I PRAY to STATS – Core Vocabulary
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Key statistical vocabulary extracted from the 'I PRAY to STATS' lecture notes, covering basic descriptive statistics, sampling methods, experimental design, common fallacies, graphical displays, regression, probability distributions, confidence intervals, hypothesis testing, and useful combinatorial principles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Mean (Arithmetic)
Sum of all measurements divided by the number of observations; symbol μ for a population and x̄ for a sample.
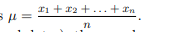
Median
The middle value that splits an ordered dataset into two equal halves.
Mode
The most frequently occurring value in a dataset.
Interquartile Range (IQR)
Difference between the third quartile (Q3) and the first quartile (Q1); measures spread of the middle 50 %. IQR = 3 - Q1
Range
Largest value minus smallest value in a dataset; a crude measure of variability.
Standard Deviation (σ or s)
A measure of the amount of variation a variable has about its mean. σ for a population. s for a sample. For a sample standard deviation, you must divide by n -1.
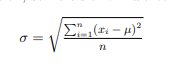
Variance
Square of the standard deviation; additive for independent variables.
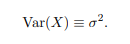
Outlier
A data point that differs markedly from the overall pattern of the data.
IQR Rule
A point is an outlier if it is < Q1 – 1.5·IQR or > Q3 + 1.5·IQR.
Robust Estimator
Statistic that is little-affected by outliers (e.g., median, IQR).
Unbiased Estimator
Statistic whose expected value equals the true population parameter (e.g., sample mean for μ).
Sampling
Selecting a subset of individuals from a population to estimate characteristics of the whole.
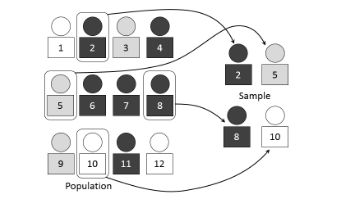
Simple Random Sample (SRS)
Every subset of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
Stratified Sampling
Population divided into homogeneous strata (similar characteristics), and an is SRS taken within each stratum.
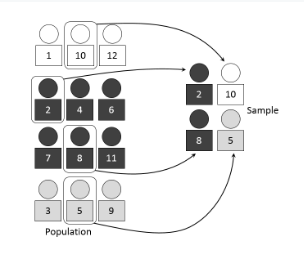
Cluster Sampling
Population split into clusters (naturally occurring groups); some clusters randomly chosen and all members studied.
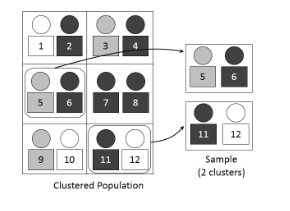
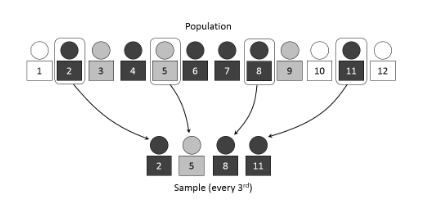
Systematic Sampling
Selecting every k-th element after a random start in an ordered list.
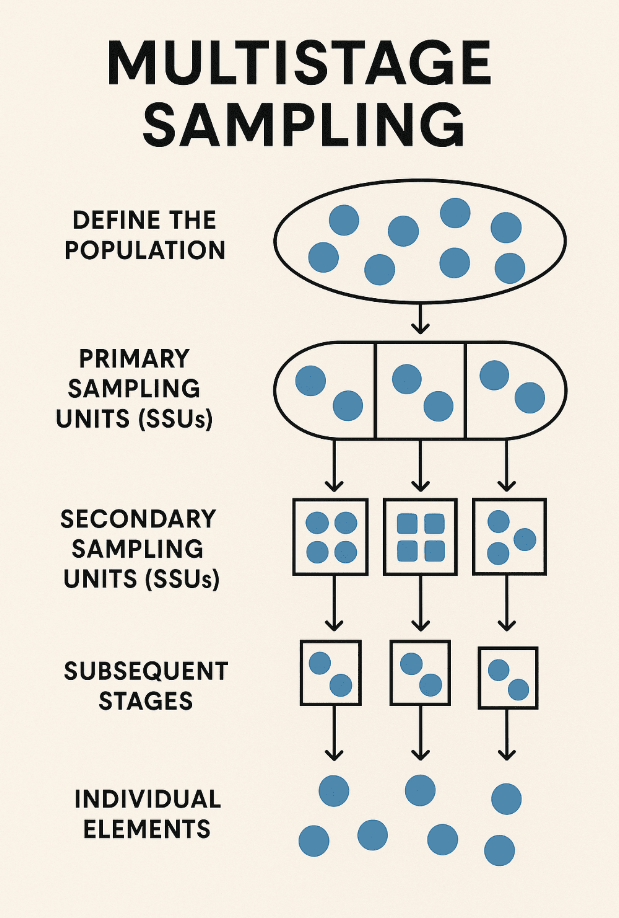
Multistage Sampling
Successive sampling of clusters within clusters until reaching the final sampling units.
Probability-Proportional-to-Size Sampling
Selection probability of each element is proportional to how big its subgroup is
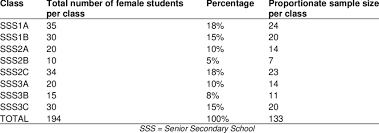
Line-Intercept Sampling
Elements included if intersected by a pre-chosen line segment (transect). Used to measure any features that intersect a line, usually used in vegetation
Panel Sampling
Same sampled individuals are surveyed repeatedly over time.
Nonprobability Sampling
Sampling procedure where some population members have unknown or zero chance of selection.
Bias (Statistical)
Systematic tendency that skews results away from the true value.
Sampling Bias
Sample not representative because selection probabilities differ across population members.
Non-response Bias
When people respond to a poll or a survey differ meaningfully from non-respondents, distorting results. Also known as participation bias
Undercoverage Bias
Part of the population is systematically excluded from the sampling frame.
Self-selection Bias
Individuals decide themselves to participate, often those with strong opinions.
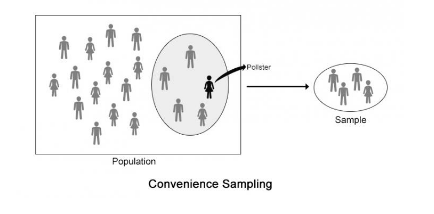
Convenience Sampling
Sample drawn from units that are easiest to access.
Voluntary Response Sampling
Participants volunteer to respond; prone to extreme opinions.
Quota Sampling
Like SRS but does NOT randomly select members to fill each quota. Instead, researchers fill quotas based on specific characteristics until they reach a predetermined number for each category, which can lead to bias.
Snowball Sampling
Existing participants recruit future participants, building a sample via referrals. This can cause bias through participants being more likely to refer people with similar opinions.
Experimental Factor
Variable that is deliberately manipulated by the researcher in an experiment.
Treatment
Specific combination of conditions applied to experimental units.
Block
A group of similar experimental units or observations that are grouped together to reduce variability in an experiment or analysis.
Experimental Unit
Smallest entity to which a treatment is independently applied. The thing being experimented on
Level (of a factor)
Specific setting, value, category, or just the name of an experimental factor (independent variable) that is being tested.
Simpson’s Paradox
Trend that appears in several groups that dissapears or reverses when groups are combined.
Gambler’s Fallacy
Belief that deviations from expected behavior must be corrected in the short run.
Hot-Hand Fallacy
Assuming a run of successes makes further success more likely. Also known as the Monte-Carlo fallacy.
Base-Rate Fallacy
Ignoring relevant statistical information (base rates) when evaluating specific evidence.
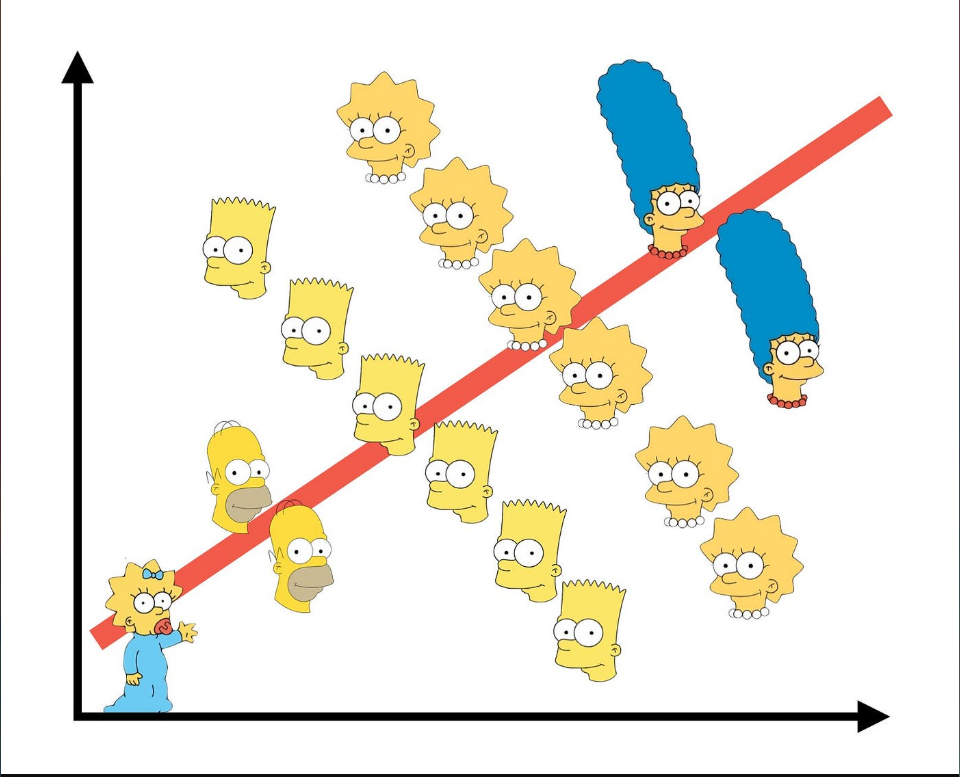
Will Rogers Phenomenon
Moving an observation from one group to another increases both groups’ averages. Also known as the Okie Paradox.
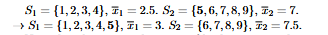
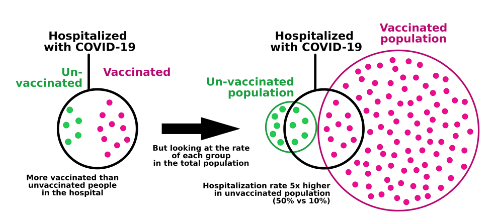
Berkson’s Paradox
A result that makes it seem that two unrelated variables appear to be correlated (usually negatively).
Nominal Data
Categorical data with no intrinsic ordering (e.g., eye color).
Ordinal Data
Categorical data with a meaningful order but unequal intervals (e.g., class rank).
Interval Data
Numeric data with equal intervals but no true zero (e.g., temperature °C).
Ratio Data
Numeric data with equal intervals and a true zero (e.g., weight).
Pie Chart
Circular chart where slice areas show category proportions.
Bar Chart
Rectangular bars represent categorical frequencies or values.
Mosaic Plot
Tile plot showing joint distribution of two (or more) categorical variables.
Scatter Plot
Graph of paired quantitative data; used to study relationships.
Histogram
Bar graph of binned numerical data frequencies.
Box Plot
Displays median, quartiles and potential outliers of numerical data.
Dot Plot
Dots along a number line show individual data points; good for small n.
Stem-and-Leaf Plot
Splits numbers into stems and leaves to display shape and raw data.
Line Graph
Connects data points with lines to show trends over time or sequence.
Normal Q–Q Plot
Plots data quantiles against theoretical normal quantiles to assess normality.
Residual Plot
Graph of residuals versus predicted values; checks model fit assumptions.
Ogive
Cumulative frequency curve of numerical data.
Least-Squares Regression Line (LSRL)
Line that minimizes the sum of squared vertical residuals.
Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r)
Measures strength and direction of linear relationship (−1 to +1).
Coefficient of Determination (r²)
Proportion of variance in y explained by x via the model.
Covariance
Average product of deviations of two variables; sign indicates relationship direction.
Residual (e)
Observed value minus predicted value (y – ŷ).
High Leverage Point
Observation with an extreme x-value relative to others.
Influential Point
Observation that markedly changes regression slope or intercept if removed.
Extrapolation
Predicting beyond the range of observed x; often unreliable.
Interpolation
Predicting within the range of observed x; usually reliable.
Homoscedasticity
Residual variance is constant across levels of the predictor.
Heteroscedasticity
Residual variance changes with the predictor; fan-shape pattern.
Sum of Squares Total (SST)
Total variability in y: Σ(yi – ȳ)².
Sum of Squares Regression (SSR)
Explained variability: Σ(ŷi – ȳ)².
Sum of Squares Error (SSE)
Unexplained variability: Σ(yi – ŷi)².
Probability Distribution
Function that assigns probabilities to all possible outcomes of a random variable.
Normal Distribution
Bell-shaped, symmetric continuous distribution described by μ and σ.
Empirical Rule (68-95-99.7)
For normal data, ~68 % within 1 σ, 95 % within 2 σ, 99.7 % within 3 σ.
z-Score
Standardized value: (x – μ)/σ; counts SDs from the mean.
Percentile
Value below which a specified percentage of observations fall.
Student’s t-Distribution
Symmetric distribution with heavier tails; used when σ unknown and n small (df = n–1).
t-Score
Standardized statistic using sample s and t-distribution.
Sampling Distribution
Probability distribution of a statistic over all possible samples of a fixed size.
Central Limit Theorem (CLT)
Sampling distribution of the mean approaches normal as n increases, regardless of population shape.
Law of Large Numbers
Sample mean converges to the population mean as sample size grows.
Uniform Distribution
All outcomes in an interval are equally likely.
Binomial Distribution
Counts number of successes in n independent Bernoulli trials with probability p.
Geometric Distribution
Counts trials needed to get the first success in repeated Bernoulli trials.
Chi-Square Distribution
Distribution of the sum of squared standard normals; parameter df (k).
Negative Binomial Distribution
Number of failures before r successes occur in Bernoulli trials.
Hypergeometric Distribution
Success count in draws without replacement from a finite population.
Poisson Distribution
Models number of events in a fixed interval given constant mean rate λ.
Confidence Interval
Interval estimate that likely contains the population parameter at a stated confidence level.
Confidence Level
Long-run proportion of CIs that capture the true parameter (e.g., 95 %).
Critical Value (z* or t*)
Cutoff on the reference distribution that matches the desired confidence level.
Margin of Error
Half-width of a confidence interval; (critical value) × (standard error).
Null Hypothesis (H₀)
Default claim that there is no effect or difference.
Alternative Hypothesis (Hₐ)
Claim of an effect or difference that we seek evidence for.
p-Value
Probability of observing a result at least as extreme as the sample, assuming H₀ is true.
Significance Level (α)
Threshold probability for rejecting H₀ (commonly 0.05).
Type I Error
Rejecting a true null hypothesis; false positive; probability = α.
Type II Error
Failing to reject a false null hypothesis; false negative.
Power (1 – β)
Probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis.
Bayes’ Theorem
P(A | B) = P(B | A) · P(A) / P(B); updates probabilities with new evidence.