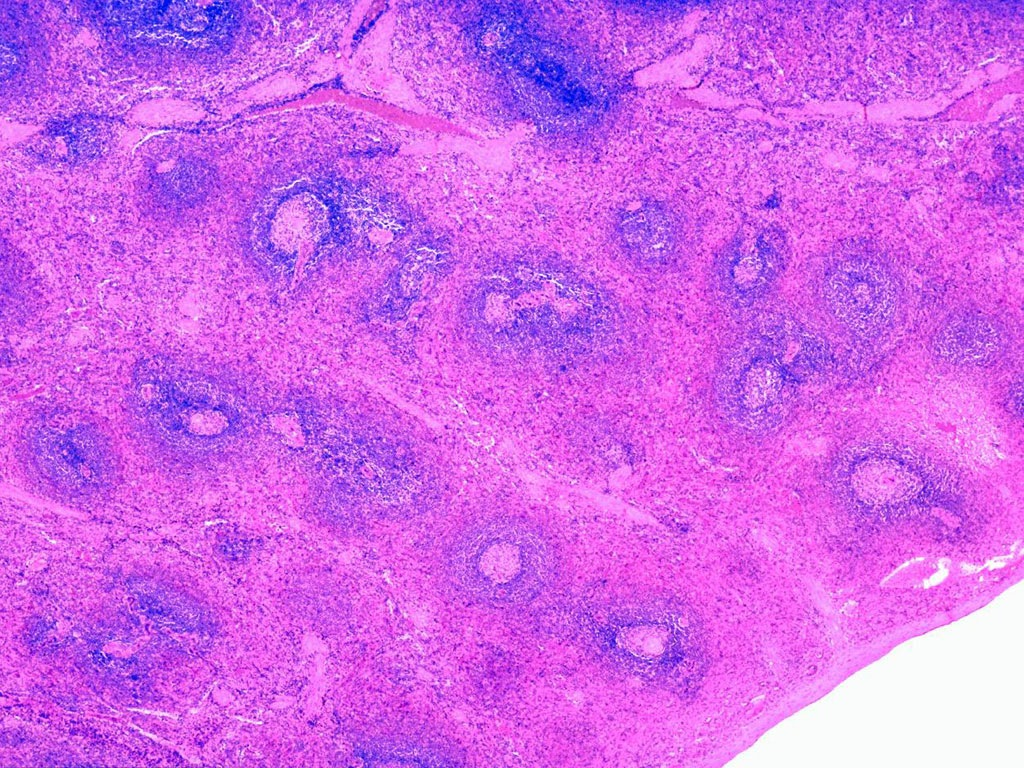
What is this a slide of?
spleen
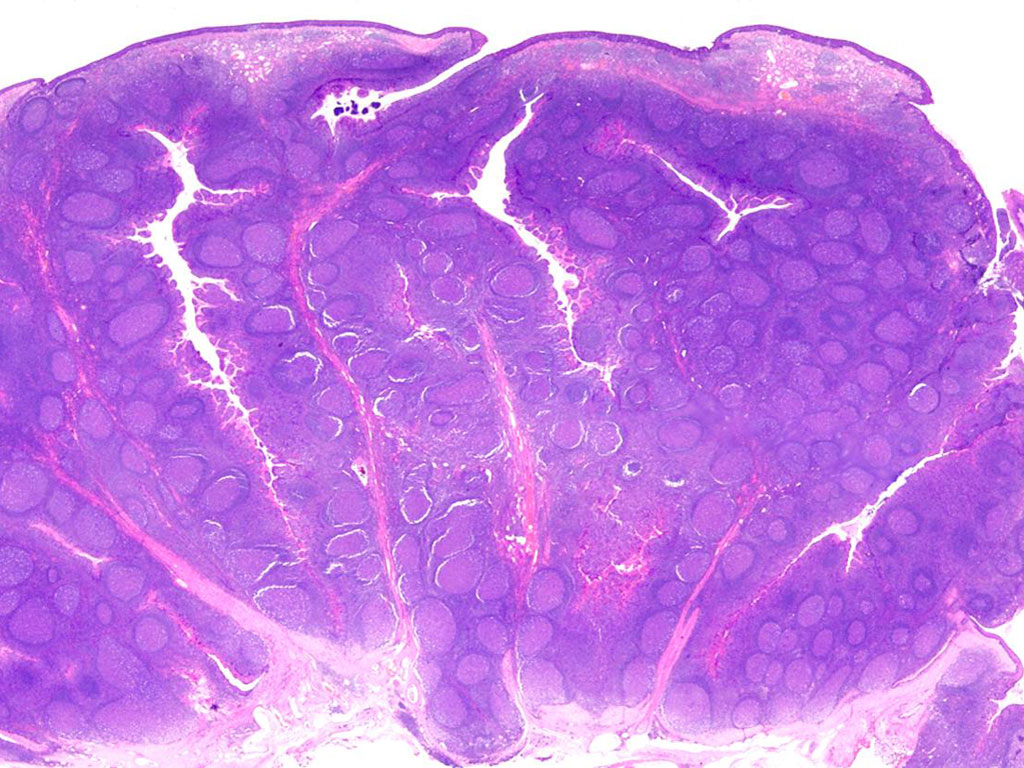
What is this a slide of ?
Palatine Tonsil
What happens in the red pulp?
filtering blood by removing the old and damaged
What happens in the white pulp?
detects pathogens and adaptive immune response