Peds Unit 3 Review
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
what is a thrill?
vibration felt on the chest due to murmur (valve not closing) or stenosis (contraction of artery)
congestive heart failure patho, symptoms, care
heart can’t pump blood so fluid gets back up into lungs and body; sx: HR and RR increases, muscle walls thicken, retractions and flaring, fatigue, poor feeding (diaphoresis), decreased urine output, weight gain, edema (periorbital), SOB, exercise intolerance; care: weights, VS, I&O, energy-saving interventions
foramen ovale
hole that closes during infancy between the right and left atria
ductus arteriosus
blood vessel connects aorta and pulmonary artery that closes in first 72 hours of lifea
atrial septal defect (ASD)
hole between the atria where oxygenated blood from left atrium is shunted to the right atrium and lungs, systolic murmur is heard, surgical closure before school age, acyanotic
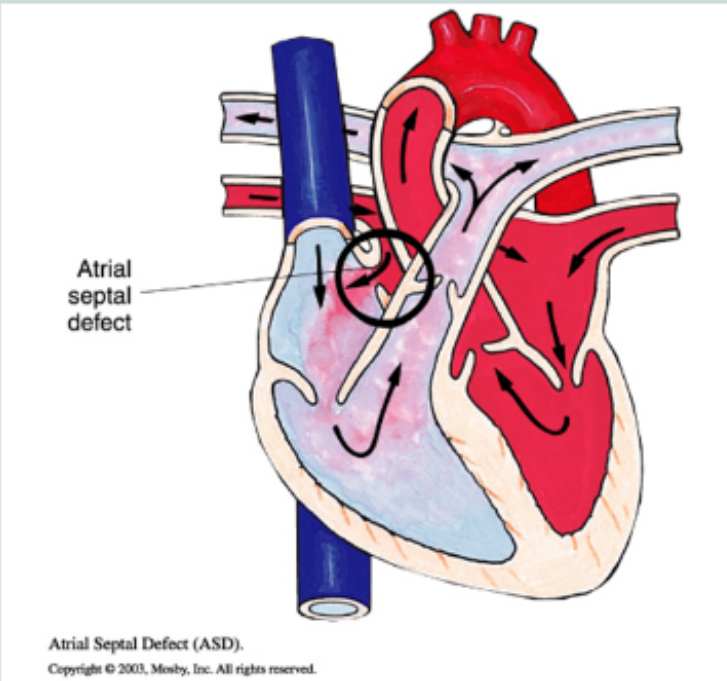
ventricular septal defect (VSD)
oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the right ventricle and lungs, loud and harsh systolic murmur, large defects can cause Eisenmenger syndrome and require surgical closure, acyanotic
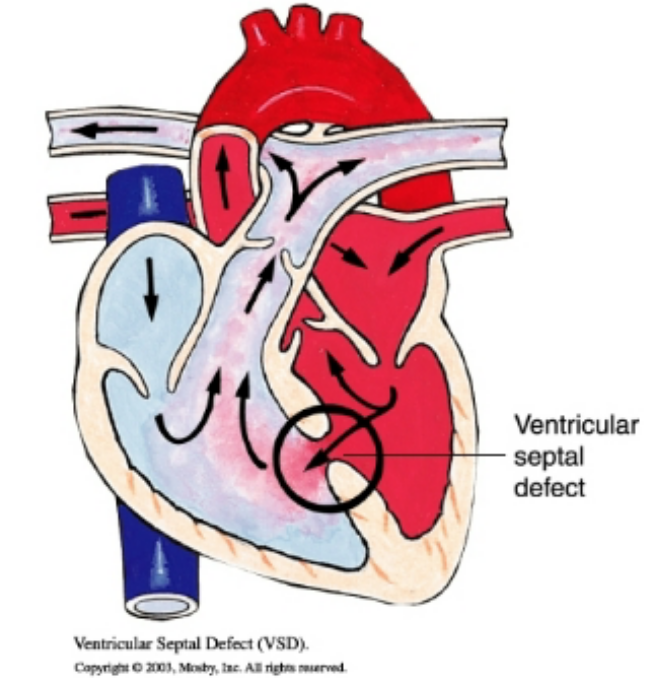
patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
opening between aorta and pulmonary artery so that oxygenated blood from aorta returns to the pulmonary artery and lungs causing pulmonary hypertension, “machine-like murmur”, indomethacin (NSAID inhibits synthesis of prostaglandin) or surgical intervention, increase risk for stroke, infection, and aneurysm, acyanotic
Eisenmenger syndrome
pulmonary resistance equals or exceeds systemic resistance due to long term pulmonary blood flow so blood flow switches to cause cyanosis, can cause permanent irreversible damage, life-threatening, from unrepaired ASD, VSD, PDA
coarctation of the aorta
obstructive narrowing of the aorta near aortic valve or DA, systolic murmur with an ejection click or palpable thrill, upper extremity bounding pulse with hypertension but lower extremity have weak pulses, may require surgical correction with dilation
hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS)
mixed cyanotic, underdevelopment of left-side heart structures (left ventricle, mitral and/or aortic valves, and aorta and aortic arch), nonfunctioning LV is bypassed entirely, ASD typically present and needed to allow oxygenated pulmonary venous blood to mix with deoxygenated venous blood in RA, Prostaglandin E is given to keep PDA until surgery
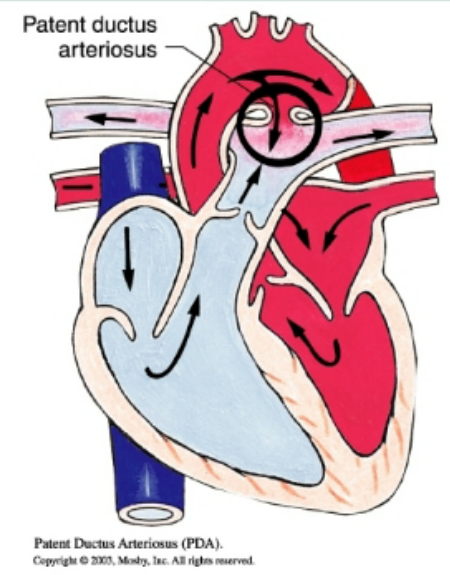
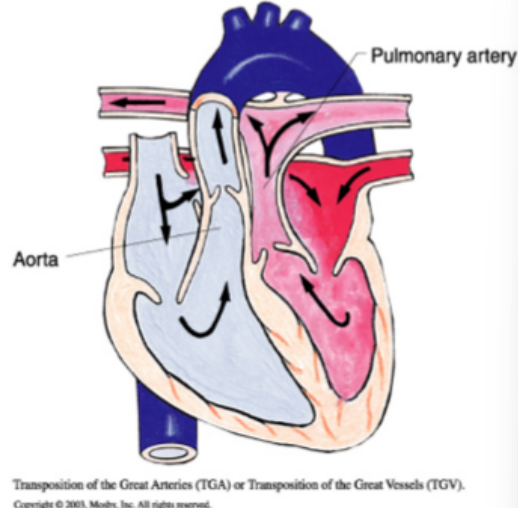
transposition of the great vessels/arteries
pulmonary artery leaves the left ventricle and aorta leave the right ventricle, “egg on a string” appearance on X-Ray, incompatible with life unless ASD, VSD, and/or PDA is present, prostaglandin E given to maintain PDA, cyanotic
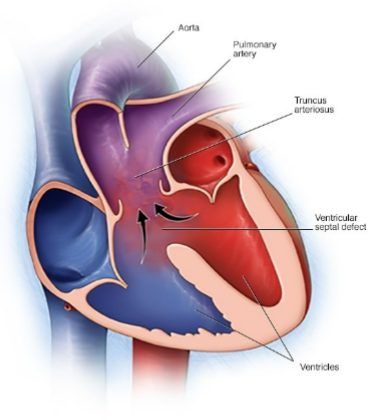
truncus arteriosus
pulmonary artery and aorta do not separate so one main vessel receives blood from RV and LV, large VSD mixed blood in RV and LV, mixed cyanosis, increases pulmonary resistance, VSD is only reason for life, needs surgical correction
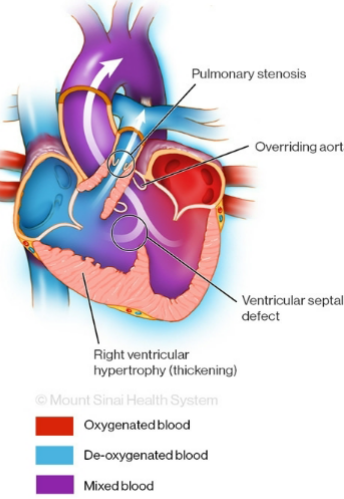
tetralogy of Fallot (TOF)
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Aorta displacement (open to LV and RV)
Pulmonary valve stenosis
Septal defect (VSD)
“boot shaped heart” on x-ray, child experiences “tet” spells which are relieved by squatting or knee-chest position, needs staged surgeries
tet spell
decreased O2 Sat and development of cyanosis after crying, feeding, activity or when agitated, knee to chest position or squatting increases systemic vascular resistance which decreases right-to-left shunting
kawasaki disease definition and treatment
Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome, acute systemic vasculitis that damages vessels and coronary artery after defective immune response to infection, leads to aneurysm or myocarditis
treated with aspirin (reduce clots and inflammation) and IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) to decrease inflammatory effect
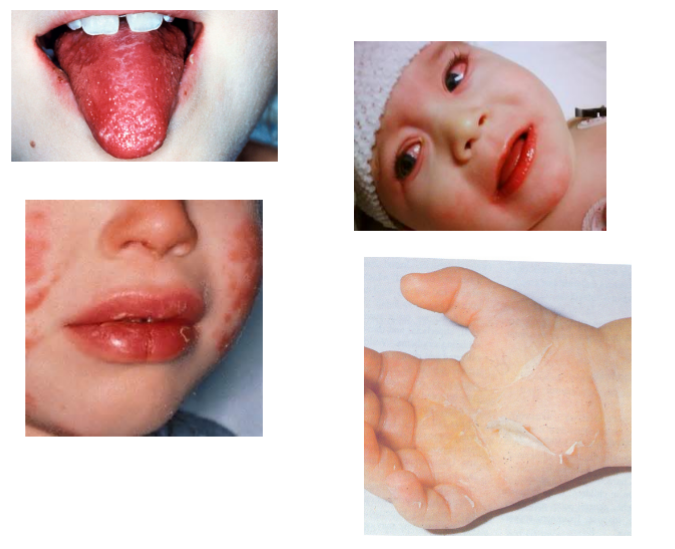
kawasaki disease symptoms
conjunctivitis, rash, adenopathy (enlarged cervical lymph nodes), strawberry tongue (erythematous mouth and throat and dry cracked lips), hands (edema and erythema with peeling skin on palms), fever (high fever for 5 or more days in kids less than 5 years)
CRASH- burn
rheumatic fever definition and signs
inflammatory disease caused by group A strep that injures heart, blood vessels, joints, and SQ; signs: temporary involuntary movement, chest pain and SOB (damage to cardiac valves), rash (erythema marginatum), polyarthritis, fever, abdominal pain, SQ nodules over bony prominences
rheumatic fever nursing care
vital signs, signs of cardiac distress, bed rest during febrile illness, reassure chorea (movements) are temporary, treat with penicillin or erythromycin, anti-inflammatories, prophylactic antibiotics (PCN) required
subacute bacterial endocarditis definition
inflammation resulting from infection of cardiac valves and endocardium by bacteria from poor dental care or surgery, those with known heart problems are at higher risk
subacute bacterial endocarditis signs and treatment
signs: vague or acute signs of infection, treat with antibiotics and monitoring VS, cardiac, perfusion, and hemodynamic stability
care for cardiac catheterization
affected leg stays straight for 4-6 hr, supine or prone if held, older kids may have HOB slightly raised; VS and site check every 5 min for first hr(s), listen to heart for 1 min initially, affected extremity will be mottled and cooler but distal pulses should be palpable
hyperlipidemia
Total cholesterol >200 mg/dL, Low-density lipoprotein >130 mg/dL, High-density lipoprotein <40 mg/dL
first treat with lifestyle, dietary, and behavioral changes
general GI symptoms
failure to grow, spitting up, vomiting (projectile), constipation/diarrhea, bowel sounds, distention, Hematochezia (bright blood in stool), melena (old blood making stool black and tarry), encopresis, Dysphagia
weight gain milestone
back to birth weight by 2 weeks, Double birth weight by 6 months, Triple birth weight by 1 year
how to assess hydration status
LOC, tachycardia/pnea, hypotension, fever, dry mucous membranes, skin turgor, skin color, minimum of 1mL/kg/hr of urine (2-3 is best), high urine specific gravity, decreased tear output, >3 secs cap refill, pulses, sunken fontanel and eyes, irritable then lethargic
esophageal atresia
esophagus terminated before reaching the stomach so it ends in pouch or fistula with trachea, food can enter lungs and air enters stomach, treated with surgery
signs: Coughing and Choking with feedings and Cyanosis, frothy saliva, vomiting, abdominal distention, respiratory distress during and after feeding
hirschsprung disease
congenital aganglionic megacolon, absence of ganglion cells in colon (distal) resulting in no motility due to inability to relax, genetic and male link, most common cause of bowel obstruction in neonates
signs: failure to pass meconium in first 2 days, foul-smelling ribbon-like stool, FTT, poor feeding, constipation/diarrhea
rectal biopsy, stool regiment, most requires surgical repair
omphalocele
herniation of abdominal contents through umbilical ring with an intact peritoneal sac (thin layer of tissue covering intestines), cover sac with soaked sterile gauze before surgical repair
gastroschisis
herniation of intestine lateral to the umbilical ring with no membranes covering bowel, cover bowels with soaked sterile gauze before surgical repair
imperforate anus
anorectal malformation where the normal anal opening is absent or covered, stool in urine or vagina indicates fistula, surgery
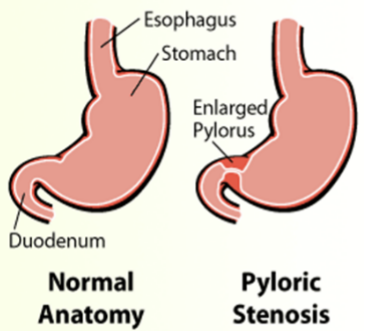
hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
constriction of the pyloric sphincter obstructing the gastric outlet, develops first few weeks of life-familial predisposition
signs: projectile vomiting (after feeding), hungry immediately after feeding, weight loss, FTT, dehydration, constipation, pyloric olive
treatment: pyloromyotomy, small frequent feedings in beginning
intussusception
portion of intestine slides into adjacent part, starts with intermittent colicky pain them currant-jelly stools (blood and mucus), abdominal distention, severe paroxysmal abdominal pain, sausage-shaped mass in abdomen
treatment: air or water enema or surgery, slowly reintroduce feedings, NG tube for decompression
umbilical hernia
protrusion of bowel through abnormal opening in umbilical ring, usually reducible and painless but could lead to incarcerated hernia when blood supply is cut off (surgery for this), surgery if not resolved spontaneously before 4-5
inguinal hernia
protrusion of bowel into lower abdominal wall, communicating hernia: hernia that remains open from the scrotum causing fluid collection in groin or scrotum (hydrocele)
appendicitis
inflammation of the appendix likely due to blockage
signs: umbilical abdominal pain migrating to RLQ, fever/chills, N/V, diarrhea, neutrophilia
treatment: may only need antibiotics but often needs laparoscopic appendectomy
vomiting types
non-bilious: infection or pyloric stenosis, clear, milky or other non-green colors
bilious: concern for obstructive process, green or yellow
constipation in infants
meconium should be passes in first 24-36 hrs, doesn’t happen in breastfed infants but does in formula-fed
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
reflux associated with physical dysfunction usually only considered after 18 months
treatment: upright for 30 min after feeding, antacids, PPI or H2 antagonists, small frequent feedings, thicken formula, burp after feedings, solids then liquids for toddlers, avoid vigorous play after feeding
irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
increased motility which can lead to spasm and pain, bloating, diarrhea and/or constipation, moderate-fiber and low-fat diet
lead poisoning
sign: developmental delays, abdominal pain, neurologic changes, irritability
pinworm infections (enterobiasis)
female pinworms hatch eggs around anus during night causing anal pruritus (especially at night),s insomnia, irritability, restlessness, abdominal pain, nausea
tape test in morning to test, anthelmintics
symptoms of mild vs severe anemia
fatigue, SOB, headache, dizziness, pale skin, difficulty concentrating, may have none
tachycardia, chest pain, SOB, extreme fatigue, dizziness, cold extremities, irritability, poor wound healing, sore/swollen tongue
iron deficiency anemia through the stage
infants: need iron supplementation at 4-6 months
toddler: risk when drinking too much milk and not eating iron foods
adolescents: vegetarian diet, menstruation, and rapid growth
screened at various ages
aplastic anemia
bone marrow fails to produce adequate blood cells, pancytopenia (anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia), congenital or acquired
signs: decreased RBC, bleeding risk, infection, non-healing oral ulcers
treatment: immunosuppressive drugs, Hematopoietic growth factors, transfusion, bone marrow transplant
sickle cell disease
replacement of normal hemoglobin with hemoglobin S which ox is unable to attach to and die faster, S stick to vessel walls which can cause tissue ischemia from occlusions/obstructions, part of newborn screening
sickle cell disease management
hydroxyurea helps complications but may increase risk for infection, hydration, transfusions (too many may need iron chelation therapy (Deferoxamine) to stop hemosiderosis (iron overload), avoid precipitating factors (dehydration, temp extremes, infection and stress)
acute chest syndrome (SCD)
sickling cells get stuck in small blood vessels in the lungs causing a pulmonary infarction/emboli or pneumonia that can rapidly progress to death
signs: fever, cough, tachypnea, wheezing, hypoxemia, abdominal pain common in kids, chest pain when breathing in adults
acute splenic sequestration
sudden enlargement of the spleen when sickled cells get rapped in the spleen that can be life-threatening
fluids to allow for hemodynamics and perfusion and removal of spleen
hemophilia
recessive hereditary bleeding disorder from deficiency of specific clotting factors, x-linked recessive, diagnosed with CVS or amniocentesis and prolonged PTT
signs: prolonged bleeding from anywhere, bruising, hemarthrosis (bleeding into joint cavity), pain
hemophilia treatment
replacement of clotting factors, fresh frozen plasma/cryo, vasopressin (DDAVP) to increase factor in mild case, corticosteroids, no NSAIDs or aspirin or heat, careful with exercise (non-contact sports), RICE for injuries
von willebrand disease
hereditary deficiency or abnormality of vWF clotting factor so platelets fail to adhere to wall of ruptured vessel
treatment: DDAVP (desmopressin acetate) to stimulate release of vWF from cells-fluid restrictions to prevent hyponatremia, cryo or factor replacement therapy
thalassemia
autosomal recessive disorder that reduces production of on globin chains in hemoglobin
treatment: supportive care with transfusions (watch for hemosiderosis), bone marrow, possible splenectomy
immune thrombocytopenia purpura (ITP)
unknown acquired disease causing autoimmune destruction of platelets in spleen that exceeds platelet production resulting in thrombocytopenia
purpura-purple discoloration caused by petechiae under skin, bruising, epistaxis
resolves spontaneously so supportive care includes steroids, IVIG, restrict activity when platelet count is low, Splenectomy if no response to drug therapy after 6 months to a year
disseminated intravascular coagulation
blood clots form inside vessels so they can’t be used to stop bleeding in other places because of inflammation, infection or cancer; signs include blood clots and bleeding from many sites; goal is to treat cause and support with IV fluids and transfusions
neutropenia
absolute neutrophil count less than 1500 mcL in child greater than 1 year, may be asymptomatic or have signs of infection
treat: Hematopoietic Growth Factors (Neupogen), Bone Marrow Transplant, infection prevention, no live vaccine, evaluate ANC
urine specific gravity
urine density, higher means more dehydrated, normal is 1.002-1.03
urine nitrates
normally negative, positive means presence of gram-negative rod bacteria
blood cells in urine
RBC: less than or equal to 2
WBC: 0-4
signs of UTI across the stage
infant: unexplained fever
toddler: belly ache, V/D, flank pain, fever (pyelonephritis), malodor, altered voiding pattern (frequency or holding it), accidents, malaise
school/adolescent: accidents, malodor, classic UTI (frequency, urgency, discomfort), fever (pylo), abdominal and flank pain, tired
pyelonephritis
UTI that ascended into kidneys, increases sepsis risk and renal scarring
signs: UTI, fever, chills, irritability, vomiting
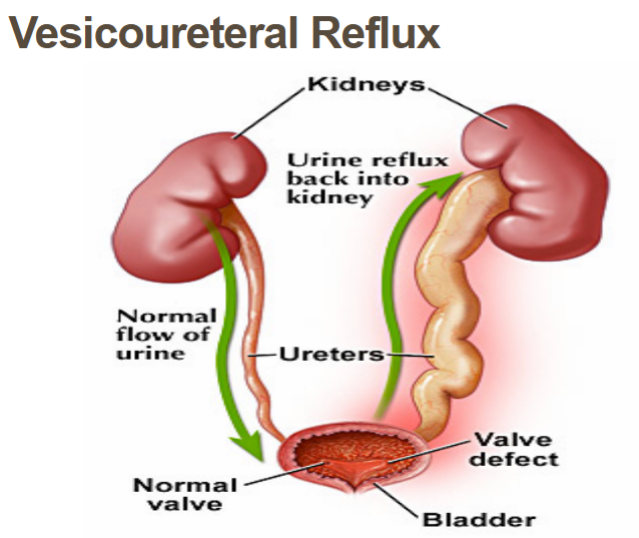
vesicoureteral reflux
disorder of the vesicoureteral junction which causes abnormal backflow of urine into ureters that could lead to hydronephrosis (kidney swelling), tested with voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG): cath puts contrast dye in bladder and child bears down to void to see reflux, treated with reimplantation surgery
bladder exstrophy
bladder develops outside the fetus and doesn’t store urine resulting in incontinence, treated with surgery
hypospadias
urethra opens on underside (ventral) of penis instead of tip, more common than epispadias (upper/dorsal side), surgery
cryptorchidism
testicles should descend around 3-6 months but if not it requires surgery and even after repair is at increased risk for testicular cancer
testicular torsion
testicle rotates twisting the spermatic cord and limiting perfusion to the testicle causing sudden and severe scrotal pain, swelling, frequent urination, and a higher sitting testicle, medical surgery emergency
acute glomerulonephritis
inflammation of the glomeruli due to immune complex (10-21 days after streptococcus infection) leading to difficulty filtering waste
signs: gross hematuria and proteinuria, edema (periorbital), headache, hypertension, decreased urine output, possible renal failure
treat: antibiotics if strep is still active, VS, fluid balance, daily weight, I&O, may need diuretic or anti-hypertensive
nephrotic syndrome
increased glomerular permeability to plasma protein so massive amounts of urinary protein loss, idiopathic onset
signs: severe edema, weight gain, decreased urine production (dark and frothy), hypoalbuminemia, ascites (resp problems)
treat: prednisone (induce remission, reduce inflammation), diuretics, albumin replacement in severe cases, DW and I&O, skin and infection
hemolytic uremic syndrome
e. coli toxins damage small blood vessels causing inflammation and clots which damages kidneys, diarrhea to dialysis (petechial rash, edema, pallor, fatigue, SOB, decrease urine, HTN, neruo changes), typical onset 6months-3 years
thrombocytopenia
anemia
acute renal failure
DW/I&O, monitor for internal bleeding, IV transfusion (plasma/cryo), dialysis, kidney transplant
dysfunctional elimination syndrome
bladder control, bowel control or both and range in severity often related to an underlying medical condition (UTI, neurological disorders, congenital problems)
enuresis
involuntary discharge of urine while sleeping, primary: child has never been dry secondary: dry for 6-12 months then started wetting (UIT?), normal until age 6 due to small bladder, difficulty arousing at night, stress
under 7 years not usually treated if not distressing, teach parents to eliminate guilt shame and punishment, regular voiding schedule, alarms, DDAVP desmopressin (assess for hyponatremia)
anterior pituitary hypofunction
growth hormone deficiency that is idiopathic, normal birth weight and length but growth rate diminishes and gets below 5th percentile
signs: hypoglycemia, short stature, delayed skeletal growth
treat: daily SQ injection of growth hormone until growth goal is met, side effects: increased ICP and intraocular pressure, gynecomastia, edema, scoliosis, SCFE
diabetes insipidus definition and signs
inability to concentrate urine due to deficiency of vasopressin/ADH that isn’t produced in the hypothalamus and/or released by the posterior pituitary
signs: “high and dry”, increased urination, thirst (polydipsia), dehydration, hypernatremia, urine specific gravity below 1.005, serum osmolarity
diabetes insipidus labs and treatments
24-hour urine, urine concentration, water deprivation test (no intake but continues to produce urine and serum Na increases)
DW, I&O, low solute diet, DDAP desmopressin (over treatment leads to fluid retention and hyponatremia)
syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)
excessive secretion of vasopressin (ADH) causes reabsorption of water in kidney, water is retained and dilutes sodium causing hyponatremia
hypothyroidism
underproduction of thyroid hormone, newborn screening because causes intellectual impairment if untreated
high thyroid stimulating hormone but low thyroxine (T4 and T3), replaced with levothyroxine based on age and development
hypothyroidism signs
late signs in newborns: jaundice, hoarse cry, poor appetite, constipation, slow bone growth, poor muscle tone
children: slow growth, abnormal short extremities, delayed tooth development
adolescents: dry skin, bradycardia, weight gain, fatigue, depression, constipation, delayed puberty, puffy face, brittle hair
phenylketonuria (PKU)
inherited autosomal recessive disorder that increases the levels of phenylalanine in the blood that can cause brain damage, intellectual disabilities, behavioral symptoms, or seizures, tested in newborn metabolic screening
labs for type 1 diabetes
fasting blood sugar >126 mg/dL, random blood sugar >200 mg/dl (random), HGb A1c equal to or greater than 6.5% (5.7 is normal)
diabetic ketoacidosis
not enough insulin for blood sugar to be used by cells for energy so liver breaks down fat for fuel which produced ketones, if ketones are produced too fast the body can’t excrete them which is dangerous, more common in type 1, needs fluid and electrolyte replacement and insulin
diabetic ketoacidosis signs
dehydration (dry skin and mouth) from polyuria, increased thirst, sleepiness, confusion, abdominal pain, Kussmaul respiration, ketones in urine, flushed face, fruit breath, N/V,